zkLink, as a stable and reliable multi-chain trading platform infrastructure, has laid a solid foundation for the future comprehensive applications, including finance.
Author: JUMPENG, Senior Researcher at Shiliantou Research Institute
zkLink is a multi-chain middleware based on ZK-Rollup technology, with trading at its core. It achieves multi-chain functionality and extends the classic ZK-Rollup through the mechanism of "ZK-Rollup + oracle network." Its main feature lies in its ability to connect multiple L1 and L2 chains, aggregate liquidity from different ecosystems, and provide seamless multi-chain liquidity for dApps built on the zkLink network, offering fast deployment solutions for decentralized and non-custodial order books, AMM, derivatives, and NFT MarketPlace.
1. Research Points
1.1. Core Investment Logic
zkLink, as a trustless, permissionless, and non-custodial interoperability protocol, aims to connect different chains, eliminate differences in different tokens, and solve the liquidity silo problem formed on isolated chains. Its core investment logic is reflected in several aspects:
As a pioneer in the multi-chain decentralized trading field, zkLink faces broad market prospects. With its unique first-mover advantage, zkLink fully covers the public chain track through multi-chain aggregation, demonstrating strong vitality. At the same time, it effectively improves user experience pain points using ZK technology, attracting more users to participate in industry development. zkLink not only focuses on meeting the current high-speed growth market demand for decentralized trading but also values the infinite potential for long-term industry development. The programmable and customizable nature of zkLink's technology enables it to adapt to various changes in the future blockchain business landscape, meeting diverse needs for trading and interaction, and fully exploring the potential for business models, potentially becoming a key cornerstone supporting the long-term prosperity of the entire industry. Additionally, with its open and general technical roadmap, zkLink can drive the entire decentralized industry forward, aggregating resources from various chains and promoting the growth of various application ecosystems.
Innovative and practical technical solutions: zkLink's technical solutions effectively address the significant pain points in the current blockchain industry. Technological breakthroughs are a key driver of industry progress, and zkLink, with its strong capabilities in this area, continuously opens up new frontiers for multi-chain exchange and DeFi interaction. It combines new technologies such as ZK-Rollup to create a practical and efficient cross-chain interaction mechanism. For example, by customizing ZK proofs to support rapid integration of different dApps, it significantly improves ecosystem integration efficiency, ensuring rich interaction of multi-chain resources and contributing to the long-term sustainable expansion and optimization of the project. At the same time, zkLink continues to optimize details such as trading pairs and liquidity management, constantly improving the trading experience at all levels. Overall, zkLink adheres to the concept of driving industry development through technological innovation, continuously absorbing the latest technological achievements, and supporting the overall progress of the industry while ensuring the long-term robustness of its product architecture. These rich technical highlights will be the key to zkLink standing out in homogeneous competition, ensuring its core competitive advantage.
Security of funds is the lifeline of any project and is also one of zkLink's most important competitive advantages: zkLink adopts the principle of minimal security assumptions in its security design, fully utilizing the security mechanisms of multiple mainstream public chains to achieve a security level equivalent to the mainnet. In addition, zkLink has designed a witnessing mechanism on the main chain, where multiple main chain nodes can track and verify zkLink's status, forming multi-party supervision to effectively prevent single-point attacks and operational risks. More importantly, zkLink has passed the "Dunkirk" test, testing its resilience in the face of attacks, further enhancing user confidence. This exceptional recovery capability elevates zkLink's security to a new level, laying a solid foundation for its commercial operation. Overall, zkLink's achievement in fund protection mechanisms is at the industry-leading level, which will help it gain broader user trust in the current backdrop of significant demand for multi-chain finance.
1.2. Valuation
So far, zkLink has completed two rounds of financing, with a total amount of $18.5 million. However, as the details of the two rounds of financing have not been fully disclosed, we cannot determine zkLink's specific valuation, and its economic model and token distribution details are yet to be announced, increasing the difficulty of valuation. Nevertheless, considering the vast market space where zkLink operates and its technical advantages in the multi-chain trading field, zkLink's future valuation potential remains promising. If zkLink can make new progress in developer ecosystem and commercial applications, gradually establishing a sound ecosystem, its valuation space will rapidly increase with the expansion of actual business scale.
1.3. Project Risks
zkLink's project risks mainly include risks related to complex technical implementation, early-stage ecological construction, complex multi-chain environment, and competitive risks, as detailed in the 5.2 SWOT analysis section of the report.
2. Project Overview
2.1. Project Introduction
zkLink is a multi-chain ZK-Rollup infrastructure that aggregates and trades assets on different chains using zero-knowledge proof technology, providing an efficient, secure, low-cost, and privacy-protected decentralized trading experience. zkLink's vision is to become a bridge connecting all blockchain networks, allowing users to freely trade any asset on any chain without switching networks or wallets, creating a truly decentralized, frictionless, and borderless encrypted world.
2.2. Team Situation
2.2.1. Overall Situation
According to Crunchbase data, the team currently consists of 11-50 people, with headquarters located in Singapore. Information about team members, other than the founder, has not been publicly disclosed. However, according to the official blog, zkLink's global engineering and expert team is distributed worldwide, with research and work experience in network security, cloud computing, cryptography, zero-knowledge proofs, and other fields, having studied at institutions such as ENSPM Paris, Imperial College London, Harbin Institute of Technology, Duke University, Peking University, and Tsinghua University.
2.2.2. Core Members

Vince Yang: Co-founder and CEO of zkLink, responsible for overall strategic planning and daily operations. Vince has extensive experience in internet entrepreneurship and has been involved in the founding of several well-known internet companies. Vince has maintained a low profile and rarely appears in public, and detailed information about him is currently unavailable. In recent promotional activities, he has used different avatars for coverage, possibly due to anonymity or privacy considerations.
2.3. Financing Situation
On October 22, 2021, zkLink completed an $8.5 million seed round of financing, led by Republic Crypto, with participation from Arrington Capital, DeFi Alliance, Huobi Ventures, Ascensive Assets, Morningstar Ventures, GSR, and Marshland Capital. zkLink plans to expand its team and support other features on the platform.
On May 4, 2023, zkLink announced the completion of a $10 million financing round, with participation from Coinbase Ventures, Ascensive Assets, SIG DTI, BigBrain Holdings, and Efficient Frontier. This round of fundraising will help drive zkLink to launch its mainnet in the third quarter.

2.4. Project Partnerships
### 2.5. Development History and Roadmap
2.5.1. Development History
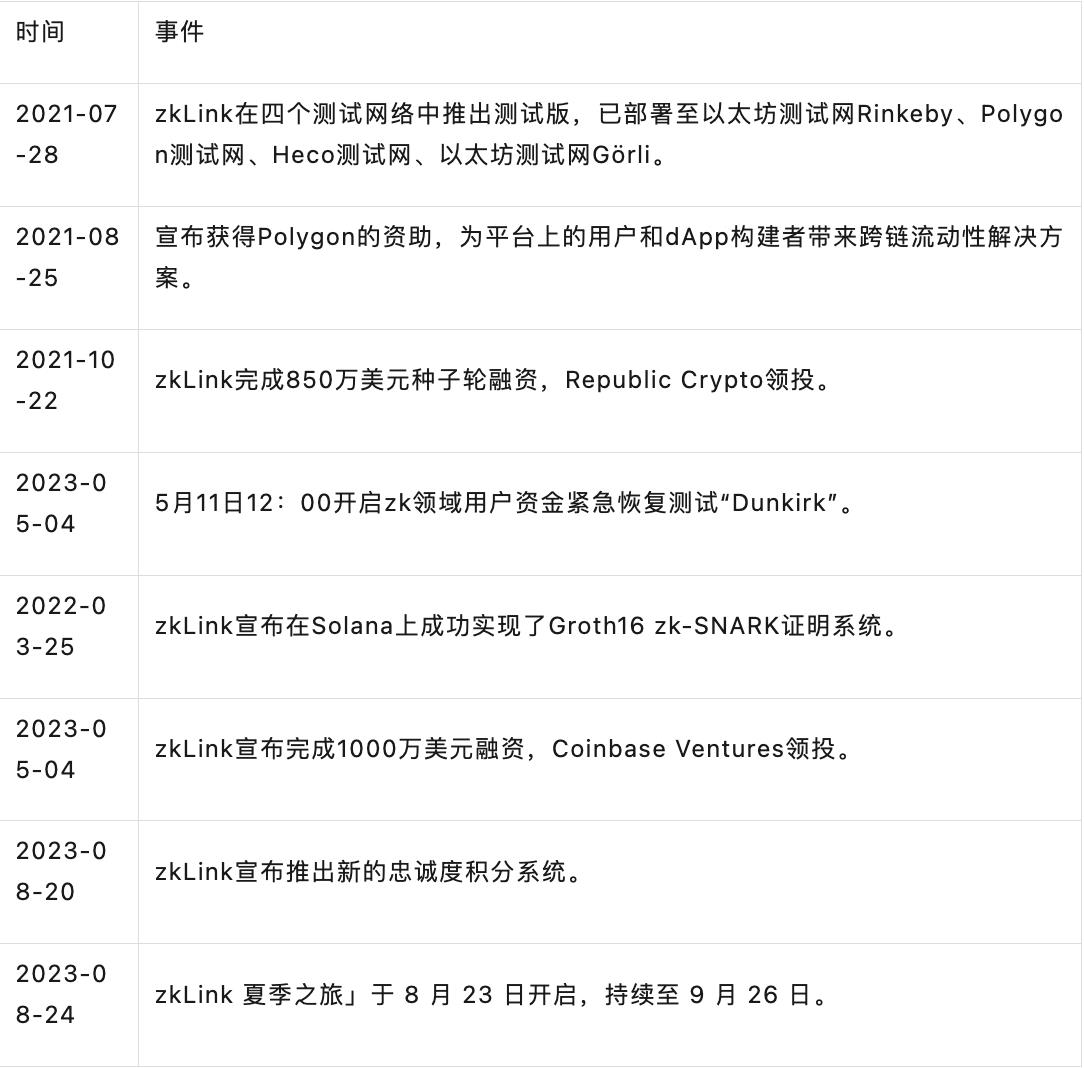
2.5.2. Development Plan and Roadmap

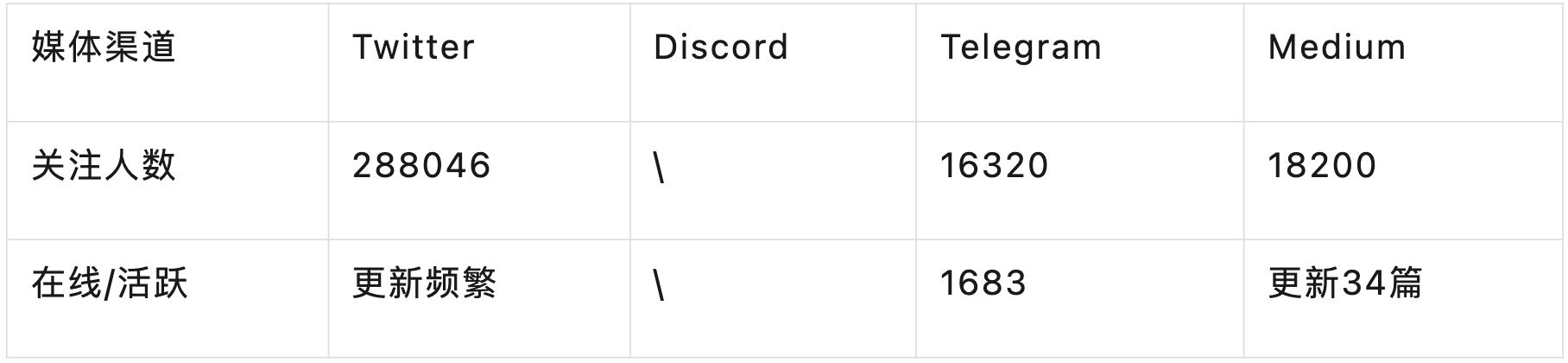
2.6. Social Media Data
As of September 30, 2023, zkLink has performed well on social media platforms, indicating high project popularity. The main operating channels for the project currently include Twitter, Discord (server invitation expired), Telegram, and Medium. Currently, zkLink's Twitter account has attracted close to 290,000 followers, with frequent updates and interactions, making it one of the most popular channels. Below are the specific data for each platform:
3. Project Analysis
3.1. Project Background
With the rapid development of blockchain technology, various public chains, side chains, and Layer 2 solutions have emerged, leading to a multi-chain coexistence situation. This provides users and developers with more choices but also results in significant liquidity fragmentation. In this multi-chain world, assets and liquidity on different chains are isolated within their respective systems, making effective cross-chain interoperability difficult. This inconvenience leads to significant challenges in asset allocation and trading for users, requiring multiple transfers between different chains and incurring various fees, making operations cumbersome. It also creates liquidity bottlenecks for trading projects, making it difficult to obtain sufficient user scale and trading volume. Additionally, frequent cross-chain operations also pose certain security risks, as assets need to be verified and transferred by third-party institutions during the cross-chain process, requiring users to trust and authorize these entities. Any operational errors or abuse of power could lead to potential loss of user assets.
Faced with these pain points, the original intention of decentralization and self-management of assets has driven people to seek new solutions. zkLink has emerged with the goal of building a multi-chain interconnected trading infrastructure to truly achieve the free flow of cross-chain assets. By aggregating liquidity from different chains, reducing transaction costs, and ensuring transaction security through zero-knowledge proofs, zkLink aims to address the liquidity fragmentation and interoperability challenges in the multi-chain world, driving the development of decentralized trading.
3.2. Project Principles
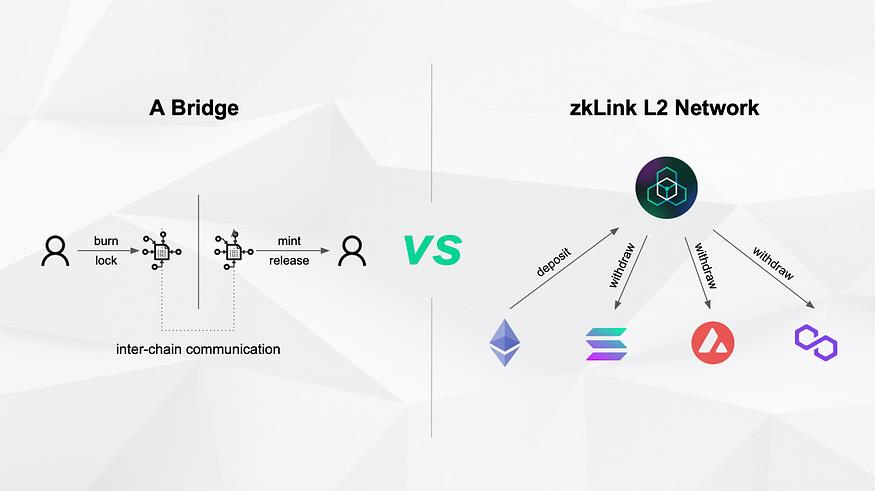
zkLink is not an independent public chain or side chain but rather a Layer 2 infrastructure built on multiple public chains and Layer 2 networks. It is more like a Layer 2.5 network, utilizing the decentralized consensus and security guarantees of the underlying chains. The working principle of zkLink involves deploying smart contracts on multiple underlying chains, allowing users to deposit and withdraw coins directly to and from the contracts, enabling cross-chain transfers and operations without the need for bridge operations. This simplifies the cross-chain usage process and makes it more secure and cost-effective. Additionally, zkLink can truly aggregate cross-chain asset liquidity. Through stablecoin aggregation and other means, zkLink can significantly improve liquidity utilization efficiency, similar to the liquidity aggregation function of centralized exchanges.
In simple terms, zkLink has created a Layer 2 infrastructure for cross-chain transactions through its bridgeless multi-chain mechanism and liquidity aggregation technology. It combines the security and reliability of public chains with the liquidity network effects of centralized exchanges, greatly optimizing the user experience and promoting the prosperity of multi-chain ecosystems.
3.2.1. zkLink Network Architecture
After understanding the basic principles of zkLink, for ease of understanding, let's visualize the network architecture of zkLink as consisting of three layers:
① The bottom layer consists of multiple L1 chains and L2 networks, such as ETH, BSC, Arbitrum, and Optimism.
② The middle layer is the zkLink protocol layer, which is a middleware layer based on ZK-Rollup, connecting different L1 chains and L2 networks and enabling the aggregation and verification of cross-chain transactions.
③ The top layer is the zkLink Dapp layer, an open platform supporting various decentralized trading products such as DEX, lending platforms, NFT markets, and RWA trading.
According to the project whitepaper, zkLink uses multiple Rollup states to improve network performance. Specifically:
A Rollup state can support multiple dApps running simultaneously, allowing different dApps to collaborate and share resources. However, the number of allowed dApps is limited and specific analysis is required to consider performance factors.
zkLink deploys multiple Rollup states, but these states do not directly share the same liquidity pool.
When dApps run on zkLink, they also act as transaction ordering roles, responsible for managing transaction order. This improves efficiency and fairness but may also pose some risks, such as the potential for some dApps to exploit their advantages to gain more profit (MEV) or disrupt the normal operation of other dApps. To prevent such situations, dApps need to establish rules and protective measures.
Multiple Rollup states can collaborate and optimize costs through zkLink's recursive zk verification mechanism, allowing them to share computational work and accelerate the process of each Rollup state, thereby improving network efficiency. The recursive zk verification mechanism uses zero-knowledge proofs (ZKP) to verify other ZKPs, reducing data volume and verification time, enabling better collaboration and communication between different Rollup states, and enhancing overall network efficiency and security.
In summary, zkLink uses multiple Rollup states to increase throughput, but the number of dApps supported by each Rollup state and the configuration of liquidity pools need to be specifically designed to balance performance and security. Additionally, dApps acting as ordering roles need to guard against MEV-related risks. Furthermore, zkLink supports collaborative optimization of computational costs between Rollup states.
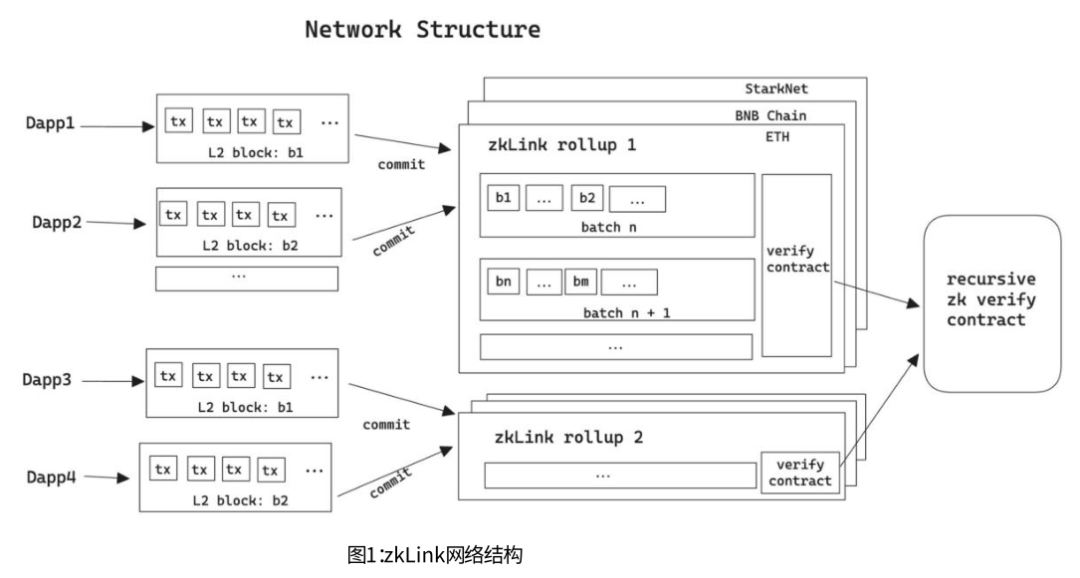
Source: zkLink Whitepaper
3.2.2. zkLink Network Operation Principles
Based on zkLink's network structure, it is evident that the project primarily utilizes two core technologies to achieve its function as a cross-chain trading infrastructure:
1) ZK-Rollup
ZK-Rollup technology can batch and aggregate transactions from multiple chains, generate a verifiable proof, and submit it to Layer 1, significantly reducing the verification load and storage requirements on the main chain. The working principle of ZK-Rollup is as follows:
- ZK-Rollup consists of two types of participants: Provers and Validators. Provers are responsible for batching multiple transactions and generating a zero-knowledge proof to prove the validity of these transactions. Validators verify the zero-knowledge proof provided by Provers and update the transaction state on the main chain.
This concludes the translation of the provided content. If you have any further requests or need additional assistance, feel free to ask!
By compressing multiple transactions into a zero-knowledge proof, ZK-Rollup reduces the data storage and computational requirements on the main chain, thereby increasing transaction throughput and lowering transaction fees. Additionally, ZK-Rollup uses zero-knowledge proof technology to protect the privacy and security of user transactions, preventing transaction data leakage or tampering.
By inheriting the security and decentralization of the main chain, zkLink ensures the security and recoverability of user assets. Users can withdraw their assets from the ZK-Rollup network to the main chain at any time without relying on any third party or trust assumptions.
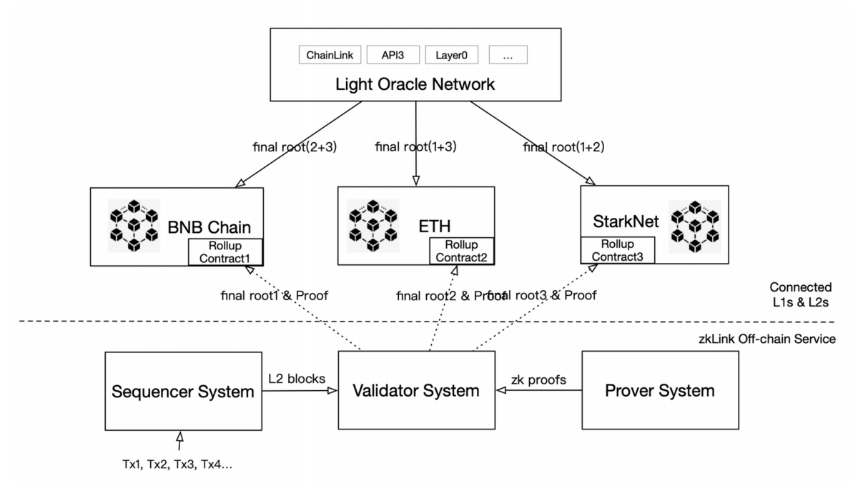
Source: zkLink Whitepaper
Additionally, a normal ZK-Rollup runs in three stages: the submission stage, proof stage, and execution stage. zkLink adds a synchronization stage in the proof and execution stages on top of the ZK-Rollup technology. The zkLink ZK-Rollup process is as follows:
① Submission Stage: Users initiate transaction requests on different chains through smart contracts, and DApps act as sequencers, taking on the responsibility of sorting transactions and sending the sorted transaction list to the Prover.
② Proof Stage: The Prover packages the received transaction list into a batch and generates a zero-knowledge proof to prove the validity of these transactions. The Prover then submits the batch and proof to the main chain. (In zkLink's design, the Prover is more like an auxiliary institution of the Validator system and does not directly interact with the zkLink protocol.)
③ Synchronization Stage: As zkLink is a multi-chain system, the synchronization stage unifies the states of different chains. The synchronization stage is the process of the oracle network, facilitating the exchange of final roots between different chains and comparing the consistency of the final roots of two chains.
④ Execution Stage: Validators verify the zero-knowledge proof provided by the Prover and update the transaction status of the batch to the respective chain.
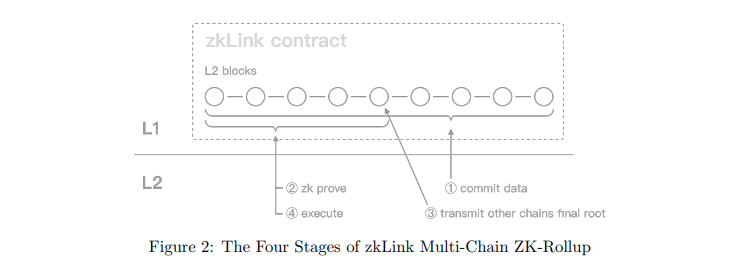
Source: zkLink Whitepaper
Through this process, zkLink utilizes ZK-Rollup technology to aggregate transaction information from different chains into a ZK-Rollup, creating a cross-chain transaction state layer.
2) zkSNARKs
zkSNARKs can prove the validity of transactions without revealing transaction details. zkLink ensures the correctness and validity of offline states through zkSNARKs, verifying the finite nature of offline states through zero-knowledge proof and introducing a lightweight oracle network in specific network requirements to ensure transaction validity. The zkLink zkSNARKs process is as follows:
① Generation Stage: The Prover generates a proof based on the transaction list and a random number, proving that they know how to correctly execute these transactions without revealing any details.
② Verification Stage: The Validator verifies the Prover's knowledge based on the proof and public parameters, without needing to know the transaction list or random number.
③ Update Stage: The Validator updates the on-chain state based on the proof's result, completing the execution of the transactions.
By combining these two technologies, zkLink has built an efficient and secure multi-chain interconnected infrastructure. It connects different blockchain networks, supports seamless trading of cross-chain assets and liquidity aggregation, and provides a superior user experience and higher security compared to single chains or simple cross-chain bridges/atomic swaps. This lays the foundation for creating a boundless multi-chain DeFi trading network.
3.3. Project Operation Process
After understanding the principles of zkLink, let's briefly introduce the operational process of zkLink to deepen the understanding of the project. The operational process can be divided into the following steps:
1) User Registration
Users register an account on zkLink and map their assets on different L1 chains or L2 networks to the zkLink protocol layer. This step requires users to "deposit" tokens to zkLink's smart contract on L1 chains or L2 networks, creating a corresponding account and balance on the zkLink protocol layer. Users can manage multiple accounts and assets on the zkLink network without switching between different chains or wallets.
2) Initiating Transactions
Users initiate cross-chain transactions on the zkLink application layer, such as exchanging on different DEXs, borrowing, or purchasing NFTs. Users can enjoy efficient, low-cost, high-speed, and private transactions on the zkLink application layer without worrying about compatibility or liquidity issues between different chains.
3) Transaction Sorting
The Sequencer collects users' cross-chain transactions and batches them into a proof, acting as a DApp. The Sequencer collects users' cross-chain transactions on the zkLink protocol layer, packages them into a batch according to certain rules, and then calls the Prover's service to convert the batch into a zero-knowledge proof, paying a certain fee.
4) Proof Construction
The Prover uses zero-knowledge proof technology to compress a large amount of off-chain transactions into a small proof and submits it to the L1 chain. Upon receiving the Sequencer's request, the Prover compresses all transaction data and state changes in the batch into a small proof using cryptographic algorithms and tools, then returns it to the Sequencer. The Sequencer then submits the proof to zkLink's smart contract on the L1 chain and pays a certain fee.
5) Proof Verification
After the light oracle network synchronizes the final root state, the Validator executes zkLink's smart contract on the L1 chain to verify the proof submitted by the Prover and update the user's asset balances on various chains or networks based on the verification results. The Validator pays a certain fee on the L1 chain to complete the proof verification and state update. If the proof is invalid or incorrect, the Validator rejects the proof and reports the abnormal information to zkLink.
6) Asset Withdrawal
Users can withdraw their assets from the zkLink protocol layer to the original L1 chain or L2 network at any time. This step requires users to "withdraw" tokens from zkLink's smart contract on the L1 chain or L2 network, then destroy the corresponding account and balance on the zkLink protocol layer. Users can freely transfer assets between different chains without waiting for confirmation time or paying high fees.
3.4. Simplification of Wallets and User Funds
zkLink supports integration with advanced account abstraction (AA) wallets, providing users with a more flexible and convenient way to manage assets. AA wallets control accounts through smart contracts, allowing users to set access permissions, transaction restrictions, and better wallet recovery. This is very user-friendly for non-technical users, compared to traditional private key wallets, which are more singular and rigid. To integrate with zkLink, AA wallets need to support specific signature formats, key generation specifications, and most importantly, ensure that account security does not depend on zkLink. Even if zkLink services go down, users can still retrieve their assets.
In terms of deposits, users can directly call zkLink's deposit function or implement deposits through a transfer intermediary contract to meet different usage scenarios.
For withdrawals, zkLink supports fast withdrawals, allowing users to instantly receive quotes from multiple chain brokers and choose the best quote provider for their withdrawals, without waiting for on-chain confirmations, greatly improving withdrawal speed.
In summary, through integration with AA wallets and optimization of the deposit and withdrawal process, zkLink allows ordinary users to enjoy a simple, secure, and smooth Layer 2 asset management experience, significantly lowering the barrier to using public chains and promoting the widespread adoption of zkLink.
3.5. Project Security
zkLink is committed to maximizing application security through technical means. Specifically, it employs multiple security mechanisms:
① The security of zkLink is primarily ensured by the underlying ecosystem and SNARK proof technology. Only transactions verified through zero-knowledge proofs can be executed by Layer-1 contracts, expanding the functionality of the classic ZK-Rollup model to support multiple chains.
② To meet the different ecological and security needs of various dApps, zkLink provides customized solutions for developers deploying networks. When dApps are only connected to the Ethereum ecosystem and its Rollup VM (such as zkSync, Scroll, etc.), their security inherits from the Ethereum mainnet.
③ When dApps choose to connect to Ethereum + other L1 chains, zkLink uses minimal security assumptions and introduces a role called the Witness. The Witness's task is simple: it only needs to read the state roots it receives on different chains and compare them with the unified state. The unified state records all asset information and user account changes coming from different chains. If the states are consistent, the off-chain information is completely consistent, mathematically eliminating the possibility of "False Prove" or "Rug Pull." The security assumption is that zkLink will not collude with all components of the oracle. By adopting this mechanism, zkLink ensures fund security while increasing support for other Ethereum Rollups and multi-chain ecosystems.
④ Conducted a "Dunkirk" security test, simulating a scenario where users urgently withdraw funds on a large scale: zkLink conducted a security test called "Dunkirk," which aimed to simulate a scenario where users urgently withdraw funds on a large scale under extreme conditions. During the test, zkLink shut down its servers, simulating a situation where all protocol operators disappear or the servers crash in a real environment. It invited reputable third parties in the industry to run the recovery process, allowing users to retrieve tokens from zkLink through the recovery process, proving its fund security and recoverability. This test also educated users on how to protect their funds in crisis situations, increasing their confidence in decentralized trading security.
Through the above multiple compatibility mechanisms, zkLink not only ensures fund security but also significantly expands its application support range, paving the way for users to choose the optimal path. This solution achieves a hybrid enhancement of security and versatility.
3.6. Project Technical Features
1) Native Asset Aggregation Capability
Supports listing and trading of cross-chain tokens, allowing users to operate assets such as FTs, NFTs, and RWAs from multiple public chains through a single interface, without the need for any asset bridging. This avoids cross-chain risks and expensive bridging fees. Additionally, zkLink supports cross-chain portfolio management, allowing users to manage portfolios of the same tokens from multiple public chains on the zkLink network without the need to switch between different chains or networks.
2) Liquidity Aggregation
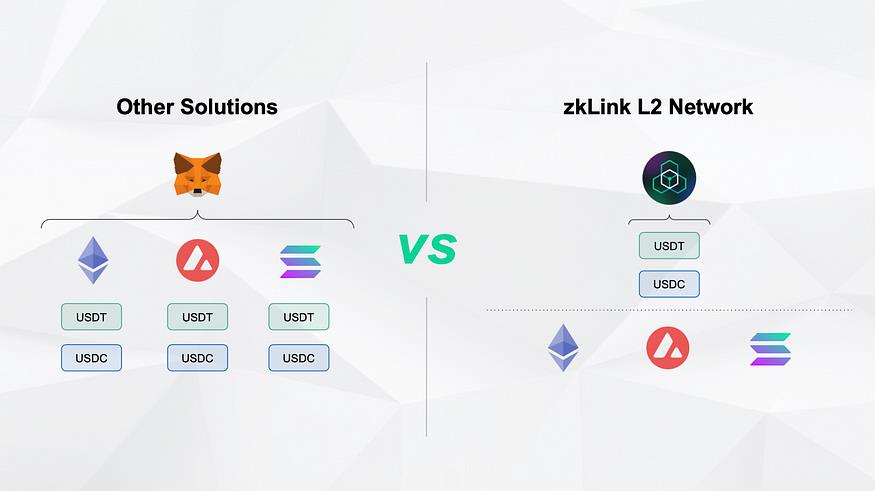
zkLink consolidates tokens and unifies stablecoins, eliminating differences in homogeneous assets on different chains. For example, USDT issued on different chains is consolidated into a single USDT within the zkLink network. Additionally, zkLink introduces USD as the unified pricing currency for stablecoins such as USDC, USDT, and BUSD, eliminating price differences between fiat-anchored stablecoins. USD can be freely transferred within the zkLink system and used as the primary currency for any trading pair. For example, an order book DEX can list trading pairs such as ETH/USD, BTC/USD, BNB/USD, whether for spot or derivative trading. An NFT marketplace can also list NFT assets priced in USD, reducing friction costs and user entry barriers.

3) Improved Capital Utilization
Users and organizations can benefit from higher capital utilization. Token consolidation promotes circulation, thereby increasing utilization. Users do not need to hold a long list of mostly idle tokens on each chain, but only need a small variety of tokens to participate in multi-chain protocols. Additionally, deeper liquidity enables additional yield strategies such as LP reinvestment.
4) Application-Specific Zero-Knowledge Proofs
For developers, zkLink's zero-knowledge system is customized to support industry-leading performance (1000+ TPS) for order book trading, bridging the gap between the needs of high-frequency traders and on-chain products. Currently, the development of zero-knowledge circuits remains complex, expensive, and time-consuming. zkLink's infrastructure achieves the following core advantages through application-specific circuit design:
● Customizable design to support high-performance proof systems for specific applications such as order books.
● Strong API usability with low development costs.
● Application-specific circuits are much smaller in scale than general ZK circuits, offering higher efficiency and lower transaction costs.
● Continuously optimizing transaction performance to reduce the cost per transaction.
3.7. Project Use Cases
As a cross-chain trading infrastructure, zkLink theoretically supports any decentralized application scenario. However, due to its emphasis on security and performance, it currently serves as a protocol agnostic to chains, providing a series of plug-and-play APIs specifically designed for this purpose. Here are some API use cases:
1) Order Book DEX Trading
A decentralized exchange that supports cross-chain asset trading, combining the advantages of CEX and the security of DEX. It has the following key features:
● Users can use CEX-like features on a single platform, such as limit orders, market orders, and portfolio margin, to trade assets from different chains, such as ETH, BTC, SOL, etc.
● Users can custody their own assets without needing to trust any third party. The protocol uses a centralized matching engine to quickly complete buy and sell pairs, but uses zero-knowledge proofs (ZK) to ensure on-chain security and correctness.
● The protocol can improve capital efficiency, allowing users to engage in spot and perpetual contract trading simultaneously, as well as manage their positions using leverage and margin.
2) Multi-Chain AMM
A decentralized protocol that supports liquidity provision and exchange of cross-chain assets, using different types of automated market makers (AMM) to adapt to various market demands. It has the following key features:
● Users can create or join liquidity pools composed of native assets from different chains, such as ETH-SOL, UNI-CAKE, etc., and receive corresponding liquidity tokens (LP Tokens).
● Users can use different AMMs on the protocol to exchange any cross-chain assets, such as constant product (UNI V2), optimized stablecoins (Curve.fi), and concentrated liquidity models (UNI V3). These can improve trading efficiency, reduce slippage, and increase liquidity depth.
● The protocol enables seamless transfer of cross-chain assets without requiring additional user actions or payment of extra fees.
3) Unified Homogeneous Tokens (OFT) Across Chains
A decentralized protocol that supports the issuance and bridging of homogeneous tokens (OFT) across multiple chains, using a unified standard to define and manage cross-chain assets. It has the following key features:
● Users can issue their own OFT on the protocol and bridge it to other chains that support the protocol, such as ETH, BSC, SOL, etc. They can also bridge existing OFTs from other chains to the protocol and transfer them between different chains.
● The protocol ensures the total amount of cross-chain assets remains unchanged and prevents double spending or replay attacks. Users can query and verify their OFT balances and status at any time.
4) Multi-Chain NFT Minting and Trading
### 3.7. Project Use Cases
Support for minting and trading NFTs across multiple chains, using a unified pricing unit to evaluate and compare NFTs on different chains. It has the following key features:
● Users can create their own NFTs on the protocol and mint them on other chains that support the protocol. They can also mint NFTs from other chains on this protocol and transfer them between different chains.
● Provides a unified NFT marketplace, allowing users to browse and purchase NFTs from different chains on a single platform.
5) Real World Assets (RWA)
Supports users to access and trade real-world assets (RWA) in a single account, ensuring user autonomy and on-chain security.
● Users can use on-chain assets on the protocol to buy and sell real-world assets (such as fixed income, stocks, etc.) and arbitrage and hedge between different markets.
● Users can self-custody, retaining local autonomy and on-chain security.
3.8. Project Ecosystem
zkLink is currently in the testnet phase and plans to launch the mainnet in the third quarter of 2023. zkLink has already deployed three on-chain DApps on the testnet.
1) ZKEX
ZKEX is the first bridgeless multi-chain DEX, built on three leading L2 ZK-Rollups - zkLink, Starkware, and zkSync. ZKEX aims to combine the security and autonomy advantages of decentralized applications with the trading experience of CEX, near CEX, better DEX. Here are the application advantages zkLink brings to ZKEX:
● Rich liquidity: Integrates stablecoins from multiple public chains to form massive multi-chain liquidity pools.
● Efficient trading: Utilizes ZK-Rollup technology, with no gas fees at the L2 level, fast transaction speed, and no slippage fees.
● Superior orders: Supports partial fills and multiple pending orders, maximizing user trading needs.
● User-friendly: Provides a CEX-like user interface while retaining decentralized characteristics. The underlying implementation holds private keys for self-custody, providing permissionless on-chain access without KYC.
● Transparent data: Every transaction requires valid verification through ZK proofs, ensuring asset security and consistency, with transaction data openly accessible.
● Powerful performance: Supports up to 32 open orders, deterministic process, meeting high-frequency trading demands.
● Minimal trust: The underlying gossip network is continuously improved by the community, with extremely low single-point failure risk.
2) zkJump
zkJump is a cross-chain bridge based on zkLink, currently supporting 12 chains including BNB Chain, Avalanche, zk-Sync, Starknet, and Optimism. (Test phase)
3) OpenWorld Exchange
OpenWorld is a decentralized derivatives exchange for "multi-assets (RWA & Crypto)" based on zkLink (test phase), supporting non-custodial trading of crypto assets and other synthetic financial assets. It offers the following advantages:
● It is the world's first decentralized exchange supporting seamless trading of real-world assets (such as stocks, bonds, commodities, forex) and crypto assets.
● It adopts order book and perpetual contract models, providing a CEX-like user experience and performance.
● By establishing an open and transparent financial protocol, it matches traders with different trading capabilities (such as long, short, leveraged trading) with liquidity providers.
● Based on ZK-Rollups technology, it ensures asset security and data availability, while using validity proofs to verify transaction correctness.
● It is a fully decentralized, self-custodial, trustless, permissionless, and KYC-free trading platform, enabling users to enjoy true financial freedom.
As the zkLink network has not yet fully launched, the ecosystem is still under construction. As a decentralized infrastructure, it relies on DApps to provide services and enhance user experience. However, compared to other L1 and L2 networks, the difficulty of DApp development on zkLink may be higher for the following reasons:
● zkLink uses zkRollup technology, requiring some DApps to act as sequencers, which technically increases the difficulty.
● The zkLink ecosystem is still in its early stages, with relatively limited ecosystem resources such as documentation and tool support, increasing the learning cost for DApp developers.
● The multi-chain design of zkLink makes its structure more complex, placing higher demands on DApp development.
● DApps need to be compatible with the continuously optimized zkLink technical framework, increasing maintenance difficulty.
Therefore, during the transition period, zkLink needs to strengthen support for developers, improve learning resources and access processes, and reduce costs for DApp developers to truly attract large-scale adoption and enhance the overall ecosystem.
3.9. Project Data
zkLink currently supports connections to the following types of networks: 1) EVM-compatible public chains such as Ethereum, BNB Chain, Matic, etc.; 2) ZK Rollup virtual machines based on Ethereum, such as zkSync, Scroll, etc.; 3) ZK Rollup virtual machines incompatible with EVM, such as StarkNet; 4) EVM-compatible optimized Rollups, such as Arbitrum, Optimism. According to official data, zkLink currently supports 12 networks. Additionally, based on testnet data, the network has processed over 1 million transfers and has over 200,000 unique addresses, demonstrating strong performance.
zkLink aims to build on secure and reliable mainstream public chains and Layer 2 networks, and in the future, will connect to more recognized blockchain networks based on community demand. Currently, zkLink is primarily focused on building around the Ethereum ecosystem and does not yet support other non-EVM chains such as Solana, Algorand, etc. Different network deployment combinations require adjustments to the required infrastructure components based on DApp scenarios. As technology continues to improve, zkLink will evolve towards true multi-chain compatibility, providing users and developers with a unified multi-chain experience.

4. Track Space and Potential
4.1. Track Overview
4.1.1. Track Positioning
zkLink belongs to the multi-chain infrastructure field, subdivided into application-specific and trade-centric order book infrastructure.
4.1.2. Track Scale
According to CoinGecko's data, Binance is currently the largest centralized cryptocurrency exchange in terms of trading volume, with a registered user base exceeding 120 million. Its trading volume significantly surpasses that of other competitors.
Specifically, as of September 2022, Binance's monthly trading volume reached 5.28 trillion USD, maintaining an absolute leading position among exchanges. Compared to the entire decentralized exchange market, Binance's daily trading volume (September 29, 2023) reached 3.815 billion USD, approximately 2.5 times the total DEX daily trading volume (1.518 billion USD).
With the advancement of technology, the gradual replacement of centralized exchanges by decentralized exchanges has become a major trend. Given Binance's market position as the leader in trading volume, it is evident that the market space for decentralized multi-chain order book trading will be extremely vast, presenting a huge opportunity targeted and seized by projects such as zkLink.
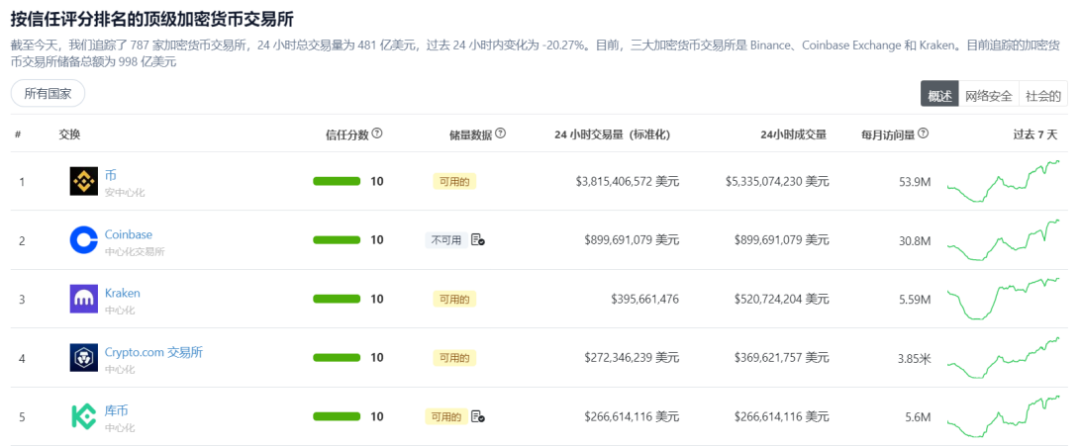
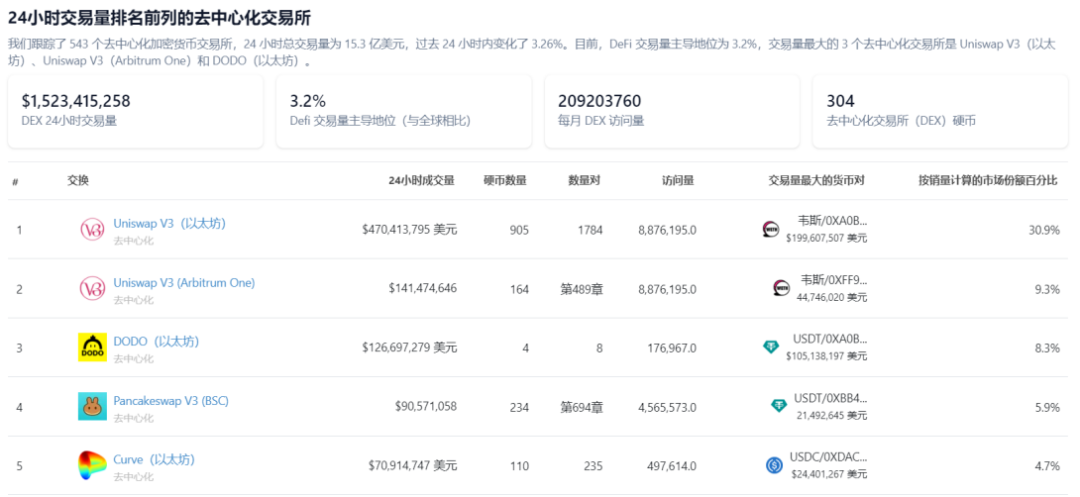
Source: Coingecko
4.1.3. Track Pattern
Early Uniswap adopted the AMM mechanism to pioneer decentralized exchanges, but the trading experience was subpar. Subsequently, L1 emerged to bring performance breakthroughs to DEX, but at the cost of security. Following that, L2 as an Ethereum scaling solution balanced security and high performance, but generally, L2 still needs improvement in cross-chain interaction. In recent years, a new generation of application-specific infrastructure based on the order book mechanism has emerged, further improving the user experience. These solutions, centered around trading, reshape and innovate on the technology on L1 and L2, utilizing high-performance and secure environments for frequent trading, laying the foundation for building decentralized order book exchanges (similar to "decentralized Binance"). These constructive technological evolutions have effectively and consistently propelled decentralized exchanges towards a more perfect direction.
From the initial AMM mechanism to the order book mechanism, from L1 to specialized L2, various innovations have collectively addressed the pain points of decentralized exchanges in performance, security, and interactivity, bringing the goal of achieving the performance and user experience of "decentralized Binance" closer. Currently, the most popular types of decentralized trading infrastructure include application-specific ZK-Rollups (such as StarkEx and zkLink), general-purpose ZK-Rollups (such as StarkNet and zkSync), Optimistic Rollups (such as Arbitrum), and high-performance Layer 1 (such as Cosmos). They each have their advantages and disadvantages, requiring comparative analysis based on dimensions such as user experience, security, performance, and cost.
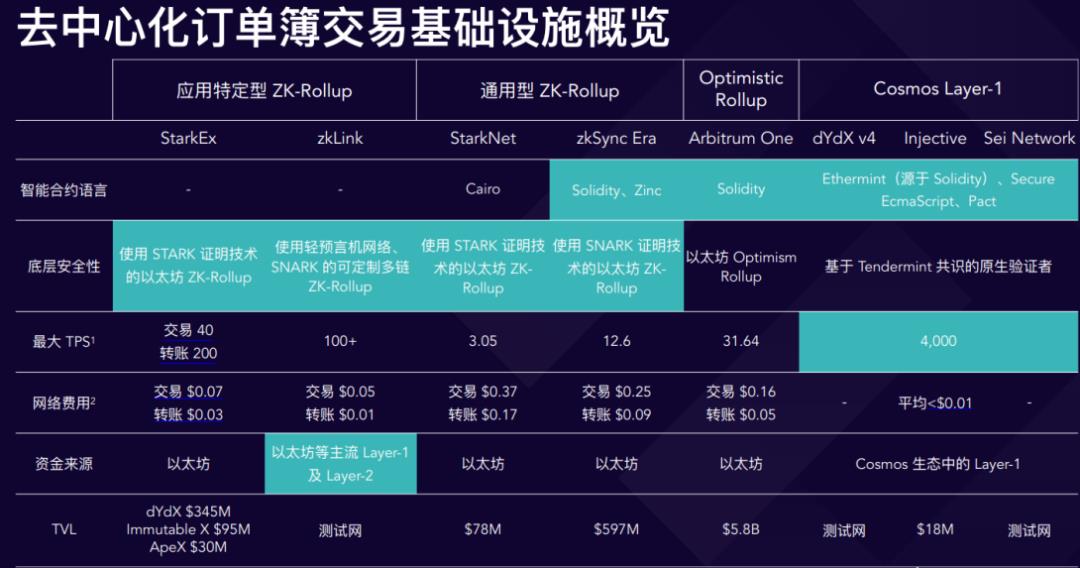
Source: TokenInsight
4.2. Competitive Analysis
4.2.1. Core Competitive Factors
The core competitive factors among order book infrastructures centered around trading mainly manifest in the following aspects:
● Performance: Transaction speed, throughput, and determinism, impacting user trading experience and efficiency.
● Cost: Transaction fees and gas fees, affecting user trading returns and cost-effectiveness.
● Security: Transaction reliability, resistance to attacks, and data integrity, influencing asset security and trust.
● Ecosystem Implementation: User scale, project quantity, and liquidity scale of the infrastructure, affecting user choice range and trading convenience.
We will focus on these four dimensions and, in combination with the current track landscape, conduct a competitive analysis of zkLink against the most popular infrastructures.
4.2.2. Competitive Projects
1) Application-Specific ZK-Rollup
Application-specific ZK-Rollup refers to infrastructure that provides customized ZK-Rollup services for specific applications or domains. The advantage of such infrastructure is the ability to optimize and innovate for specific scenarios, providing a better user experience and functionality. Representatives of this type of infrastructure include StarkEx and zkLink.
① StarkEx
StarkEx is an application-specific ZK-Rollup engine developed by StarkWare, specifically providing ZK-Rollup services for independent applications. It can process thousands of transactions per second while ensuring fund security and data availability. It currently supports projects such as dYdX V3, Immutable X, Sorare, and ApeX. The advantage of StarkEx lies in its use of STARK technology as a zero-knowledge proof system, offering high scalability and low computational costs, without relying on trusted third parties or cryptographic assumptions. The challenge of StarkEx is that it requires programming in the Cairo language, which is a new and complex language for developers, and it currently only supports the ETH network, lacking multi-chain interoperability.
② zkLink
As an application-specific ZK-Rollup middleware, zkLink is designed for multi-chain decentralized trading, enabling seamless interchange and aggregation of assets on different chains. It uses zk-SNARKs as a zero-knowledge proof system and can process over 1000 transactions per second. The advantage of zkLink is its ability to connect multiple L1 and L2 chains, aggregating liquidity from different ecosystems, making it possible to trade and combine native DeFi assets on different chains. The challenge for zkLink is that it is still in the early stages, has not yet launched the mainnet, and requires collaboration with oracle networks to achieve cross-chain data transmission and verification.
2) General-Purpose ZK-Rollup
General-purpose ZK-Rollup refers to a ZK-Rollup network that supports the deployment and execution of arbitrary smart contracts, utilizing zero-knowledge proof technology to achieve high performance, low cost, and high security on the L2 network. The advantage of such infrastructure is its ability to support various types and domains of decentralized applications, with applications being able to combine and interoperate with each other. Representatives of this type of infrastructure include StarkNet and zkSync.
① StarkNet
StarkNet is a general-purpose ZK-Rollup network developed by StarkWare, allowing developers to deploy arbitrary smart contracts and create various types of decentralized applications, with applications being able to combine with each other. It uses STARK technology to ensure fund security and data availability. The advantage of StarkNet lies in its use of STARK technology as a zero-knowledge proof system, offering high scalability and low computational costs. The challenge of StarkNet is similar to StarkEx, in that it is limited by the Cairo language.
② zkSync
zkSync has two versions: zkSync 1.0 (later renamed zkSyncLite) and zkSync 2.0 (later renamed zkSyncEra). zkSyncLite was launched in June 2020, and zkSyncEra was launched in March 2023, mainly providing ZKEVM functionality, supporting the deployment and execution of arbitrary EVM-compatible smart contracts. zkSync uses zk-SNARKs as a zero-knowledge proof system and can process over 2000 transactions per second while ensuring fund security and data availability. The advantage of zkSync is its support for programming in the Solidity language, which is familiar and simple for developers, facilitating seamless application migration. The challenge for zkSync is that asset transfers between zkSync and ETH require third-party cross-chain bridges, which may introduce certain cross-chain security risks.
3) Optimistic Rollup
Optimistic Rollup refers to infrastructure that uses fraud proofs to ensure the security of transactions on the L2 network, utilizing the Optimistic Virtual Machine (OVM) to achieve compatibility with EVM and support the deployment and execution of arbitrary smart contracts. The advantage of such infrastructure is its support for various types and domains of decentralized applications, as well as high compatibility and interoperability with Ethereum. A representative of this type of infrastructure is Arbitrum.
① Arbitrum
Arbitrum currently includes two products: Arbitrum One (general-purpose) and Arbitrum Nova (exclusive for gaming/social applications). Arbitrum One is the main product of Arbitrum, with most DeFi applications concentrated on Arbitrum One. Arbitrum One uses Arbitrum Nitro technology to implement Optimistic Rollup, using AVM (Arbitrum Virtual Machine) and ArbitrumEVM to execute smart contracts, supporting programming in Solidity and WASM languages.
4) Cosmos
Cosmos is a mesh network composed of multiple L1 chains, based on the Tendermint consensus mechanism, supporting each chain as an independent, fully functional PoS chain. Additionally, it provides the IBC protocol, enabling cross-chain communication and sharing of security and liquidity between chains. Furthermore, Cosmos offers the Cosmos SDK, a custom blockchain development toolkit that allows developers to use existing modules to meet various blockchain development needs, providing a high degree of flexibility.
Cosmos has maintained high popularity in the market due to its mature technology, and there has been a continuous stream of funding for application chains built around it. However, compared to the mature Ethereum ecosystem, the Cosmos ecosystem is still in the early stages of development, with a limited variety of tradable assets and relatively scarce liquidity within the ecosystem. This may impact the user trading experience to some extent. Therefore, for trading application chains and their products built on Cosmos, enriching the variety of tradable assets within the ecosystem and obtaining liquidity to improve the trading experience is crucial. Representative decentralized trading application chains built on Cosmos include dYdX V4 and Injective.
1) dYdX V4
dYdX is a Layer-1 blockchain network based on Cosmos, focusing on decentralized derivatives trading. It uses the dYdX token for governance and incentive assets to support various derivative products such as spot, margin, and perpetual contracts. It uses the Tendermint consensus to achieve high performance, low latency, and low-cost transactions, and can communicate with other chains through the IBC protocol. The advantage of dYdX V4 is that it provides a professional decentralized derivatives trading platform, supporting various trading strategies and tools, and has a large user base and trading volume. The challenge for dYdX V4 is that as an independent chain, it needs to maintain its own security and stability, which may lead to a certain degree of security compromise.
2) Injective
Injective is an L1 chain network based on the Cosmos SDK, providing various trading infrastructure modules, supporting developers to create diverse DeFi applications such as decentralized derivatives trading platforms, prediction markets, and lending protocols. Unlike dYdX, Injective is essentially a trading-oriented L1 network that serves multiple DeFi applications, using the Tendermint consensus to achieve high performance, low latency, and low-cost transactions. The advantage of Injective lies in its strong multi-chain interoperability, enabling cross-chain communication and asset transfers with multiple L1 and L2 chains, aggregating liquidity from different ecosystems and native assets. The challenge is similar to dYdX V4, as its security is supervised by internal network nodes, and its built-in multiple cross-chain bridges may increase security risks related to cross-chain interaction, requiring a higher level of security consideration.
4.2.3. Competitive Advantages
Based on the above competitive analysis, let's briefly compare various trading infrastructures:
● Application-Specific ZK-Rollup: Holds an advantage in technical maturity and transaction security but is limited in functionality expansion. In a horizontal comparison, applications of StarkEx are currently deployed on Ethereum, providing better basic security. On the other hand, zkLink supports native multi-chain trading assets, providing a richer source of assets and liquidity.
● General-Purpose ZK-Rollup: Starknet and zkSync support Turing-complete development, offering strong flexibility, but face inherent Layer 2 limitations, such as the potential for many applications to run simultaneously. Therefore, similar to the expensive gas fees and on-chain congestion issues currently faced by Ethereum, Starknet and zkSync will also face similar challenges in the future.
● Optimistic Rollup: Represents Arbitrum, which is highly compatible with ETH, offering convenient development but inferior security and cost compared to ZK-Rollup.
● Cosmos Layer-1: Utilizes Tendermint, providing performance advantages and supporting rapid application development through the SDK. However, it exhibits average decentralization and security performance, and due to the early stage of the entire Cosmos ecosystem compared to Ethereum, it has certain disadvantages in key indicators affecting the trading experience, such as the variety of tradable assets and liquidity.
Compared to the aforementioned infrastructures, zkLink, as an application-specific ZK-Rollup middleware, has the following competitive advantages:
● Pioneering the design of a truly unified multi-chain liquidity pool, supporting seamless exchange of assets across multiple mainstream public chains.
● Utilizing zk-SNARKs zero-knowledge proofs, offering high transaction speed and stronger security compared to other Layer 2 solutions.
● Aggregating liquidity from different ecosystems, providing users with a wide range of DeFi product choices.
● As an application-specific infrastructure, it allows for easier customization to achieve a powerful user experience.
● Technologically independent and not reliant on any third party, offering better long-term reliability.
Through technological innovation, zkLink has the potential to become a leading infrastructure in the multi-chain trading industry.
### 4.3. Token Economic Model Analysis
4.3.1. Token Total Supply and Distribution
ZKL is the universal token and governance token of the zkLink protocol, with a fixed total supply of 10 billion and no inflation. ZKL will be issued following the ERC20 standard and may be deployed on other chains in the future, but details of allocation and distribution have not been disclosed (mainnet not yet launched).
4.3.2. Token Value Capture
● ZKL serves as the payment currency for block fees in the zkLink network, and DApp servers and validator nodes need to hold ZKL to participate in services and consensus to receive rewards.
● ZKL holders can participate in governance to influence the direction of zkLink development and gain more rewards.
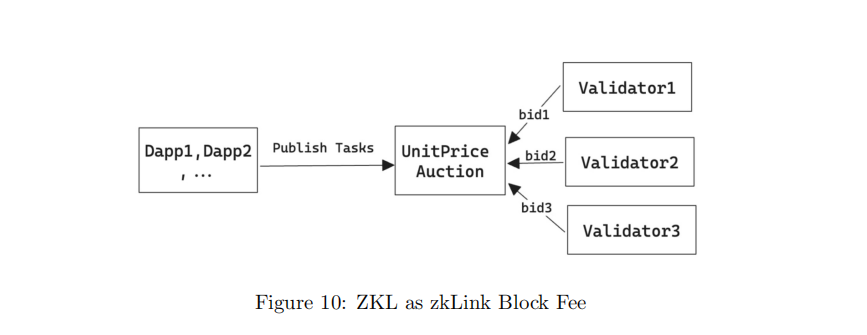
4.3.3. Core Demand for Tokens
● DApp developers: To deploy DApp contracts on the zkLink platform, DApp developers need to hold a certain amount of ZKL as collateral, ensuring the normal operation of the zkLink network and providing a high-performance, low-cost development and operation environment for DApp developers.
● Validator nodes: Validator nodes participate in the consensus operation of the zkLink network by staking ZKL as collateral, earning block rewards and transaction fee income, thereby enhancing the efficient and reliable operation of the zkLink network.
● Trading users: Users can enjoy business privileges by maintaining a ZKL balance, such as free or discounted gas fees, which will incentivize user participation in the zkLink ecosystem.
● Governance participants: ZKL holders can stake ZKL to obtain veZKL to participate in DApp governance voting and proposals, influencing the future development direction of the zkLink network and converting rewards into higher ZKL value.
zkLink captures value through ZKL, incentivizing various parties to participate in ecosystem development. With its reasonable design, ZKL has the potential to become a cornerstone of the zkLink ecosystem.
5. Preliminary Valuation
To conduct a preliminary evaluation of zkLink's value, we can analyze based on the following questions:
5.1. Core Issues
At which stage of the business cycle is the project? Is it in the mature stage or in the early to mid-stage of development?
The zkLink whitepaper was released in 2021, and the mainnet has not yet been officially launched, only in the testing network stage. The project is in the early stage of development, with the potential to become a leader in multi-chain infrastructure:
● zkLink has innovatively achieved a unified multi-chain liquidity pool design using ZK technology, but it still needs time to accumulate experience in practical application and verification.
● To date, zkLink has not established deep connections with mainstream public chains, and its cross-chain capabilities and application compatibility need to be verified.
● The zkLink ecosystem applications are in the early stages, with a limited number of cross-chain DeFi products and DApps, and a relatively small user base and liquidity.
● The target token ZKL was issued this year, and its related economic mechanisms have not been long-term verified, and the governance mechanism needs to be clarified in practice.
● The project team needs to continuously optimize zkLink technology, improve TPS, reduce gas costs, and enhance decentralization.
However, as an infrastructure aimed at leading the development of multi-chains, zkLink's technical concepts and designs are forward-looking. With the advantage of ZK acceleration and collaboration with the Cosmos project, it has enormous potential for future development. As long as it can deeply integrate into various ecosystems and promote application landing, zkLink has the potential to become one of the leading infrastructures for multi-chain trading. It is currently in an important stage of technical validation and ecosystem development.
What are the main variable factors in the project's operations? Are these factors easy to quantify and measure?
As a decentralized infrastructure project in the early stages, the main variable factors in zkLink's operations include:
● Ecosystem development: This mainly refers to the number of new DApps and trading volume, which are easy to quantify and measure.
● User experience: Metrics such as average order waiting time and failure rates are more difficult to track accurately over the long term.
● User and transaction volume: The number of daily/ monthly active users, reflecting user stickiness, is of significant importance for long-term operations. The number of daily/ monthly transactions reflects the level of application activity. These data are easy to quantify and measure.
What is the project's management and governance model?
zkLink's governance model is based on DAO community autonomy, using the ZKL token to incentivize and coordinate the behavior of participants, including validators, witnesses, developers, and liquidity providers. The ZKL token can also be used to pay transaction fees, participate in governance voting, and enjoy platform benefits.
5.2. SWOT Analysis
5.2.1. Strengths
For the project's strengths, please refer to section 1.1 Core Investment Logic.
5.2.2. Weaknesses
Complexity and risks in technical implementation: As a multi-chain decentralized middleware, zkLink faces significant challenges in technical implementation. It needs to address various difficulties in decentralized trading, cross-chain operations, and asset circulation, relying on cutting-edge technologies such as ZK proofs and Rollup. These technologies are still in the rapid iteration and validation stage, and each individual technology implementation requires iterative optimization. Integration of these technologies becomes even more challenging. For example, designing a high-performance and universal ZK proof template to meet the customized requirements of different chains and applications still presents many unresolved issues. Additionally, zkLink's cross-chain transactions require validation from oracle networks, which also face security and performance challenges. Any issues with the oracles could impact asset confirmation. Furthermore, establishing technical collaborations with different chains is not simple. As one of the early projects attempting this, zkLink is likely to face many unknown risks in integrating and applying new technologies.
Early-stage ecosystem development risks: Despite its technological leadership, zkLink is still in the early stages of practical promotion and ecosystem accumulation. It needs to build credibility through real-world cases in a competitive environment, which is a long-term process. Currently, the zkLink ecosystem has a relatively limited number of DApps and user base, which hinders the creation of real added value. This is one of its biggest obstacles, making it difficult to attract more users in the short term by creating a cluster of high-quality products and services to generate a positive development effect. Additionally, asset value anchoring and liquidity accumulation between different chains also require long-term operation for validation. Any issues at critical points could affect ecosystem trust, requiring continuous optimization and collaboration across multiple industries to gradually address deficiencies. Failure to gather user feedback in a timely manner, improve product experiences, and actively empower ecosystem development will make it difficult for zkLink to continuously build brand loyalty in the competitive market, affecting its ability to truly grow into a strong multi-chain cornerstone in the future.
5.2.3. Opportunities
Strong demand for multi-chain decentralized trading: With the rapid globalization of decentralized finance, the demand for cross-chain functionality is increasing. In the growing decentralized applications, supporting asset liquidity and cross-chain operations has become a consensus requirement. zkLink aims to become a multi-chain decentralized financial infrastructure, connecting major public chains and contributing to the construction of an open and inclusive decentralized financial environment. It effectively aggregates multi-chain assets and liquidity using technologies such as ZK-Rollup, significantly reducing the cost threshold for cross-chain transactions. As the DeFi sector continues to grow, the demand for cross-chain DEX, lending, and swap applications is increasing, making multi-chain functionality particularly important. zkLink can aggregate liquidity from various chains, meeting users' expectations for cross-chain DeFi operations on a single platform, which will lead to a surge in demand. Additionally, zkLink provides custom interfaces, allowing any chain to integrate with zkLink as an L2 scaling solution. It can also help different chains address various business challenges, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. These functions and potential applications will attract more projects to choose zkLink as their infrastructure partner, creating a collaborative future.
Rapid development of the Layer2 ecosystem presents a great opportunity for zkLink's interoperability services: Over the past year, Layer2 solutions have made significant progress in solving Ethereum's performance bottlenecks and achieving significant scalability. Various Layer2 solutions have been deployed on different chains, attracting a large number of users. However, for the continued rapid development of the decentralized ecosystem, interoperability between Layer2 solutions is equally important. A single Layer2 solution often cannot cover all on-chain resources, and aggregating liquidity is also challenging. This presents an opportunity for zkLink. As an all-in-one multi-chain Layer2 solution, zkLink can fully utilize the ecological dividends brought by Layer2 upgrades, attracting various scaling solutions and their user bases. It supports seamless circulation of multi-chain assets, with the potential to quickly gather a large amount of liquidity, boosting overall DeFi traffic. Overall, the flourishing development of Layer2 solutions presents a significant opportunity for zkLink to achieve higher growth, establish a leading position in the decentralized ecosystem, and should not be missed.
5.2.4. Threats
Competitors are progressing rapidly, but there is insufficient application implementation. With the booming development of cross-chain applications, various solutions continue to emerge. Many zkLink-like products have emerged, and these emerging competitors not only have impressive technical capabilities but also significant financial strength. Some competitors have already received support of over a billion in funding, which adds greater market competition pressure on zkLink. Additionally, competitors are continuously optimizing their products and expanding their ecosystem coverage. In specific chains or application scenarios, competitors may have a technological and more mature user experience advantage over zkLink. Furthermore, large public chains such as Polygon and Cosmos are also continuously expanding into the multi-chain service field, leveraging their ecosystem advantages. It is difficult to ignore these chains as important potential competitors, and they may also introduce more professional solutions in the future.
Complexity of the multi-chain environment: zkLink needs to provide seamless connections across multiple public chains and Layer2 networks, which places high demands on technical implementation. There are differences between different chains in technical architecture, ecosystem languages, consensus rules, and many other aspects, posing significant challenges for zkLink. For each target chain added, zkLink needs to optimize it specifically to smoothly integrate into the aggregation system. This requires in-depth study of each chain's documentation and extensive practical verification, resulting in a significant workload. Additionally, due to the dynamic development of chains, any future architecture or parameter adjustments could affect the data verification and exchange processes between the chains. zkLink needs to continuously follow up and iterate upgrades, consuming resources and effort in maintenance work. Furthermore, compatibility issues between different chains due to technical or organizational reasons could lead to an unfriendly user experience, posing one of the hidden systemic risks.
The complexity of the multi-chain environment presents higher barriers for zkLink's technical planning and daily operational management. Long-term management of uncertainty in this area remains a significant obstacle.
5.3. Reflection
zkLink has strong technological advantages and commercial prospects. With continuous enhancement of its features and ecosystem development, it has the potential to become a benchmark project for future multi-chain interactions. After analyzing the project, we believe that zkLink still has some room for development:
● Support for more public chains: Currently, it mainly supports Ethereum EVM-compatible chains, but it can potentially support a wider variety of public chains in the future.
● Improved DApp integration mechanism: Providing a large number of API interfaces and standardized development kits to enhance DApp integration mechanisms.
● Introduction of sequencing mechanisms: Supporting transaction supply and consistency mechanism maintenance to further enhance decentralization.
● Exploration of application scenarios: Actively exploring areas such as cross-border payments and supply chain finance to stimulate zkLink's commercial potential.
● Ecosystem development: Actively nurturing the DApp developer community and building a complete open zkLink ecosystem.
In summary, as a stable and reliable multi-chain trading platform infrastructure, zkLink has laid a solid foundation for the future comprehensive applications, including finance. As long as it continues to consolidate its technological advantages and deepen its ecosystem development, zkLink will undoubtedly gradually become a leading project in this field. From this perspective, zkLink still has significant opportunities worth exploring.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




