On April 19, 2024, the Hedgey Token Claim contract was attacked on multiple chains such as Ethereum and Arbitrum, resulting in losses of tens of millions of dollars. The Hedgey project team immediately issued a security alert, reminding users who created token claim activities to cancel them through official channels. (https://twitter.com/hedgeyfinance/status/1781257581488418862)
Attack Summary
Hedgey helps DAOs and on-chain organizations distribute tokens to their teams, contributors, investors, and communities through on-chain, programmatic token issuance. The vulnerable tool in this attack was its Token Claims product, which allows users to create a token claim page, add up to over 100,000 recipients to the whitelist via a CSV file, and control how claimed tokens are released through streams, time locks, and recovery methods.
The contract vulnerability exploited in this attack was within the ClaimCampaigns contract of the Token Claims product. When creating a token claim activity, the ClaimCampaigns contract authorized the creator to a specified address. When the creator canceled the claim activity, the tokens transferred to the creator during the activity creation phase were returned to another specified address, but the token authorization was not revoked, allowing the creator's address to still use the tokens authorized by the ClaimCampaigns contract.
Key Addresses Involved in the Attack
Multiple transactions were involved in this attack, but we will analyze the attack principle using the transaction that stole NOBL tokens as an example.
Attack transaction: https://etherscan.io/tx/0x017ce9593350cba65d506e1a87e52d2c20079fdfa80a350a89fe6fc875f2d9f9
Attacker's EOA:
0xded2b1a426e1b7d415a40bcad44e98f47181dda2
Attacker (contract):
0xd818ff3d5cfc938014b270d0c8029ba04629b549
Vulnerable contract (ClaimCampaigns):
0xbc452fdc8f851d7c5b72e1fe74dfb63bb793d511
Stolen token (NobleBlocks: NOBL Token):
0x88b9f5c66342ebaf661b3e2836b807c8cb1b3195
Attack Process Analysis
1. Implementation of the Attack
During the attack implementation phase, the attacker called the "createLockedCampaign" function of the vulnerable contract multiple times to create a campaign, and then called the "cancelCampaign" function to delete the campaign. When creating the campaign, the attacker transferred a specified amount of NOBL tokens to the vulnerable contract and obtained the authorized usage of NOBL tokens from the vulnerable contract. When deleting the campaign, the vulnerable contract returned the NOBL tokens transferred by the attacker during the campaign creation, but at this point, the vulnerable contract did not revoke the authorized usage of NOBL tokens given to the attacker. Therefore, by creating and deleting campaigns, the attacker was able to gain the authority to spend the NOBL tokens held by the vulnerable contract.
The specific attack steps are as follows:
The attacker called the "createLockedCampaign" function of the vulnerable contract to create a campaign, setting "campaign.manager" and "claimLockup.tokenLocker" to the attacker's own address, "campaign.token" to NOBL token, "campaign.amount" to "680000000000000000000000" (NOBL token's decimal is 18, so this represents 680,000 NOBL tokens), and "donation.amount" to 0. From the "createLockedCampaign" function code, it can be seen that the attacker first transferred NOBL tokens to the vulnerable contract, and then used the "safeIncreaseAllowance" function to authorize the "claimLockup.tokenLocker" (attacker) to spend the NOBL tokens held by the vulnerable contract, authorizing the attacker to spend the specified amount.

The attacker called the "cancelCampaign" function to delete the campaign created in step 1. From the function code, it can be seen that the vulnerable contract deleted the campaign data and called the "withdrawTokens" function of the TransferHelper library to return the NOBL tokens transferred by the attacker in step 1 to "campaign.manager" (attacker). At this point, the campaign was successfully canceled, but the authorized usage of NOBL tokens given to the attacker by the vulnerable contract was not revoked. Therefore, the attacker still had the authority to spend the NOBL tokens held by the vulnerable contract.

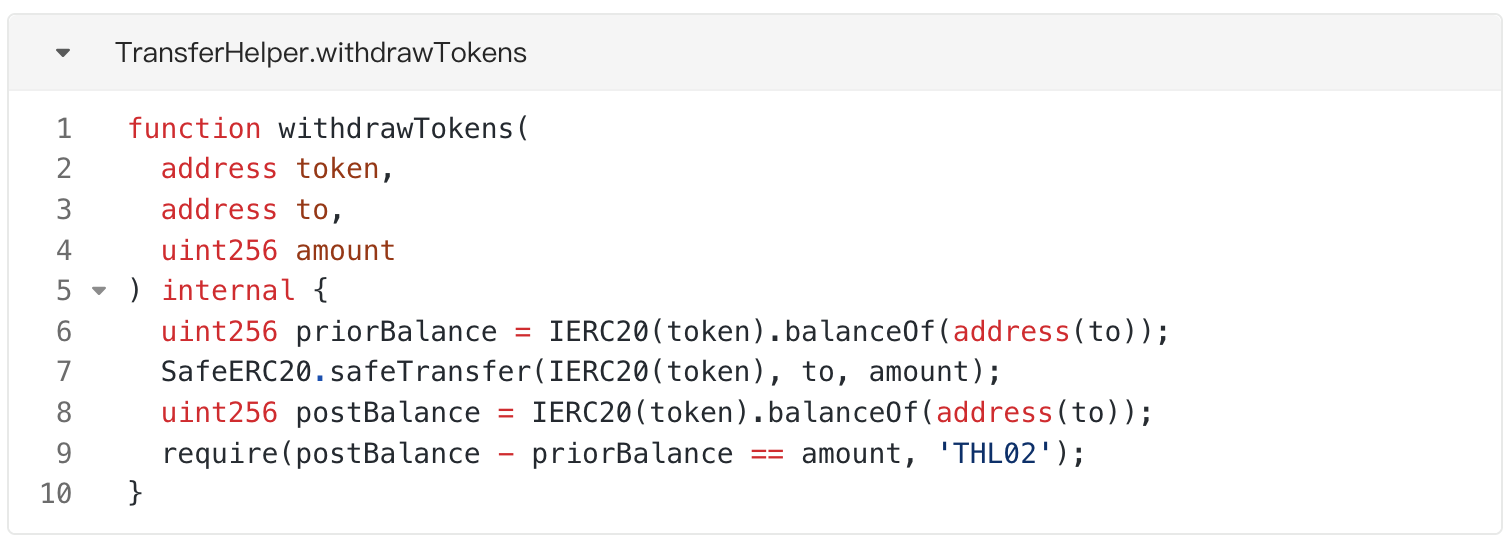
The attacker repeated steps 1 and 2 25 times, ultimately gaining the authorized usage of 17,000,000 NOBL tokens from the vulnerable contract.
2. Harvesting the Stolen Funds
During the fund harvesting phase, the attacker directly called the "transferFrom" function of the NOBL token to transfer the NOBL tokens from the vulnerable contract to the attacker's EOA address. Since the attacker had already obtained the authority to spend the NOBL tokens held by the vulnerable contract during the attack implementation phase, the authorization check in the "transferFrom" function was successfully passed, allowing the attacker to successfully steal the NOBL tokens from the vulnerable contract.
Please see the specific details in the transaction: https://etherscan.io/tx/0x47da1ac72d488f746865891c9196c1632ae04f018b285b762b2b564ad1d3a9e5
Transactions Involved in the Attack
According to ZAN KYT data analysis, before the attacker withdrew NOBL tokens from the vulnerable contract, they used a contract vulnerability to have the vulnerable contract approve the tokens for the attacker. The transaction hash is as follows (only Ethereum transactions are listed):

Currently, the attacker has transferred some of the illegal gains to another address 0xd84f48b7D1AaFA7bd5905c95c5d1ffB2625AdA46, and there are currently no further actions. The developer of the claims contract (0x5a4bC2bdA1f6B9929b6efdCef4728246bEc4C635) contacted the attacker through Blockscan chat, acknowledging the vulnerability in the contract and assuming their actions to be white-hat actions, and they hope the attacker will contact them within 24 hours.
Security Recommendations
Based on the analysis of this attack, we have the following recommendations:
Thoroughly review token authorization operations in projects. Project developers and contract auditors should clearly define which business scenarios require token authorization and which scenarios require revocation of token authorization to prevent attackers from exploiting unrecovered or unexpected excess authorizations.
Projects should establish emergency pause mechanisms. It is recommended that projects involving fund transfers establish comprehensive pause mechanisms to mitigate losses in the event of an attack.
This article was co-authored by Cara from the ZAN Team (X account: @Cara6289) and XiG (X account: @SHXiGi).
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



