
Author: CITIC Construction Investment
Summary
Overall, 2026 is the starting year for solidifying the foundation and making comprehensive efforts during the "14th Five-Year Plan"; from the external environment, 2026 is a year of strategic counterattack; from the economic structure, 2026 is a year of innovation and nurturing new growth; from the growth drivers, 2026 is a year to boost domestic demand; from the policy space, 2026 is a year of "dual easing" in fiscal and monetary policies; from the risk challenges, 2026 is a year of risk convergence. With the support of "policy support + stabilization of domestic demand + industrial upgrading," the expected GDP growth for 2026 will be around 5%.
A-share Market: The bull market in A-shares is expected to continue in 2026, with the index likely to remain volatile but with a slowing growth rate. Investors will pay more attention to improvements in fundamentals and verification of prosperity. We believe that caution is warranted regarding structural/periodic pullback risks in the technology sector, and resource products may become a new main line direction for A-shares after the technology theme. The comprehensive competition between China and the U.S. may have a significant impact on A-share investments, and it is recommended to focus on future industries and key resources, as well as military industry directions. Key industries to focus on include: new energy, non-ferrous metals, basic chemicals, oil and petrochemicals, non-bank financials, military industry, machinery and equipment, and computers. Key themes to focus on include: new materials, solid-state batteries, commercial aerospace, nuclear power, and cross-strait integration.
Hong Kong Stock Market: The concept of "new four bulls" for A-shares and Hong Kong stocks was proposed in 2025, namely "capital inflow bull," "technology innovation bull," "institutional reform bull," and "consumption upgrade bull." The strength of these four bulls will continue to drive the market upward in a stable manner in 2026. With a large number of high-quality domestic companies listing in Hong Kong and the evolution of the U.S. interest rate cut cycle, the activity in the Hong Kong stock market is expected to be further stimulated in 2026, and there remains significant upward potential.
Global Market: In 2026, there are three clues worth tracking regarding global asset pricing. First, the most eye-catching assets in 2025 were precious metals (gold and silver) priced for hedging and the Federal Reserve's monetary easing; under the resonance of anti-fragility and major waves in 2026, the most eye-catching assets may be non-ferrous metals (copper and aluminum). Second, the global market is still in the process of risk preference repair, and the AI industry chain is still worth tracking under the U.S.-China technology security competition. Third, the U.S. Treasury bond yields and inflation centers are unlikely to decline significantly in 2025, and the three major waves and a small global recovery will keep global interest rates and inflation centers operating at relatively high levels in 2026.
Bond Market: In terms of interest rate bonds, short-term risks are generally limited, and the yield curve is expected to steepen; credit bond spreads are expected to remain at low levels, and widening spreads due to incremental events will create opportunities for allocation; convertible bond assets may still show significant range-bound characteristics under the constraints of equity asset catalysis and high redemption probabilities.
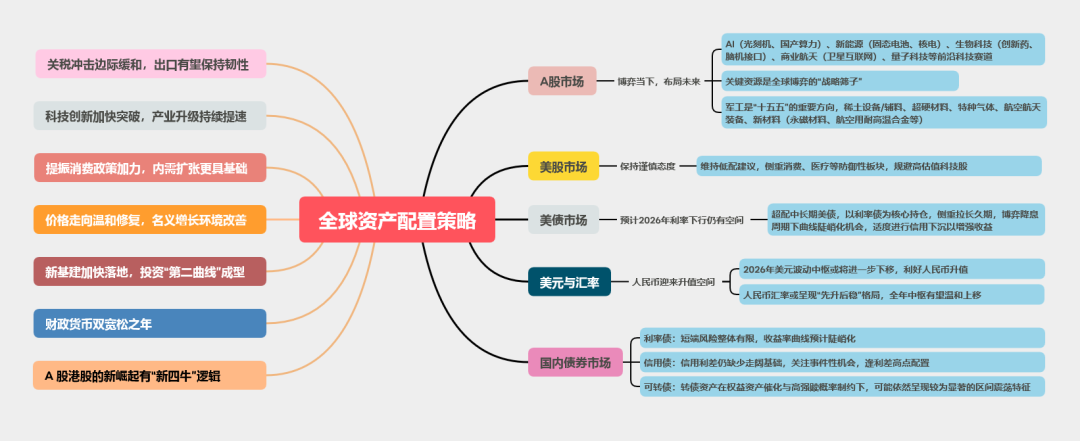
Image Source: CITIC Construction Investment Securities Research and Development Department
Macroeconomic Policy: Stabilizing the Foundation and Seeking Change
In 2025, multiple economic indicators showed that the domestic economy is growing steadily in total, with a structural focus on high-quality development. On the policy front, the focus is on expanding domestic demand to boost consumption, reversing involution to improve supply, advancing technological innovation and industrial upgrading, and continuing to strengthen social welfare. Looking ahead to 2026, macro policy will focus on three aspects: (1) Growth Drivers: The GDP growth target is around 5%, with technological industry dividends gradually being released, consumption significantly driving economic growth, and real estate expected to structurally stabilize at the bottom. (2) Policy Context: The "14th Five-Year Plan" outline is expected to announce quantitative indicators and major engineering projects. Fiscal policy emphasizes sustainability, is moderately proactive, while monetary policy focuses on support, maintaining stability with some easing, and optimizing industrial policy to achieve structural adjustments. (3) External Risks: The Federal Reserve's interest rate cut process, the U.S. midterm elections, U.S.-China strategic competition, and global geopolitical risks may cause disturbances. It is recommended to focus on investment opportunities in four main lines: technological innovation, cyclical infrastructure, service consumption, and public utilities.
Fiscal Policy: As a key year for the start of the "14th Five-Year Plan," China's fiscal deficit rate in 2026 will continue to expand, with the narrow fiscal deficit rate maintained at around 4%, and the broad fiscal deficit rate expected to slightly expand to around 8.3%, showing a core characteristic of "central fiscal expansion being greater than local." This arrangement aligns with the long-term orientation of "moderate expansion of deficits" during the "14th Five-Year Plan" period and addresses the practical needs for economic recovery and strategic investment in 2026.
Monetary Policy: In 2026, China's monetary policy will continue to maintain a moderately loose main tone, a judgment based on external environmental support and deeply rooted in the real needs of internal economic operations, with policy operations focusing more on the synergy of total control and structural guidance.
Industrial Policy: Based on current industrial pain points and policy guidance, the key to structural adjustment in 2026 lies in repairing the price transmission chain through anti-involution policies, with the strength of demand-side supporting measures determining their effectiveness.
Macroeconomic Outlook: Emerging from the Inflation Low
Looking ahead to the second half of the year, global stocks, bonds, currencies, and commodities will still align with major trends, but there will be slight fluctuations in rhythm.
U.S. Stocks and Bonds: Repeated fluctuations under major trends.
Chinese Assets: The bond market may have a "bull tail"; stock market trading liquidity.
Global Commodities: One side with high volatility; the other side remains stagnant.
U.S. Dollar Index and Renminbi Exchange Rate: Weakening of reverse dollar trading and range-bound fluctuations.
Exports: After the surge in exports, the divergence trend of industrial production prices (PPI) and resident inflation (core CPI) may converge in the first half of this year. At that time, domestic industrial production prices (PPI) may further transmit to resident inflation (CPI), with two key clues to focus on: Clue one, the PPI price structure may further differentiate, with downstream manufacturing profit expectations possibly weaker than in the first half. Clue two, corporate cash flow pressures may further transmit to residents, potentially constraining the upward momentum of core CPI.
Consumption: The impact of U.S. tariffs on domestic demand may gradually manifest in the second half of the year, increasing the vulnerability of risk assets. On one hand, as the U.S. solidifies its tariff levels against China, the previous "export rush" is gradually cooling. On the other hand, tariffs may pressure small and medium-sized export enterprises in the mid-to-low end, affecting domestic demand through channels of resident income and employment. The real estate sector, still in a bottoming phase, along with potentially weakening corporate production and operations, may also lead to lower real estate rents.
Policy: Evaluating the second half of the year under a new framework may yield policies, with expected directions and rhythms of policy efforts as follows: ① The old-for-new policy progressed rapidly in the first half, but as funding consumption approaches its end in the second half, the old-for-new policy will no longer be a highlight. ② In the second half, focus on fertility and employment assistance subsidies. ③ In terms of monetary policy, the easing intensity may open up in the second half, especially towards the end of the third quarter and the beginning of the fourth quarter; if the U.S. proceeds with interest rate cuts, China's easing pace may accelerate.
A-share Outlook: A New Journey of Slow Bull
The bull market in A-shares is expected to continue in 2026, with the index likely to remain volatile but with a slowing growth rate. Investors will pay more attention to improvements in fundamentals and verification of prosperity. We believe that caution is warranted regarding structural/periodic pullback risks in the technology sector, and resource products may become a new main line direction for A-shares after the technology theme. The comprehensive competition between China and the U.S. may have a significant impact on A-share investments, and it is recommended to focus on future industries and key resources, as well as military industry directions. Key industries to focus on include: new energy, non-ferrous metals, basic chemicals, oil and petrochemicals, non-bank financials, military industry, machinery and equipment, and computers. Key themes to focus on include: new materials, solid-state batteries, commercial aerospace, nuclear power, and cross-strait integration.
Rapid increases are prone to reversals, while slow progress leads to longevity—this is the rhythm and space of the current bull market. This bull market began with a policy shift and is centered on liquidity improvement; the core logic supporting the bull market is expected to continue or even strengthen in 2026. We believe the current market has entered the mid-stage of the bull market, with the cost-effectiveness of equity assets having declined. Excessive short-term increases may lead to an early peak and premature end of the bull market. In terms of market rhythm: A-shares are entering a critical period for verifying prosperity. During this phase, the index is likely to remain volatile but with a slowing growth rate, as economic fundamentals improve or emerging industries/track performances digest elevated valuation levels; this phase may see a style switch, with sectors that have high valuations but lowered growth expectations potentially undergoing periodic adjustments, while varieties with improved fundamental expectations lead the market, favoring a prosperity investment style.
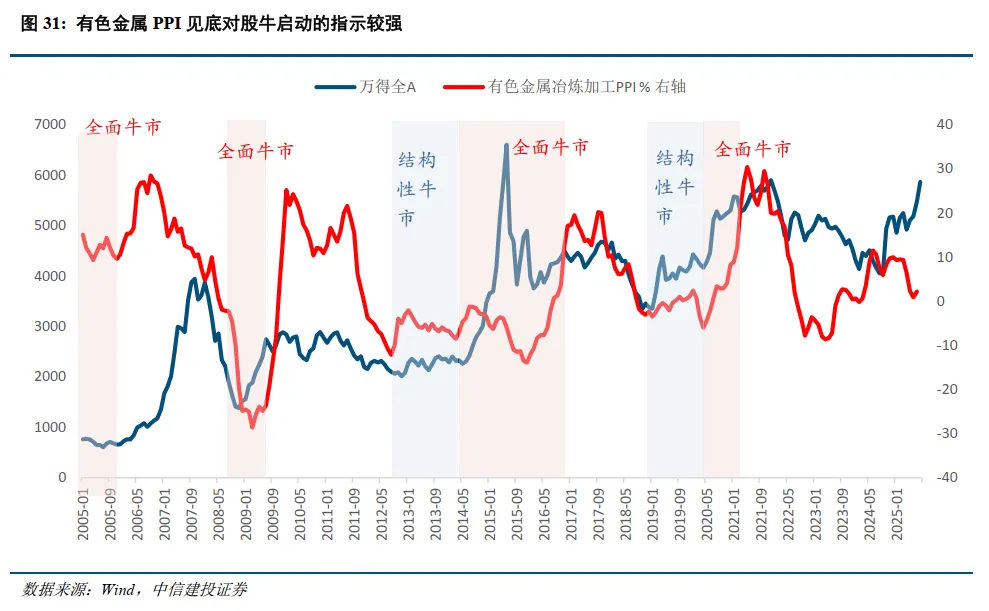
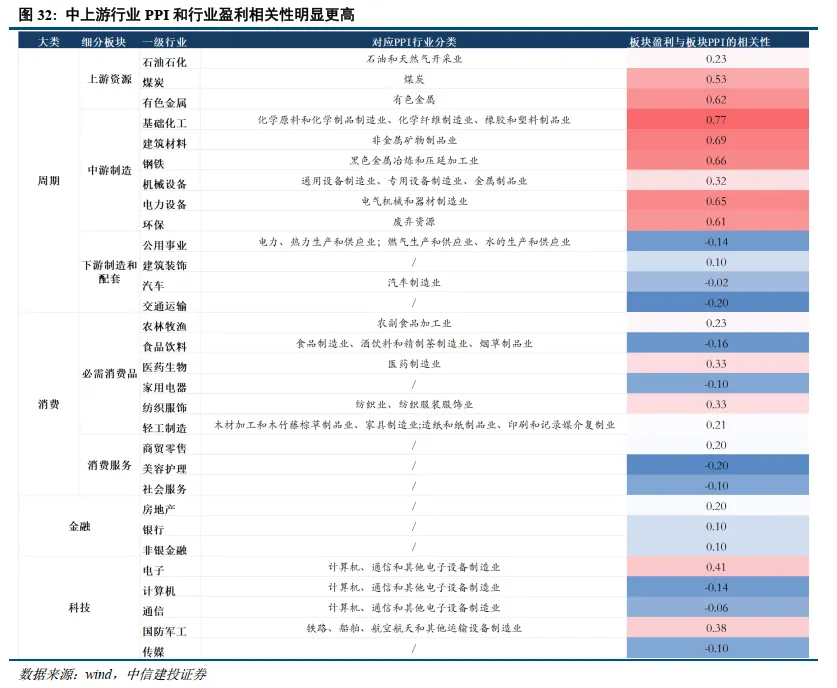
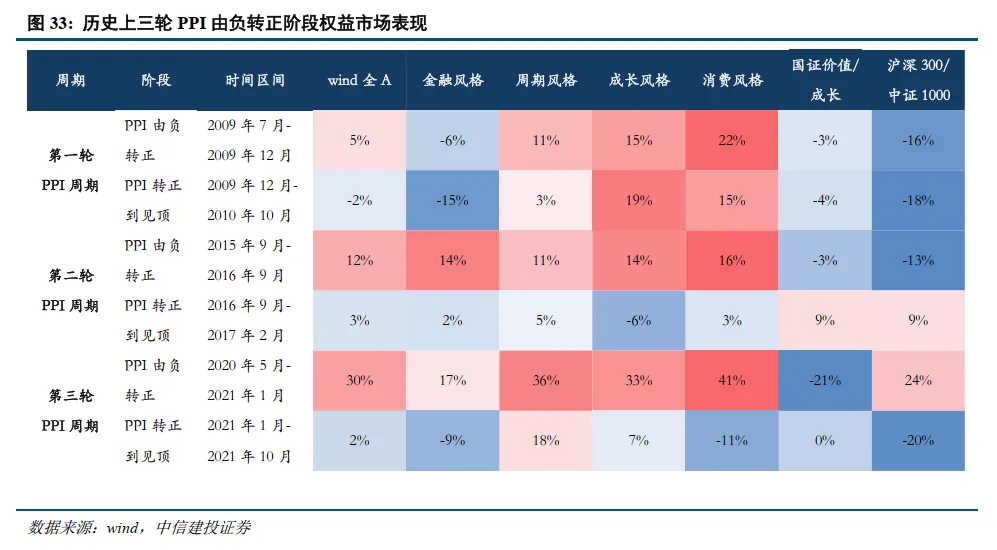
In a strong technological environment, hidden currents of rotation—this is the choice of the main line of the market. The current market consensus is that from the perspectives of policy, fundamentals, and capital, technological growth is the most logical direction. Our view: Be cautious of structural/periodic pullback risks in the technology sector. It is recommended to seek performance elasticity and grasp structural market opportunities, focusing on: AI, new energy, key resources, etc. After the technology bull, focus on the resource bull market. Currently, conditions for a bull market in resource products are accumulating, and resource products may become a new main line direction for A-shares after the technology theme. The logic supporting the rise in resource prices mainly includes: global monetary easing, gold price ratios, supply-demand gaps, price trends, and the initiation of domestic replenishment cycles; additionally, the current comprehensive competition phase between China and the U.S. is expected to make the competition for key resources a key factor in the rise of resource products.

 Planning for the future, competing in the present—The U.S.-China decisive battle behind A-shares. The U.S. and China have entered a phase of comprehensive competition. Planning for the future: The competition between the U.S. and China in future industry layouts and cutting-edge technologies is intensifying; it is recommended to focus on: AI (lithography machines, domestic computing power), new energy (solid-state batteries, nuclear power), biotechnology (innovative drugs, brain-computer interfaces), commercial aerospace (satellite internet), quantum technology, and other cutting-edge technology tracks. Competing in the present: Key resources are the "strategic sieve" of global competition, and the military industry is an important direction of the "14th Five-Year Plan"; focus on: rare earth equipment/accessories, superhard materials, special gases, aerospace equipment, and new materials (permanent magnet materials, high-temperature resistant alloys for aviation, etc.).
Planning for the future, competing in the present—The U.S.-China decisive battle behind A-shares. The U.S. and China have entered a phase of comprehensive competition. Planning for the future: The competition between the U.S. and China in future industry layouts and cutting-edge technologies is intensifying; it is recommended to focus on: AI (lithography machines, domestic computing power), new energy (solid-state batteries, nuclear power), biotechnology (innovative drugs, brain-computer interfaces), commercial aerospace (satellite internet), quantum technology, and other cutting-edge technology tracks. Competing in the present: Key resources are the "strategic sieve" of global competition, and the military industry is an important direction of the "14th Five-Year Plan"; focus on: rare earth equipment/accessories, superhard materials, special gases, aerospace equipment, and new materials (permanent magnet materials, high-temperature resistant alloys for aviation, etc.).
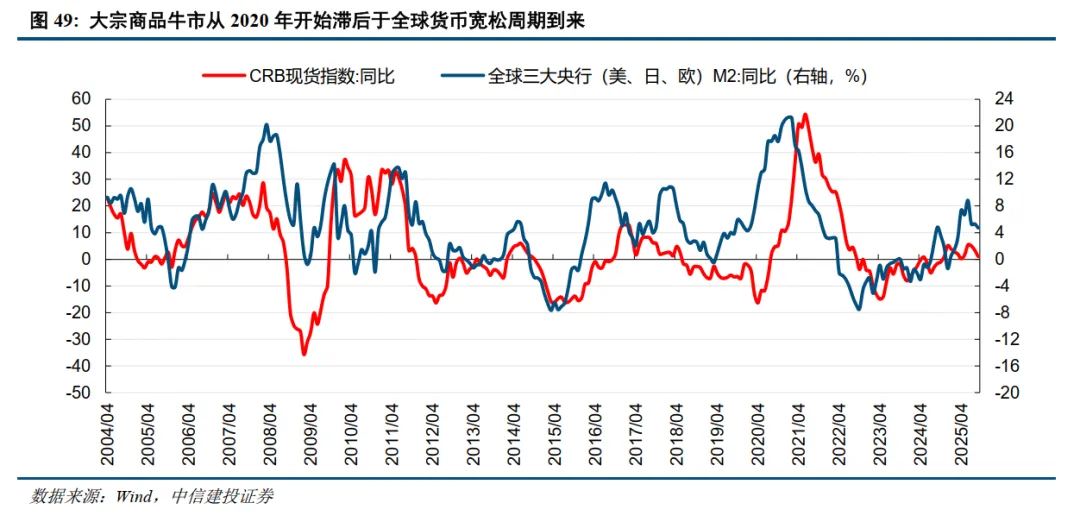
Global Market Outlook: Major Waves and Anti-Fragility
Looking ahead to 2026, the macro big variable is the U.S.-China great power competition shifting from tariff confrontations to strategic competition.
In 2026, the big variable is the direction of U.S.-China relations. We provide judgments on U.S.-China relations from two perspectives: transitioning from comprehensive total tariff confrontations to strategic competition in security technology.
From the U.S. Strategic Perspective, the midterm election year forces the U.S. to focus more on domestic affairs. In 2025, although Trump will still emphasize foreign policy, compared to the Biden administration, this Trump administration's handling of diplomatic relations will focus more on "returning to the Asia-Pacific" and initiating a new round of trade wars to engage in competition over the Chinese supply chain. In 2026, the U.S. will face midterm elections, confronting increasingly apparent four major "American fractures": ① strong government sectors, weak private sectors; ② weak traditional economy, strong technology sector; ③ strong consumption sector, weak production sector; ④ the wealthy class profits significantly, while the middle and low-income groups are at a disadvantage. The U.S. needs to return to "American-style stable growth," stabilizing the U.S. economy to create more space for buffering conflicts and contradictions.
From the Perspective of Great Power Competition, the U.S.-China competition has transitioned from capacity transfer to a technology security race. In 2025, who wins and who loses in the tariff competition? Behind this simple question lies a more essential issue: what is the ultimate goal of tariff confrontations? We have previously answered this question based on the essence of U.S.-China economic and trade relations and the U.S. trade war experience after World War II: the purpose of tariff confrontations is not solely based on the consideration of manufacturing returning to the U.S., but rather to reconstruct the global supply chain and buffer the contradictions between the U.S. and China in terms of supply and demand. Currently, there is a general consensus among China, the U.S., and third-party countries regarding tariff confrontations, as evidenced by the U.S. trade agreements with multiple countries in July and the meeting between the leaders of China and the U.S. in Busan. The phase of tariff confrontations between China and the U.S. is coming to an end, and in the future, the two countries are likely to enter a period of significant easing in overall economic and trade relations. However, in strategic areas—security and technology—the great power competition between the U.S. and China is just beginning. This is also why we believe that in 2026, the U.S. and China will enter a competition in security and technology, a model that will profoundly influence the direction of global political and economic trends.
The global political and economic direction driven by U.S.-China relations in 2026: transitioning from overall tariff confrontations to security and technology competition.
In 2026, the U.S. policy focus will return to American-style stable growth, with monetary and fiscal easing being the inevitable choice of the Trump administration. After fiscal and monetary easing, we may see a small cyclical rebound in U.S. economic demand in 2026.
In 2026, the economies of Japan and Europe will also experience a phase of rebound in demand, which is not complicated; the impact of tariff confrontations will gradually fade, fiscal policies will revert, and the effects of monetary easing will gradually accumulate and become evident.
Therefore, under a neutral scenario, we provide two important judgments: ① In 2026, the global economic cycle position will shift from risk aversion to recovery. ② In 2026, global asset pricing changes will shift from weak pricing to anti-fragile pricing.
In 2026, the three major global trends will continue to surge forward—technological revolution, fiscal expansion, and supply chain reshaping.
In addition to focusing on important variable turning points, we also need to pay attention to longer-term trends and undercurrents. These undercurrents will influence our judgments on macro variables and major trends.
Currently, the world is in a period of explosive growth in a new round of technological revolution. The trade war has not hindered AI technological progress; U.S. tech giants' capital expenditures remain strong, and the narrative around technology continues to evolve. Whether from the perspective of the U.S.-China competition shift or the U.S. returning to domestic affairs, technological capital expenditure will be a key investment area for both countries in 2026.
Major mainstream economies will temporarily return to fiscal expansion in 2026. This is both a continuation of the post-pandemic global fiscal framework and a phased response to the demand for global growth in 2026.
In the face of each tariff increase, Chinese enterprises will proactively respond—accelerating overseas expansion, i.e., capacity transfer. After the 2018 trade war, China entered the overseas expansion 1.0 phase, and a round of reshaping of the global supply chain has already occurred. The new trade rules established by Trump in 2025 will once again reshape the global supply chain, ushering in overseas expansion 2.0 for China, with enterprises moving towards greater diversification.
Under the three major trends, which asset pricing shows longer-term trend changes?
The asset implications of the fiscal expansion wave include high inflation centers, high nominal interest rates, and high government debt.
The asset implications of the technological revolution wave include higher real interest rates, more extreme asset differentiation, and a stronger dollar center.
The asset implications of supply chain reshaping include short-term supply tightness and a sustained wave of global capital expenditure.

In 2026, what will global assets price? Anti-fragility and major trends.
With the three major trend waves and small cyclical anti-fragility, the global asset pricing in 2026 may have the following three clues worth tracking.
First, the most eye-catching assets in 2025 were precious metals (gold and silver) priced for hedging and the Federal Reserve's monetary easing; under the resonance of anti-fragility and major trends in 2026, the most eye-catching assets may be non-ferrous metals (copper and aluminum).
Second, the global market is still in the process of risk preference repair, and the AI industry chain is still worth tracking under the U.S.-China technology security competition.
Third, the U.S. Treasury bond yields and inflation centers are unlikely to decline significantly in 2025; the three major trends and a small global recovery will keep global interest rates and inflation centers operating at relatively high levels in 2026.
Industry Outlook
Technology Industry: Computing Power First, Focus on New Technological Breakthroughs
The National "14th Five-Year Plan" clearly states: The new round of technological revolution and industrial transformation will accelerate breakthroughs, and the "Artificial Intelligence +" initiative will be fully implemented. We believe that the world is currently in an AI industrial revolution, comparable to the industrial revolution, with far-reaching impacts that cannot be simply compared to recent years' cloud computing and new energy; it requires a longer-term perspective and a higher vision to observe.
Telecommunications: Currently, the world is in an AI industrial revolution, comparable to the industrial revolution, with far-reaching impacts that cannot be simply compared to recent years' cloud computing and new energy; it requires a longer-term perspective and a higher vision to observe. Therefore, we are very optimistic about the demand for computing power driven by AI and its applications, including optical modules/optical devices/optical chips, switches, liquid cooling, IDC, and edge-side AI. Additionally, the traditional telecommunications industry chain is affected by the decline in capital expenditure from telecom operators, leading to low market expectations. However, the R&D of key 6G technologies has begun, and with operators increasing their investment in AI, it is worth paying attention to. Both China and the U.S. place high importance on quantum technology, with related companies in the U.S. stock market experiencing significant increases; it is recommended to focus on dilution refrigerators, low-temperature coaxial cables, and other segments.
Computers: AI leads the main line of computer industry development, and with the resonance of domestic production, quantum technology, financial IT, and intelligent driving sectors, the industry is expected to welcome a dual recovery in performance and valuation. In the AI field, rapid iteration of models, high demand for computing power, and the gradual formation of ecosystems are accelerating the commercialization process; domestic production is moving towards the "deep water zone" driven by policies and orders, with industrial software becoming a core support for a manufacturing powerhouse; quantum technology, as a future industry, is opening up a new competitive track globally; at the same time, high-prosperity tracks such as financial IT and intelligent driving continue to emerge with structural opportunities. It is recommended to focus on AI, domestic production, and cutting-edge technology directions.
Artificial Intelligence: 1) On the computing power side, seek investment opportunities around leading certainties, new technology upgrade directions, accelerated localization of industrial clusters, and order spillover, with a focus on heat dissipation, PCBs, power supplies, and power direction. 2) From a medium-term perspective, the trend of orders shifting towards domestic chips is inevitable. Considering that domestic chips are gradually entering the mass production and delivery stage, it is expected that market concentration will see significant improvement, with a focus on chip manufacturers that have shown a noticeable increase in market share among cloud vendors. 3) Companies represented by OpenAI have accelerated the commercialization of applications this year, with rapid revenue growth, seeking investment opportunities in how AI empowers and transforms various industries.
Media and Internet: In 2026, we continue to be optimistic about AI applications and content consumption. AI applications accelerated commercialization in 2025, and in 2026, the focus will be on the integration of AI with existing products. Platforms like WeChat, Douyin, and Doubao are expected to become traffic entry points in the AI era. Additionally, AI + advertising is expected to deliver results, such as OneRec improving efficiency and reducing costs. At the same time, AI is speeding up overseas expansion, leveraging high product quality and cost-effectiveness to capture overseas markets. In gaming, prosperity and profit margins continue to rise, with supply-side growth in game approvals (up 23% year-on-year in the first ten months of 2025) supporting subsequent revenue streams. Tencent, NetEase, and miHoYo are launching new games intensively, while medium-sized companies are innovating in categories (such as SLG + elimination, creative board games, emerging female-oriented games, etc.), with potential for channel bargaining power to weaken and AI to enhance efficiency, leading to continuous profit margin growth. In content consumption, leading IP toy companies are accelerating overseas expansion and improving single-store efficiency, while the consumption of millet is shifting from wild growth to quality integration; music platforms are driven by volume and price, with live performances experiencing high prosperity; film and television benefit from policy support, with AI aiding content innovation (such as comic dramas and group broadcasts), and both policy and supply are building a foundation for recovery.
Electronics: On the model side, the user and revenue scale of AI large model manufacturers are in a period of rapid expansion, with OpenAI and Anthropic's ARR still growing exponentially. As AI applications and edge-side implementations accelerate, CSPs are also increasing capital expenditures, conducting the largest infrastructure investments in history. On the hardware side, NVIDIA's GB300 server solution has now entered the mass production phase, and the Rubin architecture solution is gradually becoming apparent, with ASIC players also making efforts. The high growth in demand for computing power is driving high growth in sub-industries such as GPUs, storage, advanced packaging, and PCBs, providing a golden development period for domestic semiconductor development. On the edge side, generative AI is driving a new round of content generation, search, and productivity-related applications, covering terminal categories including smartphones, PCs, cars, XR, and the Internet of Things, providing a new user experience, with new terminals such as AI glasses, toys, and robots poised for explosive growth.
Consumer Industry: Supply and Demand Reversal Drives Quality-Price Ratio, Emotional Value Gives Rise to New Trends
Food and Beverage: Currently, the food and beverage sector is experiencing a long-term correction, with low attention to domestic demand, significantly reduced valuations, and market expectations at a low level. The bottom logic for quality assets like liquor is clear. We are particularly optimistic about four sectors: 1) Liquor. Focus on three types of quality targets, waiting for demand to warm up. Stimulus policies are expected to increase, and economic data is likely to hit bottom and drive consumption recovery. 2) Snacks, health products & beverages. New channels and new categories for snacks resonate, creating multiple investment opportunities. The trend of health and functionality in beverages is popular, with high prosperity in segmented categories. New consumption drives in health products are leading to a revaluation of the health product sector. 3) Dairy products. Milk prices are expected to rise cyclically, liquid milk may reach a turning point, and deep processing industries are on the rise. 4) Restaurant chains. Focus on efficiency as internal competition eases, embracing trends to expand new sales channels.
Light Industry, Textiles, and Education: Looking ahead to 2026, we believe that the external demand β is relatively better, and we recommend selecting strong α stocks; on the domestic demand side, supply innovation remains the biggest structural highlight, with the sector overall at the bottom of the valuation range, paying attention to future marginal changes in consumption and real estate policies, ready for action. 1) Export priority: U.S.-China relations are progressing steadily, with U.S. tariffs on Southeast Asia and others basically settled, and downstream orders gradually recovering from Q3. Tariff transmission and terminal price increases may affect some demand, while the Federal Reserve's interest rate cuts are expected to boost U.S. consumption, especially in the post-cycle real estate sector. Export companies sharing the burden of tariffs may affect gross margins, but leading companies leveraging overseas capacity and manufacturing advantages are likely to increase their market share. 2) Domestic demand accumulation: China's real estate completion and sales data remain under pressure, with social retail performance being flat. Supply innovation remains the biggest structural highlight for domestic demand, which is still in an accumulation phase. The current sector is at the bottom of the valuation range, and it is recommended to pay attention to changes in real estate and consumption stimulus policies, waiting for a right-side turning point.
Home Appliances: In 2025, the home appliance sector was hindered by tariff increases, fluctuations in the old-for-new policy, and high base expectations in the second half of the year, overall underperforming the CSI 300. From a long-term perspective, the competitiveness of enterprises will ultimately return to the essence of product innovation and efficiency advantages. Therefore, from an investment perspective, we believe there are two main lines: one is that overseas expansion continues to be the most important source of growth, and the other is the reform dividend. In summary, we believe that investment opportunities in 2026 will mainly be in 1) the era of overseas expansion; 2) the new cycle of reform.
Social Services and Trade: While policies focus on quality consumption and opening up to the outside world, they also provide guidance for structural optimization. We expect that in the new year, growth will continue to emerge from both upgraded consumption and basic consumption. The duty-free industry is transitioning from consumption repatriation to welcoming new benefits from border closures and inbound tourism, with tax reforms on gold resonating with fashion brands going overseas. The high-quality development of the service industry, accompanied by high-quality supply, is stimulating new consumer demand. Starting from the 14th Five-Year Plan, consumption is expected to gradually emerge from a pattern of weak expectations and realities, with Chinese brand stories becoming increasingly rich.
Pharmaceuticals: Value Restructuring, Waiting for Bloom
China's pharmaceutical industry has entered a critical stage of "innovation realization + global layout," with population and domestic demand bases, as well as full industrial chain manufacturing capabilities, forming core support. Enterprises are actively exploring diversified overseas paths. In the face of global competition and deepening policies, the industry needs to "focus on the domestic market, lead with innovation, and expand internationally," strengthening supply chain security and compliance capabilities domestically while deepening diversified overseas layouts. Looking ahead to 2026, we should focus on opportunities brought by innovative commercialization, breakthroughs in globalization, policy optimization, and industry mergers and acquisitions.
Pharmaceutical Consumption and Bioproducts: The short-term pressure on the traditional Chinese medicine industry is expected to ease, with channel inventory accelerating clearance. We are optimistic about demand warming at the end of the year and subsequent opportunities for fundamental and valuation improvement. The innovative field will help build a second growth curve, with ample brand extension space for traditional Chinese medicine consumer goods companies. In the blood products industry, attention should be paid to the "14th Five-Year Plan" for plasma station construction and industry mergers and acquisitions progress, with a positive outlook on the demand for immunoglobulin and factor products and new product development. In the vaccine industry, we should focus on the sales improvement of key products and the progress of innovative pipeline research and development, as policy introductions and vaccine exports are expected to further promote corporate development. The transformation of the pharmaceutical retail industry is steadily advancing, with attention to subsequent diversified catalysts. The pharmaceutical distribution industry is seeing stable revenue growth, with a focus on receivables and the "14th Five-Year Plan."
Medical Devices: In the short term, with policy easing, clearance of centralized procurement, expansion of new products and new business, and overseas layouts, it is expected that several leading medical device companies will reach a performance inflection point in 2026. We recommend seizing investment opportunities for performance valuation recovery, as well as investment opportunities in new medical technologies such as brain-computer interfaces and AI healthcare. The long-term investment opportunities in the medical device sector come from innovation, overseas expansion, and mergers and acquisitions, with the sector's innovation and internationalization capabilities gradually being recognized and valuations being reassessed.
Innovative Drugs: The innovative drug sector is showing three major trends: Internationalization 2.0 is deepening, with the number of license-out transactions reaching 103 in 2025 and upfront payments hitting a historic high of $8.45 billion, allowing self-expanding companies to enjoy valuation premiums; policy support is unprecedented, with improved efficiency in medical insurance negotiations and the establishment of a directory for innovative drugs under commercial insurance for the first time; and technology-driven breakthroughs continue, with ADCs, IO dual antibodies, GLP-1 weight loss drugs, and small nucleic acid drugs flourishing. The CXO industry adjustment is basically complete, with stable overseas demand and a rebound in domestic investment and financing, focusing on CDMO companies with strong overseas capabilities and leading clinical CROs. The upstream industrial chain is showing significant recovery, with ample room for domestic production rates to increase, driven by intelligent and digital production and international expansion. We are optimistic about the future development of the domestic pharmaceutical industry chain.
High-end Manufacturing
Machinery: Looking ahead to 2026, in the context of relatively weak domestic demand, the industry is showing structural prosperity. In terms of investment strategy, ① focus on new technologies: select emerging industries with intensive technological changes and strong capital expenditures, such as humanoid robots, solid-state battery equipment, controllable nuclear fusion, and PCB equipment; ② seek new growth: from exports to overseas expansion, look for beneficiaries under the backdrop of interest rate cuts and manufacturing capacity transfer, such as engineering machinery, tool hardware, mining machinery, oil service equipment, and injection molding machines. These companies generally have lower valuations and higher growth rates, making them worthy of close attention.
Military Industry: The pattern of "domestic demand as the foundation, foreign trade expansion, and civilian support" is profoundly reshaping the appearance and boundaries of China's military industry. The industry is shifting from "cyclical growth" to "comprehensive growth." 1) Domestic military demand: Focus on "preparing for war" and equipment modernization, with demand stemming from stable growth in defense budgets and equipment upgrades. Strong deterrence with high precision and systematic unmanned low-cost capabilities is the main growth direction. 2) Military trade overseas: Leveraging cost-performance advantages, systematic combat capabilities, and geopolitical strategic cooperation, China's military trade share continues to rise, becoming an important global supplier and achieving a win-win situation in strategic influence and economic benefits. 3) Civilian application of military technology: Cutting-edge military technology is spilling over into civilian fields, giving rise to trillion-level new industries such as commercial aerospace, low-altitude economy, future energy, deep-sea technology, and large aircraft, driving the development of new processes, new materials, and new devices, forming a virtuous cycle of "military technology for civilian use, supporting military industry."
Automobile: The automotive industry has three investment directions: cyclical, growth, and overseas expansion. With policy expectations weakening in 2026, the cyclical attributes of the industry are diminishing. It is recommended to downplay total domestic demand expectations and focus on industry structure and trends. Overseas expansion and growth are expected to become core investment directions, with commercial vehicles possessing undervalued and stable dividend attributes. The growth main line lies in intelligent driving/Robotaxi and AI applications in robotics, with the technological attributes of whole vehicle stocks expected to reshape valuations, while components will benefit from breakthroughs in supply chains such as robotics, opening up new growth spaces.
New Energy: After three years of capacity digestion, the power equipment new energy industry is standing at the starting point of a new cycle against the backdrop of demand exceeding expectations. During the 14th Five-Year Plan period, the global new energy installed capacity is expected to reach new heights, which will bring revolutionary changes to the power system: ① A high proportion of wind and solar access will generate massive storage and capacity demand. ② Global power grids, especially in Europe and the U.S., will continue to increase investments to adapt to the carbon neutrality process. ③ The aforementioned adjustment costs and grid transformation costs will further drive up electricity prices, opening up long-term demand space for energy storage and industrial and commercial storage. ④ AI will drive an increase in global electricity consumption growth, and the importance of low-carbon, high-density power sources (offshore wind, SOFC, nuclear power, gas turbines) will also rise, with data center power supply models shifting towards high voltage. All these changes will herald the beginning of fundamental realization in 2026.
Banking: Funding and market factors jointly guide, with a preference for stability and high dividend attributes
In 2025, the macro economy will continue to show a weak recovery trend, and the banking industry's fundamentals have not yet shown significant improvement, with high dividend strategies continuing to play out. From a funding perspective, long-term funds from insurance companies, state teams, and public funds still have strong motivation to increase allocations to banks. The fundamentals of domestic banks continue to stabilize, with the safety margin of configuration-type demand, which is centered on bottom-line thinking, high confidence, and high win rates, further improving. The current economic environment has not yet shown strong recovery characteristics, and we continue to be optimistic about high dividend strategies while paying attention to undervalued and changing targets.
Securities: Looking ahead to the 14th Five-Year Plan, the securities industry will support the high-quality development of the capital market
Anchoring the core direction of the 14th Five-Year Plan to "improve the inclusiveness and adaptability of the capital market system," the securities industry is expected to usher in a new round of upward cycles, contributing to the construction of a strong financial nation.
The core drivers come from three major policy opportunities:
First, policies guide the capital market to serve new quality productivity. The deepening reforms of the Sci-Tech Innovation Board and the Growth Enterprise Market promote the upgrading of investment banks' value creation capabilities, matching the full lifecycle financing needs of high-tech entities and opening up medium- to long-term growth space for investment banking business.
Second, policies improve the ecosystem for long-term capital and long-term investment. Channels for medium- to long-term funds such as social security and insurance to enter the market remain smooth, and the expansion of equity products activates incremental growth in brokerage asset management and institutional business, promoting the industry to shift towards configuration-driven transformation.
Third, policies promote the cultivation of first-class investment banks and internationalization. Chinese securities firms can leverage the Hong Kong market and interconnectivity policies to accelerate breakthroughs in international business, and mergers and acquisitions will help concentrate industry resources towards leading firms, enhancing the capital strength and international competitiveness of top securities firms.
Insurance: Looking ahead to the 14th Five-Year Plan, eight major trends in the insurance industry
The 14th Five-Year Plan period is not only a key time for strategic transformation in the insurance industry but also an important configuration period for the continuous emergence of investment value in the industry. From an investment perspective, we recommend placing high importance on the configuration value of the insurance sector. The performance of listed insurance companies on both the asset and liability sides is expected to resonate and improve, and we suggest focusing on the long-term performance growth and valuation recovery investment opportunities of the insurance industry, known as the "Davis Double-Play."
Cyclical Industries
Real Estate: With continued policy support for the real estate industry, the decline in industry sales has shown a significant narrowing. We predict that by 2026, market sales will stabilize after a decline, while investment, due to its inherent lag, may still face pressure. We expect the year-on-year growth rates for national commercial housing sales area, real estate development investment, new construction area, and completed area in 2026 to be -5.2%, -9.8%, -13.6%, and -10.5%, respectively. After nearly four years of reshuffling, the peak of debt defaults among real estate companies has passed, and there has been positive progress in the debt restructuring of distressed companies. The investment logic in the real estate industry has fully shifted from survival to a new start, with quality enterprises in various tracks expected to gain first-mover advantages. In the development track, we are optimistic about companies with land reserves concentrated in core cities and strong product capabilities; in the commercial track, we favor companies with rich quality commercial real estate and strong operational capabilities; in the property management track, we focus on companies with high levels of digital intelligence and excellent cost control capabilities.
Construction: The 14th Five-Year Plan emphasizes building a modern industrial system and accelerating the achievement of high-level technological self-reliance. As a traditional industry, the construction sector needs to seek new growth sources in the context of real estate downturns and the era of existing infrastructure, while also relying on industrial upgrades and technological advancements to build a modern infrastructure system for new quality productivity, empowering industrial development and seeking transformation to achieve industrial upgrades. At the same time, in terms of expanding domestic demand, new urbanization construction and urban renewal will be key investment directions, and overseas expansion will continue to contribute incremental growth for construction companies. We recommend focusing on three major directions: empowering the modern industrial system, expanding domestic demand, and overseas expansion.
REITs: The C-REITs market experienced a rise to a new high followed by a pullback in 2025, and the market has now bottomed out and stabilized. In the third quarter, performance differentiation continued both between and within sectors, with strong operational and anti-cyclical assets remaining stable, while some fiercely competitive sectors still face challenges. In the short to medium term, market allocation funds still have very strong demand for quality assets. Looking ahead to 2026, policy dividends are poised to emerge, and considering this year's policy rhythm, there is expected to be significant counter-cyclical adjustment space before the end of the year. Specific policy directions include index products that are maturing, improved tax policies, and highly supported holding-type real estate ABS. We recommend shifting the primary market strategy from "general selection" to "careful selection," while focusing on three main lines in the secondary market: anti-cyclical, improving prosperity, and strong fundraising.
Metals and New Metal Materials: At the beginning of 2024, we clearly proposed a bull market for resource products constrained by supply, which was confirmed in 2024 and 2025, with non-ferrous metals experiencing a magnificent market. Standing at this point, we remain optimistic about the further advancement of non-ferrous metals in 2026, maintaining a bull market pattern. The demand terminal in 2006 pointed to "real estate infrastructure," while this round of the bull market points to "new quality productivity." We prefer to call it the "new quality productivity bull market," benefiting from China's rapid rise and significant industrial advantages. In 2026, elements of new quality productivity will continue to maintain a bull market pattern, with supply constraints and strong demand being characteristics of this round of the bull market. New materials for AI and robotics will also rise to welcome a strong growth cycle.
Chemicals: In the 2026 chemical industry strategy, under the backdrop of slowing capital expenditures in the industry and an approaching cyclical turning point, we recommend focusing on varieties that are expected to benefit from anti-involution, including pesticides, urea, soda ash, filament, silicone, and spandex. Additionally, during the interest rate cut cycle, China's counter-cyclical policies will help domestic demand recover, so we recommend paying attention to polyurethane, coal chemical, petrochemical, and fluorochemical sectors. Furthermore, developing new quality productivity, self-control, and industrial upgrades is a firm choice in the context of great power competition. New materials remain one of the main development directions of China's chemical industry, with a focus on the continuous development of semiconductor materials, OLED materials, COC materials, and other high-value-added products. Additionally, high shareholder returns from quality enterprises will continue on the path of revaluation, with attention to state-owned enterprises in oil and gas petrochemicals represented by the "three barrels of oil," coal chemicals, compound fertilizer industries, phosphorus chemicals, and leading white horses in the monosodium glutamate/feed amino acid industries.
Transportation: Spring, summer, autumn, and winter— not every season is suitable for sowing! 1. Insurance and passive capital prefer dividends, with a reduction in AH premium rates. 2. Container shipping: The U.S. inventory cycle is entering a recession, putting pressure on container shipping demand. 3. Oil shipping: Gradually moving towards compliance-driven growth. 4. Special transportation: The export of new three types of goods is driving demand for special transportation, with continued prosperity in special cargo exports. 5. Express delivery: Supply and demand are both approaching a turning point, with a historic moment in the competitive landscape imminent. 6. Aviation: Increasing passenger load factor by exchanging price for volume, with oil prices and exchange rates becoming supportive factors.
Public Utilities and Environmental Protection: Since 2025, the performance of the electricity index has been at a relatively low level compared to various industries. As of October 22, 2025, the Wind electricity sector has risen by 2.7% this year; during the same period, the CSI 300 index has increased by 16.7%. The environmental protection index has risen by 19.1% this year, ranking in the middle compared to other Wind primary industries, cumulatively outperforming the market by 2.4 percentage points. Recently, the implementation details of Document No. 136 have been largely finalized across provinces. Overall, Document No. 136 requires each province to formulate policies based on their own electricity market operations, showing a trend of regional differentiation in policy implementation. In terms of thermal power, the utilization hours of thermal power have decreased year-on-year due to the pressure from the growth of renewable energy generation. From January to September 2025, the cumulative power generation from thermal power decreased by 1.2% year-on-year. Regarding fuel costs, since 2025, the price of thermal coal has generally declined, gradually rebounding since mid-year. In summary, against the backdrop of an overall decline in thermal power utilization hours, the likelihood of a significant increase in thermal coal prices is low, and the profitability of thermal power is expected to be maintained.
FICC Investment Strategy
Interest Rate Bonds: In terms of operations, we believe that in a market environment where long-term interest rates are primarily fluctuating widely and the yield center may slowly rise in the medium term, it is not advisable to bet unilaterally on duration strategies. We recommend that investors focus on coupon strategies, using short-duration credit bonds as the base; at the same time, under the backdrop of the central bank's monetary policy still supporting the real economy, continue to moderately engage in interest rate arbitrage through leverage strategies; and appropriately supplement with more flexible long-end volatility operations to enhance returns, which is a better strategy.
Credit Bonds: This year, credit spreads have generally been at low levels, with significant characteristics of band fluctuations. Looking ahead to 2026, under the backdrop of overall weak financing demand and no significant increase in credit risk, credit spreads are expected to remain at low levels, with widening spreads from incremental events creating configuration opportunities. Specifically, the current compression of short-end spreads is more extreme, and in terms of configuration, more attention can be paid to high-spread compression opportunities for 5Y and above varieties. For urban investment bonds, attention should be paid to debt restructuring progress, and it may be appropriate to consider extending duration for high-quality entities and regions; for industrial bonds, focus on "distress reversals" for weaker quality entities after fundamental shifts; for financial bonds, utilize the high elasticity characteristics of perpetual bonds to capture more valuation fluctuation returns; and for Chinese overseas bonds, trade in line with the Fed's interest rate cut path. In terms of market timing, valuation pullbacks from incremental events still present configuration opportunities. Based on recent experiences from five rounds of pullbacks, it has been observed that after a pullback of over 30 basis points, active positioning can be beneficial.
Convertible Bonds: Looking ahead to 2026, we believe that convertible bond assets may still exhibit significant range fluctuation characteristics under the dual constraints of equity asset catalysis and high redemption probability. On one hand, due to the expected increase in equity asset returns and the inherent scarcity of convertible bonds, it is difficult for convertible bond assets to experience significant pullbacks; on the other hand, constrained by the overall increasing strong redemption probability of convertible bond assets and the continuously shortening average remaining maturity, the time value of convertible bond assets may further diminish, making it difficult for the market to price them at higher valuations. Therefore, we recommend paying attention to the fluctuations in convertible bond valuations and price centers, flexibly adjusting the allocation of convertible bonds to capture trading returns. For newly issued convertible bonds, in addition to actively subscribing in the primary market, continuous attention can still be given during the initial listing period, as there are statistical arbitrage opportunities.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




