原文作者:MichaelZhao,Grayscale
原文编译:GaryMa,吴说区块链
供应影响:比特币的发行量将在 2024 年 4 月左右减半。尽管矿工在短期内面临收入挑战,但基础的链上活动和积极的市场结构更新使得这次的减半在根本上与以往不同。
矿工处境:面对减少的区块奖励收入和高昂的生产成本,矿工通过发行股权/债务和出售储备筹集资金,试图缓解短期财务压力。
链上活动持续增长:铭文的出现使得链上活动焕发新生,截至 2024 年 2 月,已有超过 5900 万个类似非同质化代币(NFT)的收藏品被铭刻,为矿工带来了超过 2 亿美元的交易费用。预计这一趋势将持续下去,得益于开发者的重新关注和比特币区块链上的持续创新。
比特币 ETF 对市场的影响:比特币 ETF 的持续采用可能会显著吸收卖压,潜在地重塑比特币的市场结构,提供新的稳定需求来源,这对价格是积极的。
随着我们越来越接近 2024 年的减半,比特币不仅仅依旧活着,它还在进化。随着美国对现货比特币 ETF 的历史性批准和资金流向的变化,比特币市场的结构正在发生变化。在这篇文章中,我们将深入探讨减半的含义、重要性以及对比特币表现的历史影响。然后,我们将检视比特币的当前格局,以及为什么与仅仅一年前相比,情况大不相同。
减半是什么?
新比特币是通过一种称为“挖矿”的过程生成的,计算机通过解决计算密集型问题来获得新比特币的区块奖励。比特币的发行受设计限制——大约每四年,挖矿奖励“减半”,实际上也减半了新代币的发行数量。
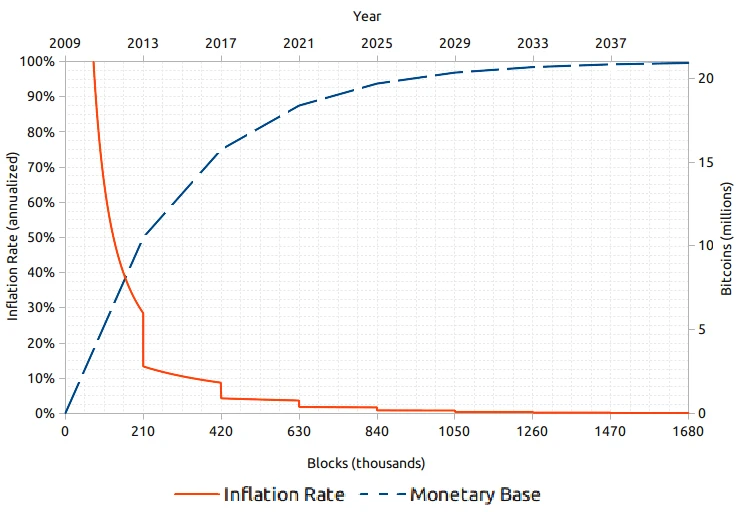
这种通货紧缩的特性是许多比特币持有者的根本吸引力所在。尽管法定货币供应依赖于中央银行,而贵金属供应受自然力的影响,但比特币的发行速度和总供应量自其诞生以来就由其基础协议规定。固定总供应量与逐渐降低的通货膨胀率的结合不仅创造了稀缺性,而且将通货紧缩特性内嵌到比特币中。
除了显而易见的供应影响外,围绕比特币减半的引人注目的兴奋和期待还源于其与比特币价格上涨的历史关联:
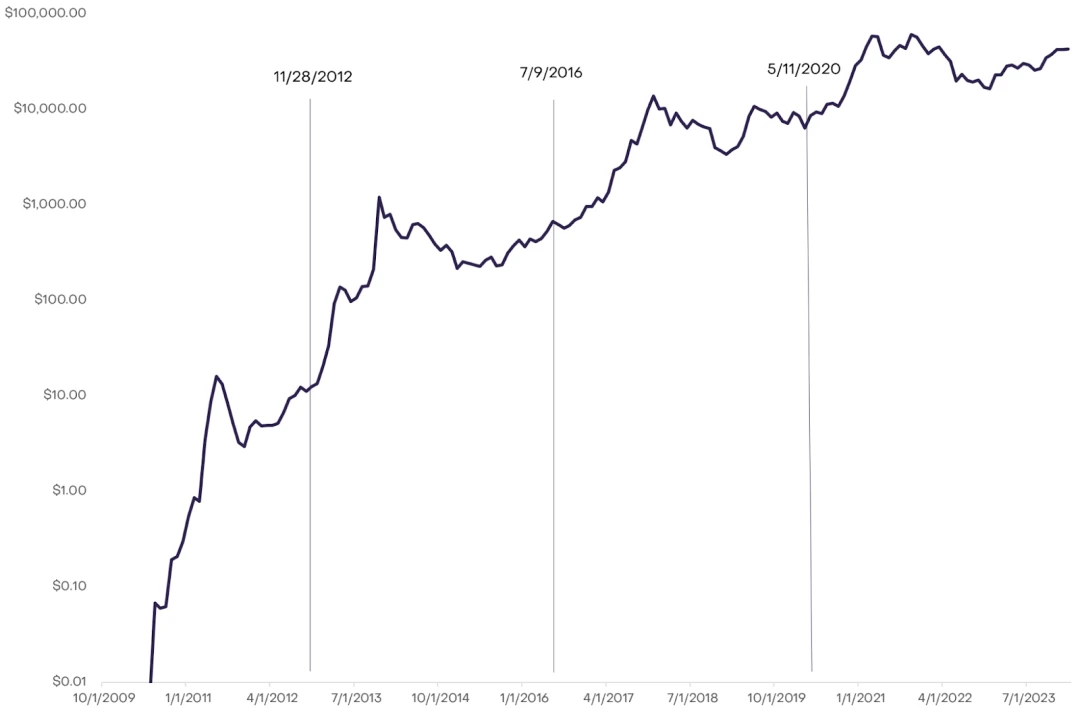
然而,重要的是要理解,减半后的比特币价格上涨并不是一定会发生的。鉴于这些事件备受期待,如果价格激增是确定的,理性投资者很可能会提前购买,导致减半之前价格上涨。这就引出了像 Stock-to-Flow 模型这样的框架。虽然它通过将稀缺性与价格上涨相关联而创建了视觉上吸引人的图表,但该模型忽视了这种稀缺性不仅是可预测的,而且是广泛提前知道的事实。通过观察其他采用类似减半机制的加密货币,如莱特币,我们可以得出这一结论,后者并没有在减半后持续看到价格上涨。这表明,尽管稀缺性有时会影响价格,但其他因素也起着重要作用。
与将减半后的价格上涨归因于减半本身不同,似乎这些时期与重大的宏观经济事件相吻合。例如,在 2012 年,欧洲债务危机突显了比特币在经济动荡中作为替代价值存储的潜力,导致其价格从 12 美元上涨到 2013 年 11 月的 1100 美元。类似地,在 2016 年的首次代币发行热潮中——将超过 56 亿美元注入到山寨币中——间接地也使比特币受益,将其价格从 650 美元上涨到 2017 年 12 月的 20,000 美元。尤其值得注意的是,在 2020 年的 COVID-19 大流行期间,大规模的刺激措施加剧了通货膨胀担忧,可能会将投资者推向比特币作为避险工具,导致其价格从 8600 美元上涨到 2021 年 11 月的 68,000 美元。这些宏观经济不确定性和对替代投资选择的探索似乎与比特币引起的兴趣增加的时期相吻合,巧合地发生在减半之时。这种模式表明,尽管减半有助于强化比特币的稀缺性叙事,但更广泛的经济背景及其对投资者行为的影响也可能对比特币的价格产生重大影响。
尽管未来的宏观经济环境仍然不确定,但减半对比特币供应结构的影响是确定的。让我们深入探讨一下。
矿工威胁
减半对比特币矿工构成了挑战。随着比特币发行量从每个区块的 6.25 个 BTC 减少到 3.125 个 BTC,矿工从区块奖励中获得的收入实际上减少了一半。此外,支出也在增加。哈希率是衡量用于在比特币网络上挖矿和处理交易的总计算能力的指标,是计算矿工支出的关键输入。2023 年,7 天平均哈希率从 255 EH/s 飙升到了 516 EH/s,增长了 102%,明显超过了 2022 年的 41% 的增长率。这一激增部分是由于比特币在 2023 年全年价格的上涨以及公司为应对良好的市场条件而获取更高效的挖矿设备,突显了矿工面临的不断加剧的挑战。收入下降和成本增加的结合可能会使许多矿工在短期内处于紧张状态。
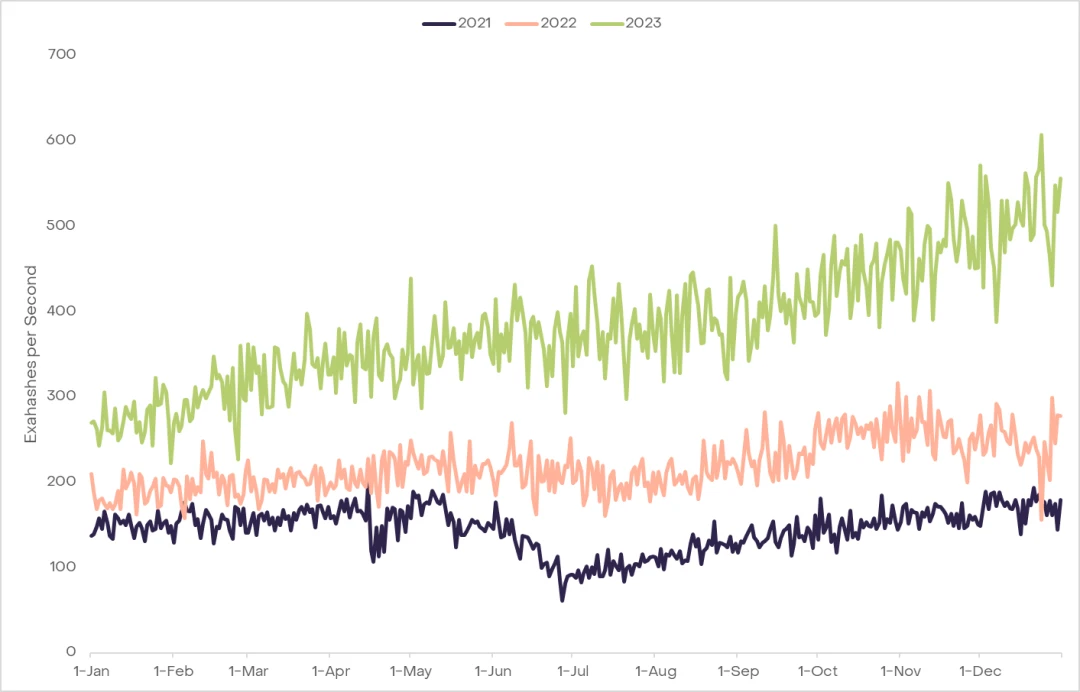
虽然情况可能看似严峻,但有证据表明,矿工早已为减半的财务后果做好了准备。2023 年第四季度,有矿工明显将他们的比特币链上持仓出售,可能是为了在减少区块奖励之前提前建立流动性。此外,重大的筹资活动,如 Core Scientific 的 5500 万美元股权发行、Stronghold的 1500 万美元股权融资和 Marathon Digital 雄心勃勃的 7.5 亿美元混合股权融资,突显了行业在增强储备方面的主动态度。这些举措共同表明,比特币矿工在短期内至少能够很好地应对即将到来的挑战。即使一些矿工完全退出市场,导致哈希率下降,也可能会导致挖矿难度调整,潜在地降低剩余矿工每个币的成本,并保持网络的平衡。
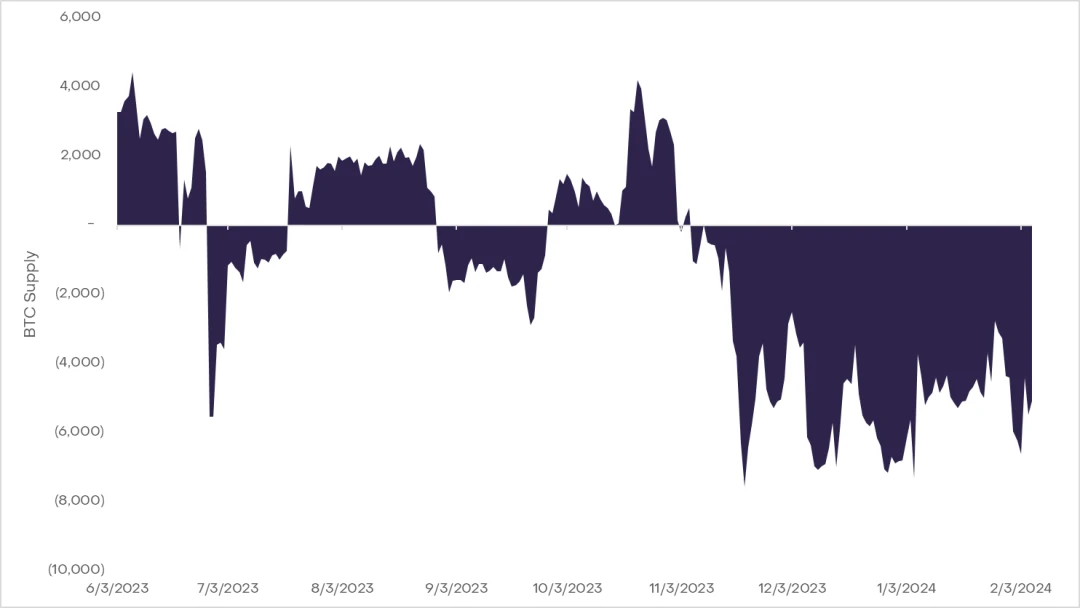
尽管区块奖励的减少带来了挑战,但在比特币生态系统内,铭文和 L2 的作用越来越大,最近已经成为了有前景的应用案例。这些创新可能为矿工提供了一线希望,可能会提高交易吞吐量并增加网络的交易费用。
铭文
正如我们之前探讨过的那样,铭文(“ordinals”)代表了比特币生态系统内的一项开创性创新。从简单的图像到自定义的“BRC-20”代币,数字收藏品可以被独特地“铭刻”到特定的聪(比特币的最小单位,因为每个比特币可分成 1 亿聪)。这种新的比特币实用性维度已经刺激了显著增长:迄今为止,已经有超过 5900 万资产被铭刻,为矿工带来了超过 2 亿美元的交易费用(陈列 5)。
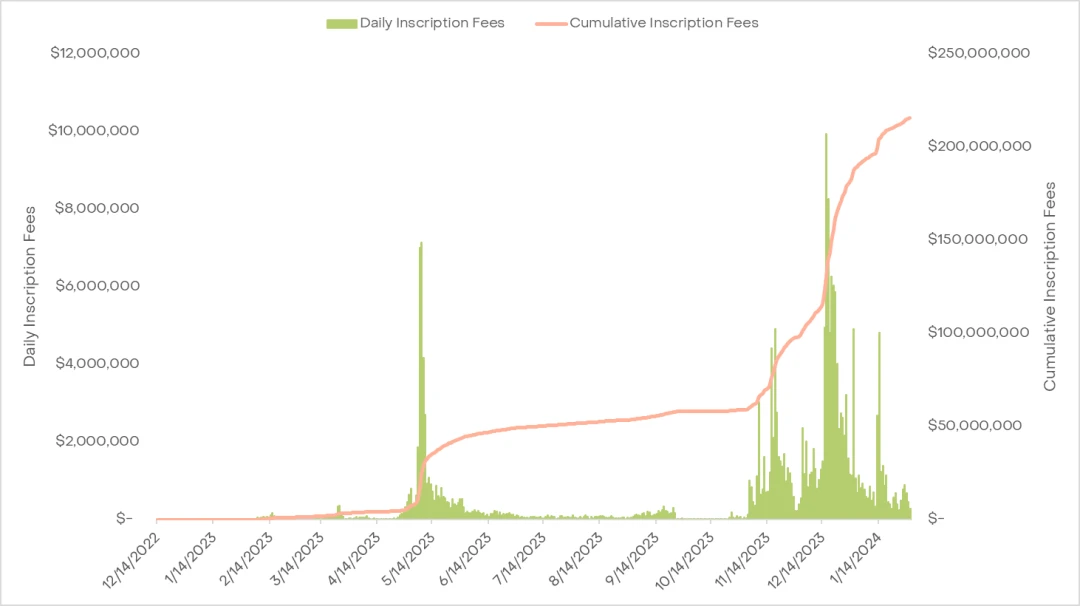
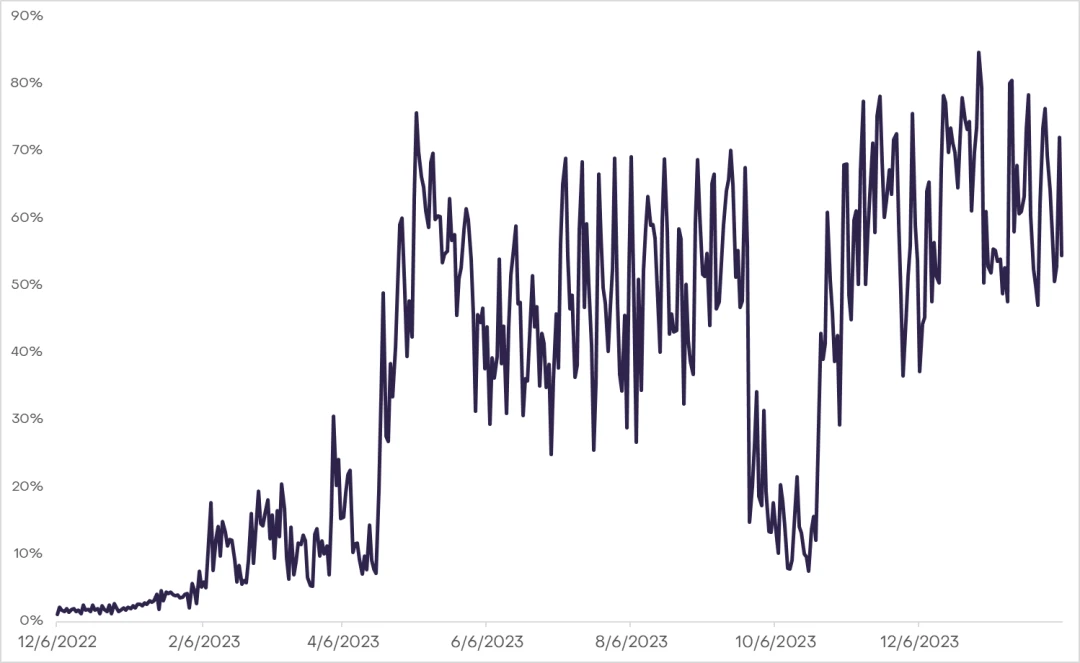
网络费用的激增产生了深远影响,特别是在 2023 年 11 月 20 日,比特币网络的交易费首次超过了以太坊网络,创下了最近历史上的新纪录。自序数铭文问世以来,矿工从铭文费中获得超过总交易费的 20% 已经有多次。即使与其他链上 NFT 的总量相比,比特币在 2023 年 11 月和 12 月的 NFT 交易量中也占据了主导地位,这是 2022 年底很少有人能预料到的发展。
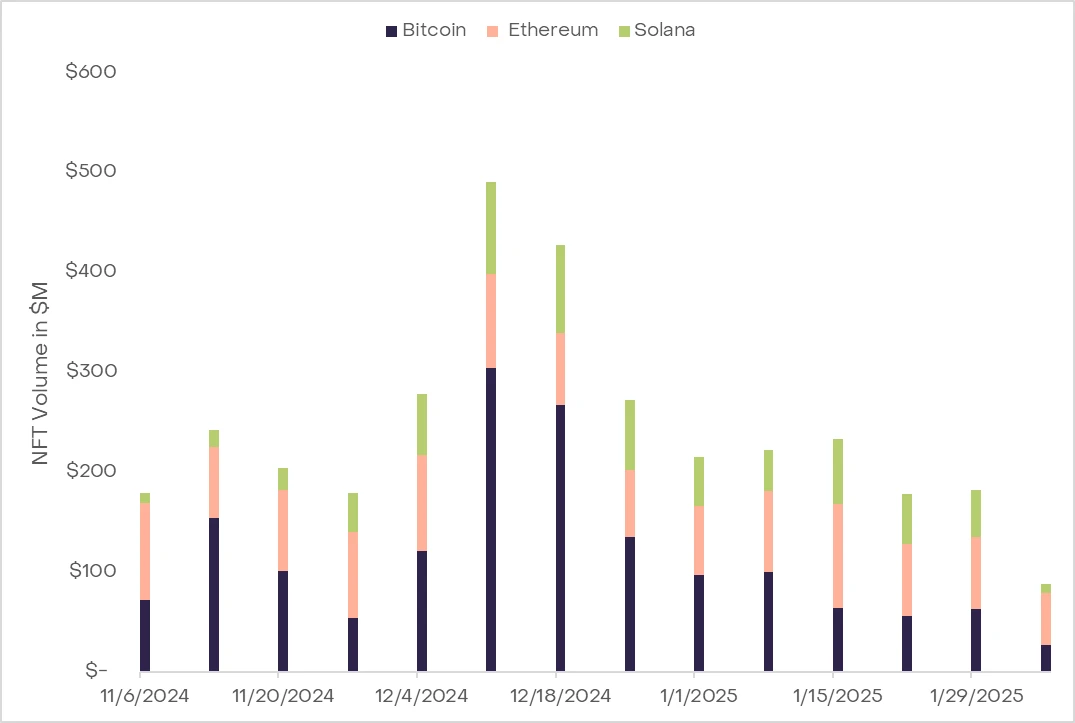
铭文的成功对比特币网络产生了影响。随着时间的推移,随着区块奖励的减少,矿工如何被激励来保护网络的问题变得更加紧迫。由于来自序数的交易费已经约占总矿工收入的 20%,这种新兴的铭文活动趋势为通过增加交易费来维持网络安全提供了一条新路径,至少目前是这样。
然而,这一成功也凸显出了可扩展性挑战,因为用户将不得不承担更高的交易费用。这可能会阻碍用户进行像转账这样的基本交易。此外,比特币的架构限制了可编程性,这进一步限制了开发能够使用这些铭文的复杂应用程序的障碍。这种情况强调了需要扩展解决方案,既可以增加吞吐量以进行高效交易,又可以扩展用例,比如交易 NFT 和 BRC20 代币。
作为回应,社区正在探索类似以太坊所采取的 Layer 2 Rollups 等途径,以增强可扩展性和可用性。对支持Taproot的钱包越来越感兴趣,这些钱包通过增强的隐私和效率功能提供了更高的可编程性,表明了共同应对这些挑战的举措。随着比特币主链上的交易费用的增加,L2 网络的发展成为可能迈出的一步。
正如我们在之前关于铭文的文章中所讨论的那样,铭文的复兴和 BRC-20 代币的引入已经在比特币社区内引发了一场文化转变,吸引了一批新的开发人员,他们对网络扩展的可能性感到兴奋。这种转变可以说是比特币最重要的发展之一,因为它不仅使生态系统多样化,还为社区注入了新的观点和创新项目,推动着未来的发展。
在现有的第二层(L2)解决方案中,一些已经在默默为这种演变奠定基础多年。Stacks 是一个引入了完全表达式智能合约到比特币的平台。它促进了各种利用比特币安全性的去中心化应用程序(dApps)的开发,使功能从 DeFi 到 NFTs 都得以实现。这些 dApps 代表了比特币向多方面生态系统过渡的前沿,能够支持各种基于区块链的应用程序。
ETF 资金流
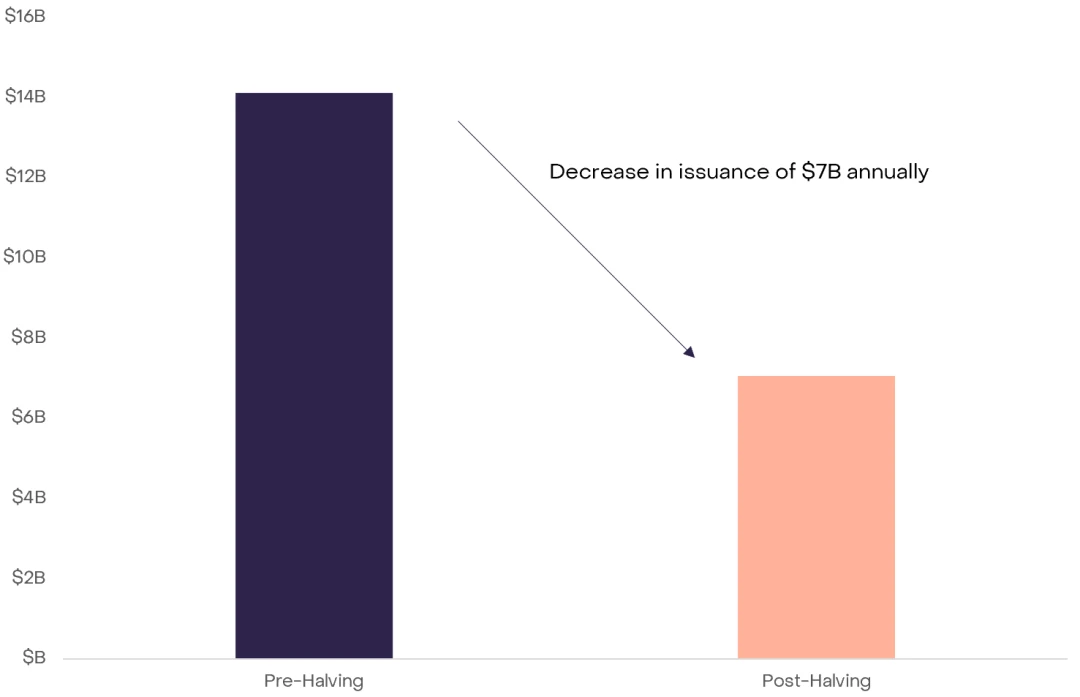
除了基本上积极的链上基本面之外,比特币的市场结构看起来有利于减半后的价格。从历史上看,区块奖励给市场带来了潜在的卖压,可能导致所有新挖掘的比特币都被出售,从而影响价格。目前每个区块挖掘的 6.25 比特币相当于每年约 140 亿美元(假设比特币价格为 43,000 美元)。为了维持当前的价格,每年需要相应的购买压力为 140 亿美元。减半后,这些需求将减半:每个区块只有挖掘的 3.125 比特币,这相当于每年减少到 70 亿美元,有效减轻了卖压力。
ETFs一般为更广泛的投资者、财务顾问和资本市场配置者提供了获取比特币敞口的途径,随着时间的推移,这可能会导致主流采用的增加。在美国现货比特币 ETF 获得批准之后,这些新推出的产品在最初的 15 个交易日内的净流入额达到了约 15 亿美元,几乎相当于三个月的潜在减半后的卖压。虽然最初几天内净流入额激增可能是由于最初的兴奋和被压抑的需求,但假设在持续的比特币生态系统采用和成熟的情况下,净流入额保持稳定状态,ETF 流动性可能会对来自挖矿发行的持续卖压起到一定的抵消作用。对每日净流入额从 100 万美元到 1000 万美元的敏感性分析表明,在较高端,抛售压力的减少可能会反映出另一次减半的效果,以积极的方式从根本上转变比特币的市场结构。
结论
比特币不仅经受住了熊市的风暴,而且还以过去一年的发展挑战了过时的认知。虽然它长期被誉为数字黄金,但最近的发展表明,比特币正在演变成为更重要的东西。受到链上活动的激增的推动,受到重大市场结构的势头的支撑,并且以其固有的稀缺性为背书,比特币显示出了其韧性。Grayscale 研究团队将密切关注其在 2024 年 4 月减半前后的发展,因为我们相信比特币的未来光明璀璨。
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




