The initiative was announced Jan. 23, 2026, and is driven by a reassessment of how quickly quantum computers could threaten existing cryptographic standards used across blockchain networks, according to internal documentation and developer commentary.
Ethereum researcher Justin Drake remarked on X that the shift reflects a broader understanding that preparation must begin years before any credible quantum attack becomes possible. At the center of the effort is a newly organized team led by Thomas Coratger, with engineering support focused on leanVM, a cryptographic framework intended to serve as a foundation for Ethereum’s post-quantum transition.

The Ethereum Foundation has committed at least $2 million toward research grants, prizes, and testing aimed at achieving quantum computing (QC) resistance without network downtime or loss of funds. The primary concern is the vulnerability of the Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA), which currently secures most blockchain wallets.
Advances in quantum research by major technology firms in 2025 have shortened the perceived timeline for when such systems could become vulnerable, prompting Ethereum developers to accelerate planning.
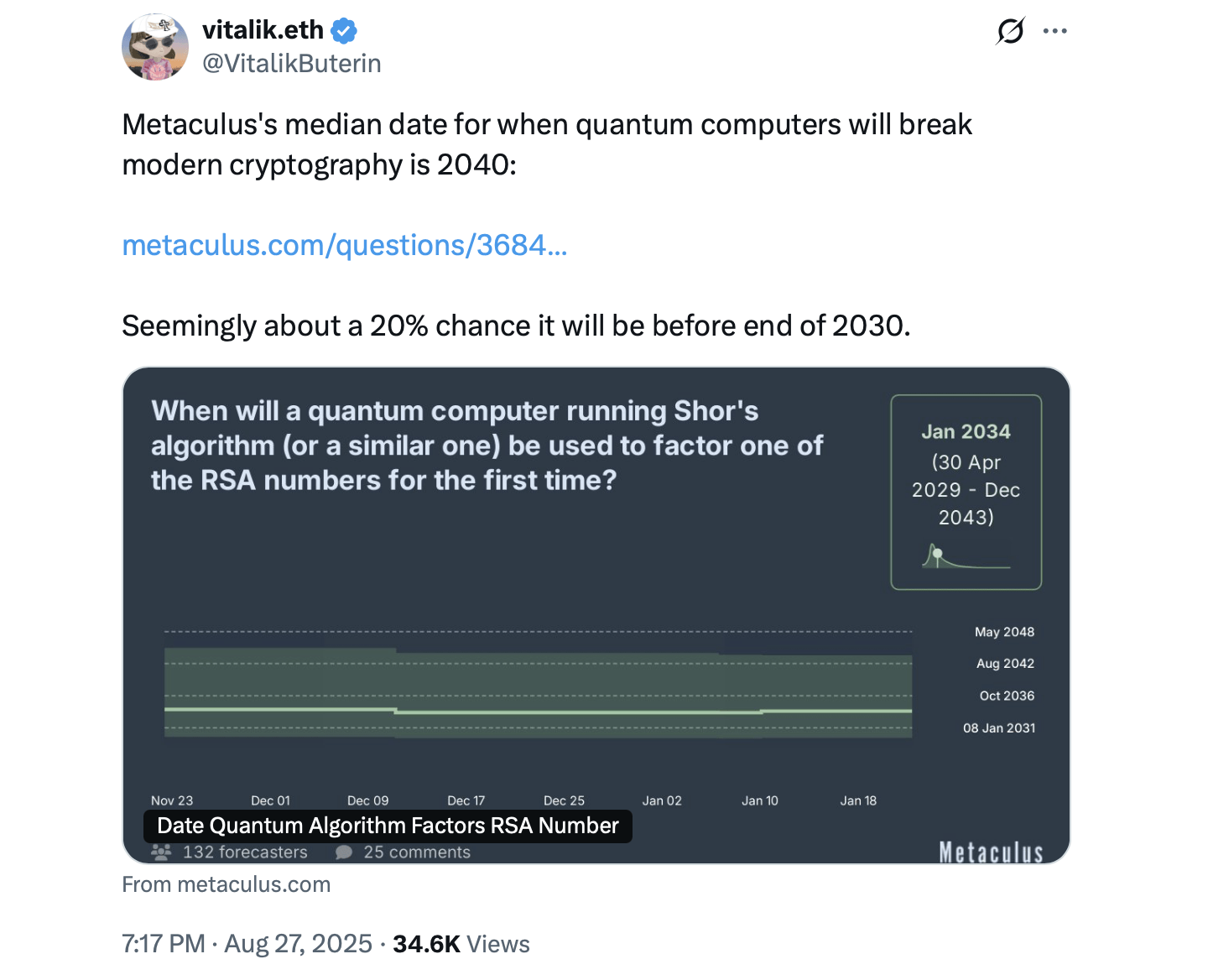
Vitalik Buterin has previously cited estimates suggesting a 20% probability that quantum computers could break modern cryptography before the end of the decade. He has argued that Ethereum’s long-term credibility depends on cryptographic security that can endure for generations, rather than relying on repeated emergency upgrades.
The post-quantum strategy spans multiple fronts. Research funding includes a $1 million prize to harden the Poseidon hash function and another $1 million to support broader post-quantum cryptography development, with an emphasis on hash-based systems and zero-knowledge STARKs.
On the engineering side, multi-client development networks are already running, involving Lighthouse, Grandine, and Prysm, to test interoperability under post-quantum assumptions. Weekly coordination calls and biweekly developer sessions are scheduled to address user-facing issues such as account abstraction and signature aggregation.
Community outreach is also part of the plan. The Ethereum Foundation is organizing workshops in Europe and publishing educational materials aimed at developers, enterprises, and institutions evaluating long-term cryptographic risk.
Also read: Quantum Threat Looms, New Whales Rising, and More — Week in Review
Ethereum’s coordinated approach contrasts with other networks. While several blockchains are experimenting with post-quantum techniques, Ethereum’s centralized funding and execution model allows it to pursue a unified roadmap, including a formal transition plan expected to be published on pq.ethereum.org.
Bitcoin developers, meanwhile, have also begun addressing quantum risks, as this past week, onchain analyst Willy Woo highlighted QC discussions increasing in 2025 and early planning underway. Although the Ethereum initiative represents one of the most structured efforts announced to date. At the same time, Coinbase disclosed this past week, the formation of a QC advisory task force, as chatter around quantum computing has turned increasingly heated.
- What is the post-quantum threat to Ethereum?
Quantum computers could eventually break cryptographic signatures that secure Ethereum accounts. - Who is leading Ethereum’s post-quantum effort?
The initiative is led by Thomas Coratger with support from Ethereum researchers and client teams. - How much funding is allocated to this initiative?
At least $2 million has been committed for research, prizes and engineering work. - Are other blockchains addressing quantum risks?
Yes, including Bitcoin, though Ethereum’s approach is currently more centralized and execution-focused.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




