Source: TMTPOST

Image Source: Generated by Wujie AI
The current situation of the large model track: on one side, startups are rapidly developing based on open-source large models, while on the other side, big companies are competing with various overfitting large model parameters.
According to incomplete statistics from agencies, there are currently 79 large models in China with over 1 billion parameters. In the process of overfitting large parameters, another voice has emerged in the market, "Improving parameters without a development direction is meaningless."
As a result, in terms of development direction, some large models are now focusing on vertical field applications. Based on the development of thousands of models, the foundation may change, but upon careful consideration, there still needs to be someone who can emerge in the vertical industry.
At the same time, in the early stages of development, although closed-source large models are of higher quality and relatively safer, the large model ecosystem ultimately needs a certain degree of overfitting. In reality, open-source can actually promote the prosperity of large models. From another perspective, based on open-source, many companies have the qualifications to compete in the track, but there are always those who easily stumble at the first hurdle—lack of computing power.
In the end, the number of large models is growing exponentially, but if the increasing number of large models is viewed one-sidedly, it may also overlook the decisions, struggles, and even the possibility of abandonment by some companies behind the growing number of large models.
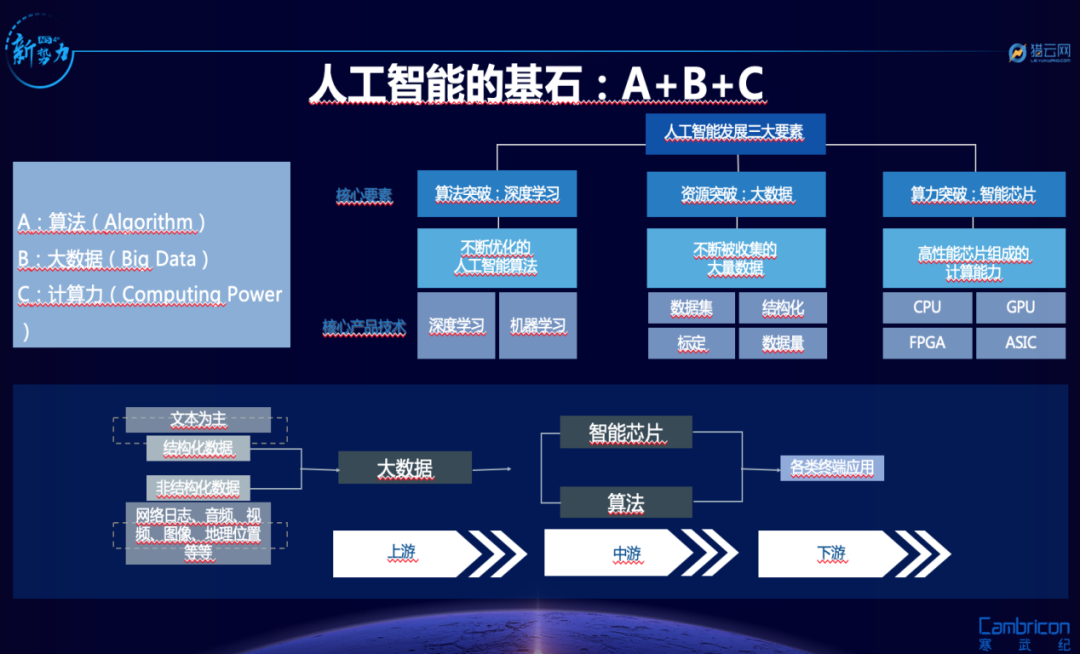
It is well known that the three elements of artificial intelligence are: computing power, algorithms, and data. Open source is only at the algorithm stage, and afterwards, enterprises need a large amount of computing power support and data training, which comes with high costs.
01 Vertical large models, is there still hope for startups?
In the selection of open-source large models, due to cost and customized development reasons, there are quite a few startup companies that choose small parameter models, and it is even the preferred choice for such companies.
One reason is the pre-training cost issue.
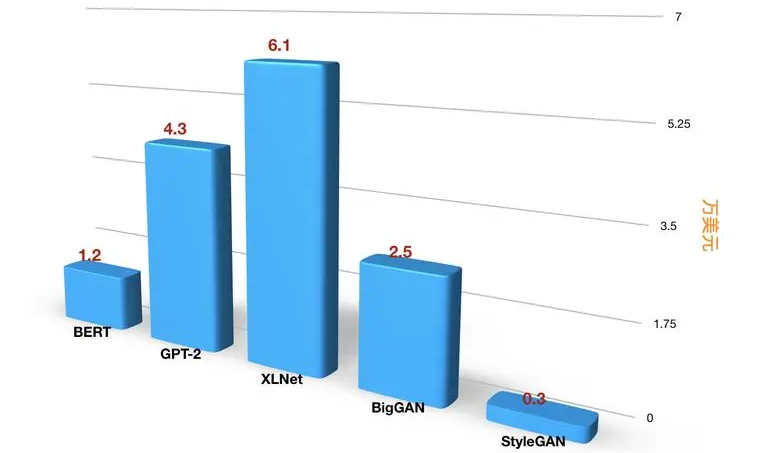
Guosheng Securities once estimated that the cost of training GPT-3 is about $1.4 million, and for larger LLM models, the training cost ranges from $2 million to $12 million.
Including in January of this year, there were about 13 million independent visitors using ChatGPT on average every day, requiring over 30,000 NVIDIA A100 GPUs, with an initial investment cost of about $800 million and a daily electricity cost of around $50,000.
Moreover, before a large amount of funds is invested, a large amount of data resources are also needed to support model training. Another reason is the demand for pre-training.
Some industry insiders have also expressed their views on this: "The generalization ability of large models is still limited by data."
Because if the high-quality data selection and training for large models are too few, the output quality issues of large models are quite obvious, and in terms of user experience, the user experience will also be greatly reduced.
It can be said that in the process of pre-training, a large amount of funds and time have already been spent solely on data accumulation.
Moreover, in the large model track, most startup companies are focused on developing in vertical industry fields, and although the investment may be relatively small, it is certainly not easy.
Specifically, if large models are to change the business model of the industry, then the simplest criterion for this is whether such large models have enough industry data. For example, to have enough understanding of the underground black market in order to avoid being used by the black market and to be in a safe passive state.
Another criterion is how the quality of the data processed by the large model during operation ultimately turns out.
In the end, in order to break the monopoly of models based on open-source models, a large amount of data needs to be sufficiently optimized and improved, and there needs to be sufficient investment in infrastructure.
Today, open-source large models are actually more like the Android of the internet era. It is not easy for startup companies without the advantages of landing scenarios and data accumulation of big companies to develop, but there are still opportunities.
In fact, Damo Academy has also regarded "collaborative development of large and small models" as one of the future trends.
Even startup company Zhuoyi Technology believes that "vertical large models are a solid opportunity, just like the discovery of the American continent is far from being an achievement of just one person."

So now we can see that many startup companies are starting to enter the large model track, including AI startup companies such as Haomo Zhixing, Chuangxin Qizhi, Yuanyu Zhineng, which have launched DriveGPT Xuehu·Hairuo, Qizhi Kongming, ChatYuan Yuanyu, and other large models.
However, although there are currently no products targeting consumers in China, big companies have already begun the initial landing process based on the business side.
It is reported that big companies are planning to output the capabilities of large models to the outside world through the cloud. Cloud computing has become the best way for the landing of large models, and Model as a Service (MaaS) is receiving more attention, which will also lead to a reduction in the cost of large models.
So, do startup companies still have hope?

02 The outcome depends on the match between product experience and market demand?
According to the authoritative magazine "Fast Company," OpenAI's revenue in 2023 is predicted to reach $200 million, including providing API data interface services, subscription fees for chatbot services, etc.
Obviously, there is a demand for large models in various industries, but due to security considerations, coupled with the cautious attitude of to B towards large models, the current security factor of large models is limited. Therefore, in relatively basic, high-demand scenarios such as dialogue, document generation, and Q&A, as well as dialogue and document generation in collaborative office work, internet giants are also prioritizing these areas.
For example, now humans only need to tell AI the information of a product, and AI can automatically generate various styles of product sales scripts and styles, and then pair it with a digital anchor to help companies sell their products. According to Baidu, compared to live human broadcasts, digital live broadcasts can achieve uninterrupted broadcasting 24/7, with a conversion rate twice that of unmanned live rooms.
Under the necessary foundation of cloud infrastructure for large model startups, internet giants with cloud computing have a certain advantage.
According to IDC's 2022 Global Cloud Computing IaaS Market Tracking data, the top 10 players in market share are all large companies from China and the United States, including Amazon, Google, Microsoft, IBM from the United States, and Alibaba, Huawei, Tencent, Baidu from China.

Although the dispute between open-source and closed-source large models will not be ended by the appearance of one or a few products, it still requires more top talents to participate, technological iteration, and financial support.
But in comparison, many AI startup companies lack the luck of a unicorn company like MiniMax. (The difference is that MiniMax focuses on general large models.)
On July 20th, Tencent Cloud disclosed its latest progress in assisting MiniMax in developing large models. Currently, Tencent Cloud has long-term support for MiniMax's thousand-calorie-level tasks running stably on Tencent Cloud, with a 99.9% availability rate.
It is reported that since June 2022, based on computing power clusters, cloud-native, big data, security, and other product capabilities, Tencent Cloud has built a cloud architecture for MiniMax from the resource layer, data layer to the business layer.
Reality seems to once again prove that getting a ticket is the first step, and what follows is the ability of market players to explore commercialization and technological upgrades. To put it bluntly, for AI startup companies to run to the end in the track, every step must not be missed.

To some extent, AI startup companies are not entirely without advantages in the development of large models.
Although some internet giants have already achieved initial scene landing or have started selling services to generate revenue, the focus of big companies and MiniMax is more on general large models.
Vertical large models are still a vacuum zone. Especially for traditional enterprise groups, considering their low IT attributes and low return on investment, the probability of choosing to develop large models on their own is low.
For example, Chuangxin Qizhi focuses on the industrial large model product "Qizhi Kongming"; with a certain data advantage, it is developing the language-based ChatYuan Yuanyu large model; and the flagship automatic driving generative large model DriveGPT Xuehu·Hairuo.
But to be honest, the cost difference is very large due to different training data and directions.
For example, the cost of training the Yuanyu large model from scratch can reach tens of millions of RMB. And in the field of automatic driving generative models, in addition to designing a new language more than ChatGPT, there is also a certain cost input to "translate" all the real road driving data into a unified language for DriveGPT Xuehu·Hairuo.
To some extent, the ability of AI startup companies to make significant investments in large models is more due to the commercial and marketing success of ChatGPT, which can instantly demonstrate the feasibility of large models, rather than continuing to hide in a long process of technological iteration.
Therefore, the first step in achieving landing at present is to ensure that the training and inference costs of large models are definitely lower than search, and also ensure real-time performance.
03 From concept to landing, how difficult is it really?
Some opinions believe that the Chinese large model startup companies that can succeed are likely to be vertically integrated.
In simple terms, while working on the underlying large models, they also identify the ultimate main application scenario of a model, collect user data, and make rapid iterations.
It seems that Yuanyu Zhineng is more inclined to this type. In summary, for a long time, Yuanyu Zhineng has been focusing on natural language large model business.
Zhu Lei, COO of Yuanyu, stated, "We will not blindly expand into image and video businesses to follow the trend. Yuanyu's goal is to achieve the full localization of cutting-edge language large models such as 'ChatGPT.' The language large model ecosystem is already large enough, so business focus is important."
But for other startup companies developing vertical large models for areas such as automatic driving and industrial production, they may lack mastery of some specific industry data.
After all, in the vertical large model track, one of the core factors of future enterprise competition is private data and private experience. When the processes of individual companies are not known to large model players, they may have unique competitiveness.
In addition, during the business focus process, it is also necessary to ensure the accuracy of data from the source to pre-training and output.
Currently, generative artificial intelligence is also receiving more attention in terms of regulation. Recently, China issued the "Administrative Measures for Generative Artificial Intelligence Services (Draft for Solicitation of Comments)," which clearly requires the prevention of discrimination and the generation of accurate and true content, and the prevention of generating false information. If such issues occur, optimization is required through content filtering and model optimization.
But if it is an inherent flaw of generative artificial intelligence, it is difficult to guarantee and completely resolve it technically.
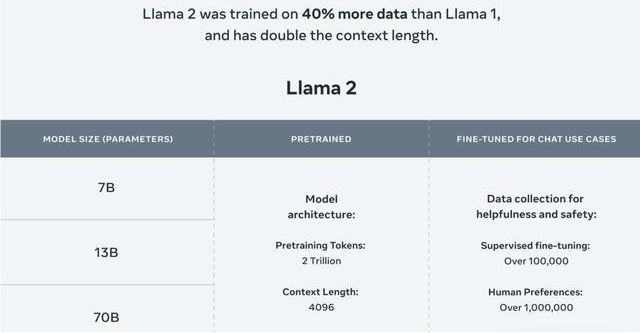
In addition, with the emergence of better open-source models, it is possible that more eager companies will rush in, which is also a form of competition for startup companies.
For example, the Llama 2, on July 18th, Meta released the first commercial version of the open-source artificial intelligence model Llama, Llama 2. Some companies believe that based on various evaluation documents, apart from slightly lower code capabilities, in many aspects, it has already begun to approach ChatGPT.
Perhaps the future wave of enthusiasm in the open-source community will make large models with basic capabilities more widespread, and in the future, private large models will be very affordable. In simple terms, companies may use private large models at a very low cost.
An even more important point is that Tang Daosheng once said, "General large models have strong capabilities, but they cannot solve specific problems for many enterprises. They can solve 70%-80% of problems in 100 scenarios, but may not fully meet the needs of a specific scenario for an enterprise. However, if enterprises build industry-specific models based on large models and fine-tune them with their own data, they can construct exclusive models and create highly available intelligent services."
Of course, this kind of private large model has not yet arrived, but for startup companies in the track, it is definitely a mix of opportunities and challenges.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



