What is the Bitcoin ecosystem, and which projects are worth paying attention to?
Author: Bitget Research Institute
Abstract
- In 2023, the wealth effect of Bitcoin is evident, with the price rising from $16,500 at the beginning of the year to $42,000. In addition to Bitcoin itself, market funds have also overflowed into its ecosystem.
- The most obvious case is the explosion of the BRC20 sector under the Ordinals protocol. The market size of BRC20 tokens has now exceeded $40 billion, compared to $1 billion in March of this year, an increase of nearly 40 times. This has also driven the continuous innovation and development of the entire Bitcoin ecosystem.
- At present, the market's attention to the Bitcoin ecosystem is focused on two aspects: asset issuance protocols, mainly covering Ordinals, Atomicals, Runes, PIPE, Taproots Assets, and scaling solutions, mainly covering Lightning Network, RSK, Stacks, RGB, BitVM.
- The main sectors with obvious wealth effects in the current stage of the Bitcoin ecosystem are: BRC-20 assets under the Ordinals protocol, ARC-20 and Realm under the Atomicals protocol, PIPE under the PIPE protocol, and tokens in the Bitcoin scaling sector (RIF, STX), among others. This article analyzes the reasons why these assets have wealth effects and introduces the ways for investors to participate.
- In addition to technological innovation, the prosperity of the Bitcoin ecosystem depends on the participation of various market participants, mainly including: individual investors, exchanges, project parties, miners, and investment institutions. Therefore, this article analyzes the opportunities and risks for the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem for the above 5 groups, providing reference for investment and business expansion.
- Based on the future macro environment and market conditions, the Bitcoin ecosystem has a good development prospect. Not only popular currencies like BTC and ORDI will have a large appreciation space, but there will also be new opportunities for hundredfold currencies in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
- The trading volume of the Bitcoin NFT market has surged, but the current scale is relatively small. Therefore, it is expected to have a growth space of over 100 times in the future. The Lightning Network is the biggest technological support to help Bitcoin payments be adopted on a larger scale in the short to medium term.
- Combining the above analysis, Bitget Research Institute has made six predictions for the future trend of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Since the second half of 2023, not only has the Fed's interest rate hike cycle come to an end, but the approval of a Bitcoin spot ETF by the U.S. SEC has almost become a market expectation. Once the Bitcoin spot ETF is approved, a massive amount of funds from traditional finance can flow into the Bitcoin ecosystem in a compliant manner. Under this huge expectation, not only has Bitcoin maintained a good upward trend, but it has also driven the development of related projects in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
The most obvious case is the resurgence of the BRC20 sector in the Bitcoin ecosystem since November, with the huge wealth effect of BRC20 coins such as ORDI, SATS, and RATS, attracting extreme attention to the Bitcoin ecosystem. So what exactly is the Bitcoin ecosystem, and which projects are worth paying attention to? Understanding these may be the key to seizing the next bull market wealth opportunity.
I. What is the Bitcoin Ecosystem
1. Definition of the Bitcoin Ecosystem
The Bitcoin ecosystem refers to a system composed of solutions, protocols, applications, and assets aimed at improving the utility and efficiency of the Bitcoin blockchain network. The current discussion on the Bitcoin ecosystem focuses on two main aspects: asset issuance protocols and scaling solutions.
- Asset Issuance Protocols: These are protocols that define the technical standards for issuing assets, mainly including Ordinals, Atomicals, Runes, PIPE, and Taproot Assets.
- Scaling Solutions: These refer to solutions aimed at improving the basic performance of the Bitcoin network, with representative solutions including Lightning, RSK, Stacks, RGB, and BitVM.
2. How the Bitcoin Ecosystem Developed from 0 to 1
To understand how the Bitcoin ecosystem developed from 0 to 1, it is essential to consider several key development milestones of Bitcoin.
On October 31, 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto published a paper titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System," detailing the concept and technical details of Bitcoin. Then, on January 3, 2009, Nakamoto mined the genesis block of the Bitcoin network, marking the birth of Bitcoin.
Since its birth, Bitcoin has attracted numerous individuals from the fields of cryptography and computer science. As Bitcoin continued to spread, the number of people accepting and building applications around Bitcoin increased, leading to the initial formation of an industry structure consisting of chips, integrated circuits, exchanges, wallets, and application software for Bitcoin production and trading. This also brought Bitcoin and various cryptocurrencies into the public eye.
In addition to Bitcoin production and trading, people began to explore the development of more applications that could be used in real life on the Bitcoin network, but encountered technical bottlenecks of the Bitcoin blockchain network itself. This is because blockchain technology faces an impossible trilemma, where it is difficult to simultaneously satisfy decentralization, security, and scalability in blockchain system design.
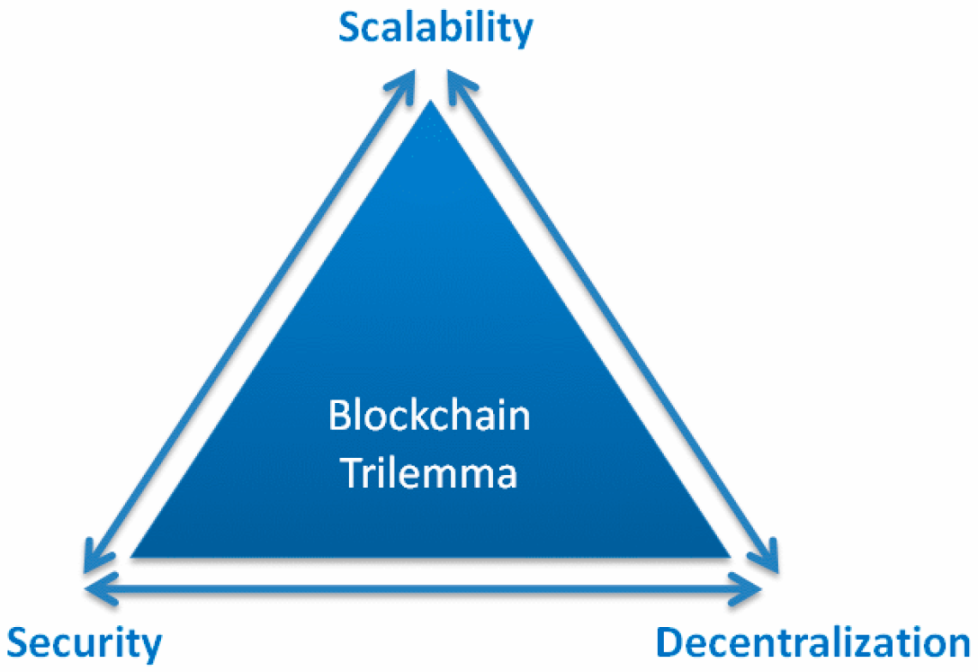
Comparison of decentralization, security, and scalability in blockchain system design
Compared to scalability, decentralization and security are generally considered more important features. Therefore, without sacrificing the decentralization and security of the Bitcoin network, the focus has been on how to increase scalability, which has become a key exploration direction for Bitcoin technology breakthroughs.
Up to now, Bitcoin has undergone two major technical upgrades, which have laid the foundation for the prosperity of the Bitcoin ecosystem today.
First Major Technical Upgrade: Segregated Witness (SegWit) Upgrade
Segregated Witness is an important technical upgrade to the Bitcoin protocol. The core technology change is to increase the original Bitcoin block size limit from 1MB to 1MB+3MB and improve the extensibility (malleability) of the Bitcoin protocol.
The structure of Bitcoin transactions before the Segregated Witness upgrade is as follows:
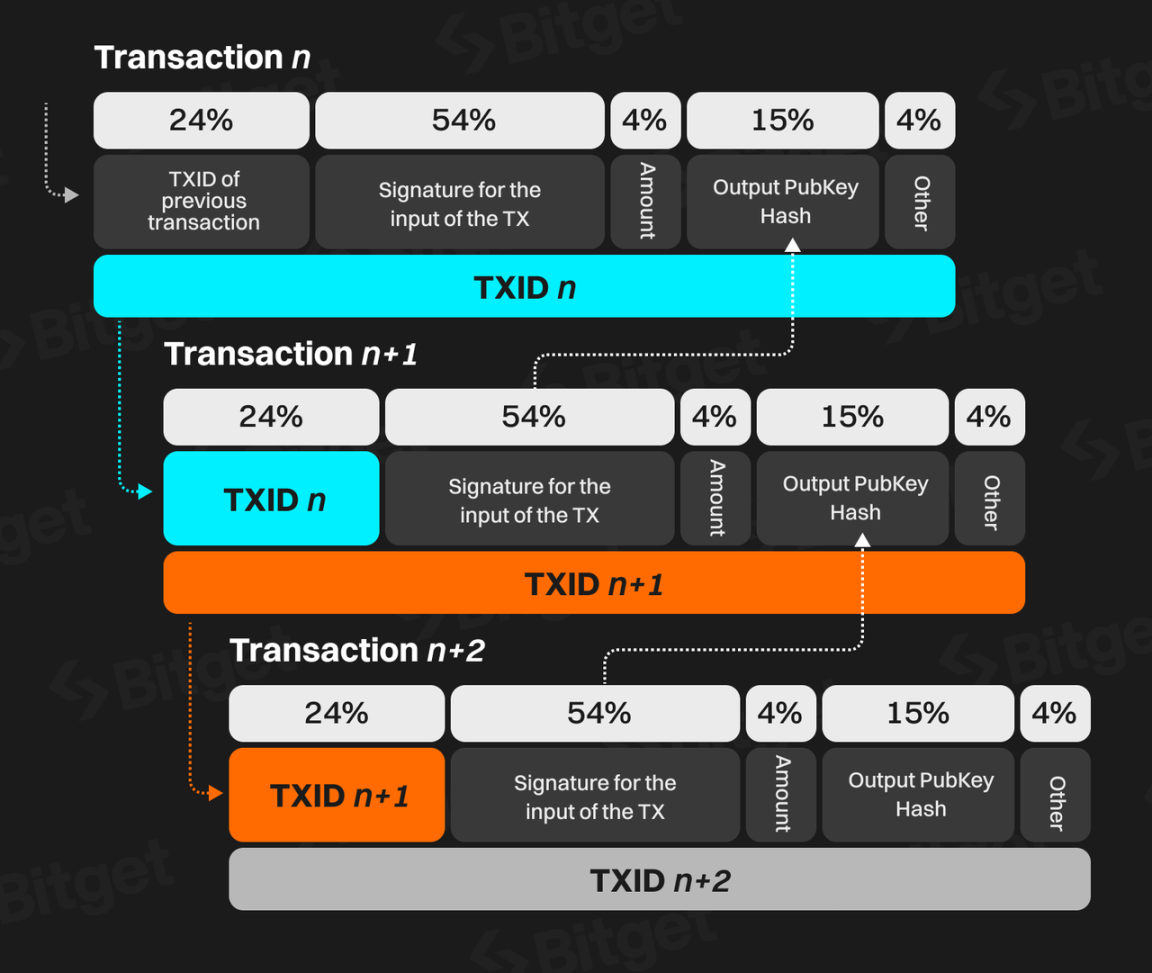
Structure of Bitcoin transactions before SegWit upgrade (Source: The SegWit Transaction Capacity Increase)
The structure of Bitcoin transactions after the Segregated Witness upgrade is as follows:
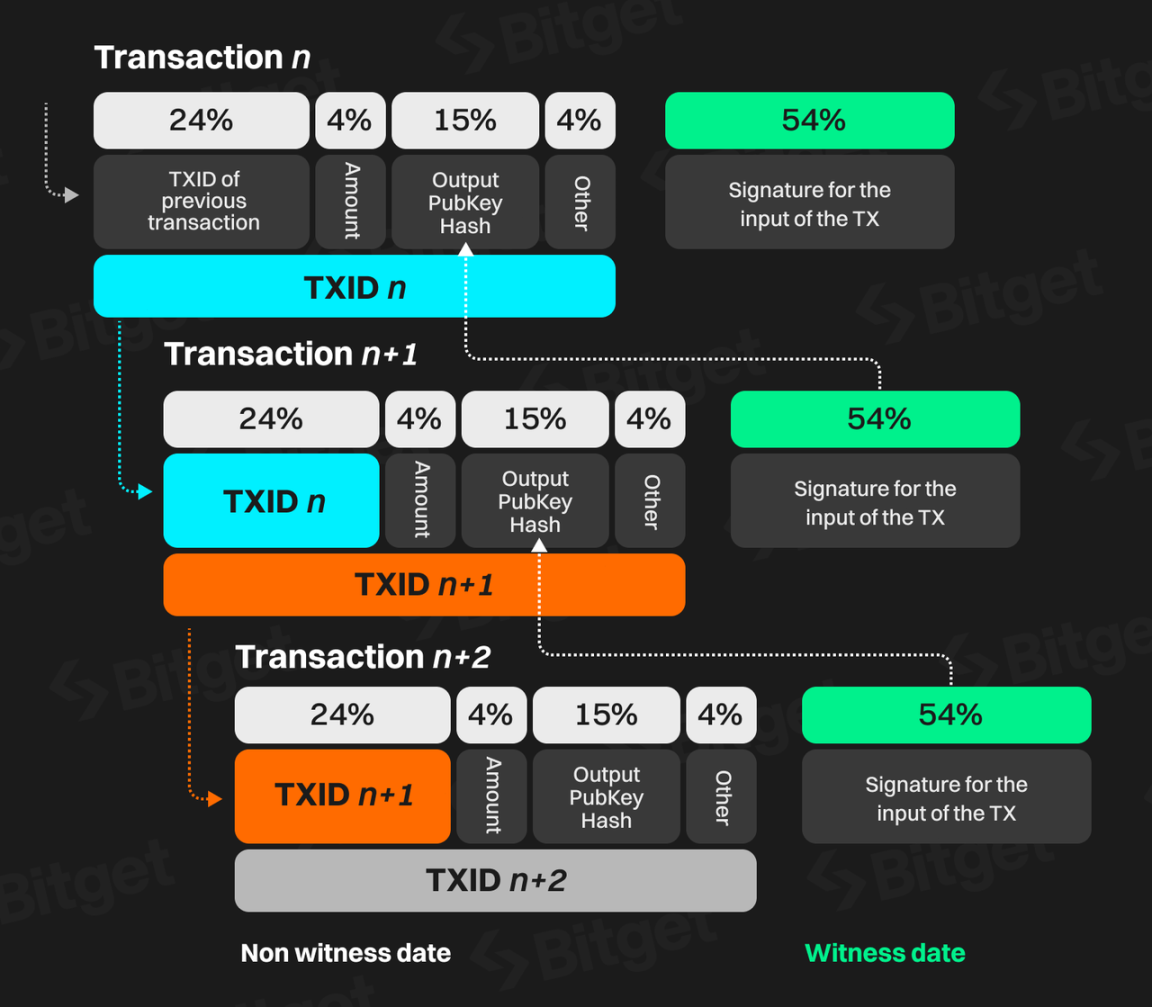
Structure of Bitcoin transactions after SegWit upgrade (Source: The SegWit Transaction Capacity Increase)
Second Major Technical Upgrade: Taproot Upgrade
The Bitcoin Taproot upgrade mainly involves three Bitcoin Improvement Proposals (BIPs), which together constitute the core content of this upgrade.
1) BIP 340 - Schnorr Signature: This proposal introduces the specification of the Schnorr signature algorithm, which is used for digital signatures in Bitcoin. Compared to the previous ECDSA signatures, Schnorr signatures provide better efficiency, smaller signature size, and stronger security. It also supports signature aggregation, which is particularly useful for multi-signature transactions, significantly reducing transaction size and enhancing privacy.
2) BIP 341 - Segregated Witness v1 (SegWit v1) and Taproot: This proposal describes how to improve the transaction structure of Bitcoin through Taproot and SegWit v1. It allows smart contracts to appear indistinguishable from regular transactions externally, increasing privacy. Additionally, it reduces transaction size, thereby lowering transaction fees. This BIP also includes detailed rules for using Schnorr signatures.
3) BIP 342 - Tapscript: This proposal updates Bitcoin's scripting language to be compatible with Schnorr signatures and Taproot. These changes make it more flexible and efficient to write and execute smart contracts in Bitcoin.
These three BIPs collectively bring significant improvements to the Bitcoin network, including higher efficiency, better privacy, and more flexible and powerful smart contract capabilities. These improvements are of great significance for the future development of the Bitcoin network, particularly in driving the construction of its ecosystem applications and decentralized finance.

After laying the foundation with two major technical upgrades, the development direction of the Bitcoin ecosystem has focused on two aspects: scaling solutions, continuing to explore new technological solutions with the goal of increasing Bitcoin's scalability, such as the Lightning Network, sidechain technology, and BitVM; and asset issuance protocols, seeking to issue more assets and deploy applications on the Bitcoin network, similar to Ethereum, such as the Ordinals protocol, Atomicals protocol, and Runes protocol.
In this trend, the first token ORDI based on the BRC-20 standard under the Ordinals protocol, which appeared in March 2023, further opened the vigorous construction process of the Bitcoin ecosystem through the huge wealth effect.
3. Current Focus of the Bitcoin Ecosystem
Note: For easier expression and understanding, the following content will represent the transaction fee of the BTC network as gas.
The Bitcoin ecosystem encompasses many aspects, but the current market's main focus is on two aspects: asset issuance protocols and scaling solutions.
3.1 Asset Issuance Protocols
In 2023, the asset issuance protocols on Bitcoin have experienced explosive development. After several tokens based on the BRC20 format under the Ordinals protocol demonstrated significant wealth effects, more protocols have emerged, including: Ordinals, Atomicals, Taproot Assets, Runes, and PIPE.
3.1.1 Ordinals Protocol
What is the Ordinals Protocol
The Ordinals protocol is an asset issuance protocol based on Bitcoin, introduced by Bitcoin developer Casey Rodarmor in January 2023. The protocol consists of two parts: Ordinals ordinal theory and Inscription. The ordinal theory provides a method for assigning unique identifiers to 21 trillion Satoshis (the smallest unit of Bitcoin), while Inscription is the process of associating content with UTXO.
The Ordinals protocol can be understood in simple terms as follows: the asset issuance process of the Ordinals protocol is like writing content into a space (witness data), such as writing token information (recorded in JSON format) for BRC20 into this space, and writing image information for NFT into this space. The process of writing is called Inscription.
Why the Ordinals Protocol Emerged
Because there has always been a lack of a simple and secure way to issue assets on the Bitcoin network. The author of the Ordinals protocol, Casey, uses Inscription to carry content on UTXO, leveraging the security of the Bitcoin network and the scalability brought by Taprootscript, making it possible to issue assets simply and securely on the Bitcoin network.
Current Status of the Ordinals Protocol
Based on the Ordinals protocol itself, two main types of assets have emerged: BRC-20 tokens and Ordinals NFT.
1. BRC-20 Tokens
BRC-20 is an experimental token standard for Bitcoin created by Twitter user @domodata on March 8, 2023. It enables the creation (Deploy), minting (Mint), and transfer (Transfer) of tokens using JSON data from Ordinal inscriptions. These are the three main functions of the BRC-20 standard tokens.
As of December 4, 2023, the daily transaction volume of BRC-20 tokens on-chain is approximately around $22 million, while the daily transaction volume on centralized exchanges is currently between $800-900 million. The total market value of the BRC-20 sector fluctuates in the range of $3.5 billion to $4 billion.
2. Ordinals NFT
Ordinals NFT is a type of digital asset based on the Bitcoin mainnet, using the Ordinals protocol. Unlike traditional NFTs, Ordinals NFTs are represented using Satoshis (the smallest unit of Bitcoin).
As of December 4, 2023, the recent 30-day trading volume of Bitcoin NFTs reached $371 million, almost on par with the recent 30-day NFT trading volume of $387 million on Ethereum.
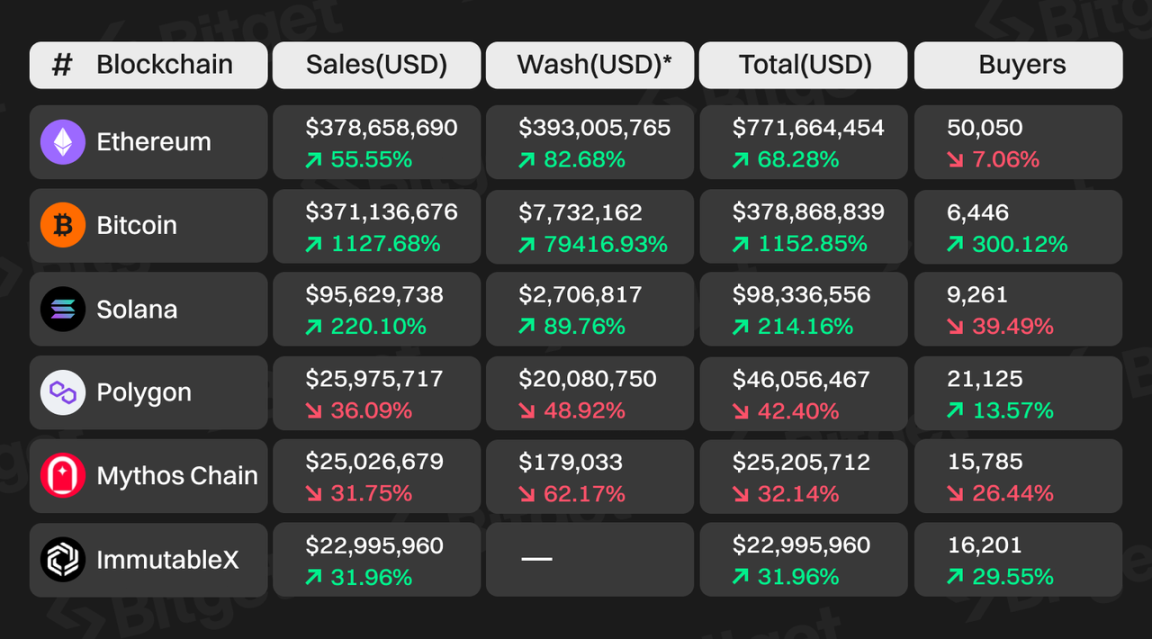
Unique Advantages of the Ordinals Protocol
BRC-20 Tokens
Although the BRC-20 token standard is still in its early stages, it is gaining more attention as enthusiasts continue to explore its potential.
- Strong Security: Because BRC-20 tokens are built on the highly secure Bitcoin protocol, it makes it difficult for hackers to invade. Additionally, because BRC-20 "tokens" are essentially inscriptions and do not involve smart contracts, they do not have contract risks like ERC-20 format tokens.
- Fair Issuance Mechanism: For a meme coin, a fair issuance method is crucial. Once created, all users holding valid BTC wallets can participate in the "initial offering" of BRC-20 tokens. The issuance of BRC-20 tokens is relatively fair, and participating in Mint requires paying gas, meaning users need to pay real money to obtain corresponding token rights.
Ordinals BTC NFT
BTC NFTs based on the Ordinals protocol also have unique and tamper-proof characteristics, but from a technical design perspective, there are some differences. Based on the current common practices of developers (with some exceptions), the differences between Bitcoin NFTs and Ethereum NFTs are as follows:
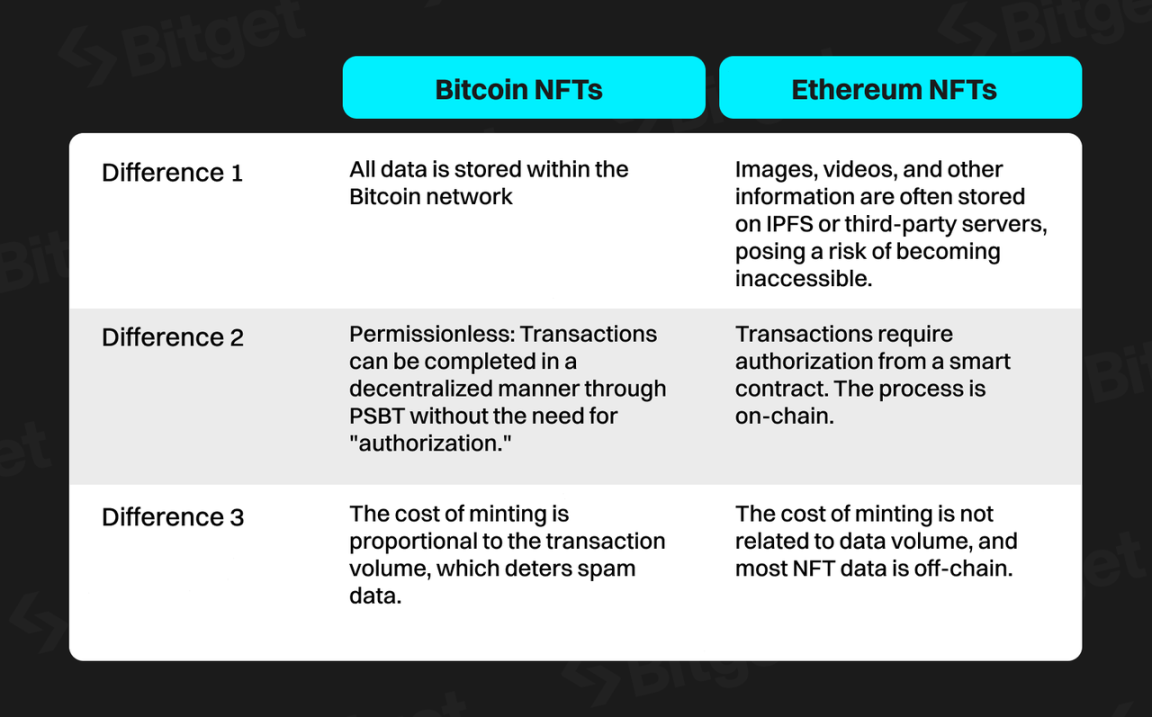
Overall, Ordinals on Bitcoin represents a technical improvement for NFTs, providing a more complete and reliable form of digital art by directly storing all data on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Potential Issues with the Ordinals Protocol
While the introduction of the Ordinals protocol has brought new functionality and possibilities to the Bitcoin network, it has also presented a series of challenges and issues that need to be addressed and resolved by the community, developers, and regulatory agencies. The core issues include:
- Decreased blockchain space efficiency: Ordinals works by embedding data in individual Bitcoin transactions, which may occupy a significant amount of blockchain space. This could lead to miners needing to store a large volume of Bitcoin network UTXO information, affecting network processing speed and transaction costs.
- High user learning curve: The Ordinals protocol increases the complexity of using the Bitcoin network. Ordinals maps BRC-20 and Ordinals NFTs to specific "Satoshi," and to avoid affecting the meaning of these "Satoshi" in asset order, users need to store these "Satoshi" in segregated wallets, increasing the difficulty for users to participate and the difficulty for project teams to develop wallet infrastructure.
3.1.2 Atomicals Protocol
What is the Atomicals Protocol
The Atomicals protocol is an asset issuance protocol on UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) type blockchains. It supports a variety of asset types, including homogeneous tokens under the ARC20 standard, NFTs, Realms, and Collection Containers. For homogeneous token assets, the Atomicals protocol follows atomic definitions, using the smallest unit of Bitcoin, Satoshi, as the minimum unit for issuing assets. On the issuance side, the Atomicals protocol has two methods: decentralized minting and direct minting.
Why the Atomicals Protocol Emerged
The Atomicals protocol emerged to build a more comprehensive asset issuance protocol compared to the Ordinals protocol. Unlike Ordinals, which relies on a third-party sorter to sort asset transactions, the Atomicals protocol ARC20 standard uses Satoshi as the minimum unit for issuing assets, allowing Atomicals assets to trace complete transaction histories without relying on any third-party sorter.
Atomicals assets have two methods for distribution: decentralized minting and direct minting. Decentralized minting introduces a POW mode called Bitwork Mining, requiring CPU/GPU to calculate specific characters to complete minting, representing a fairer distribution method to some extent.
Current Status of the Atomicals Protocol
The Atomicals protocol includes four major asset types:
- ARC20: Similar to BRC20 on Ordinals, this token format standard is mainly represented by projects such as $ATOM, $PEPE, and $REALM.
- NFT: Main projects include PUNK, XCSS (the first original collection), and Atommap (comparable to bitmap).
- Realm: A concept introduced by Atomicals, aiming to disrupt traditional domain names and use domain names as prefixes.
- Collection Containers: This is a data type for defining NFT collections, mainly used to store readable NFT collections and related metadata, similar to a form of on-chain data object storage.
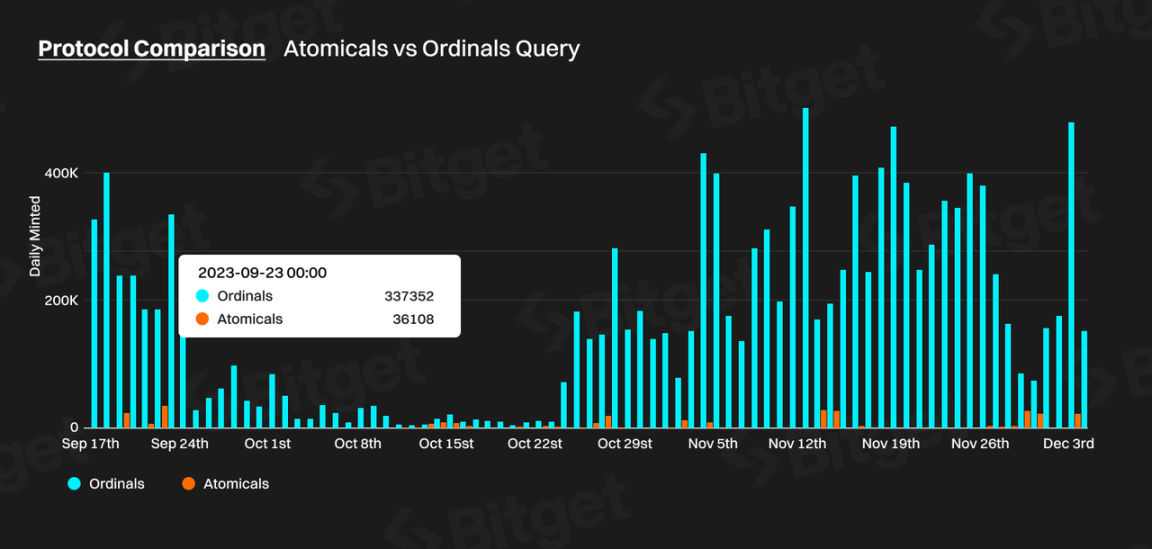
Data as of December 4, 2023, shows that the total number of mints under the Atomicals protocol is 366,879, with a total expenditure of 55.8 BTC. The total number of mints under this protocol accounts for 2.69% of the total mints under Ordinals. The daily minting situation is shown in the following chart:
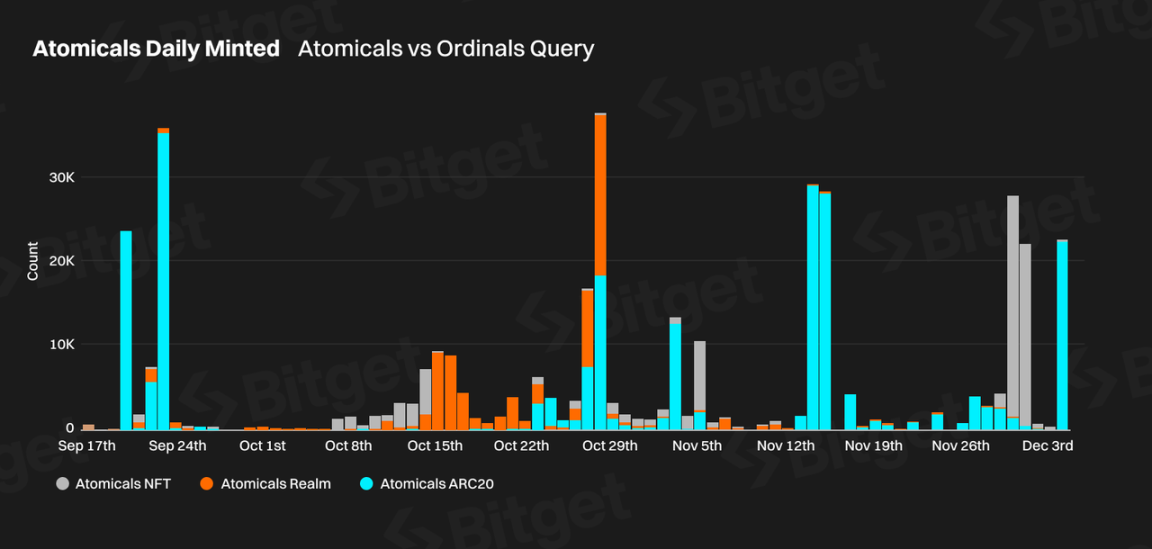
Compared to Ordinals, Atomicals is still in its early stages, with the peak daily minting volume being less than one-tenth of the peak minting volume of Ordinals.
Unique Advantages of the Atomicals Protocol
- Reduced error risk: The Atomicals protocol has a splat operation, allowing users to selectively separate multiple Atomicals assets combined into the same UTXO, effectively avoiding the risk of assets being accidentally consumed as transaction fees.
- Diverse asset distribution methods: The Atomicals protocol provides decentralized minting and direct minting. Decentralized minting requires CPU/GPU to calculate specific characters to complete minting, representing a fairer distribution method to some extent. Direct minting is relatively centralized but can also address some special distribution scenarios.
- Wide-ranging application potential: The Atomicals protocol allows users to represent assets on the Bitcoin blockchain in more complex and diverse ways, surpassing the traditional simple payment function.
Potential Issues with the Atomicals Protocol
- Complexity of Technology: The implementation of the Atomicals protocol may be relatively complex, requiring a deep understanding of Bitcoin scripts and blockchain technology, which may limit its popularity and application. Due to the complexity of operations and concepts, ordinary users may find it difficult to understand and accept the Atomicals protocol, which may limit its widespread use.
- Slow Current Infrastructure Development: Atomicals assets currently do not have a good trading market. The two main trading platforms have experienced multiple security incidents, and recently Atomicals Market also experienced "zero-dollar purchases" due to technical vulnerabilities. Currently, most trading demand relies on C2C. There are only three public node services (Atomicals official, Atomical Market, nextdao), and occasional network connection instability of nodes may lead to trading requests not being sent, resulting in the inability to mint or the failure of minting due to waiting too long.
3.1.3 Runes Protocol
What is the Runes Protocol
The Runes Protocol is a homogeneous token (Fungible Token) protocol based on the Bitcoin UTXO model, managed and transferred through simple tuples (ID, OUTPUT, AMOUNT) and the OP_RETURN operation. Its main feature is the simplicity of the protocol, which does not require additional off-chain data or native tokens to support certain operations, optimizing on-chain data usage and improving user experience.
Why the Runes Protocol Emerged
The emergence of the Runes protocol is due to developer Casey's dissatisfaction with the creation of a large number of "junk" UTXOs using the BRC20 protocol based on the Ordinals protocol. Therefore, a homogeneous token (Fungible Token) protocol based on the Bitcoin UTXO model was proposed. Unlike RGB and Taproot, which require off-chain data storage and retrieval infrastructure, or BRC-20, which generates "junk UTXOs" and occupies space on the BTC network, the design concept proposed by the Runes Protocol can solve user experience issues without wasting space on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Current Status of the Runes Protocol
The Runes Protocol is still a concept by Casey and currently does not have a complete client or development tools.
Unique Advantages of the Runes Protocol
- Based on the UTXO Model: Tightly integrated with Bitcoin's existing UTXO model, improving compatibility and natural integration with Bitcoin itself.
- Simplified Operations: The protocol makes token creation, transfer, and distribution intuitive and easy to understand through the simple (ID, OUTPUT, AMOUNT) tuple mechanism.
- User-Friendly: The Runes Protocol is committed to simplifying the user experience, reducing reliance on complex operations, making it easier for users to understand and use.
- Transparency and Security: All operations are visible on the chain, providing higher transparency, and the burning mechanism of runes also ensures the security of the protocol.
Potential Issues with the Runes Protocol
- Symbol Preemption Issue: Lack of a mechanism to prevent symbol preemption may lead to early users occupying short and valuable symbols.
- Inability for Fair Minting: The Runes Protocol does not provide fair minting functions similar to the BRC-20 standard, so users cannot mint fairly.
- Slow Development Progress: The Runes Protocol is still a concept by Casey and currently does not have a complete client or development tools.
3.1.4 PIPE Protocol
What is the PIPE Protocol
The PIPE Protocol is an asset issuance protocol developed by Benny, inspired by Casey's Runes protocol and Domo's BRC-20 standard based on Ordinals, integrating the advantages of both protocol standards. The PIPE protocol provides three main functions: deployment, minting, and transfer, abbreviated as DMT. These functions allow PIPE protocol assets to be created, distributed, and transferred within the Bitcoin network. In addition to homogeneous tokens, the PIPE protocol also provides a complete data structure and standard for non-fungible tokens.
Why the PIPE Protocol Emerged
The emergence of the PIPE protocol stems from the shortcomings of asset issuance protocols in the current Bitcoin ecosystem. The PIPE protocol combines the respective advantages of the RUNES protocol and the BRC-20 standard, forming a new asset issuance solution.
Current Status of the PIPE Protocol
The PIPE protocol is designed by Benny as part of the Trac System to create a comprehensive BTC ecosystem, as shown in the following figure. The protocol has lower complexity in asset issuance compared to BRC-20.

Based on the PIPE protocol, there are now two types of projects deployed: FT (homogeneous tokens) and NFT (non-fungible tokens). As of November 16, 2023, a total of 16,976 tokens have been issued based on this protocol, and the leading FT $PIPE has seen hundreds of times increase.
Unique Advantages of the PIPE Protocol
- Compatibility with the UTXO Model: The PIPE protocol retains the tight integration with Bitcoin's UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) model, ensuring compatibility with Bitcoin's native architecture.
- Simplified Operation Process: Similar to the design of RUNES, the PIPE protocol adopts a simplified approach, making it easy for users to interact.
- Fair Minting Mechanism: Similar to BRC-20, which considers fairness in the token minting process, the PIPE protocol also incorporates this and provides a fair minting mechanism.
Potential Issues with the PIPE Protocol
- Technical Complexity: Implementing the PIPE protocol requires adding additional complexity within the existing framework of Bitcoin, which may make it more challenging for ordinary users and developers to understand and implement the protocol.
3.1.5 Taproot Assets Protocol
What is the Taproot Assets Protocol
The Taproot Assets Protocol is a native asset overlay layer built on the Bitcoin blockchain's Taproot, with primary functions including asset issuance and transfer.
Why the Taproot Assets Protocol Emerged
The Taproot Assets Protocol primarily addresses the effective and efficient issuance and transfer of arbitrary assets on the Bitcoin blockchain. This protocol specifically focuses on keeping these operations off-chain to avoid wasting blockchain block space.
Early attempts at Bitcoin asset protocols, such as Mastercoin and Counterparty, used the OP_RETURN opcode to directly represent assets on the Bitcoin main chain. This led to data bloat and efficiency issues on the Bitcoin public chain. Taproot Assets reduces the demand for main chain space by representing and operating assets off-chain. Additionally, Taproot Assets enhances asset programmability and privacy by introducing asset scripts that can be operated off-chain.
The Taproot Assets Protocol primarily relies on the following key technologies:
- Merkle-Sum Sparse Merkle Trees (MS-SMTs): This data structure is used to effectively prove the existence, non-existence, and division and merging of assets. It supports proving the total amount of specific assets, ensuring that assets are not created or destroyed unnecessarily during the transfer process.
- Taproot Asset Trees: This is a structure embedded in the Taproot script tree to carry assets. Each asset is represented by a series of MS-SMTs, with each asset ID corresponding to an MS-SMT.
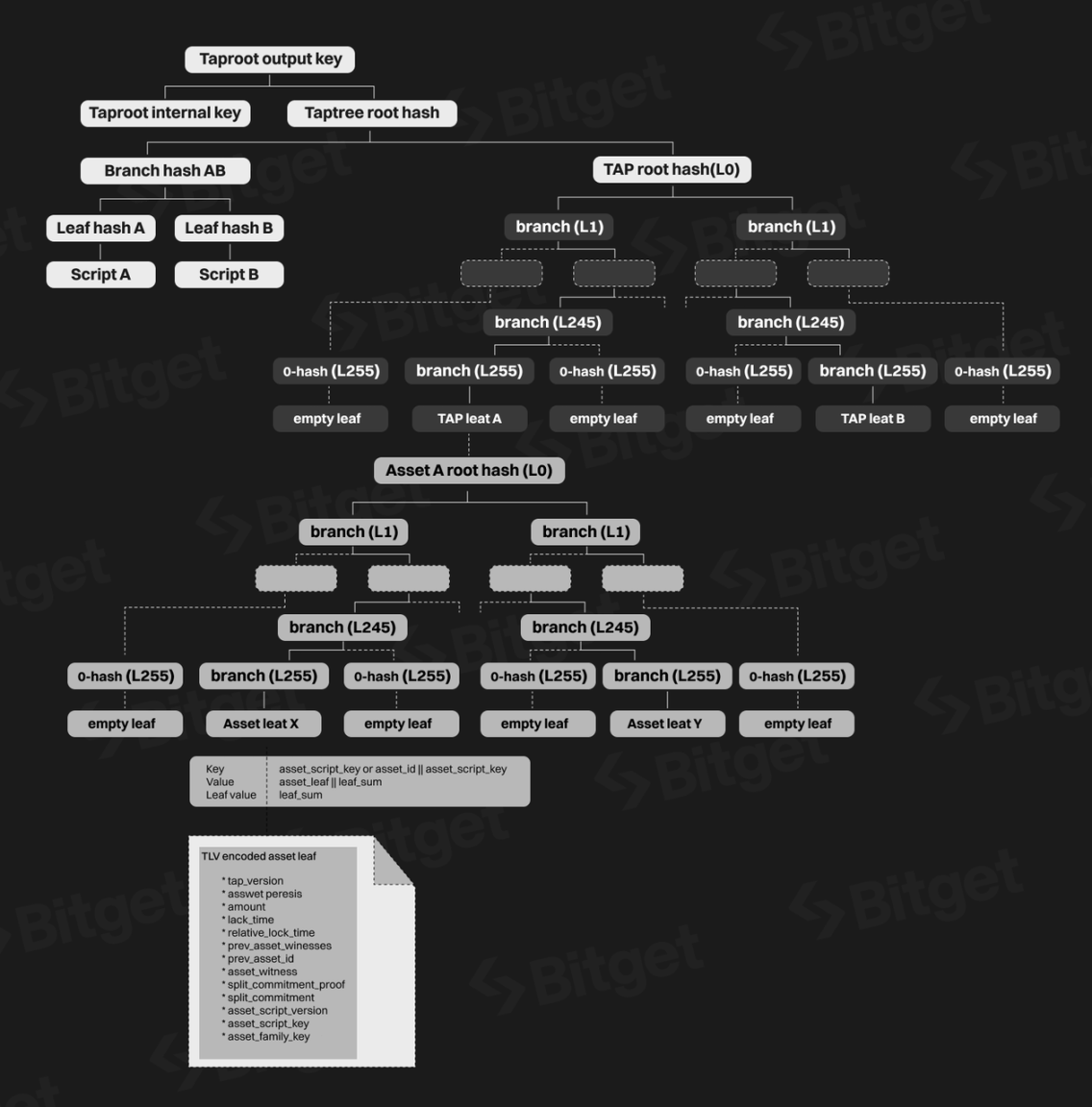
MS-SMTs Structure Diagram (Source: Taproot Assets on Lightning)
Introduction to the Current Status of the Taproot Assets Protocol
Asset Situation
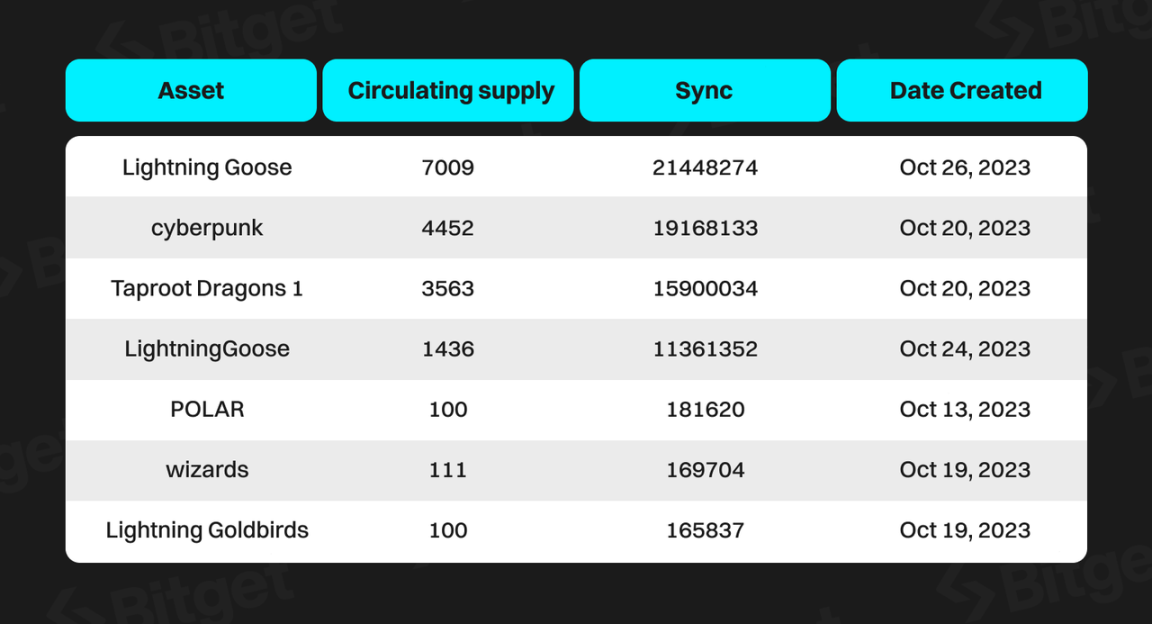
Ecological Situation
Currently, the Taproot Assets ecosystem is still in its early stages, with few mature projects, assets, and participants, and no mature trading market. The most well-known project is Nostr Assets.
Nostr Assets has created two types of tokens, Trick and Treat. Nostr Assets has airdropped Taproot assets Trick and Treat to over 7900 Nostr addresses, with approximately 10,000 tokens per address. The cost is almost zero, and the profit can be over 1000 times.
Characteristics of NostrAssets Products:
- No gas fee: Transfer Taproot Assets through the NostrAsset website client or other decentralized social messaging applications on Nostr without gas fees.
- Fair sale: Nostr Assets has introduced the function of fair sale of Taproot Assets, similar to deploying contract tokens on Ethereum, setting token names, symbols, total supply, progress, avatars, and other social information.
Unique Advantages of the Taproot Assets Protocol
- Good adaptability: Taproot Assets is fully based on UTXO, which means it can integrate well with Bitcoin's native technologies such as RGB, Lightning, and DLC.
- Low transaction costs: Taproot Assets are directly integrated with the Lightning Network. This means users can use Taproot to initiate Lightning channels and deposit BTC and Taproot assets into Lightning channels in a single Bitcoin transaction.
- Minimal on-chain resource usage: Taproot Assets use Taproot to create assets on Bitcoin. Data is stored in the main root tree, and token metadata is stored by default on the creator's device or optionally in a off-chain data repository/indexer called "Universe." This means the on-chain footprint of large transactions is minimal.
- More efficient: Users can mint three new categories of three different assets at once, pay a single mining fee, and then sell all newly minted assets to buyers using different Taproot assets through a single vPSBT, without paying for each asset transfer.
Potential Issues with the Taproot Assets Protocol
- High centralization: Taproot Assets rely on third-party storage indexers. If there are no storage indexers, these tokens will be permanently lost. Therefore, users either need to run a BTC full node and Taproot Assets client themselves, or rely entirely on a centralized server to transact Taproot Assets tokens. This makes this solution the most centralized among BTC token protocols.
- Unfair chip allocation: Users cannot directly send transactions to mint tokens on the BTC mainnet. Instead, there is a project address that issues (or registers) all tokens at once, and then the project transfers them to the Lightning Network. Allocation relies on institutions, and institutions are needed for endorsement and operation, with project creators controlling the entire asset issuance process.
3.2 Scaling Solutions
Bitcoin scaling solutions can be divided into on-chain scaling and off-chain scaling. On-chain scaling aims to directly increase transaction processing capacity by changing block size or data structure, such as the fork of BCH and BSV from BTC. Off-chain scaling involves establishing a second-layer transaction network outside the Bitcoin main chain, such as the Lightning Network and sidechain technology.
Due to the technical difficulty and the resulting consensus split in the BTC community, off-chain scaling solutions have become mainstream. At present, off-chain scaling solutions mainly include the following categories:
- State channels: Such as the Lightning Network, which can transfer some high-frequency transactions off-chain.
- Sidechain technology: Such as Liquid, Stacks, and Rootstock.
- Others: Utilizing Rollup technology and fraud proofs of BitVM.
3.2.1 Lightning Network
What is the Lightning Network
The Bitcoin Lightning Network is a second-layer protocol designed to improve the speed and efficiency of Bitcoin transactions. It achieves this by creating an additional transaction layer on top of the Bitcoin blockchain. The concept of the Bitcoin Lightning Network was initially proposed in 2015. This concept was detailed by Joseph Poon and Thaddeus Dryja in their whitepaper. The actual deployment of the Bitcoin Lightning Network occurred in 2018 when Lightning Labs announced the initial release of LND (Lightning Network Daemon), marking the official launch of the Lightning Network.
Why the Lightning Network Emerged
The emergence of the Bitcoin Lightning Network is due to the significant increase in Bitcoin transactions as Bitcoin becomes more popular. However, due to Bitcoin's design of producing a block approximately every 10 minutes and the limited block size, the Bitcoin network began to face congestion issues, leading to longer transaction confirmation times and increased transaction fees. To address this problem, in 2015, Joseph Poon and Thaddeus Dryja published a whitepaper, introducing the concept of the Lightning Network for the first time.
This proposal aimed to speed up transaction times and reduce costs by establishing a second-layer network on top of Bitcoin. As a second-layer protocol, the Lightning Network allows users to establish payment channels outside the Bitcoin blockchain for transactions. Transaction information is only recorded on the main blockchain when channels are opened and closed. This allows a large number of transactions to occur off-chain, significantly reducing the burden on the blockchain.
Current Status of the Lightning Network
As of November 22, 2023, according to Glassnode data, the current Bitcoin capacity of the Lightning Network is approximately 5341.2 BTC, equivalent to approximately $197,623,444.
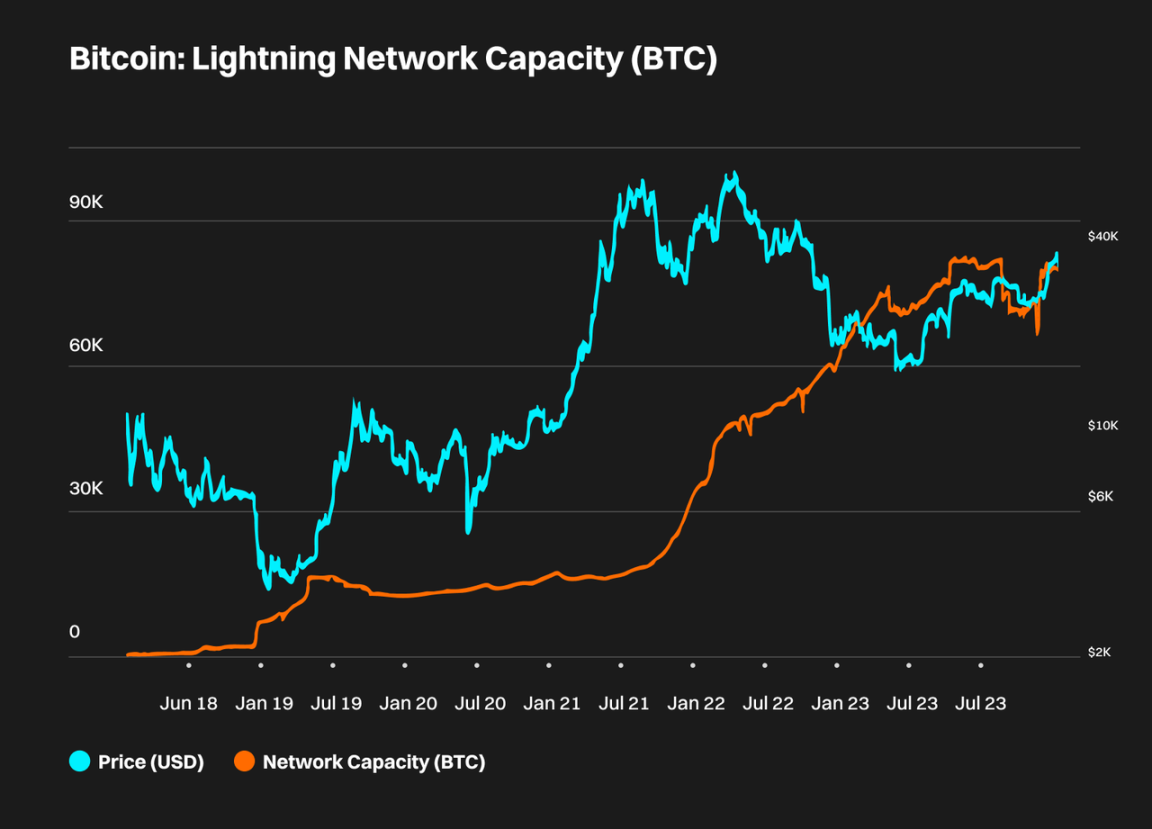
Lightning Network Capacity (Data Source: Glassnode)
The current number of channels in the Bitcoin Lightning Network is 62,385, mainly concentrated in the United States, Canada, and Germany.
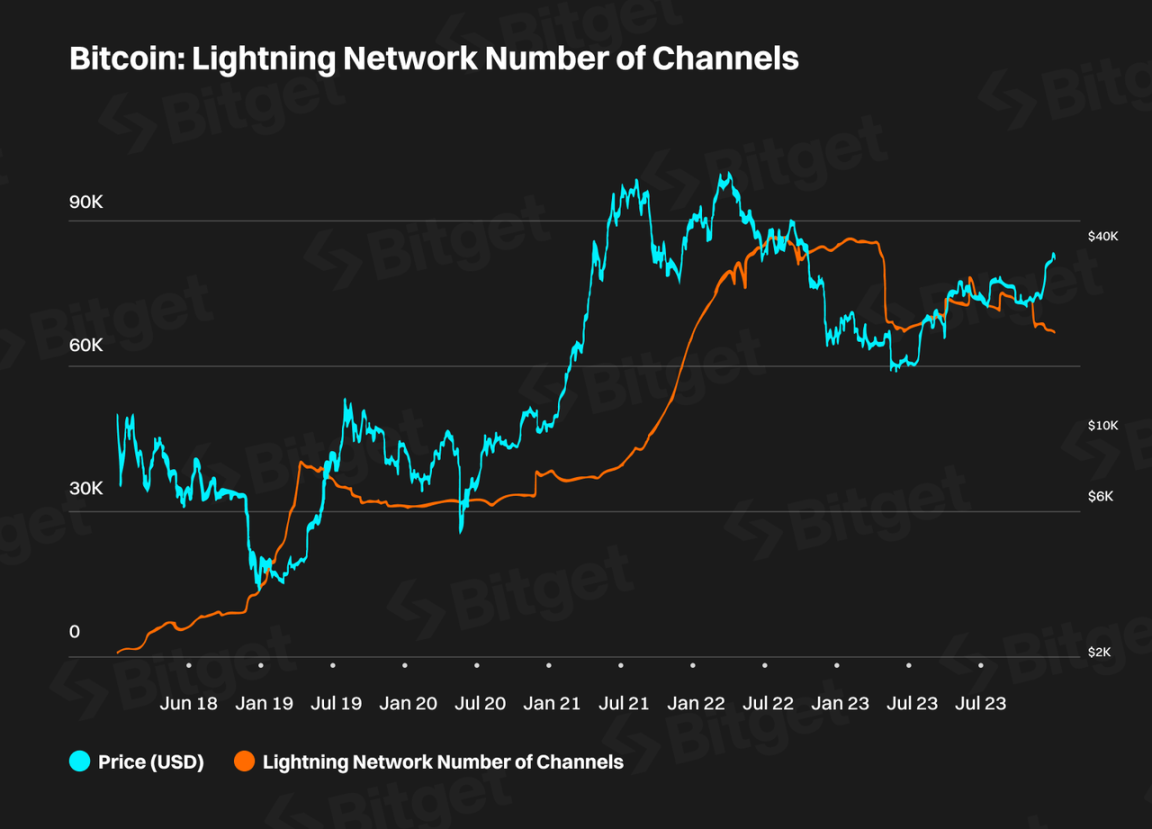
The number of Bitcoin Lightning Network nodes (Data Source: Glassnode)
Unique Advantages of the Lightning Network
The main advantages of the Bitcoin Lightning Network are as follows:
- Fast transactions: The Lightning Network allows for almost instant transaction processing, a significant improvement over transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain, which typically require confirmation. If a transaction occurs within an established payment channel, the time required to complete the payment is usually between 1-5 seconds.
- Low cost: Since transactions occur off the Bitcoin main blockchain, this significantly reduces transaction fees, especially for small transactions.
- Reduced main chain burden: By processing transactions off the blockchain, the Lightning Network reduces the burden on the Bitcoin main chain, helping to reduce network congestion and delays.
- Support for micropayments: The Lightning Network is particularly suitable for processing small transactions, providing possibilities for micropayments in the digital economy.
Potential Issues with the Lightning Network
Potential issues with the Bitcoin Lightning Network include:
- Complexity: Establishing and maintaining channels on the Lightning Network is more complex than simple Bitcoin transactions. Users need to understand how to open, manage, and close channels, increasing the barrier to entry.
- Funds locking: In the Lightning Network, participants need to lock a certain amount of Bitcoin in channels to support transactions. This means that funds cannot be used for other purposes for a period of time.
- Routing challenges: In the Lightning Network, payments need to find a valid path within the network of channels between participants. This process needs to consider multiple factors, such as the capacity and fees of each channel. If the network cannot find a path effectively, transactions may fail, or transaction costs may increase.
3.2.2 Rootstock
What is Rootstock?
Rootstock is a smart contract sidechain built on Bitcoin. RVM (Rootstock Virtual Machine) is a forked version based on the Ethereum Virtual Machine, compatible with Ethereum smart contracts and tools for deployment and interaction. RBTC is the native currency of Rootstock, used to pay for gas fees required for transaction execution. RBTC is pegged 1:1 to BTC, and the two-way peg protocol Powpeg allows BTC to be transferred between the Bitcoin and Rootstock blockchains. Rootstock shares security with Bitcoin, using merged mining and cryptographic and multi-signature technologies to ensure transaction security.
Rootstock was developed by Argentinian RSK Labs, which received seed funding from Coinbase Ventures and other investors in 2016. In 2018, RSK Labs announced a merger with IOV Labs, forming the new company IOV Labs. Following the merger, IOV Labs raised $35 million from Bitmain, Coinbase Ventures, Science Blockchain, and other investors. In 2019, they raised an additional $20 million in private funding.
Why Rootstock Emerged
The BTC network is currently the most secure network in the blockchain space. However, due to Bitcoin's initial design as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system, the Bitcoin network does not have smart contract functionality. The goal of Rootstock's creation is to provide a way to enhance Bitcoin's functionality without splitting the BTC community consensus, thus bringing more decentralized applications to Bitcoin.
Current Status of Rootstock
Rootstock currently has a market value of $108 million, reaching a peak of $300 million, and a recent low of $39 million in the past two years. According to official data, cross-chain locked BTC on Rootstock amounts to 3254 BTC (worth $120 million). According to Defillma data, the overall TVL (Total Value Locked) in the ecosystem is $106 million, reaching a peak of $230 million. The following are a few relatively well-known projects on Rootstock:
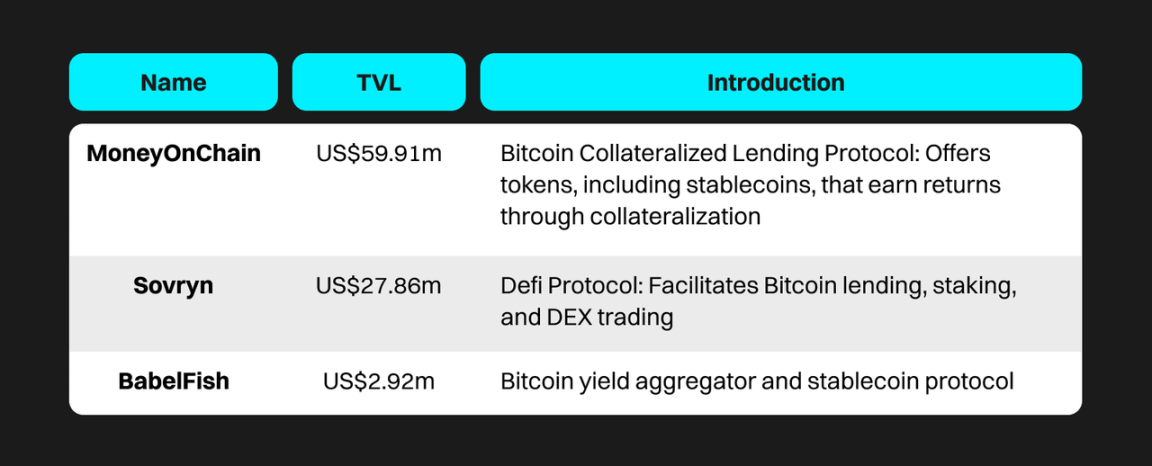
Data Source: https://defillama.com/chain/Rootstock, as of November 16th
Unique Advantages of Rootstock
- Merged mining: Using DECOR+ (a unique variant of the Nakamoto consensus), it can merge mine with Bitcoin or any other blockchain with shared Bitcoin block format and proof of work, allowing miners to receive rewards in both RSK and Bitcoin simultaneously.
- BTC two-way peg: RBTC, as the native currency of Rootstock, is used to pay gas fees and is pegged 1:1 to Bitcoin. The two-way peg protocol Powpeg allows BTC to be transferred between the Bitcoin and Rootstock blockchains, providing convenience for introducing BTC assets to Rootstock.
- EVM compatibility: RVM (Rootstock Virtual Machine) is a forked version based on the Ethereum Virtual Machine, compatible with Ethereum smart contracts and tools for deployment and interaction.
Potential Issues with Rootstock
- Insufficient performance scalability: Rootstock's scalability is up to 100 transactions per second, 20 times that of the Bitcoin network. However, compared to current high-performance L1 and L2 blockchains, it is still insufficient to support high-concurrency applications.
- Centralization in PowPeg: The notaries protecting locked funds in Rootstock are members of the PowPeg alliance, composed of well-known blockchain companies with high security standards. This third-party organization is responsible for locking and unlocking BTC funds, posing centralization issues.
- Insufficient value capture and slow ecosystem growth: With BTC's current market value reaching $700 billion, the overall Rootstock ecosystem captures only around $100 million worth of BTC assets, and the overall Defi projects in the ecosystem are less than 20, with slow TVL growth that has not exceeded the peak at the end of 2021.
3.2.3 Stacks
What is Stacks?
Stacks is a Bitcoin Layer2 project designed to enhance the functionality and scalability of Bitcoin. Developers can build smart contracts and DApps on top of the secure foundation of Bitcoin. Stacks was born in 2013 and has high recognition in the Bitcoin core community.
It is worth noting that since Stacks has not completed the Nakamoto upgrade, it does not currently rely entirely on the security of the Bitcoin chain. Instead, it is linked to the Bitcoin chain through the Proof of Transfer mechanism. Therefore, there is controversy over whether it is a Layer2, with some calling it Layer1.5. Once the Nakamoto upgrade is completed as originally planned, Stacks can become a more complete Layer2.
Why Stacks Emerged
After the early days of blockchain, people gradually developed more financial tool and other application needs for blockchain. At this point, the limitations of Bitcoin began to emerge, particularly in its lack of support for complex smart contracts and DApps. Stacks emerged to address this issue by building an additional layer that interoperates with the Bitcoin chain to enable a wider range of applications while maintaining the high security of the Bitcoin network.
Current Status of Stacks
The ecosystem development of Stacks has been very slow. According to DefiLlama's data, the TVL of Stacks is only about $20 million, with a historical peak TVL of only $45 million, and a lack of well-known projects within the ecosystem. The following are a few relatively well-known projects on Stacks:
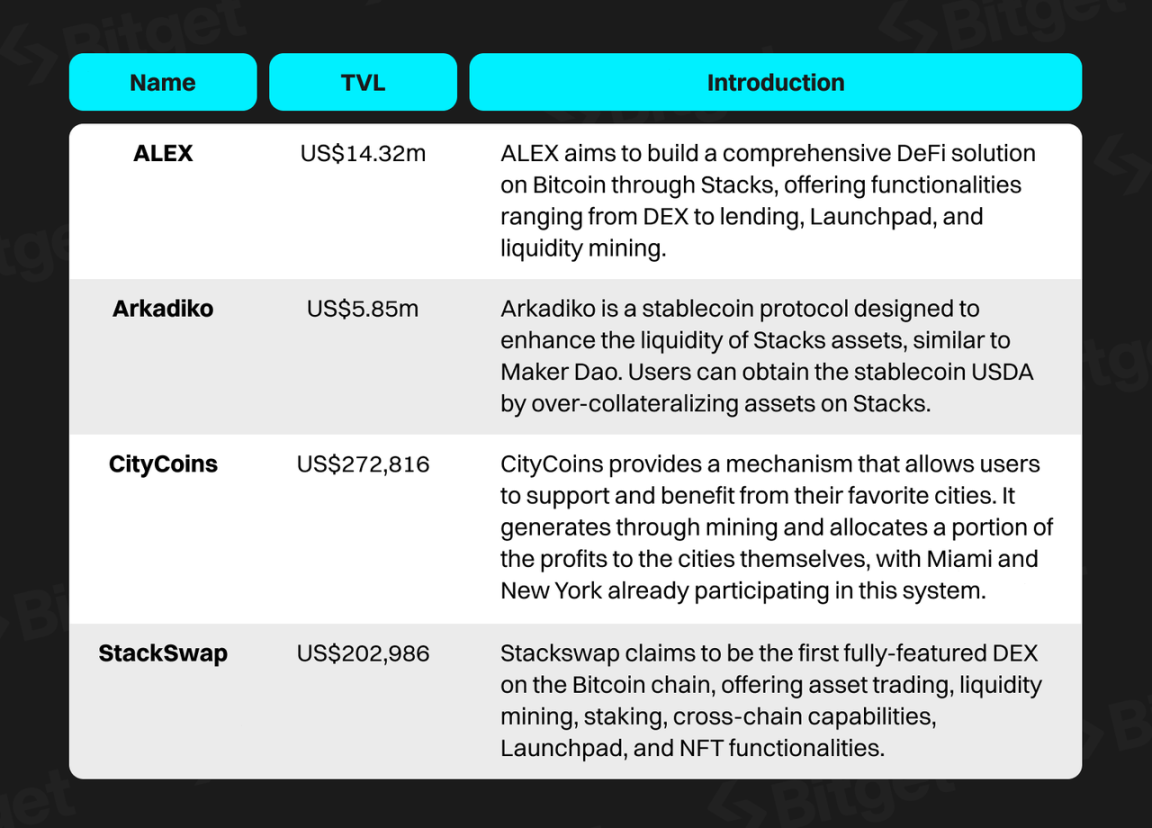
Data Source: https://defillama.com/chain/Stacks, as of November 16th
Unique Advantages of Stacks
- Main speculation target for Bitcoin Layer 2: STX of Stacks is currently the main speculation target in the market for Bitcoin Layer 2. When the Bitcoin ecosystem fully erupts, there are not many targets available in the secondary market for retail investors to speculate on.
- Compliance narrative: In Q3 2019, Stacks became the first public offering project to receive regulatory approval from the U.S. SEC, giving it a natural advantage in compliance narrative and making it less susceptible to black swan events and FUD similar to some public chain tokens being considered securities.
- Nakamoto upgrade: Expected to be launched in the first quarter of 2024, the expected upgrades include: sharing network security with BTC, settling transactions on the Bitcoin network, significantly increasing block speed (reducing from 10 minutes to 4-5 seconds), introducing the Bitcoin-pegged asset sBTC to enable smart contracts to run faster and cheaper, and supporting multiple languages such as Solidity and EVM in subnets, similar to Ethereum, facilitating the migration of existing EVM DeFi protocols.
Potential Issues with Stacks
- Technical challenges: Stacks' technical development is relatively difficult, and its Clarity language is relatively niche, leading to difficulty in increasing developer activity (but this may improve after the Nakamoto upgrade).
- Slow growth in developers and users: Stacks has been relatively slow in attracting developers and users.
- Marketing and social media operation capabilities, market recognition need improvement: Despite its unique technical advantages, Stacks clearly lacks commercial capabilities and operational capabilities to capture market attention.
3.2.4 RGB Protocol
What is the RGB Protocol
The RGB protocol, developed by the LNP/BP Standards Association, is a smart contract system built on Bitcoin and the Lightning Network. The RGB protocol is an innovative attempt in the Bitcoin ecosystem to build more complex applications and functionality without sacrificing the core features of Bitcoin, such as security and decentralization.
Why RGB Protocol Emerged
Due to the fact that Bitcoin's design itself is not Turing complete, the RGB protocol proposes to run scalable, file-based, and private smart contracts on UTXO blockchains (such as Bitcoin) while maintaining the security and decentralization of Bitcoin. Through the RGB protocol, developers can execute various complex functions such as token issuance, NFT minting, DeFi, and more, continuously stimulating innovation on Bitcoin while ensuring its security.
Current Status of the RGB Protocol
In April 2023, the LNP/BP Association announced the release of RGB v0.10, pushing RGB into the phase of a system ready for commercial use. RGB may bring fully smart contract-supported functionality to the Lightning Network, but further development will require continuous exploration by various projects.
3.2.5 BitVM
What is BitVM
BitVM is a computing paradigm that implements Turing-complete smart contracts on the Bitcoin network. Its core idea is to verify the results of computations on Bitcoin rather than directly executing them, similar to Optimistic Rollups. In this system, a prover claims that a certain function has a specific output for a specific input. If this claim is false, the verifier can provide a succinct fraud proof and penalize the prover. Using this mechanism, any computable function can be verified on Bitcoin.
Why BitVM Emerged
BitVM primarily aims to address the need for more complex and Turing-complete smart contracts on the Bitcoin network. It extends the functionality of Bitcoin, allowing users to execute more complex computations and smart contracts while maintaining the core features of the Bitcoin network. Unlike the RGB protocol, BitVM emphasizes off-chain computation and fraud protection to ensure the integrity of contract execution and transactions.
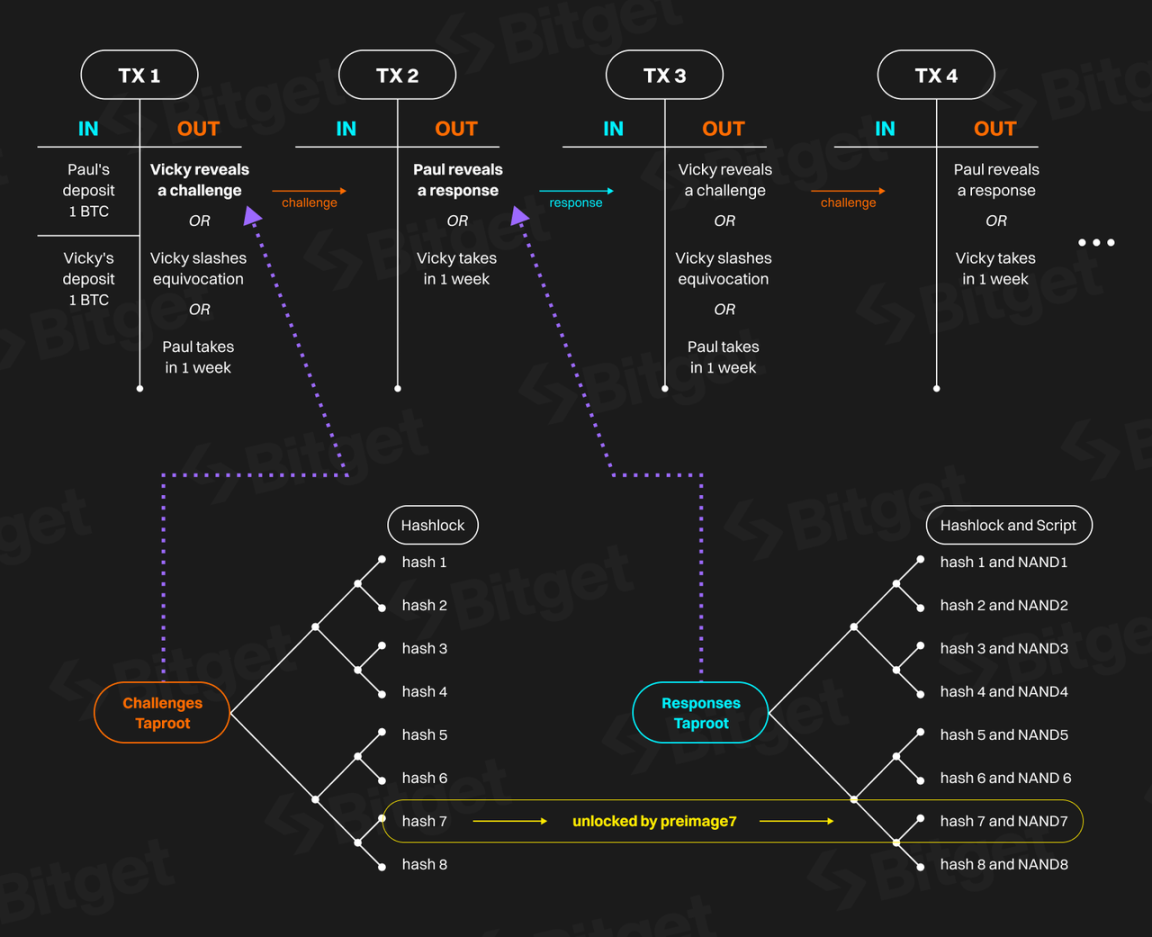
Execution of multi-round queries and responses to pre-signed transaction sequences (Source: BitVM Whitepaper)
Current Status of BitVM
It is currently in the whitepaper stage.
2. Which Sectors in the Bitcoin Ecosystem Have Strong Wealth Effects
1. Ordinals Protocol's BRC20
1.1 Huge Wealth Effect of BRC-20
According to GeniiData, as of December 4th, there are already 56,092 different tokens using the BRC20 standard in the market. The market size of BRC20 tokens has now exceeded $4 billion, compared to $100 million in March of this year, an increase of over 40 times.
Currently, the top BRC20 token $ORDI has a market value of up to $902 million, with a growth of approximately 1178% in the past three months since September, creating a remarkable wealth effect. Based on market value and growth rankings, BRC20 assets with strong wealth effects typically have the following characteristics:
- Tokens with a viral name: Most assets are related to Bitcoin and meme culture, such as $ORDI and $SATS, or named after animals, such as $RATS, continuing the trend of the 21-year meme craze (like DOGE in the past).
- Originality: These assets are not simple copies of other memes, but rather original IPs with unique characteristics.
- Community strength: These projects have strong community support, clear vision, and promotion plans. The early holdings are relatively dispersed, and participants in the community can effectively drive the development of the project.
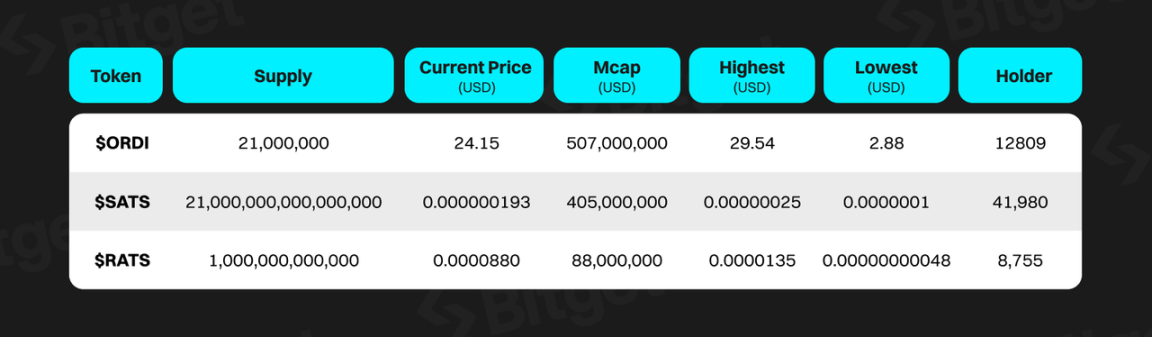
(Source: Summary from aggregated platforms such as coinmarketcap, data as of 2023/11/18)
In addition to the novel issuance of assets and original naming, the rapid development of BRC20 assets is mainly driven by multiple factors such as fund consensus, strong narratives, and other external forces.
1.2 Reasons for Strong Wealth Effects
Fund Consensus
Funding Consensus of Inscribers: Taking SATS as an example, SATS has a total supply of 21 trillion, which is 100 million times that of Bitcoin. The maximum minting amount per minting is 100 million, which means it would take 21 million mintings to complete the entire minting process. The estimated cost of gas fees for minting out 100% is roughly as high as $15 million. Therefore, at the initial launch, many users did not believe that this BRC-20 token would be fully minted. However, on September 24th, the minting progress of SATS reached 100%, with a total of 21,107,258 mintings, 36,061 holders, and a minting duration of 6 months since March 9, 2023, indicating strong funding and consensus in participating in this token.
Increasing Miner Income: The launch of the Ordinals protocol has significantly increased Bitcoin miners' transaction fee income over the past three months. On-chain transaction fees as a percentage gradually increased from 1.7% in August to a peak of 19.57% on November 10th, creating substantial additional income for miners. This has further strengthened the support of the large group of miners with substantial funds for BRC20 and the Bitcoin ecosystem.
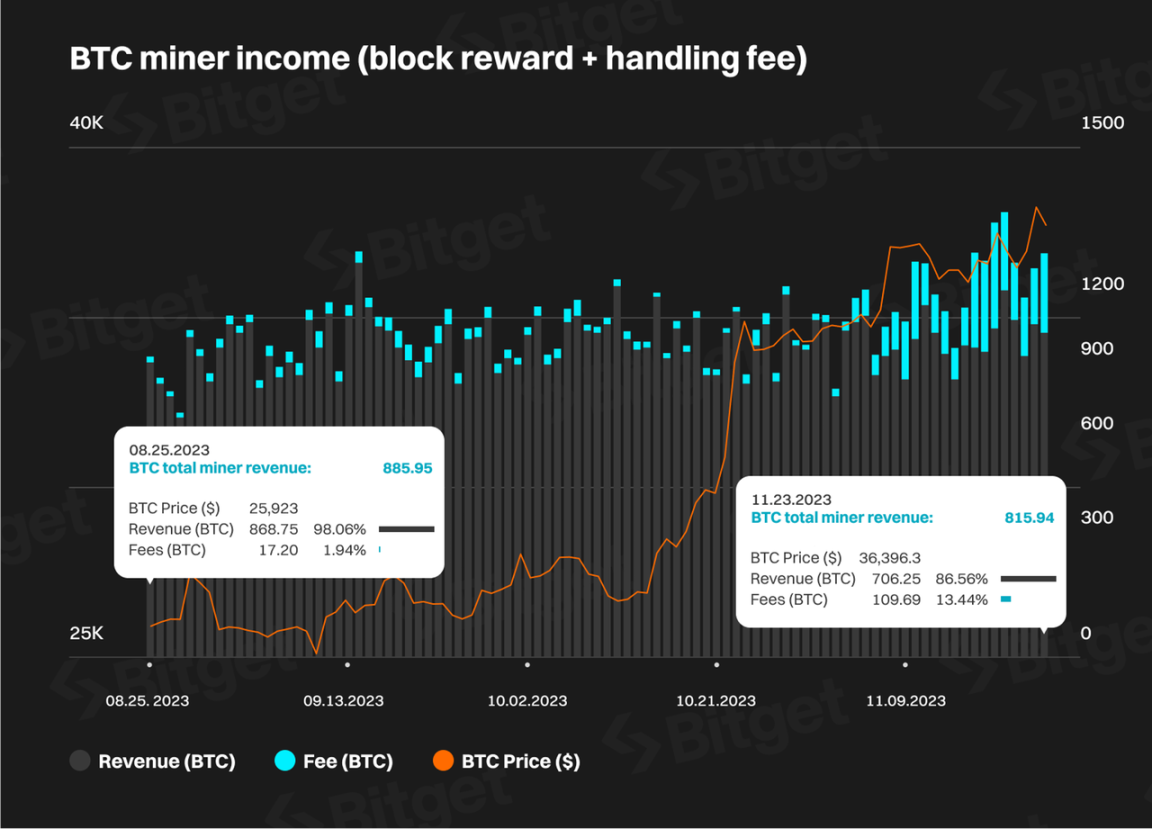
Data Source: oklink
Strong Narrative
- Fair Distribution: After all BRC20 tokens are generated, all users who own BTC only need to pay gas fees to mint, allowing ordinary users to participate fairly in the "primary market." This fairness gives BRC20 tokens a strong consensus at the outset, which will be more helpful for subsequent price increases.
- BRC20 Name Benchmarking ERC20: The naming of BRC20 is inspired by ERC20 on Ethereum, evoking memories of the wealth creation myth of ICOs when ERC20 was first introduced. Therefore, after the launch of BRC20, funds and communities used this narrative for promotion, making it easier for more people to understand and be willing to learn about it.
External Driving Forces
- KOL Influence and Community Consensus: The Bitcoin Inscribers community began promoting on March 10, 2023, and in the following months, due to the wealth effect of ORDI, many KOLs also participated in promotion, further attracting the attention of retail investors and early investors. In addition, the low entry barrier for BRC20 participation has led to a large number of users outside the circle participating under the leadership of KOLs. Since BRC20 tokens had a very low initial market value and were prone to rapid increases, the continuous wealth effect has led many users to hold onto their tokens, further perpetuating the wealth effect.
- Support from Centralized Exchanges: The listing of BRC-20 tokens on mainstream centralized exchanges such as Bitget, Binance, OKX, and Gate has greatly improved the liquidity of BRC-20 tokens. For top BRC-20 assets such as ORDI and SATS, listing on centralized exchanges has increased their exposure and attracted more trading users. Users also tend to prefer assets with strong liquidity.
1.3 Will the Wealth Effect Continue
The wealth effect of BRC20 tokens needs to be viewed in two categories: the first category is the top BRC20 token $ORDI, and the second category is the mid-to-tail BRC20 tokens.
For the first category, $ORDI, there are two valuation estimation logics:
The first logic compares it to SHIB, a top meme coin on ETH: As one of the most prominent meme coins on BTC, it is very likely to experience a significant increase. $ORDI currently has a market value of about $400 million. If compared to the $4.9 billion market value of SHIB, there is a potential for an increase of over 12 times.
The second logic views it as a top project in a niche: Even if it is not compared to the top meme coins on ETH, but rather seen as a top coin in a certain niche, based on historical experience, such new narrative projects typically rank in the top 50 in terms of market capitalization during a bull market. The 50th project in terms of market capitalization is RNDR, with a market capitalization of $1.26 billion. Therefore, with a current market capitalization of $400 million, $ORDI may still have 3-4 times the potential for growth.
For the second category of mid-to-tail BRC20 tokens, there may be a wealth effect in the short term due to minting, but as funds leave and community consensus weakens, most mid-to-tail BRC20 tokens may become worthless, so it is important to buy and sell quickly. When the hotspots shift, a rapid decline in the BRC-20 sector over a certain period may be difficult to avoid, and a liquidity crisis and value depreciation of mid-to-tail assets are likely to occur.
1.4 User Participation Opportunities
As a user, participation opportunities in BRC20 mainly fall into two categories: minting in the primary market and buying and selling in the secondary market.
Primary Minting:
1) Participating in the primary market minting of BRC-20 assets, the main way to participate is to use non-custodial wallets that support Bitcoin and Inscribers minting. For example, through the website UniSat (https://unisat.io), users can directly choose the token name and quantity they want to MINT and use the Inscribe function to mint. When minting, users can first check the gas level at (https://mempool.space/zh/) and choose the appropriate gas for payment. During the FOMO period, consider selecting a high priority gas fee to increase the success rate of minting.
2) Participating in the primary market minting of BRC-20 assets, the main source of information comes from Twitter project parties and the Ordinals BRC-20 trading market. Individual investors need to conduct thorough research on the project parties and evaluate the artistic value of their NFTs, as well as the potential community preferences, to decide whether to participate in the new token offering.
Secondary Market Trading:
1) BRC20 assets such as $ORDI, $SATS, and $RATS can be directly traded on centralized exchanges such as Bitget. BRC-20 assets on centralized exchanges have much better liquidity than the OTC market and do not require high gas fees on the BTC chain or long on-chain transaction processing times.
2) For BRC20 tokens already in circulation in the secondary market, pay attention to Inscribers assets with "strong funding consensus, high chip dispersion, and high social media discussion," just like early SATS and RATS.
According to Atomical Market data, as of November 20th, there are a total of 17 different tokens using the ARC20 standard, with a total market value of over $40 million. ATOM, as the first token issued based on the ARC20 protocol, is currently the most popular in this category. Each ATOM currently requires 6000 SATS. If we exclude the gas and computing power consumption during minting, the increase is 6000 times. If the minting cost is estimated at $10, there is also an increase of approximately 250 times.
2.1.2 Reasons for the Strong Wealth Effect of ARC20
1) PoW Mining Gameplay: ARC20 introduces the PoW mining gameplay through the Bitwork algorithm. This fair mining method allows users to relive the feeling of mining BTC with a CPU when it was first introduced, making them feel that this method is more in line with the BTC ecosystem and more decentralized.
2) Developer-Friendly Indexer: ARC20 has encapsulated token issuance and transfer, and many developers use the Python language for indexer development, allowing more developers to participate and provide convenience for the protocol's development.
3) Community Support: Some long-time players in the BTC community strongly support the issuance of coins through computing power. They have written many tutorials on setting up Atomicals nodes. As the inscriber market heats up, related information is spreading more widely, leading to a growing player community.
However, it should be noted that ARC20 is in its early stages, so liquidity and depth are poor. According to Atomical Market data, there are currently only 17 ARC20 tokens, with only about 5,000 users holding ARC20 tokens, and many ARC20 tokens are almost not traded. The leading ARC20 token, ATOM, also experiences extremely volatile price fluctuations due to poor liquidity. Therefore, opportunities and risks coexist in the current stage of ARC20.
2.1.3 Will ARC20 Continue to Have a Wealth Effect
The future wealth effect of ARC20 needs to be observed in two aspects:
First, the progress of the leading project, ATOM. Currently, the total market value of the leading ARC20 token, ATOM, is over $40 million, but the daily trading volume is only about $250,000 (data source: Atomical Market). The lack of depth and liquidity has led to extreme price fluctuations for ATOM. If the trading volume and the number of holders continue to increase, and if ARC20 tokens begin to be listed on mainstream exchanges, there will be significant room for growth and it may be worth considering participation.
Second, the popularity of the Atomicals node deployment solution and the number of available public nodes. Since minting ARC20 tokens requires computing power, and currently only three providers offer public node services, many users fail to mint due to insufficient resources when using public nodes. The popularity of the node deployment solution or the number of available public nodes indirectly reflects the demand for minting by users and is a dimension worth paying attention to.
2.1.4 User Participation Opportunities
Primary Market Minting:
1) Minting through Atomiclas public nodes or the Atomiclas trading platform. According to their official documentation, there are currently three public nodes available. Users can participate through the API according to their documentation, and can also participate in minting through the graphical interface on the Atomical Market platform or SatsX platform.
2) Participating in minting through private Atomiclas nodes. Users can set up Atomiclas nodes using their open-source code and participate in minting through their own nodes. This method has a certain technical threshold, but with proper node configuration, it offers higher stability compared to public nodes.
Secondary Market Speculation:
1) Currently, Atomical Market and SatsX support ARC20 trading. Users can buy and sell corresponding inscribers on these two platforms, using core data such as price changes and trading volume to assist in trading.
2) In addition to trading platforms, users can also choose a peer-to-peer (P2P) approach and conduct "face-to-face" transactions with community members, but this method carries certain reputation risks.
2.2 Realm
Realm is a protocol that uses prefixes to identify identities based on the Atomicals protocol. In addition to serving as traditional domain name identities, Realm can also be used to manage subdomains using its prefix.
For example, if the Realm protocol is used to register "bitget" as the main domain name, the holders of subdomains under the main domain name, such as bitget.aaa/bitget.bbb/bitget.ccc, etc., need to pay a certain registration fee to the holder of the main domain name "bitget." This design makes the applications around the main domain name very diverse, such as for brand building or DAO governance.
2.2.1 Wealth Effect of Realm
As Realm is still in its early stages, the total market trading volume is only 1 BTC (data source: Atomical Market), and there is currently no significant wealth effect. However, its innovative gameplay and economic model design have sparked widespread discussion. Against the backdrop of decentralized identity (DID) gradually becoming the mainstream social identifier, Realm may also develop products similar to ENS on the BTC network. Before that, some high-quality and unclaimed Realms may hide good opportunities.
2.2.2 Will Realm Continue to Have a Wealth Effect
Since the release of the Atomicals protocol over two months ago, the practical application of Realm has not yet been implemented, leading to a high level of uncertainty. The future wealth effect of Realm mainly depends on two points:
1) The widespread adoption of the Atomicals protocol.
2) The increasing importance of identity identification around the BTC ecosystem.
2.3 How Users Can Participate
Similar to participating in ARC20, participation mainly falls into two categories: participating in primary market minting, which requires the Atomicals node client, and participating in secondary market trading, buying and selling using BTC on the Atomical Market and SatsX platforms.
- PIPE Protocol's PIPE
$PIPE is the first token of the PIPE Protocol and is also the top token.
3.1 Wealth Effect of PIPE
As $PIPE is the first token issued by Beny based on the PIPE Protocol, according to community data, it has seen an increase of approximately 250 times, excluding the cost of about $4 during minting.
3.2 Reasons for the Strong Wealth Effect of PIPE
The wealth effect of PIPE comes from the community's recognition of Beny. Beny is very active among BTC developers and has composed multiple protocols to form the TRAC System. The early-issued BRC20 token $TRAC has also been hyped by the community, with a current market value of $62.7 million and an increase of over a thousand times (data source: OKX Marketplace). Therefore, $PIPE was highly sought after by many users as soon as it was issued.
3.3 Will PIPE Continue to Have a Wealth Effect
$PIPE is still worth paying attention to for several reasons:
1) The PIPE Protocol is developed based on Casey's Runes protocol, and the current technical solution has great potential for the issuance of assets on the BTC network.
2) The governance token $TAP of the PIPE Protocol has not yet started circulating, and holding $PIPE may have a certain airdrop expectation.
3) The infrastructure of the PIPE Protocol is still under development, and as the infrastructure gradually improves, it will also benefit $PIPE.
3.4 How Users Can Participate in PIPE
Similar to participating in BRC20, participation mainly falls into two categories: participating in primary market minting, spending a certain amount of BTC as gas to mint, and participating in secondary market trading, buying and selling on the SatsX platform using BTC.
4. Tokens in the Bitcoin Scaling Sector
Bitcoin scaling has always been one of the mainstream narratives in the Bitcoin ecosystem. Therefore, when there is a significant technological innovation or performance breakthrough that becomes a hot topic in the market, tokens in this sector will experience significant increases. Two representative tokens worth paying attention to in this sector are: Rootstock (RIF) and Stacks (STX).
4.1 Rootstock (RIF)
The RIF token has mainly followed the narrative of BTC in its history. It currently has a market value of $100 million, and at its peak in late 2021, it reached $300 million. As a scaling sector of BTC, it currently ranks second in market value among issued projects, with a relatively small market value and characteristics that make it easy to speculate on.
Constrained by its insufficient performance expansion and slow ecosystem growth, the future wealth effect of RIF mainly depends on two points:
- Further breakthroughs in performance
- Significant growth in ecosystem assets; this will directly benefit the price of RIF
If there are no significant advancements in performance or the ecosystem, RIF will continue to be one of the targets in the ecosystem sector and become a supplementary project.
4.2 Stacks (STX)
Here, we need to briefly mention the PoX (Proof of Transfer) consensus algorithm mechanism of Stacks: in Stacks, there are two roles, "miners" and "transaction validators." Transaction validators need to stake STX tokens to mine BTC, while miners need to stake BTC on the Bitcoin main chain to mine STX. It is also because of this mechanism that STX has a higher beta return correlation with the overall market, and only at certain specific times can it briefly show independent market trends, such as the significant increase in value during the recent compliance narrative hype.
If the Nakamoto upgrade scheduled for Q1 next year proceeds as planned, with the security sharing with the BTC network, a significant increase in block speed, and the introduction of sBTC, among other favorable factors, STX may attract attention from the market and capital, ushering in a new wave of speculation.
III. Opportunities and Risks Faced by Various Players in the Current Bitcoin Ecosystem
1. Individual Investors
Opportunities:
- Enjoying basic returns: Participating in asset issuance protocols within the Bitcoin ecosystem indirectly means holding Bitcoin, which has always been the leading asset in the cryptocurrency industry. Therefore, participating in the Bitcoin ecosystem and holding Bitcoin allows investors to enjoy the most basic beta returns in the industry.
- Fair issuance: Currently, the issuance of most assets in the Bitcoin ecosystem is open and fair, providing more opportunities for ordinary users to participate in early-stage projects and have a greater chance of obtaining excess returns.
- Incomplete infrastructure: The Bitcoin ecosystem is currently in a stage of intense competition, and we have seen the emergence of many asset protocols within the Bitcoin ecosystem. Most of these asset protocols can only be accessed through clients in the early stages, without mature trading markets. Therefore, early participants are more likely to capture excess returns.
Similarly, individual investment in the early Bitcoin market may encounter various risks, mainly:
- Lack of understanding of basic Bitcoin knowledge: For example, in Ordinals, users inscribe tokens on UTXOs, and if they are not careful, they may mistakenly use UTXOs with inscribed tokens as gas payments or for other purposes, resulting in the loss of the value of the inscribed tokens on the UTXOs.
- Early-stage ecosystem: Early-stage ecosystems mean opportunities but also hidden crises. For example, fatal vulnerabilities in project protocols leading to asset theft or double spending require investors to be fully aware of the risks of participation.
2. Exchanges
2.1 Listing Related Tokens to Attract New Users and Brand Exposure
Opportunities:
- The listing of popular BRC-20 tokens can attract a large number of BTC chain players to exchanges, and the huge wealth effect can bring higher trading volume and a good reputation to exchanges. The exchanges that were the first to list ORDI and SATS have already enjoyed this dividend.
- The exclusive listing of various new BTC ecosystem protocol assets (such as assets on Atomicals, Runes, PIPE, and Taproot Assets protocols) at the first opportunity can attract specific users' attention to these assets and also attract users who want to participate in such speculation but are limited to trading in centralized secondary markets due to high learning costs.
- There are some low-market-value projects within the Bitcoin Layer2 Stacks ecosystem, such as ALEX and Arkadiko, which have already issued tokens. If Bitcoin Layer2 develops rapidly and attracts vigorous funding, early listing of these low-market-value tokens can seize the opportunity and allow users to gain a huge wealth effect.
Risks:
- Potential technical risks: For exchange technical personnel more familiar with EVM public chains and other mainstream public chains, there are known challenges and unknown risks in integrating new ecosystem assets. For example, UniSat Wallet has suffered double spending attacks, and the rapid development of the Bitcoin ecosystem may expose new problems. If exchanges do not update client code for certain assets in a timely manner, it may lead to issues such as double spending.
- Market-making and low liquidity risks: Currently, in the Bitcoin ecosystem, especially in the trading of inscribed assets, there is a serious liquidity problem in asset trading. The market-making department of exchanges needs to bear significant pressure and risk.
2.2 Cloud Mining Products
Opportunities:
According to a report by Cointelegraph, on November 12, Bitcoin miners received over $44 million in block rewards and transaction fees, reaching a new high for the year. The popularity of BRC-20 and other assets has driven the consumption of gas on the BTC chain, amplifying the profitability of miners. Exchanges offering cloud mining products to provide hash power leasing services and charge a certain fee can achieve a win-win situation with users in the thriving development of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Risks:
Exchanges mainly need to bear the operational and compliance risks of cooperating with mining farms, which requires exchanges to have good due diligence capabilities to find reliable and capable mining farms to collaborate with.
2.3 NFT Market
Opportunities:
Several leading exchanges now have their own non-custodial wallet products or have their own NFT marketplaces, and can list various NFTs within the Bitcoin ecosystem, such as BRC-20 NFTs and Stacks NFTs.
Risks:
The main risk is the inability to profit due to low liquidity and low trading activity. Exchanges' efforts in the still immature BTC ecosystem NFT market may yield little results, leading to losses in certain business lines of the exchanges. However, it cannot be denied that this is a business worth trying.
3. Project Teams
3.1 Asset-based Project Teams:
Asset-based project teams mainly refer to community-based projects that primarily operate by issuing assets in various protocols.
Opportunities:
- For project teams, Taproot Assets is the most complete and user-friendly in terms of service. Users cannot directly send transactions in the BTC mainnet to mint their own tokens. Instead, there is a one-time issuance (or registration) of all tokens by the project team address, which is then distributed on the Lightning Network by the project team. Depending on institutional endorsement and issuance operations, the project creator controls the entire asset issuance process. The project team has a high degree of control over the assets.
- At the same time, these types of assets are different from ERC-20. Bitcoin itself has greater asset value and more users and purchasing power. In addition, except for BRC-20, various protocol assets are relatively scarce, and they are all in the early stages of development, making it undoubtedly a blue ocean market from a competitive perspective.
Risks:
Financial loss risk: Each protocol is currently not mature technically, posing a risk of financial loss. For example, on the night of April 23, a BTC address starting with bc1pw conducted a double spending attack on UniSat's BRC20 Marketplace. Although trading was promptly suspended by UniSat, this risk is not something the project team can repair or avoid.
3.2 Tool-based Project Teams:
Tool-based project teams mainly refer to projects that provide related derivative products and supporting user-friendly products based on protocols. Examples include Bitcoin wallets such as Unisat and Atomic Wallet, inscribed asset trading markets such as Unisat Market and Atomical Market, domain name services like BTCDomain, inscribed token minting service tools like OrdinalsBot, and asset market websites like brc20.com.
Opportunities:
- Low entry barriers: For project teams, the business models of trading markets or Bitcoin wallets and market websites are relatively uniform. Although the profit points are different, they are essentially traffic businesses. The Bitcoin ecosystem is still in a blue ocean market. Currently, apart from Unisat having the potential to become a leader in the BRC-20 asset field, the competitive landscape of various projects has not been determined, making it relatively easy for project teams to enter the market at this time.
- Larger market: Bitcoin itself has greater asset value and more users and purchasing power, indicating larger profit prospects compared to the Ethereum network.
Risks:
Due to the complexity of Bitcoin technology, lack of product technical capabilities or user awareness can lead to financial losses, resulting in public relations and customer complaint risks.
3.3 Protocol-based Project Teams:
Protocol-based project teams mainly refer to various Bitcoin derivative protocols, including but not limited to Ordinals protocol, Atomicals protocol, Taproot protocol, RGB, and other scaling solution protocols.
Opportunities:
Large valuation space: These project teams mainly provide public services, so the products generally lack a clear profit model. However, due to the speculative demand for asset-based projects, as infrastructure serving as public services and entry points for traffic, they have the ability to facilitate user and project transactions on the Bitcoin network. Due to the asset volume of Bitcoin, leading projects can obtain very substantial valuations.
Risks:
High uncertainty: Due to the complexity of Bitcoin technology and the different innovative ideas and focuses of each protocol, combined with uneven product technical capabilities, there is a high development risk for these project teams.
4. Miners
Bitcoin miners play a crucial role in the Bitcoin network, using "proof of work" to have the opportunity to validate transactions and write new transaction information into new blocks on the Bitcoin network, earning Bitcoin block rewards and processing fees.
Opportunities:
Increased miner income: With the thriving Bitcoin ecosystem, especially the high speculative enthusiasm for BRC-20 tokens, there is a need for more information to be recorded on the network, requiring miners to receive more fees. This has led to recent record-high levels of income for Bitcoin miners, mainly due to an increase in transaction fees.
Risk:
High income uncertainty: Miner income is directly related to the activity of BTC ecosystem projects and users. If there is a significant decrease in demand for transactions, miner income will also experience a noticeable decline. This leads to significant fluctuations in miner income, making it difficult to achieve the expected static return on investment.
5. Investment Institutions
For the Bitcoin ecosystem, investment institutions are still in a very early stage of deployment, and some are even in a wait-and-see phase. Representative investment institutions that have relatively early deployments include Digital Currency Group, Rabbit Capital, Foresight Ventures, HashKey, and OKX Ventures.
Opportunities:
- Allocating BTC in the secondary market: Wall Street investment institutions, large listed companies, family funds, etc., can enjoy beta returns from the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem by allocating BTC.
- Investing in primary market BTC ecosystem-related projects: Investment institutions can delve into various directions within the BTC ecosystem, especially investing in infrastructure projects needed in the early stages of the ecosystem, including wallets, trading markets, domain names, market websites, etc., under various Bitcoin protocols.
Risks:
- Difficulty in preemptive investment due to fair issuance methods: Many BTC ecosystem projects, such as BRC20 projects, have fair issuance mechanisms, placing ordinary users and investment institutions on an equal footing. This makes it difficult for investment institutions to preemptively invest based on resources, as no investment institution has been able to participate in primary market subscriptions for leading projects like ORDI, which has a market value of over $500 million from free minting.
- High ecosystem uncertainty: BTC ecosystem projects have not yet had a very successful project that can expand the performance of the Bitcoin network and support its funds. The ecosystem is in a bottleneck period, with significant uncertainty and unclear profit models, making it difficult to invest based on traditional investment concepts, and short-term losses may occur.
IV. Possible Future Trends and Bottlenecks in the Bitcoin Ecosystem
It is difficult to predict whether the Bitcoin ecosystem can maintain its current growth trend, but we can still peek into the changes occurring within the Bitcoin ecosystem through data.
As an important indicator of the Bitcoin ecosystem, UTXO, we have seen a linear increase in the number of Bitcoin UTXOs since the birth of the Ordinals protocol. This indicates that asset issuance protocols represented by Ordinals have made the Bitcoin ecosystem and community more prosperous. The increase in Bitcoin UTXOs to some extent represents the coverage of Bitcoin to more people. As a global cryptocurrency, the more people accept and participate, the stronger the consensus formed. This is the foundation of the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem and a prerequisite for Bitcoin's future higher market value scale.
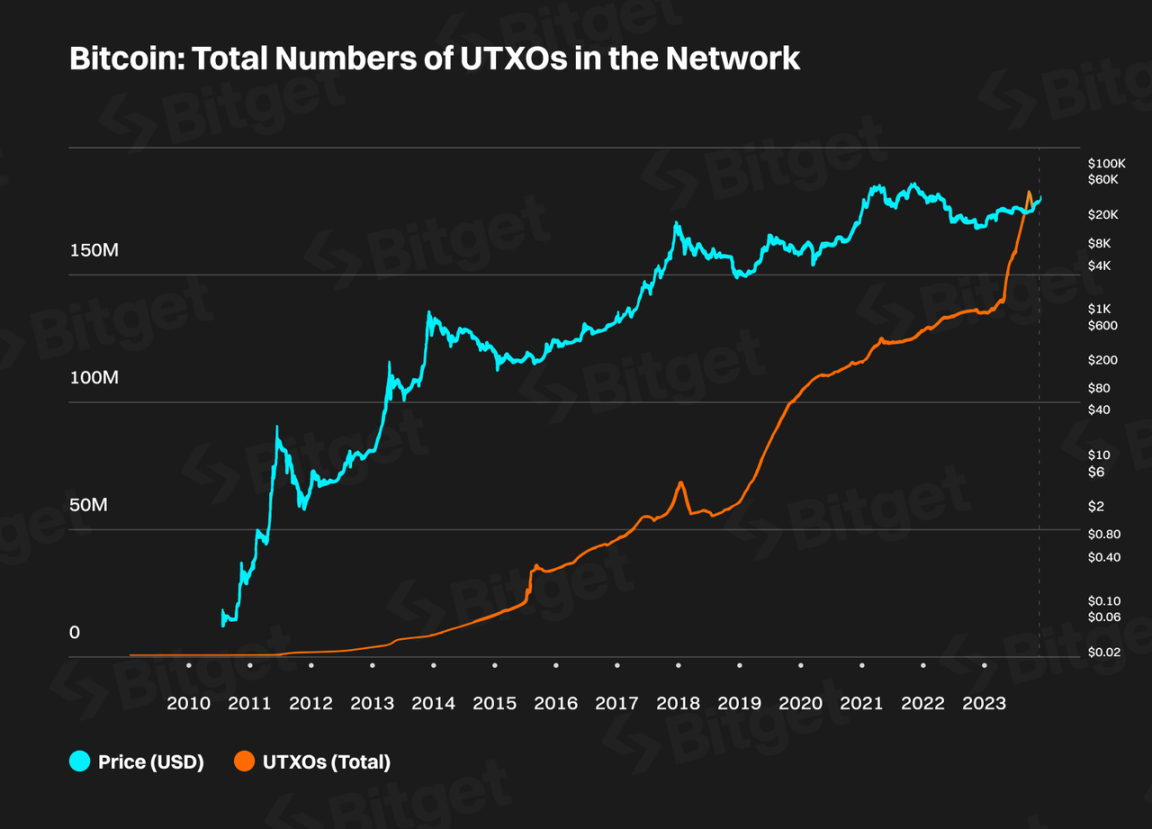
Number of Bitcoin UTXOs compared to Bitcoin price (data source: Glassnode)
However, it is evident that the future of the Bitcoin ecosystem may encounter bottlenecks, mainly due to two reasons: 1) Bitcoin itself has poor scalability, making it difficult for applications to land, and may be stuck in the current stage of insufficient scalability, ultimately affecting the overall development speed and height of the Bitcoin ecosystem; 2) Bitcoin core developers have relatively conservative views, and in fact, some developers oppose or even dislike various asset protocols in the current Bitcoin ecosystem. Therefore, if the coin price falls in the future or innovation stagnates, the ecosystem's development may be mired in a quagmire.
Based on the above possibilities, Bitget Research Institute has made the following 6 predictions regarding the Bitcoin ecosystem:
Prediction 1: If the Bitcoin ecosystem continues to develop, the significant increase in demand for Bitcoin will cause the BTC price to break through the previous high in the next bull market phase, possibly reaching $100,000.
Prediction 2: ORDI, as a leading currency in the Bitcoin ecosystem, will enter the top thirty in terms of circulating market value in the next bull market.
Prediction 3: The future Bitcoin NFT market will experience a growth of over 100 times in size.
Prediction 4: Protocols such as Ordinals, Atomicals, and Taproot Assets will present opportunities for hundredfold returns.
Prediction 5: In the short term, the Bitcoin ecosystem will maintain the status of "one project, one protocol solution," with various Bitcoin protocols continuing to maintain a situation of diverse offerings. In the long term, the Bitcoin ecosystem will introduce a virtual machine and a unified developer compilation environment.
Prediction 6: The Lightning Network will be the biggest technological support to help Bitcoin payments continue to be adopted on a larger scale, and more assets will be issued on it in the future.
V. Conclusion
Entering 2023, the price trend of Bitcoin is positive, rising from $16,500 at the beginning of the year to the current $40,000. With the high probability of the approval of Bitcoin spot ETFs, the quadrennial halving market, and the slowdown of interest rate hikes in the United States, the wealth effect of Bitcoin is highly likely to continue. In addition to the wealth effect of BTC price itself, the overflow of market funds into its ecosystem is very apparent.
The most obvious case is the resurgence of the entire BRC20 track since November, including significant wealth effects created by BRC20 currencies such as ORDI and SATS, which has also driven the development of the entire Bitcoin ecosystem, demonstrating the potential of the bull market engine. The current focus on the Bitcoin ecosystem is on two main aspects: asset issuance protocols, mainly covering Ordinals, Atomicals, Runes, PIPE, Taproots Assets, and scaling solutions, mainly covering tokens in the Bitcoin scaling sector (RIF, STX), Lightning Network, RSK, Stacks, RGB, BitVM.
The main sectors in the Bitcoin ecosystem with significant wealth effects at the current stage are: BRC-20 assets under the Ordinals protocol, ARC-20 and Realm under the Atomicals protocol, PIPE under the PIPE protocol, and tokens in the Bitcoin scaling sector (RIF, STX). This article analyzes the reasons why these assets have wealth effects and introduces ways for investors to participate.
In addition to technological innovation, the prosperity of the Bitcoin ecosystem depends on the participation of various market participants, mainly including individual investors, exchanges, project teams, miners, and investment institutions. Therefore, this article analyzes the opportunities and risks for the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem for the five categories of groups mentioned above, providing reference for investment and business expansion.
Based on the above analysis, this article provides Bitget Research Institute's judgment on the future trends and potential bottlenecks of the Bitcoin ecosystem. Overall, based on the future macro environment and market conditions, the Bitcoin ecosystem has good development prospects. Not only is there a large appreciation space for assets such as BTC, ORDI, and Bitcoin NFT, but there will also be new opportunities for hundredfold returns in the Bitcoin ecosystem, and the Lightning Network will be the biggest technological support to help Bitcoin payments continue to be adopted on a larger scale in the medium to short term.
VI. Reference Tools and Websites
1. Trading Markets
BRC-20 & NFT
Unisat: https://unisat.io/market
OKX Marketplace: https://www.okx.com/web3/marketplace/ordinals/brc20
Magic Eden: https://magiceden.io/ordinals
Ordinals Wallet: https://ordinalswallet.com/collect
Gamma: https://gamma.io/ordinals/marketplace
ARC-20 & NFT
Atomical Market: https://atomicalmarket.com/marketplace/token
SatsX: https://www.satsx.io/marketplace/atomicals/ft/sort?page=1
PIPE & NFT
SatsX: https://satsx.io
2. Minting
BRC-20 & NFT
Unisat: https://unisat.io/inscribe
iDclub: https://idclub.io/brc20
LooksOrdinal: https://looksordinal.com
ARC-20 & NFT
Atomical Market: https://atomicalmarket.com/inscribe
SatsX: https://www.satsx.io/inscribe/atomicals
PIPE & NFT
Inscrib3: https://inspip.com/mint
SatsX: https://satsx.io
ppline: https://mint.ppline.app/
3. Data Tools
BRC-20 & NFT
Ordinals: https://ordinals.com/blocks
Ordinalsbot: https://ordinalsbot.com/explorer
NFT Sniper: https://data.nftsniper.club
Bitpunks: https://bitpunks.io/Explorer/Inscriptions
Genii Data: https://geniidata.com/ordinals/home
CryptoCell Labs (Ordinals Inscription Cost Calculator): https://hub.cryptocell.guru/ordinalsturbo
Dune (Daily Minting Statistics of BRC-20 Tokens): https://dune.com/dgtl_assets/bitcoin-ordinals-analysis
ARC-20 & NFT
Atomical Market: https://atomicalmarket.com/explorer
SatsX: https://www.satsx.io/live-mint/atomicals
Dune: https://dune.com/0xmatsu0x/bitcoin-atomicals-potocol-analytics
Other Data Tools
Mempool (Memory, Transaction Viewer): https://mempool.space
Reference Materials
- Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System
- The Bitcoin Lightning Network: Scalable Off-Chain Instant Payments
- Lightning Labs Documents
- The Lightning Network
- Taproot Assets Protocol
- Taproot Assets on Lightning
- A Taproot-Native Asset Overlay - Bitcoin Miami 22
- Taproot Assets Protocol
- The SegWit Transaction Capacity Increase - Part 1
- Ordinals handbook
- BRC20
- Atomicals Guidebook
- BitVM:Compute Anything on Bitcoin
- RGB FAQ
- RGB Blackpaper
- RGB Documentation
- LNP/BP Standards
- Runes Protocol
- TROLL on Bitcoin
- PIPE Protocol repo
- Rootstock
- Rootstock Documentation
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



