Worldcoin Analysis
Upon disassembling Worldcoin, it can be seen that its DID, wallet, and tokens are not significantly different from most other digital currency projects. The important difference lies in the project's completion not being limited to blockchain, and its impact not being confined to blockchain.
Worldcoin is a token distribution project, and it has close ties with Open AI founder Sam Altman. However, the actual operation is mainly led by CEO ALEX Blania. The project may face legal regulation, privacy protection, and promotional issues. At the same time, as a representation of UBI economics, the project is powerful and has a grand vision.
Summary
Worldcoin is a token distribution project. It coordinates the interests of all participants and is committed to distributing the majority of tokens to new users as an incentive to join the network for widespread adoption.
The Worldcoin project is a concrete manifestation of UBI economics, which aims to achieve unconditional basic income. In 2020, as the COVID-19 pandemic spread globally, many governments chose to distribute consumption vouchers or cash to stabilize the social and economic operation, which is a specific manifestation of UBI economics. However, the problems brought about by these measures are also very apparent, such as inflation and a lack of willingness to work.
Currently, UBI economics relies on centralized governments to handle wealth redistribution tasks, which may come from the government cutting its own expenses or increasing currency issuance, and cannot truly create wealth. Therefore, true UBI economics may only be established when artificial intelligence is highly mature. Open AI founder Sam Altman, as a co-founder of Worldcoin, may have a certain vision for the future world through AI and Worldcoin.
The biggest challenge currently facing Worldcoin is whether the tokens can be fairly distributed and where the token value comes from. The Worldcoin project believes that it can prevent witch attacks through technologies such as iris scanning and ZKML, but the current practical effect is generally not significant, and it has raised concerns among users about privacy leaks and data regulation.
In the past, such grand projects have mostly failed. For example, Facebook's development of Libra has encountered regulatory pressures, Pi coin has been deeply embroiled in pyramid scheme debates, and although Bitcoin appears to be a successful project, its speculative value still far outweighs its utility value. Therefore, it is clear that the success rate of such projects is extremely low.
Advantages of Worldcoin:
1) Excellent background of the project team; 2) Grand vision and great development potential;
Disadvantages of Worldcoin:
1) User privacy may be compromised; 2) Token distribution cannot completely eliminate witch attacks; 3) The project may face regulatory risks and significant development resistance; 4) Low success rate of similar past projects; 5) As a UBI project, the token lacks practical support, which may have a detrimental impact on some individual investors.
Therefore, it is advisable to maintain a cautious attitude towards this project.
1. Basic Overview
1.1 Project Introduction
Worldcoin is a token distribution project that utilizes blockchain, biology, statistics, and other technologies.
1.2 Basic Information

2. Project Details
2.1 Team
The Worldcoin team consists of individuals with diverse backgrounds and experiences, including CEO ALEX Blania, who has been leading the project's operations.
2.2 Funding
Worldcoin has raised a total of $125 million in funding, with an initial $25 million in Series A funding and $100 million in initial token issuance funding.
2.3 Code
Figure 2-1: Worldcoin's code situation
Worldcoin's GitHub page shows that the project mainly uses languages such as C++, C, Python, M4, Makefile, and Shell, with a total of 694 volunteers involved.
2.4 Product
Worldcoin is an open-source protocol designed to help everyone enter the global economic system. It aims to coordinate the interests of all participants and distribute the majority of tokens to new users as an incentive for widespread adoption. The project is currently operated by two organizations: the Worldcoin Foundation and Tools for Humanity. The Worldcoin Foundation is a non-profit organization aimed at supporting and developing the Worldcoin community until it becomes sufficiently decentralized. Tools for Humanity is a technology company that aims to accelerate the transition to a more just economic system. It has led the initial development of the Worldcoin protocol and has also built other tools to support the Worldcoin protocol.
Worldcoin consists of three main parts:
1) World ID - a privacy-protecting digital identity aimed at solving many important identity-based issues, including proving the uniqueness of individuals; 2) World Token - a token distributed for free globally, used for practical purposes and governance; 3) World App - a fully self-hosted application that allows for payments, purchases, and transfers globally using Worldcoin Token, digital assets, stablecoins, and traditional currencies.
Among these, World ID is the most important component of Worldcoin, as it provides user identity verification. The team believes that the rapid development of artificial intelligence has accelerated the need to distinguish between human-generated content and AI-generated content online. Identity verification addresses two key considerations in the AI era: preventing witch attacks and minimizing the spread of misinformation generated by AI.
World ID provides a World ID SDK for developers to use. It is a digital passport that allows users to prove themselves as unique and real individuals while remaining anonymous, achieved through zero-knowledge proofs (ZKP) and other privacy-protecting encryption mechanisms. Integration and use of World ID require registration in the developer portal, creating the first application, and configuring it. World ID plans to be used in voting, social media, and fund allocation. Users' World ID exists on their devices and only on their devices. Users install compatible identity wallets, generate unique and random private keys stored on their devices, and the identity wallet may include a recovery mechanism.
According to the user's private key, a file is generated and published on the chain, which is considered a form of identity commitment. The user's wallet generates a ZKP for each verification, making it easy to verify across applications or operations, with the aim of protecting user privacy. The principle of identity verification is to allow a person to digitally prove that they are a unique real person. Building a global, scalable, and inclusive identity verification system is the core of World ID. Identity verification only needs to prove that a person is a human, not which specific person they are.
To serve other applications, World ID can now be used as an OpenID Connect provider. The following diagram outlines the general authentication process for integrating applications:
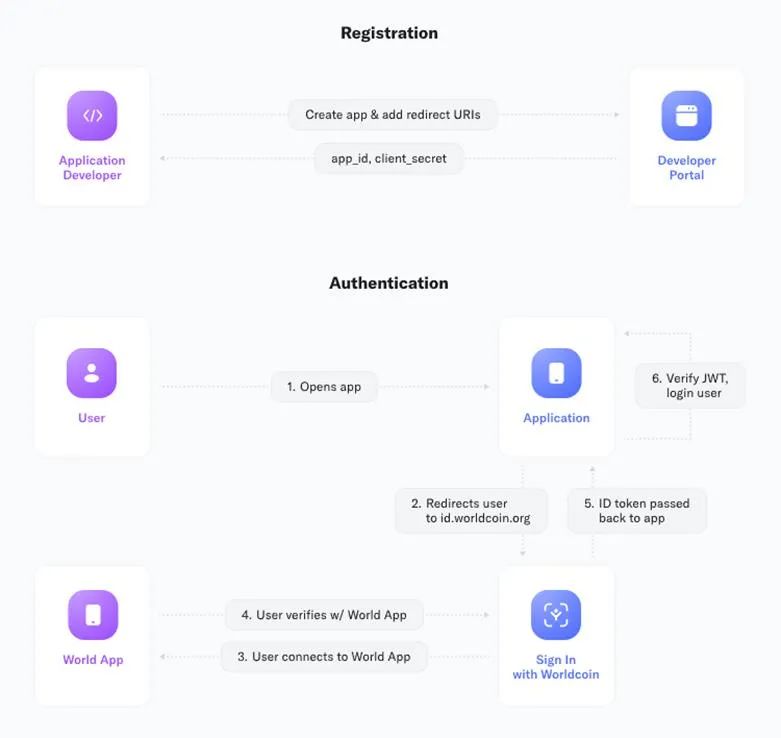
Worldcoin operates in three steps:
1) Download World App
Downloading the World App allows users to set up a Worldcoin account and access a digital wallet connected to Worldcoin, Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other digital and traditional currencies (including stablecoins). The World App is operated by Tools for Humanity, a contributor to the Worldcoin system.
2) Register World ID
World ID can be used with the World App without registration. However, to receive free shares of Worldcoin tokens and other digital currencies, users must visit the Worldcoin operator and undergo Orb verification.
3) Obtain Free Shares of Worldcoin and Other Digital Currencies
Each World App user will receive an Ethereum wallet with a smart contract deployed on the chain. The World App uses account abstraction to enhance the overall security of the wallet. At the core, Worldcoin uses an account abstraction stack developed by the multi-signature wallet Safe. Peer-to-peer payments in World App support the use of ENS usernames for more user-friendly ERC-20 transfers, and token conversion can be achieved through Uniswap.
Here are some key elements of the project:
Zero-Knowledge Machine Learning
Zero-knowledge proofs are a common concept in the blockchain industry. They are an encryption protocol that allows a prover to prove to a verifier that a given statement is true without revealing any other information about the statement. ZK brings two main "primitives": the ability to create computational integrity proofs for a given computation, making it easier to verify than performing the computation itself. The computational cost of generating zero-knowledge proofs is many times larger than the original computation, making some computations impractical. ZK technology can be used for identity verification and data tracing. Worldcoin needs to build World ID, a privacy-protecting identity verification protocol that allows anyone with World ID to provide encrypted proof that they are a unique person without revealing their identity.
Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence involving the development and application of algorithms that enable computers to learn and adapt to data, optimizing their performance through iterative processes. Large language models such as GPT-4 and Bard are state-of-the-art natural language processing systems that generate human-like text using large amounts of training data. From text to image models, such as DALL-E 2, Midjourney, and Stable Diffusion, transform text descriptions into visual representations with extraordinary fidelity.
ZKML has the potential to be used in the context of Worldcoin for iris code upgradability. World ID users will be able to store their signed biometric features in encrypted storage on their mobile devices, download ML models for iris code generation, and create zero-knowledge proofs locally to prove that their iris code was indeed generated using the correct model from the signed image. This iris code can be inserted into the collection of registered Worldcoin users without permission, and smart contracts will be able to verify the zero-knowledge proof created by the iris code.
Operator
Users can apply to become operators, and the process of becoming an operator is divided into four parts: 1) Fill out the application form; 2) Interview; 3) Receive an Orb; 4) Start promoting. Operators can earn income from each successful user registration using Orb. To become an operator, one needs to build their own promotion team and choose locations with high foot traffic for promotion.
Orb
Orb is Worldcoin's iris scanning technology used for identity verification. It is a small device that verifies a user's identity by scanning their iris. This technology aims to enhance the security and reliability of identity verification and to fairly distribute cryptocurrencies through universal basic income based on cryptocurrency. The device has been controversial since its introduction, with many concerns about the security and privacy of iris scanning technology. In response, the Worldcoin team stated that current commercial iris imaging devices do not meet the technical or security requirements of Worldcoin. The team spent several years developing custom devices to achieve universal access to the global economy in the most inclusive and privacy-protecting manner. Orb is part of the World protocol and verifies whether a person is a real human and has uniqueness. It ensures that users are real humans by using highly specialized sensors, then captures, processes, and quickly deletes a series of iris images by default to create an iris code. The message containing the iris code is sent from Orb and compared to all other iris codes scanned on Orb previously. Users who pass the verification will receive an identity certificate in a compatible digital wallet. Worldcoin promises to protect user privacy and claims that Orb can prevent deception, tampering, or hacking attacks. Each Orb is equipped with a private key stored in secure hardware for verifying Orb and signing important messages. Fraud prevention algorithms based on multispectral sensors run locally on the device to maximize privacy. By default, Orb immediately deletes iris images after creating the iris code. Additionally, a team supporting the Worldcoin project is continuously testing the device, and several teams are working every day to further enhance the security of Orb.
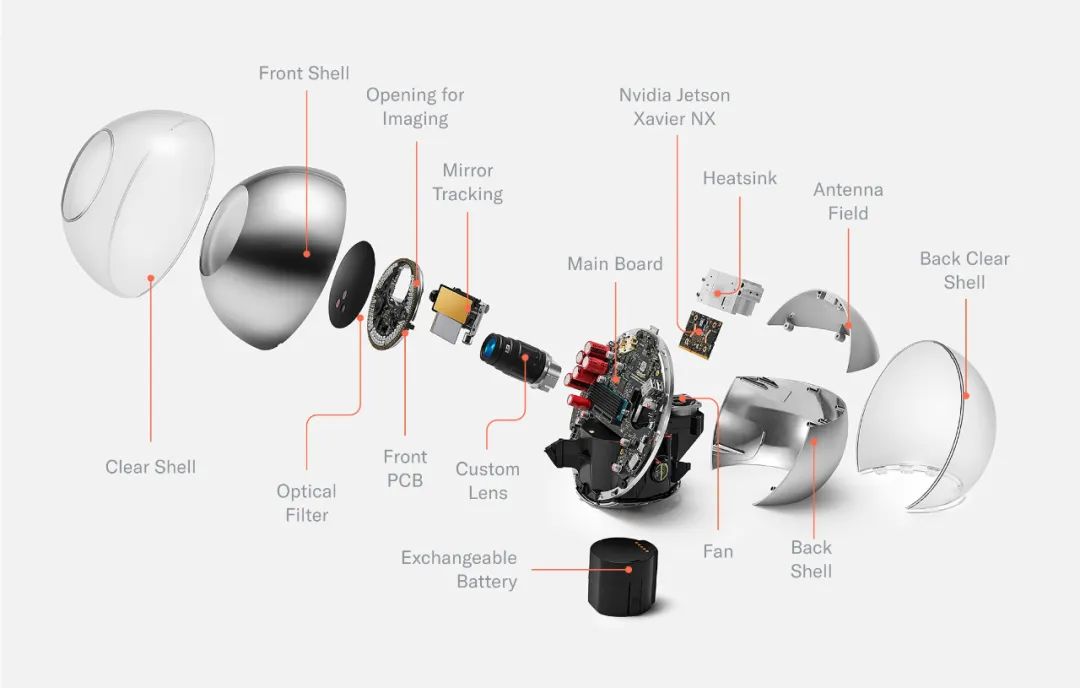
The team initially did not want to develop hardware because it requires a lot of resources. However, they believe that iris scanning is the most effective way to prevent witch attacks. The iris has strong anti-fraud and data-rich characteristics. Orb mainly consists of three parts: 1) Sphere disassembly; 2) After removing the shell, the mainboard, optical system, and cooling system are revealed; 3) Mechanical design.
Orb can be divided into four core parts: 1) Front end: optical system; 2) Middleware: the mainboard divides the device into two hemispheres; 3) Back end: the main computing unit and active cooling system; 4) Bottom: replaceable battery.
How does Orb ensure user privacy?
The team guarantees that no data will be sold. The most important issue that needs to be addressed for the distribution of Worldcoin tokens is how to ensure that a person only receives tokens once. To maintain this privacy, images collected by Orb are immediately deleted unless the user explicitly requests otherwise. By default, the only personal data that can leave Orb is digitally represented information containing the most important features of the image to verify uniqueness, i.e., World ID. World ID is designed to be completely disconnected from a person's biometric data. It uses zero-knowledge proofs, allowing users to share specific information, such as proof of uniqueness, without disclosing other information. World ID currently uses an open-source protocol called Semaphore to ensure that verification is anonymous and cannot be traced back to a person's identity. Semaphore is a zero-knowledge protocol that allows users to signal as a provable member of a group (e.g., voting or endorsement) without revealing their identity. Additionally, it provides a simple mechanism to prevent double spending.
According to BlockBeats, some crypto users in certain regions were unable to register and receive shares of Worldcoin tokens upon their release. However, a new method emerged where "scalpers" collected iris data from local villagers in Southeast Asia and sold personal crypto users for $30 or less to help complete app registrations. A Worldcoin spokesperson acknowledged this phenomenon but emphasized that the issue was limited to "a few hundred instances." The spokesperson stated, "Through ongoing threat and awareness monitoring measures, the Worldcoin team has identified suspicious and potential fraudulent activities that prompt individuals to register verified World IDs and then send them to third-party World Apps instead of their own."
At the same time, Worldcoin's handling of privacy is also facing pressure from regulators. Worldcoin has a registered subsidiary in Germany, and according to GDPR principles, any data processing or data involving EU residents is subject to EU regulation. However, Worldcoin's global operations and EU regulations are in conflict. For example, the team claims that 1% of the population of Portugal has become its users, but how global data is handled has not been fully explained. According to GDPR, "failing to adequately protect data may result in fines of up to 4% of global revenue or €20 million."
Additionally, whether Worldcoin can achieve its claimed fair distribution is also a question. Due to various national regulatory policies, residents of China and the United States can register the app but cannot be verified through World ID. According to official data, most of Worldcoin's registered users are from poor countries, such as Africa and Latin America. The number of countries and regions participating in its testing currently stands at 24, with 14 being developing countries and 8 in Africa. The specific distribution is as follows:
Africa: Benin, Ghana, Nigeria, South Africa, Sudan, Zimbabwe, Kenya, and Uganda;
Latin America: Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Mexico;
Europe: France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, the United Kingdom, Norway;
Asia: India, Indonesia, Israel, Turkey.
The distribution of its tokens worldwide is in doubt. Furthermore, Worldcoin's self-research level is low, and it mostly collaborates with well-known projects. In terms of the underlying architecture, Worldcoin collaborates with Optimism, uses Safe for accounts, and employs ENS and Uniswap for transfers and transactions. While good projects do not need to reinvent the wheel, overall, Worldcoin is not a very innovative project.
Summary: Worldcoin is an open-source protocol with the goal of promoting the use of its token worldwide. The project's biggest highlight is the co-founder's relationship with Sam Altman, the founder of Open AI, which has attracted attention from investors. Worldcoin aims to authenticate users' realness and uniqueness through iris scanning, but this method has proven to be ineffective in practice and susceptible to exploitation. Additionally, the collection of iris data raises concerns about privacy and may attract government regulation. Upon closer examination, Worldcoin's dismantling reveals that it does not differ significantly from most other cryptocurrency projects in terms of DID, wallets, and tokens. The significant difference lies in the project's completion not being limited to blockchain and its impact extending beyond the blockchain. However, the project's level of self-research is average, and its project components mostly involve collaboration with major projects.
3. Development
3.1 History
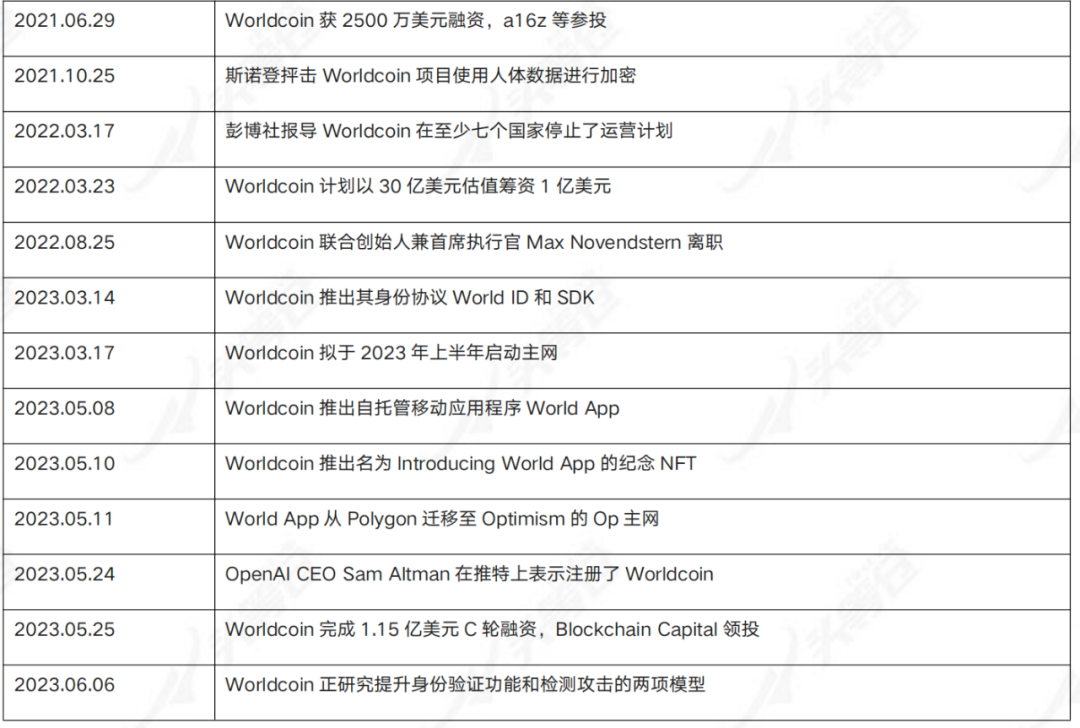
Table 3-1 Major Events in Worldcoin
3.2 Current Status
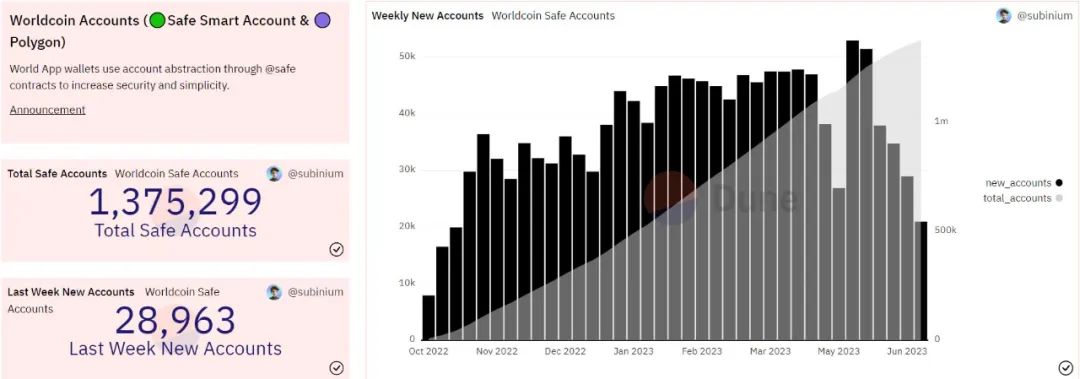
Figure 3-1 Data on Account Creation in Worldcoin
Currently, Worldcoin has a total of 1,375,299 registered accounts on Polygon, with 28,963 new accounts added last week. From the stacked chart, the current growth rate has slowed compared to the past.
Worldcoin App has issued commemorative NFTs, which are currently tradable on Opensea with a floor price of 0.008 ETH.
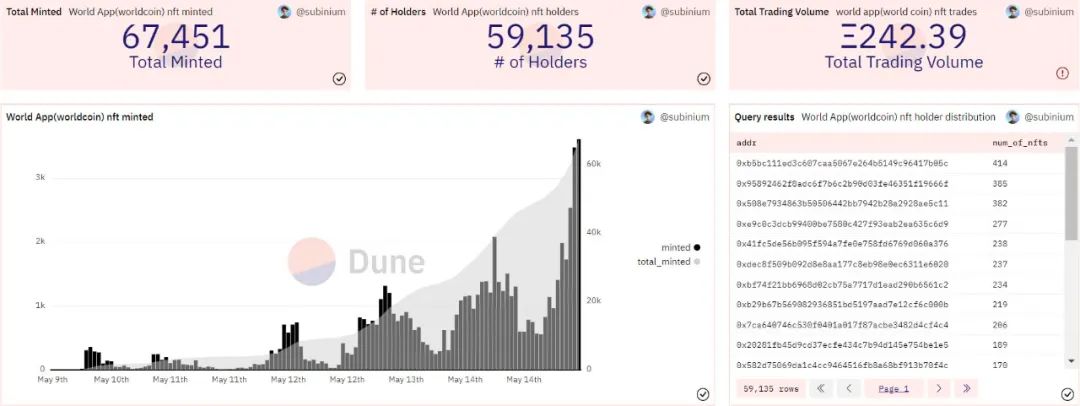
Figure 3-2 NFT Mint Data for Worldcoin
A total of 67,451 NFTs have been minted by World App, held by 59,135 individuals. The address holding the highest number of NFTs holds a total of 414, and the top ten addresses hold a minimum of 189 NFTs. The total trading volume for NFTs is 242.39 ETH (Opensea shows 246 ETH).
3.3 Future
The project has not yet released a roadmap.
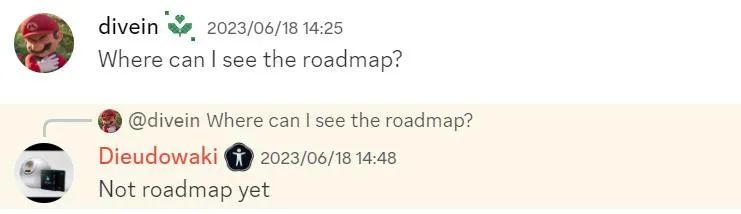
Figure 3-3 Response from Worldcoin Discord Regarding the Roadmap
4. Economic Model
Token Name: $WLD, Total Supply: 10 billion.
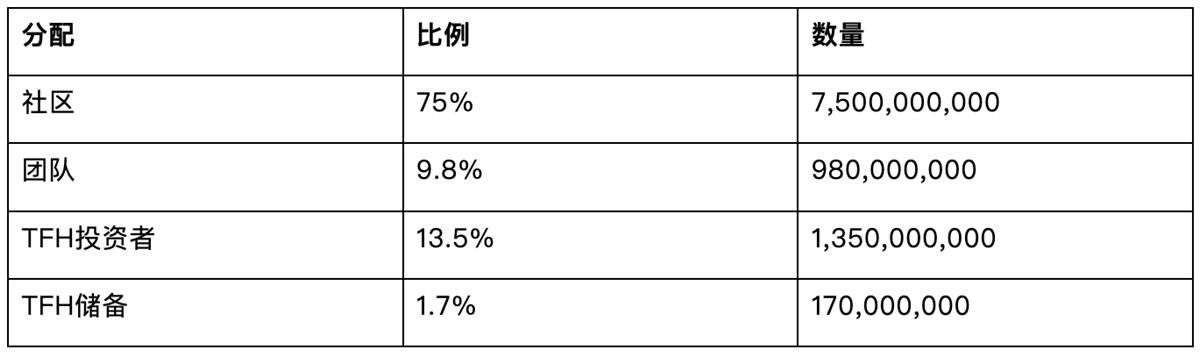
Table 4-1 Distribution of Worldcoin Tokens
5. Competition
5.1 Industry Overview
The Worldcoin project embodies UBI economics, which is the study of the concept, principles, effects, and implementation methods of unconditional basic income. UBI economics involves various issues such as the theoretical basis of UBI, financial sources, distribution impact, incentive effects, social welfare, economic growth, and social stability. UBI economics also focuses on the feasibility and adaptability of implementing UBI in different countries and regions, as well as the relationship and coordination of UBI with other social policies. UBI economics is similar to historical utopian socialism. With the continuous improvement of productivity and the development of artificial intelligence, we cannot say that this idea lacks a realistic theoretical basis. However, UBI may lead to problems such as inflation and debt crises, weaken people's work motivation and social responsibility, and cause resource waste and efficiency loss. Additionally, UBI may face challenges in implementation difficulty and sustainability, requiring consideration of issues such as funding sources, distribution standards, and regulatory mechanisms. Overall, UBI projects are ahead of the current state of social development, and these projects only redistribute wealth without truly creating wealth.
Projects like Worldcoin believe that the existing economic model has many problems and are dedicated to solving these issues to improve human life. Whether these methods can truly help improve the existing economic model or make human life better is difficult to quantify due to their macroscopic nature. Therefore, we can only theoretically argue whether these projects have the potential for success.
5.2 Competitive Comparison
Libra
In 2019, the American internet giant Facebook created Libra, a plan to create a simple global currency and financial infrastructure. It was managed by an independent non-profit organization called the Libra Association, composed of Facebook and several other companies and institutions. Libra is a stablecoin, with its value pegged to a basket of fiat currencies, allowing for fast and low-cost cross-border payments on platforms that support Libra. The release of the Libra whitepaper in June 2019 garnered unprecedented attention in the blockchain industry but also drew scrutiny from regulatory agencies worldwide, fearing that it would threaten financial stability and monetary sovereignty. Some founding members also withdrew from the project due to political pressure. To address regulatory challenges, Libra released a whitepaper 2.0 in April 2020, making significant adjustments, including:
1) Abandoning the design of a single stablecoin in favor of issuing multiple stablecoins anchored to a single fiat currency (e.g., LibraUSD, LibraEUR, etc.), as well as a composite stablecoin (Libra Coin) composed of these stablecoins;
2) Strengthening the security and transparency of reserve funds, committing to depositing reserve funds in highly reputable central banks or international institutions and subjecting them to audits and supervision;
3) Adding measures for preventing financial crime and consumer protection, requiring all network participants to comply with local laws and regulations and verify user identities and risk levels through compliant network interfaces (VAN);
4) Abandoning the goal of ultimately achieving a permissionless network and instead maintaining a permissioned network, with the future transition to permissionless being decided by association members' votes.
However, the Libra project ultimately inevitably failed for several reasons:
1) Regulatory Resistance: Since the release of the whitepaper in June 2019, the Libra project has faced strong opposition and questioning from governments and regulatory agencies worldwide, primarily concerned about its potential threat to financial stability, monetary sovereignty, consumer protection, data privacy, anti-money laundering, and counter-terrorism financing. The U.S. Congress even demanded that Facebook suspend the Libra project and held multiple hearings, questioning Libra's head David Marcus. The Libra project encountered strict regulatory barriers in the United States and Europe, unable to obtain the necessary approvals and licenses;
2) Loss of Partners: Initially led by Facebook, the Libra project was managed and operated by the Libra Association, consisting of 28 well-known companies and institutions. These partners included payment giants Visa, Mastercard, PayPal, e-commerce platforms eBay, Mercado Pago, blockchain companies Coinbase, Xapo, investment institutions Andreessen Horowitz, Union Square Ventures, and others. However, in the face of government pressure and questioning, some important partners successively withdrew from the Libra Association, including PayPal, Visa, Mastercard, eBay, Stripe, etc. The loss of these partners weakened the influence and credibility of the Libra project;
3) Business Sale: After multiple adjustments and a name change to Diem, the project still did not receive approval from the U.S. government and faced competition from other cryptocurrency projects. In January 2022, the Diem Association announced the sale of its intellectual property and other assets related to the Diem payment network to Silvergate Bank and the gradual dissolution of its subsidiaries. This marked the formal end of Facebook's dream of issuing currency.
Bitcoin
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency and a decentralized digital currency that is not controlled by any government or financial institution. It was created in 2009 by an individual or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Bitcoin allows users to transact directly without intermediaries (such as banks). Bitcoin transactions are recorded and verified using blockchain technology. The blockchain is a distributed database that stores records of all Bitcoin transactions. Each block contains multiple transactions and is linked to the previous block using a complex encryption algorithm, forming an immutable transaction history. According to Bitcoin's on-chain data, there are now over 1 billion wallet addresses, with approximately 250,000 transactions per day and around 1,000,000 active addresses per day. Assuming that every 5 independent addresses correspond to 1 independent user and the overlap rate with Ethereum users is 30%, the total number of Bitcoin users is approximately 3.8891 million. In comparison, Visa, as a digital payment company, has over 426 million active user and merchant accounts, operating in over 200 markets and supporting payments in 25 currencies. Therefore, Bitcoin still lags behind traditional payment methods.
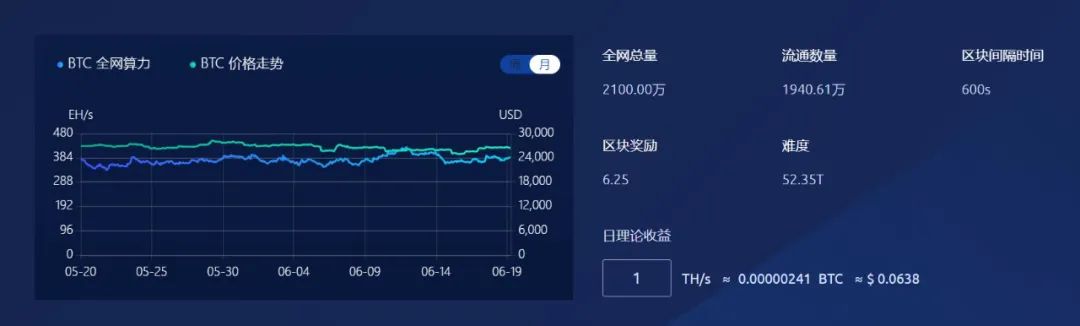
Figure 5-1 Bitcoin Hash Rate Network
Pi Network
Pi Coin is the native currency of the Pi Network and can be mined through the Pi application. Pi Coin uses a consensus mechanism called the Stellar Consensus Protocol, originally developed for the Stellar blockchain. The mission of the Pi Network is to establish a cryptocurrency and smart contract platform operated securely by ordinary people. It provides a developer platform called the Pi Apps Platform, allowing developers to build applications on the Pi Network. The platform offers an interface called Pi Browser, where developers can quickly develop, test, and deploy decentralized Pi applications. Users can access Pi applications by downloading the Pi Browser and logging in through the Pi mining application, and mining Pi Coin is free. Pi Coin has been criticized for its pyramid scheme-like nature, as it requires invitations to join. However, the team denies that the project is a pyramid scheme and believes their goal is to build a decentralized cryptocurrency network to provide easier access to digital currency for ordinary people.
Figure 5-2 Pi Coin Blockchain Browser
Practitioners in the cryptocurrency industry generally believe that the existing monetary system has some problems, such as:
1) Centralization: The existing monetary system is centralized, controlled by governments and financial institutions. This means individuals have limited control over currency and may be influenced by political and economic instability.
2) Inflation: The existing monetary system is susceptible to inflation. When governments increase the money supply, the purchasing power of the currency decreases, leading to price increases.
3) Inequality of Opportunity: The existing monetary system may be unfair. Due to financial institutions' control over credit, some people may be unable to obtain loans, thus missing out on economic opportunities.
4) High Costs: In the existing monetary system, the costs of cross-border remittances and transfers may be high, hindering global trade and investment circulation.
Cryptocurrencies attempt to address these issues by providing a decentralized, secure, transparent, and low-cost alternative. Overall, the success rate of projects attempting to change the existing economic model is very low, even Bitcoin to a large extent is more speculative than utilitarian. While there are indeed some problems with the current macroeconomic operating model, these are very large issues that will require continuous efforts over several generations to resolve. The proponents of these UBI projects believe they are improving the economic system and impacting billions of people, but the more realistic reason may be that they hope to carve out a piece of the massive financial industry. From the perspective of these UBI projects, the value of Bitcoin, Pi Coin, and Worldcoin is not substantiated, and Libra once considered using low-risk asset reserves, including bank deposits in various currencies and U.S. Treasury bonds. The Libra model is similar to that of most stablecoins, but the difference is that Libra has support from Silicon Valley giants and sees its target audience as users in the cryptocurrency industry, while Libra sees its user base as broader. Innovation in the blockchain industry is always accompanied by shadows of money laundering, terrorism financing, and more. For most regulatory agencies, the innovation in the blockchain industry not only fails to provide financial means for most people but also provides methods for criminals. The best example of this is tornado.cash. The conservative attitude of regulatory agencies is not entirely negative, as the financial innovation in the blockchain industry is not user-friendly for most ordinary users and can easily lead to losses. Additionally, Worldcoin, as a project without actual value support, raises the question of who will bear the value of the token after issuance. It is highly likely that the widespread distribution of tokens will result in investment losses for ordinary users. Given the rapid development of artificial intelligence, future economic development may significantly reduce the demand for labor, and it is possible that mature UBI projects will be developed in the future, making this project worth paying attention to.
6. Risks
1) Legal and Regulatory Risks: UBI projects may raise issues such as inflation, money laundering, and currency stability, making them susceptible to regulation.
2) Development and Promotion Risks: The Worldcoin project requires widespread user adoption, but promoting a digital currency project without actual support worldwide is very challenging.
3) Privacy Disclosure Risks: Registering for World ID requires providing iris data, and if this data is leaked, it could harm user privacy, contradicting the blockchain industry's values of decentralization and anonymity.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



