Spot demand remains weak, with increased outflows from U.S. spot ETFs and no new buying from traditional financial allocators.
Written by: Chris Beamish, CryptoVizArt, Antoine Colpaert, Glassnode
Translated by: Luffy, Foresight News
TL;DR
Bitcoin has fallen below the cost basis range for short-term holders (STH), with recent buyers under significant pressure; the $95,000 - $97,000 range has now become a key resistance level. If this range can be reclaimed, it will be an initial signal of market structure repair.
Spot demand continues to be weak, with increased outflows from U.S. spot ETFs and no new buying from traditional financial allocators.
Speculative leverage continues to unwind, with a decrease in open interest in futures and funding rates dropping to cycle lows.
The options market has significantly repriced risk, with implied volatility rising across all maturities, as traders pay high premiums to hedge against downside risk.
Bearish options dominate the flow of funds, with strong demand for key strike prices (such as $90,000), reinforcing a defensive positioning pattern, as traders are more inclined to actively hedge risks rather than increase upside exposure.
The Digital Asset Volatility Index (DVOL) has rebounded to monthly highs, reflecting a comprehensive repricing of risk indicators such as volatility, skew, and fund flows, suggesting that short-term volatility may remain elevated.
Bitcoin has fallen below the previous consolidation range, briefly touching $89,000, setting a new local low, with year-to-date gains turning negative. This deep correction continues the mild bear market trend we pointed out last week and raises questions about when structural support levels will reappear. This article will assess the market's reaction to this breakdown through on-chain pricing models and short-term holder loss realization data; further analyzing the options market, ETF fund flows, and futures positions to explore the sentiment adjustment of speculators in the context of renewed market weakness.
On-Chain Insights
Breakdown of Lower Range
Bitcoin has fallen below the lower boundary of last week's "floating range" at $97,000, indicating the risk of a deeper correction. The price subsequently plummeted to $89,000, setting a new local low below the cost basis for short-term holders (currently around $109,500) corresponding to a negative one standard deviation (approximately $95,400).
This breakdown indicates that almost all recent investor groups are in a state of loss. This pattern has historically triggered panic selling and weakened market momentum, requiring time to repair. In the short term, the $95,000 - $97,000 range will become a local resistance level, and reclaiming this range will be an initial signal of market structure repair.
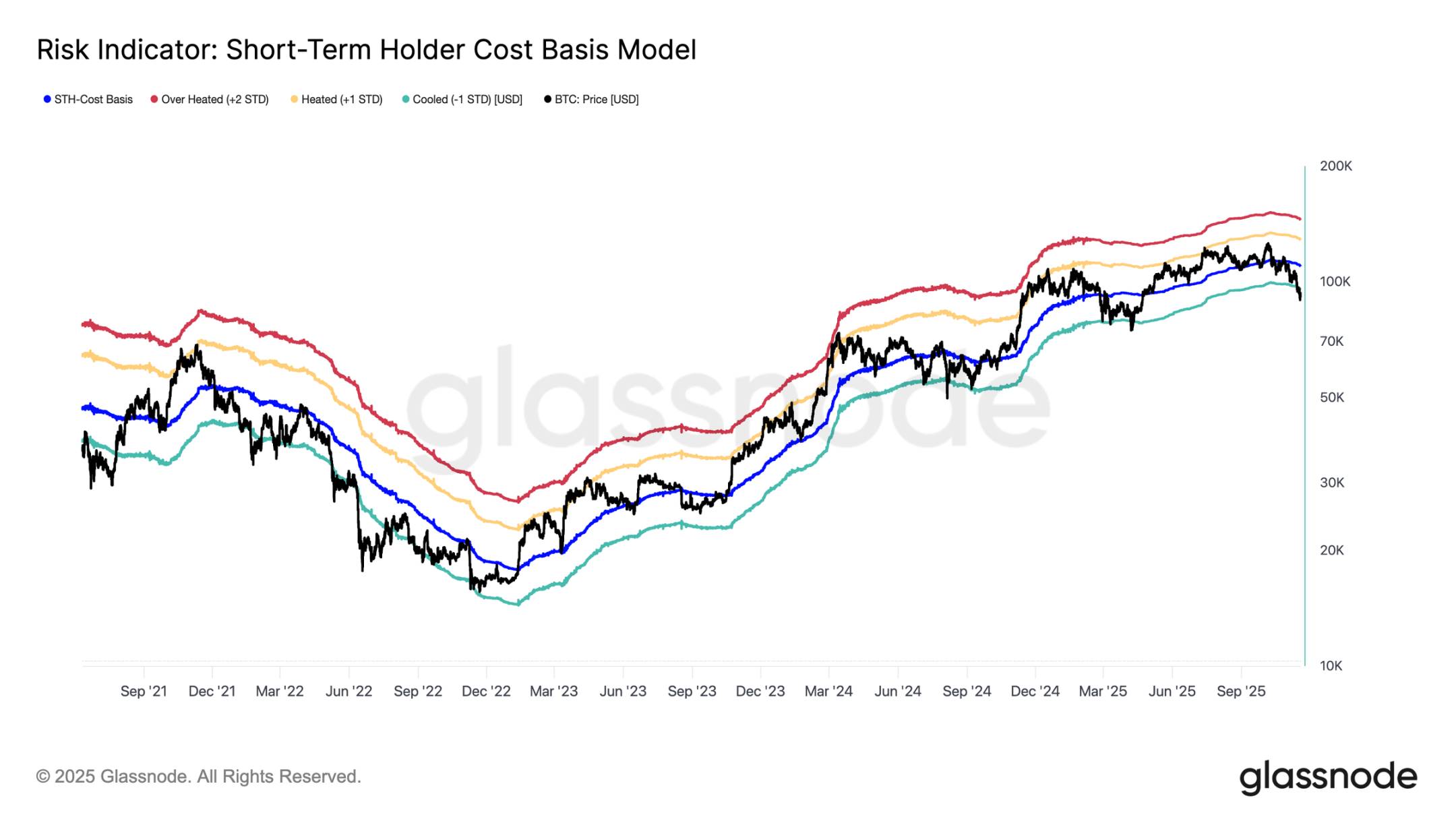
Panic Selling Reaches Peak
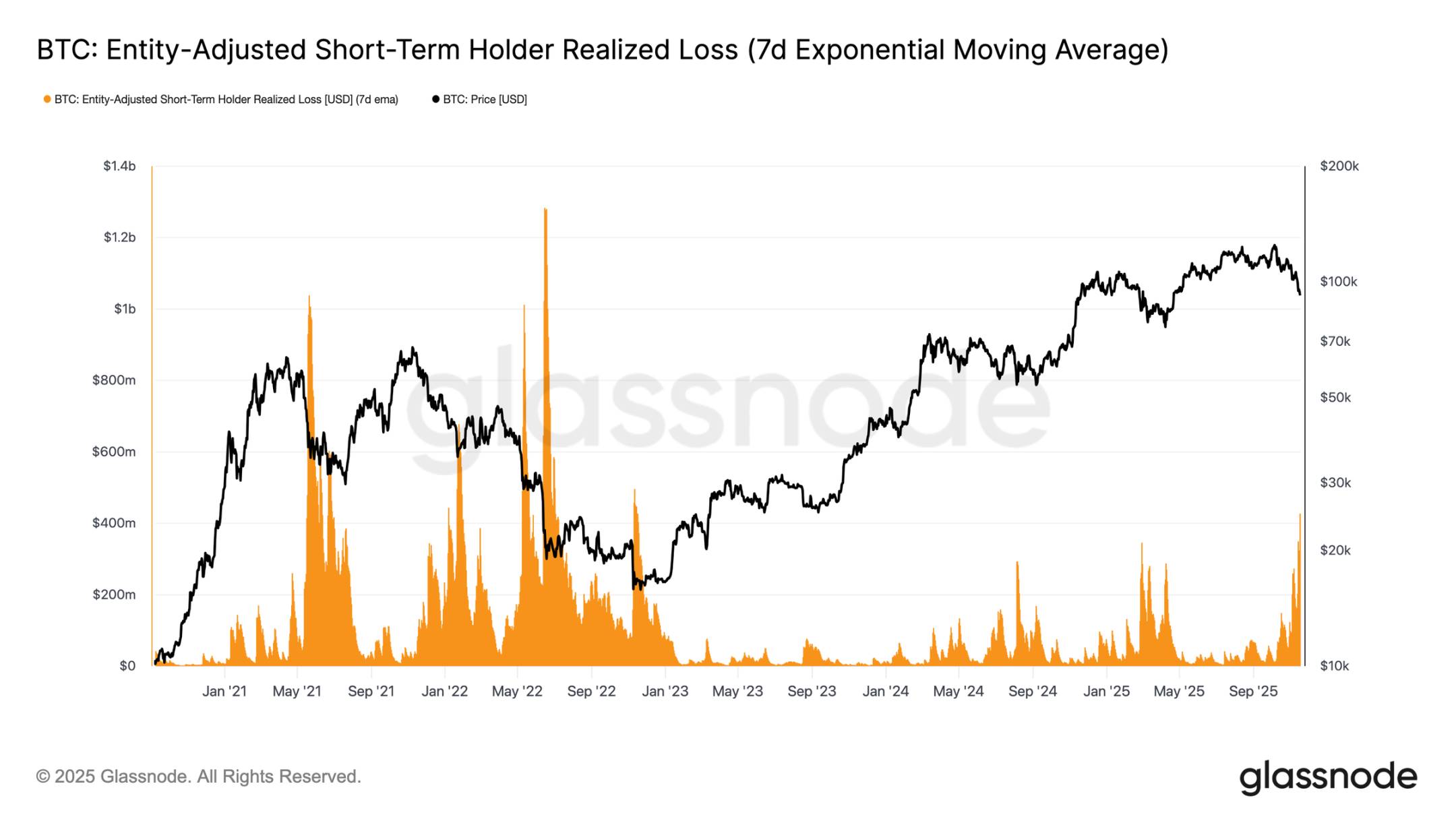
From the perspective of investor behavior, this price drop marks the third time since early 2024 that prices have fallen below the lower boundary of the short-term holder cost basis. However, the level of panic among core buyers is noticeably higher: the 7-day moving average of realized losses for short-term holders has surged to $523 million per day, the highest level since the FTX collapse.
Such a high scale of loss realization highlights the heavy top structure formed in the $106,000 - $118,000 range, where the density of chips far exceeds previous cycle peaks. This means that either stronger buying is needed to absorb the selling pressure, or the market must undergo a longer and deeper accumulation phase to restore balance.
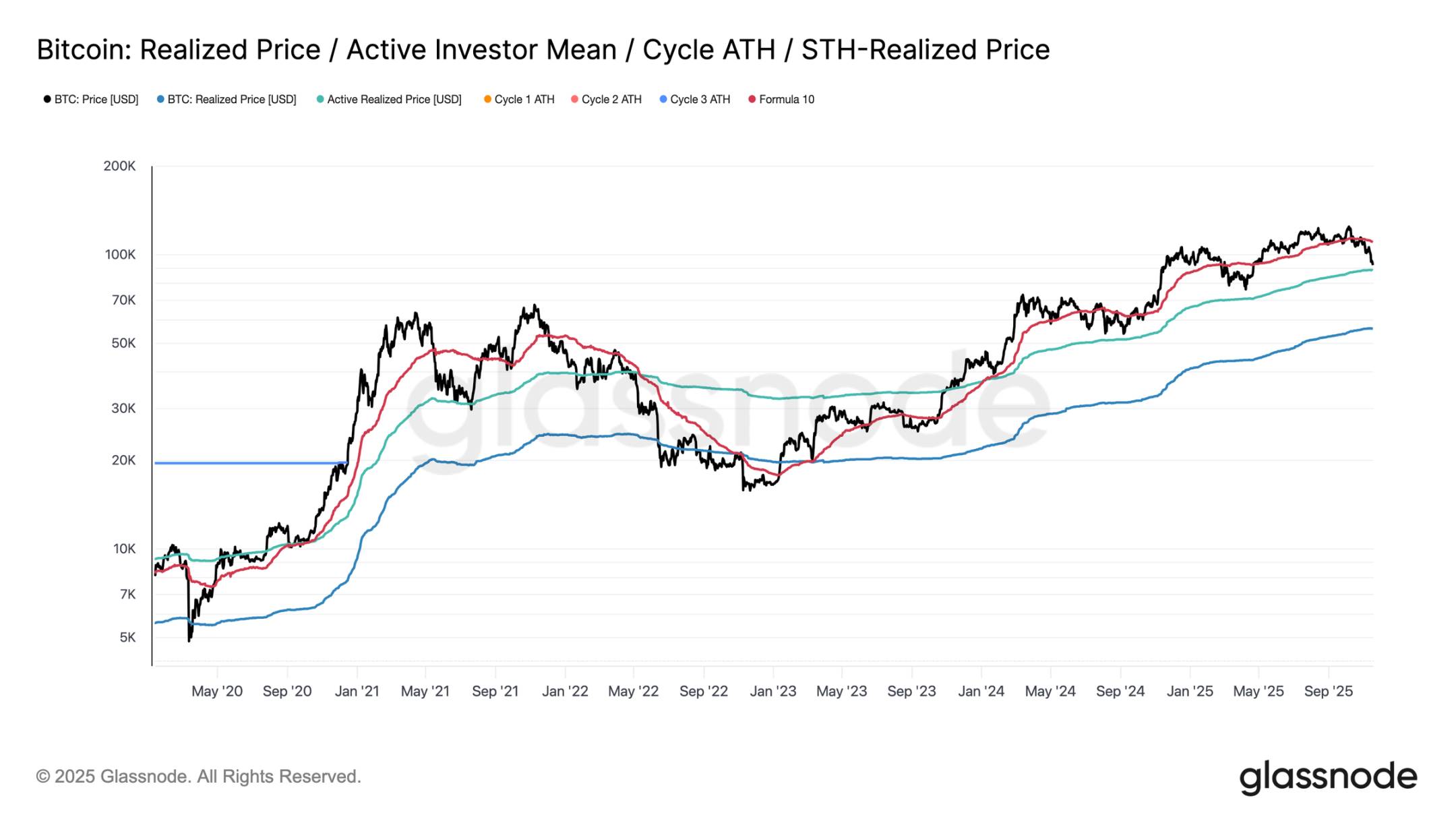
Testing Active Demand
From a valuation model perspective, the market has now entered unknown territory, with speculative interest during the mild bear market phase significantly increasing. The first major defensive range is near the realized price for active investors (currently around $88,600). The trading price of Bitcoin near this level corresponds to the cost basis of non-sleeping holders who have actively traded in recent months, making it a potential mid-term trading range.
However, if it decisively falls below this price level, it will be the first time in this cycle that prices are below the active investor cost basis, which will be a clear signal of bear market momentum dominating the market.
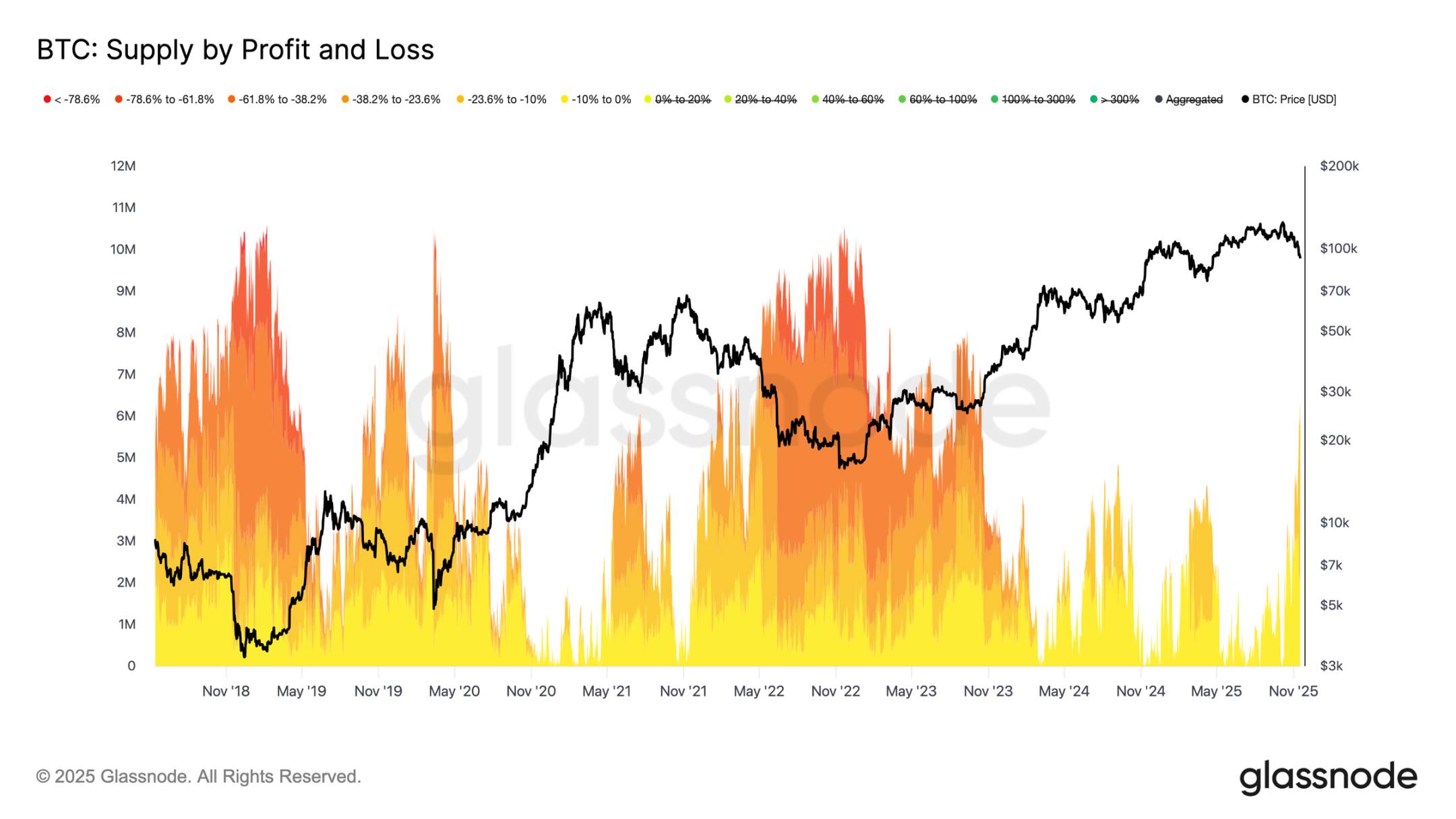
Different Types of Corrections
Although it has fallen below the main lower boundary of the short-term holder cost basis, the scale and intensity of investor losses are still far from the extreme levels seen during the 2022-2023 bear market. The chart below tracks all Bitcoin currently in a state of loss, grouped by unrealized drawdown: approximately 6.3 million Bitcoins are currently in a floating loss state, with most losses ranging between 10% and 23.6%.
This distribution is highly similar to the short-term range oscillation market in Q1 2022, rather than a deep capitulation phase. This is also why the range between the realized price for active investors ($88,600) and the actual market average ($82,000) may become a key boundary distinguishing the mild bear market phase from the comprehensive bear market structure of 2022-2023.
Off-Chain Insights
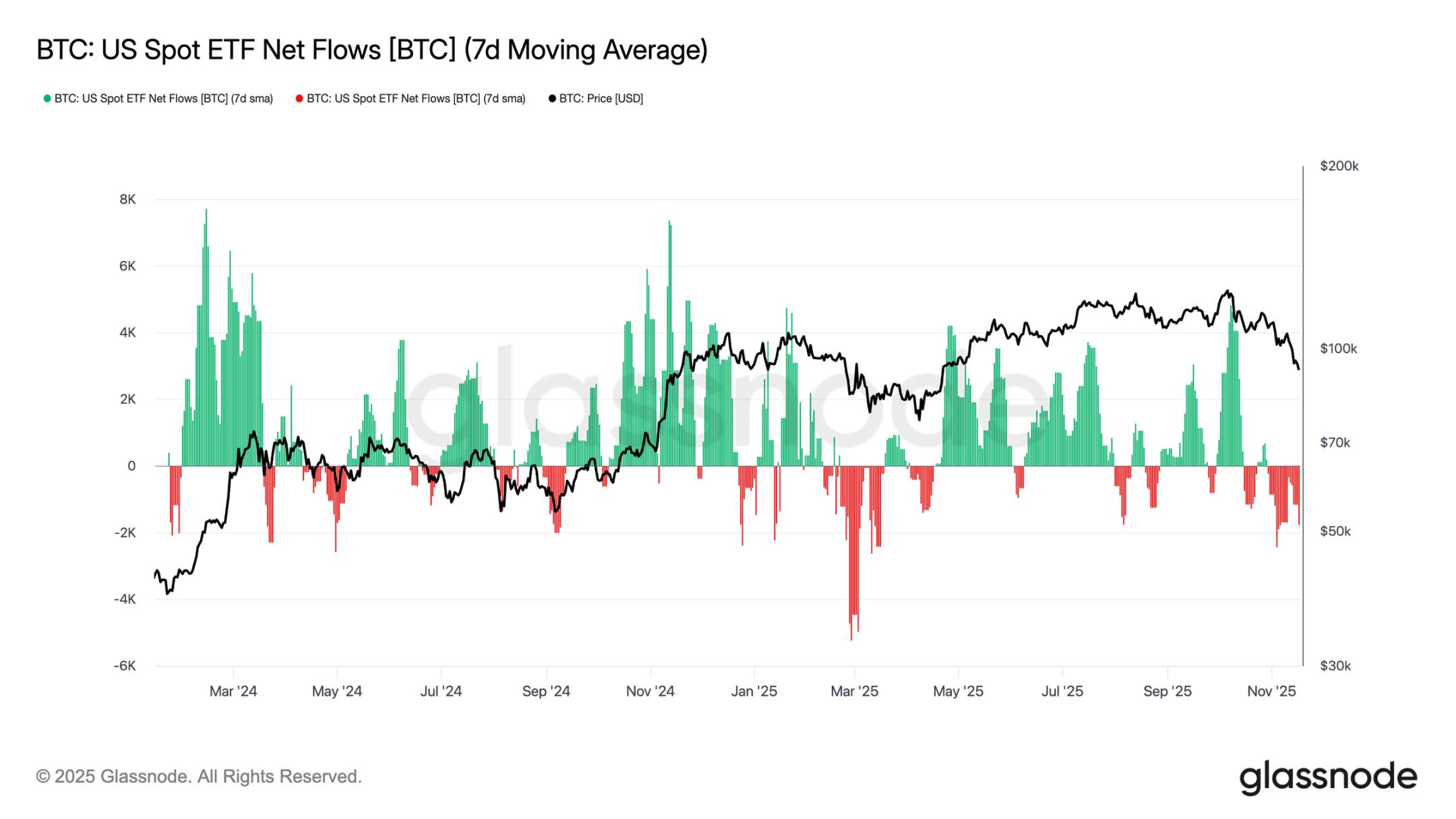
Insufficient ETF Demand
The inflows into U.S. spot ETFs continue to reflect a clear lack of demand, with the 7-day average remaining negative in recent weeks. The ongoing outflows indicate that traditional financial allocators are unwilling to increase exposure during the current correction, contrasting sharply with the strong inflow pattern that previously supported market rises. The current weak trend suggests that the willingness to self-allocate has significantly cooled, and one of the largest marginal buyer groups in the market has not shown new buying, further reinforcing the overall environment of constrained demand.
The absence of sustained inflows indicates that a key demand pillar has yet to be activated, leading to a lack of core demand sources in the current market.
No Signs of Risk Appetite Recovery
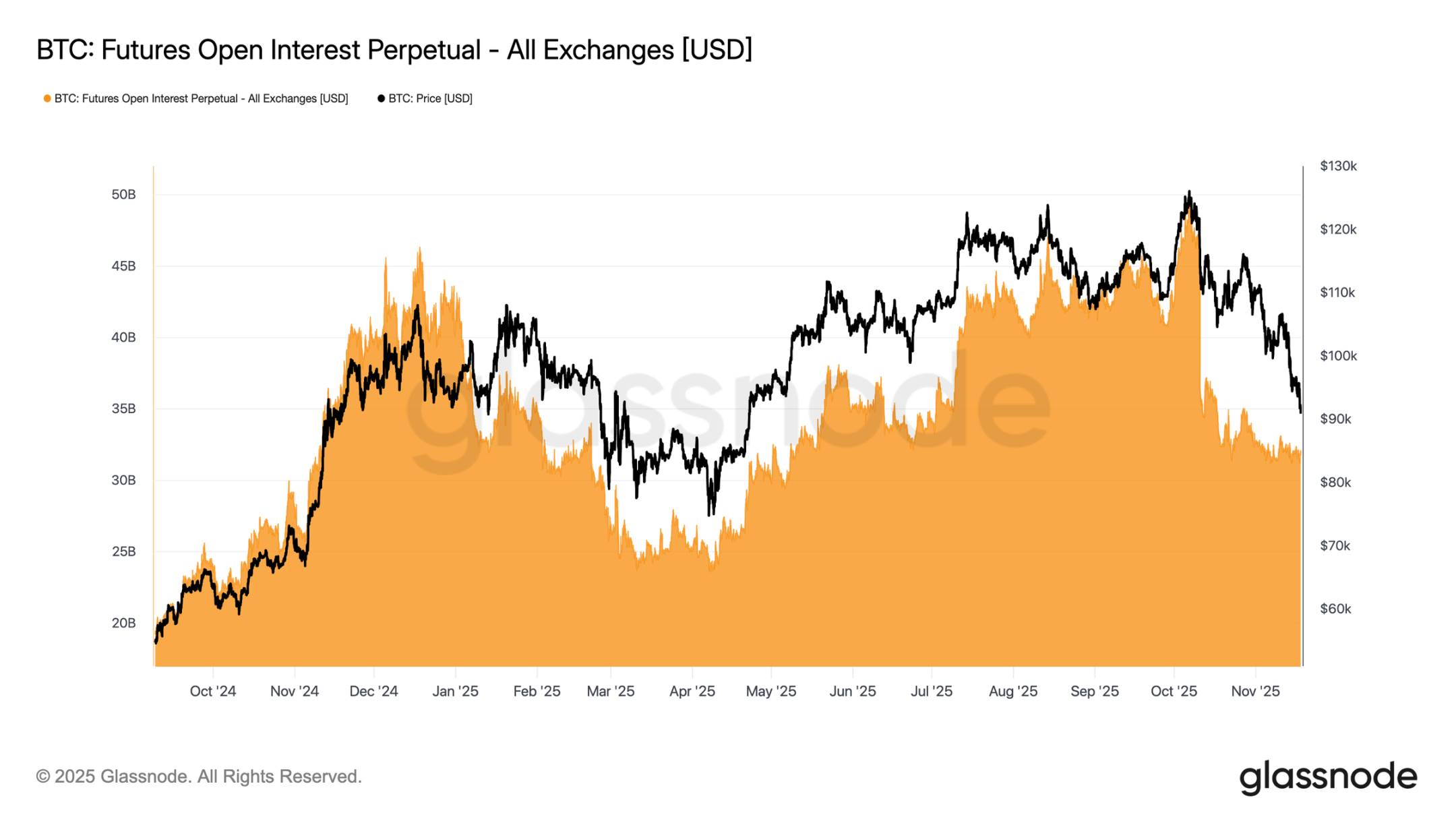
The open interest in futures has continued to decline, moving in tandem with prices, reflecting a persistent contraction in speculative activity. Traders have not increased exposure as the market weakens but have systematically unwound risks, resulting in a significantly lower position size in the derivatives market compared to previous correction phases. The absence of new leverage highlights the cautious stance of market participants, consistent with the overall trend of weakened demand among various risk-bearing groups.
The ongoing contraction in futures positions indicates that the market remains unwilling to deploy capital, confirming the lack of confidence behind the current price movements.
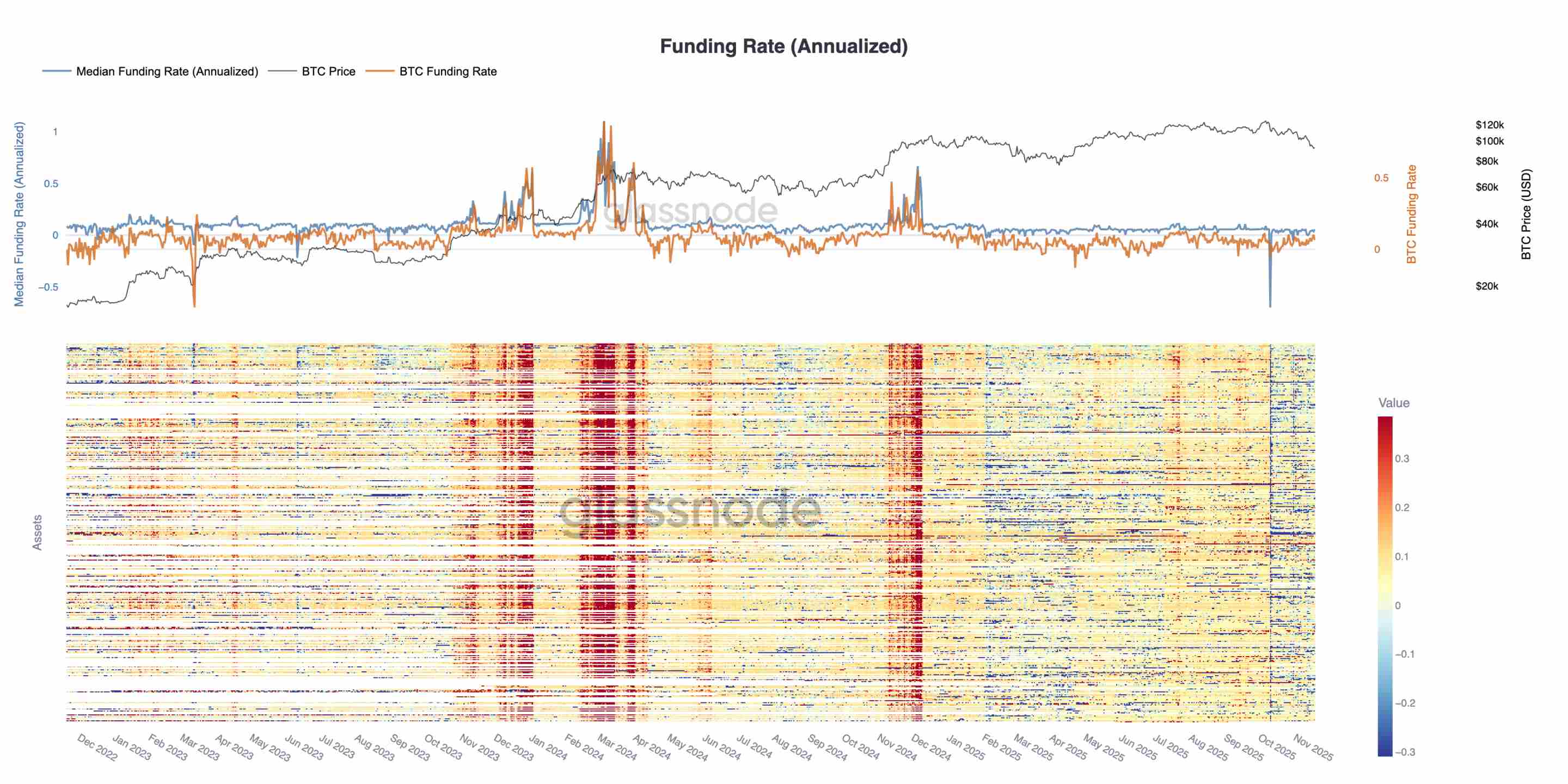
Funding Rates Hit Cycle Lows
As open interest in futures continues to decline, the derivatives market has signaled a clear contraction in speculative positions. Traders have chosen to unwind risks rather than increase exposure as the market weakens, leading to significantly lower leverage levels in open interest compared to previous correction phases.
This dynamic is also reflected in the funding rate market: the funding rates for the top 500 assets have clearly shifted to a neutral to negative range. Compared to the positive premium state at the beginning of the year, this change highlights a comprehensive cooling of leveraged long demand and a shift in the market towards more defensive positions.
The decline in open interest and negative funding rates together indicate that speculative leverage is being systematically withdrawn from the market, reinforcing risk-averse sentiment.
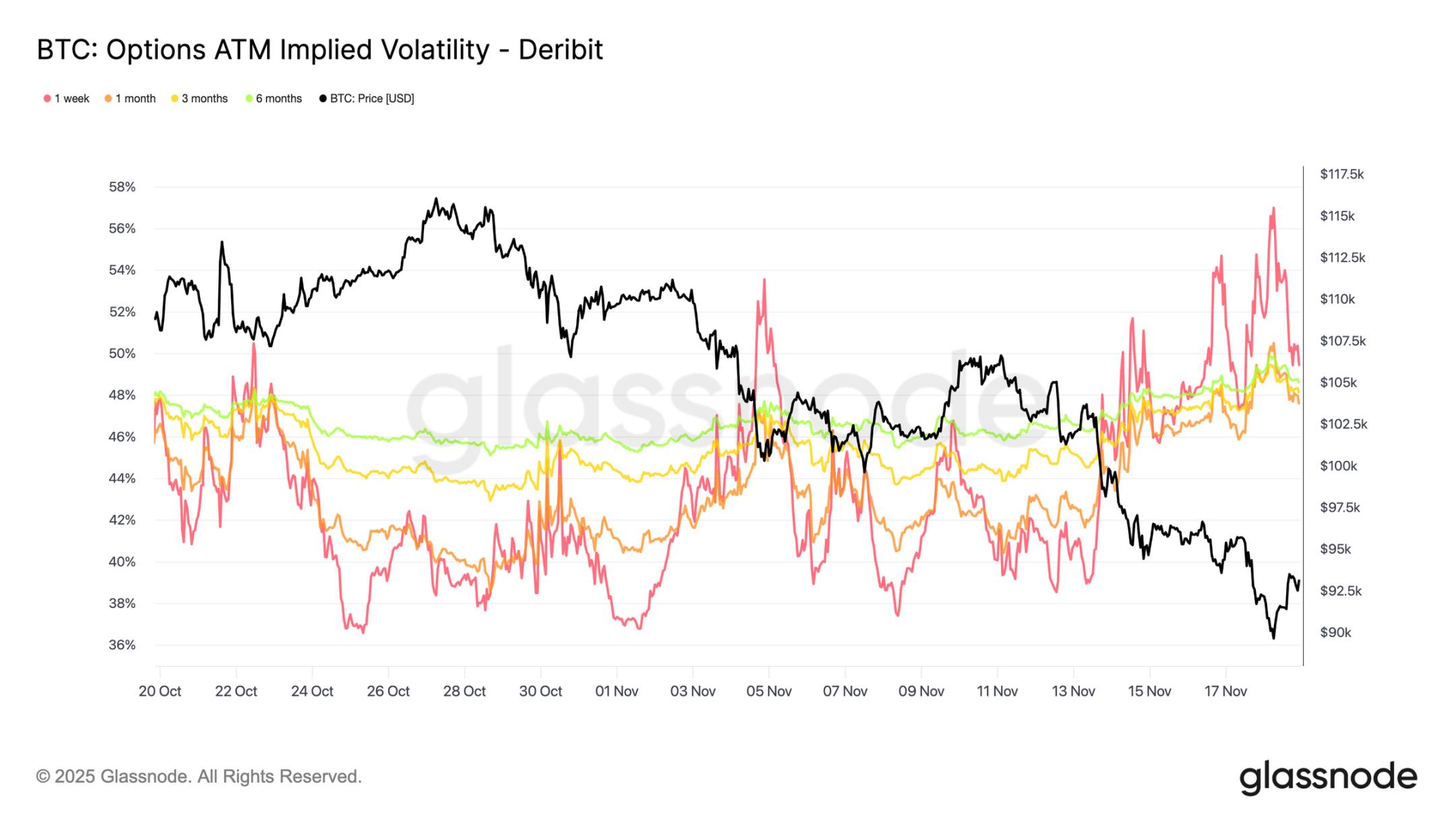
Implied Volatility Rises Sharply
The options market is typically the first area to reprice risk. After Bitcoin briefly fell below $90,000, the options market reacted swiftly: implied volatility across all maturities rose sharply, with short-term contracts reacting most intensely. The chart shows a significant rebound in short-term volatility, with a comprehensive repricing of the entire volatility curve.
This increase is driven by two main factors: first, traders' demand for downside protection has increased in response to the possibility of larger corrections; second, short Gamma traders have reacted. Many traders have had to buy back short options and roll their positions up, mechanically pushing up short-term implied volatility.
Current implied volatility is approaching levels seen during the October 10 liquidation event, indicating the rapid pace at which traders are reassessing short-term risks.
Skew Confirms Panic Sentiment
Shifting from implied volatility to skew indicators, the options market conveys the same signal: the 25 delta skew across all maturities remains negative, with the one-week skew approaching extreme bearish levels (Note: the skew indicator quantifies market sentiment and risk appetite by comparing the implied volatility differences of options with different strike prices. The 25 Delta skew is an indicator that measures the degree of volatility skew in the options market, typically calculated by comparing the implied volatility differences between 25 Delta put options and 25 Delta call options). The premium for one-week put options is about 14%, indicating that traders are willing to pay a higher cost for downside protection regardless of the spot price.
This behavior may create a self-fulfilling prophecy: when traders buy these put options, market makers often find themselves in a delta short position. To hedge this exposure, market makers will sell futures or perpetual contracts, and this selling pressure can stress the market and potentially amplify the downward trend that traders originally sought to guard against.
Longer-term skews are also leaning bearish, but to a lesser extent: the six-month skew is slightly below 5%, indicating that market concerns are primarily focused on the short term rather than the entire maturity range.
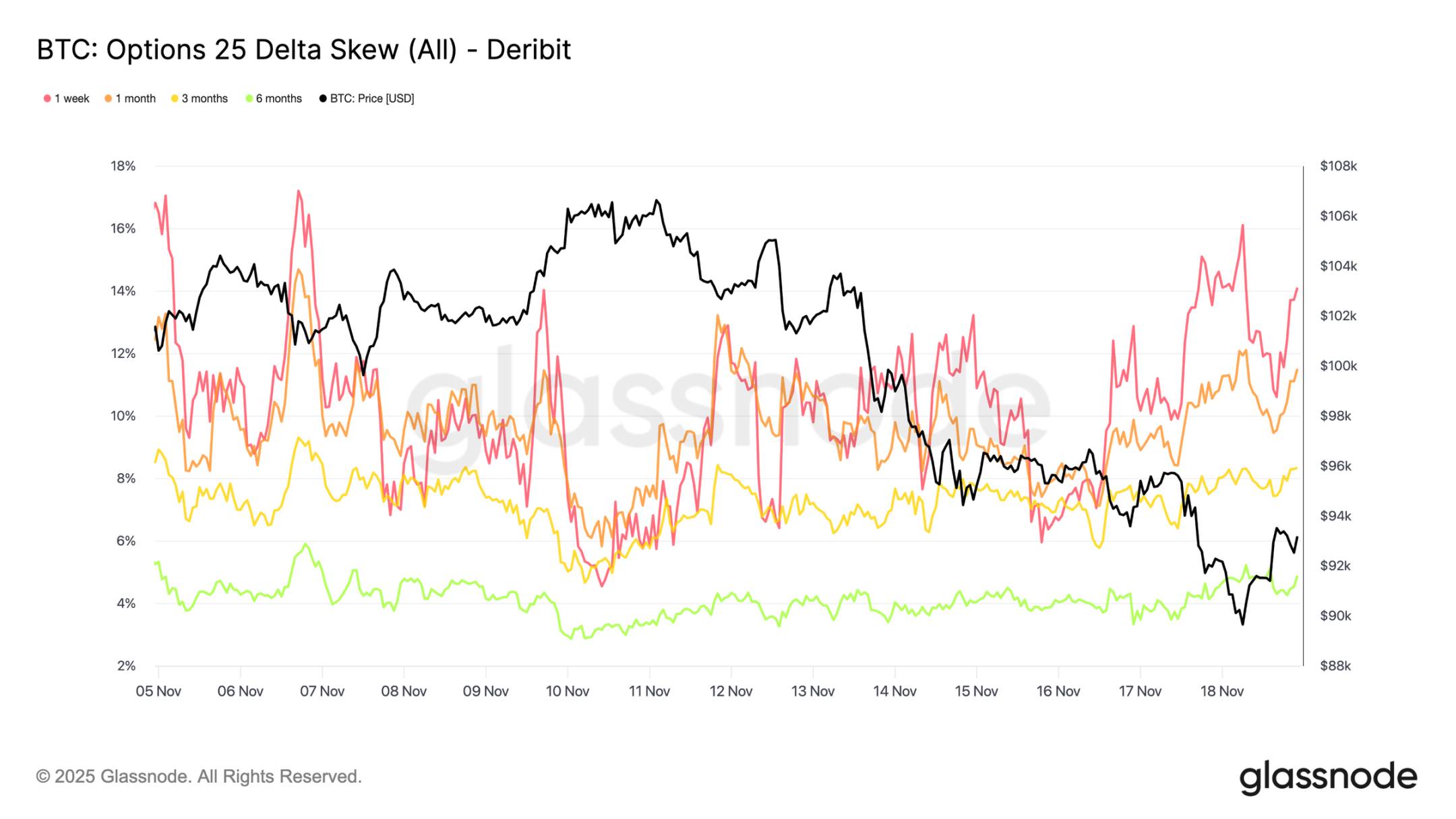
Strong Demand for Downside Protection
Shifting from skew to actual trading activity, the fund flows over the past seven days highlight the same pattern. Traders have purchased a large number of put option premiums, far exceeding demand for call options. This aligns with hedging behavior, reflecting that the market is more inclined to guard against further declines rather than bet on upside.
Trading activity in call options is limited, indicating that traders are unwilling to increase substantial risk exposure before the end of the year. Whether buying or selling call options, the scale is low compared to the fund flows for put options, supporting the view of "cautious rather than speculative dominant positions."
Overall, this flow of funds indicates that the market is preparing for increased volatility and prefers defense over exposure expansion.
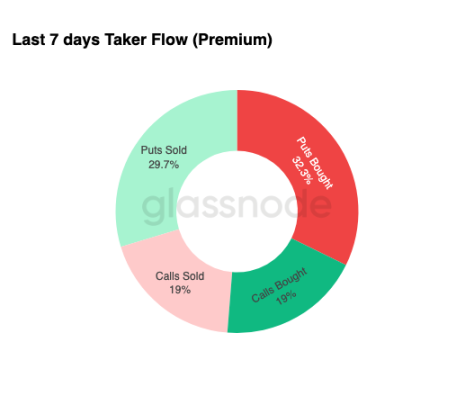
$90,000 Strike Price Option Premium
Focusing further on the overall fund flow data, the premium for put options at the $90,000 strike price shows that as prices weaken, the demand for protection accelerates. Over the past two weeks, the net premium for put options at this strike price remained relatively balanced until Bitcoin fell below the $93,000 level. Once this support level was breached, traders began actively raising their quotes for these put options, significantly increasing the buying premium for the $90,000 strike price.
This behavior indicates that as selling pressure in the spot market intensifies, traders are willing to pay increasingly higher prices for downside protection. This trend is also consistent with the previously observed rise in short-term implied volatility.
The significant repricing of the $90,000 put options highlights the acceleration of downside hedging activity when key price levels are breached.
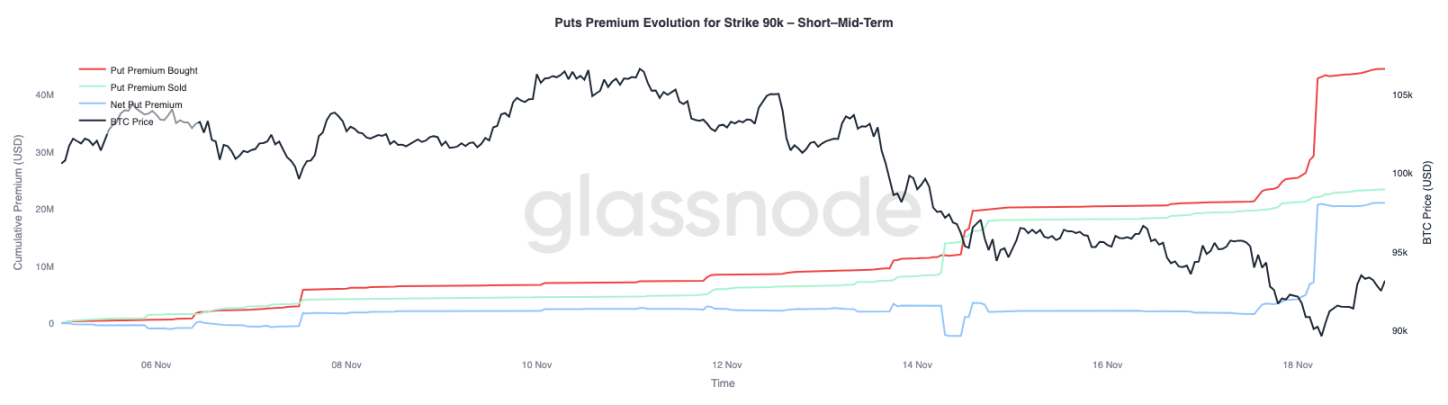
Pricing Market Vulnerability
Shifting from individual strike prices to broader volatility indicators, the DVOL index shows the extent of the market's repricing of risk: this index has risen from about 40 three weeks ago to nearly 50, a monthly high. DVOL reflects the implied volatility of a fixed-term options basket, so its rise indicates that traders expect future price fluctuations to increase.
This upward trend consolidates all observations from the options market: implied volatility across all maturities is rising, skew remains negative, recent fund flows show a negative delta, and traders have shown little willingness to increase risk exposure before the end of the year. These factors collectively depict a market preparing for unstable price movements, driven by risks such as perpetual contract liquidation, macroeconomic uncertainty, and a strong lack of core demand due to missing ETF inflows.
The next event that could change this volatility pattern is the Federal Reserve's Open Market Committee meeting in three weeks. Until then, the options market will continue to convey cautious signals, clearly favoring defensive positions.
The rise in DVOL further indicates that the market is preparing for larger fluctuations in the future, with traders adjusting their positions around volatility.
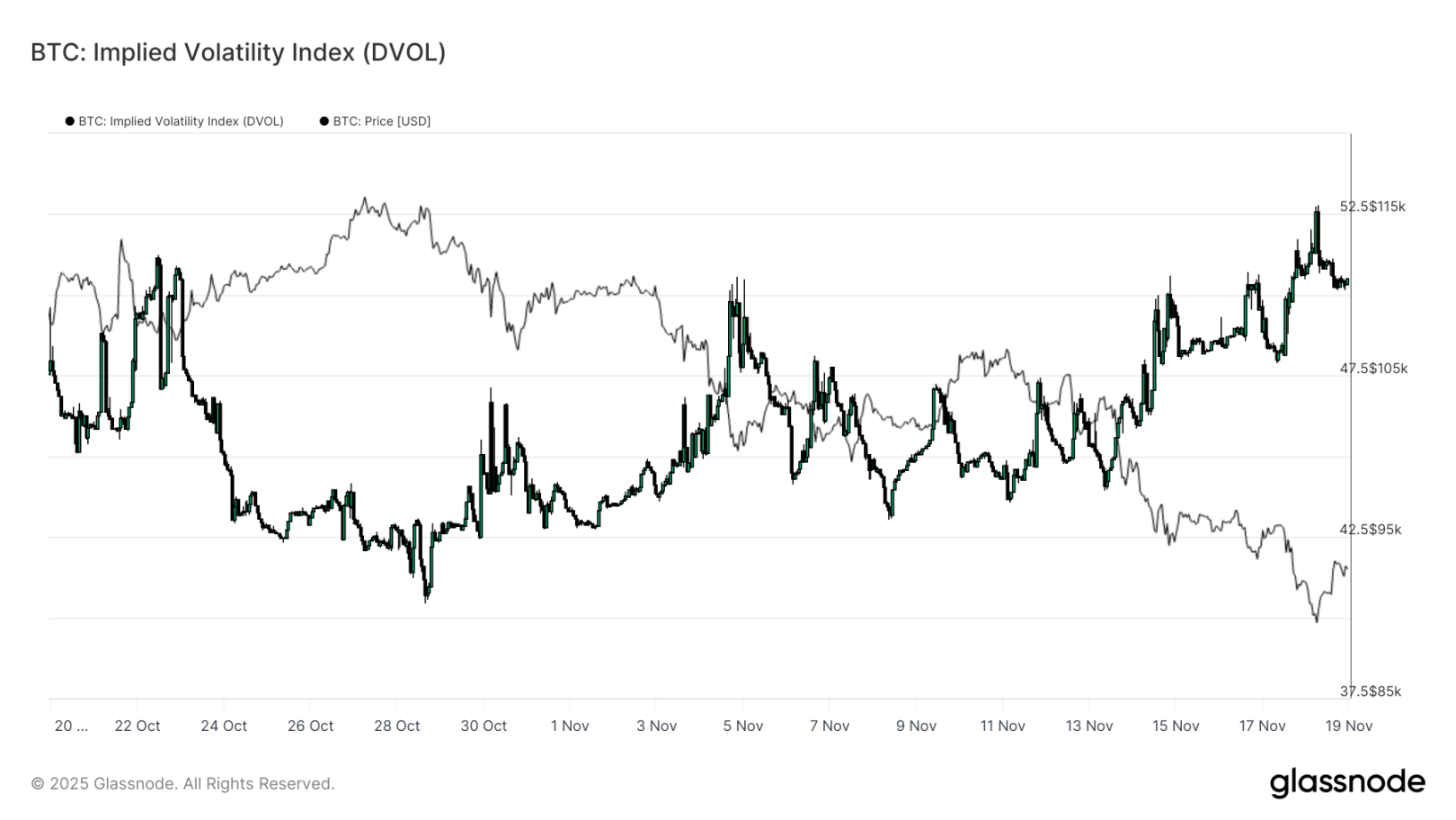
Conclusion
Bitcoin is still experiencing a challenging market phase characterized by weakened market structure, declining speculative demand, and a comprehensive shift in the derivatives market towards risk-averse positions. Spot demand continues to be lacking, ETF inflows are negative, and the futures market shows a reluctance to increase leverage during the downturn. Meanwhile, implied volatility, skew, and hedging fund flows all point to an increase in short-term downside risk, with investors paying higher premiums for protection. These dynamics collectively create a market environment that is "seeking stability." Future trends will depend on whether demand can reappear near key cost basis levels or if the current market vulnerability will evolve into a deeper correction or bear market.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



