Bitcoin was born quietly on Jan. 3, 2009, when its pseudonymous creator embedded a pointed message about bank bailouts into the first block of a brand-new blockchain. At the time, the financial system was reeling from a crisis, and Nakamoto’s Bitcoin network arrived as a radical alternative — decentralized, permissionless, and governed by code rather than committees.
In its earliest years, bitcoin (BTC) was more of a curiosity than currency. The first real-world transaction in 2010 — 10,000 BTC for two pizzas — has since become legend, not least because it highlights how little anyone understood what was coming. That same year also tested the Bitcoin protocol’s resilience when a critical software bug briefly allowed billions of bitcoins to be created, only to be swiftly fixed and reversed, preserving the network’s credibility.
By 2011, BTC crossed $1 for the first time and began attracting attention beyond cryptography circles. Its use on platforms like Silk Road brought notoriety, while exchange hacks and violent price swings introduced early lessons about custodial risk. Still, the system kept running, and the community kept building, even after Nakamoto quietly stepped away.
The first block reward halving in 2012 marked Bitcoin’s transition from experiment to engineered monetary system. The event reinforced Bitcoin’s fixed supply narrative and coincided with growing merchant adoption, including early acceptance by online platforms and mainstream cultural references that hinted this phenomenon was entering public consciousness.
Bitcoin’s breakout moment arrived in 2013. Prices vaulted from double digits to over $1,000, governments issued their first regulatory guidance, and the world’s first bitcoin automated teller machine (ATM) appeared. Law enforcement seizures and exchange failures made headlines, but so did Senate hearings that treated the crypto asset as something a bit more than a fringe novelty.
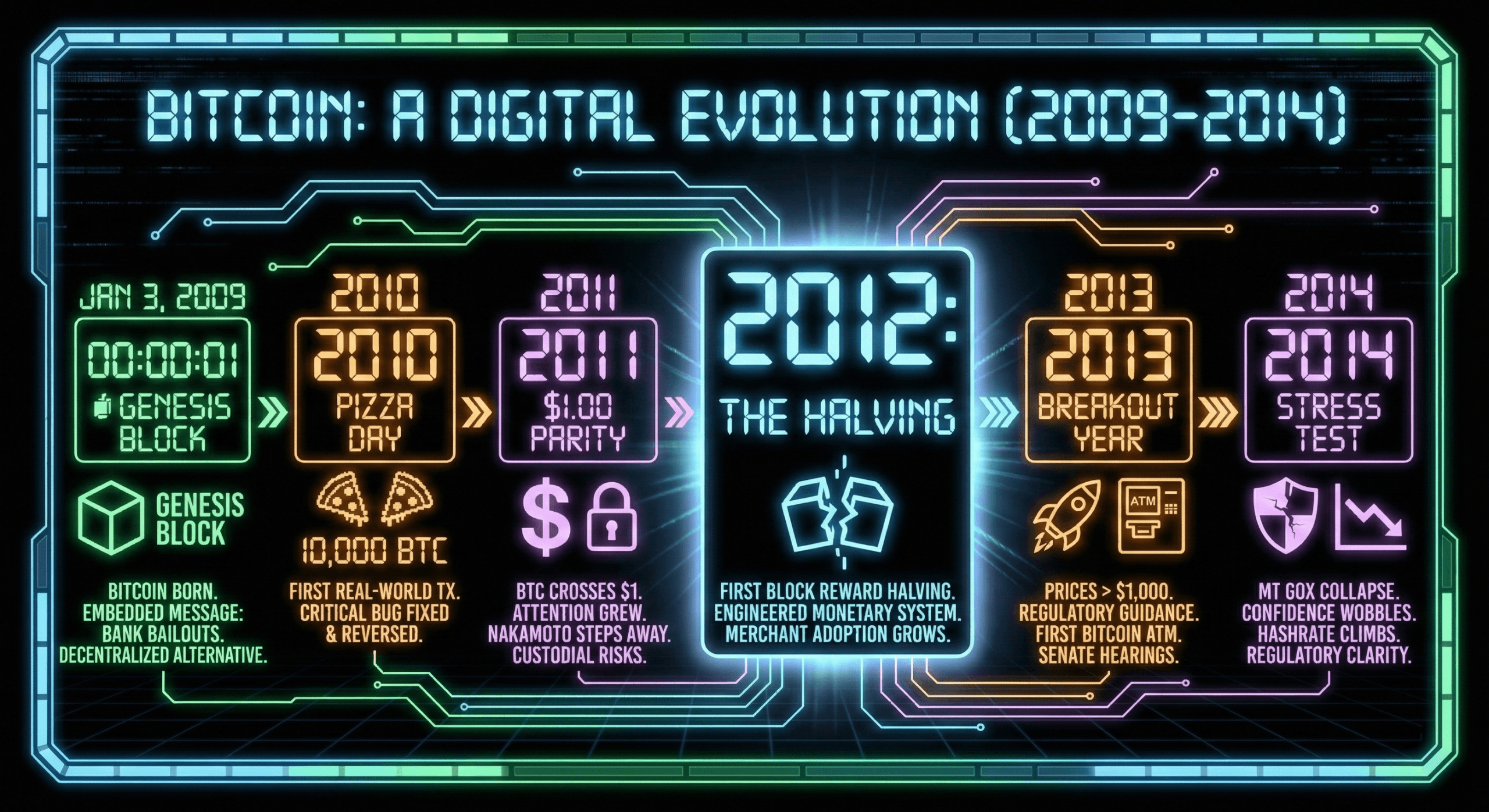
The collapse of Mt Gox in 2014 was a brutal stress test. Prices sank, confidence wobbled, and critics declared BTC was finished — again. Yet the network’s hashrate continued climbing, major retailers began accepting BTC, and regulators clarified tax treatment, laying the groundwork for a more mature ecosystem.
While prices drifted in 2015, development accelerated. Scaling debates intensified, second-layer ( L2) concepts took shape, and institutional venture funding signaled long-term interest. Bitcoin was no longer just surviving downturns; it was using them to evolve.
The second halving in 2016 tightened supply further as global uncertainties pushed investors to reconsider Bitcoin’s role. By 2017, the asset had erupted into mainstream finance. Japan recognized bitcoin for payments, and futures launched on major U.S. exchanges.
The 2018 crash erased nearly 80% of bitcoin’s value and flushed out speculative excess, forcing the ecosystem into a long, uncomfortable rebuild. While prices languished, development shifted toward incremental, behind-the-scenes work, exchanges tightened risk controls, and miners continued scaling operations, leaving bitcoin bruised but structurally intact and quietly setting the stage for its next market cycle.
Institutional doors opened wider in 2019 and 2020. Custody services, futures platforms, and treasury allocations redefined bitcoin’s image. Amid pandemic-era market chaos, Bitcoin never stopped producing blocks, and the third halving reinforced its contrast with expanding fiat supply. Corporate buyers and platforms like Paypal helped bring bitcoin to the masses.
In 2021, bitcoin hit new all-time highs, reached national currency status in El Salvador, and activated the Taproot upgrade. Even sharp midyear pullbacks failed to dent the network’s reliability, which maintained near-perfect uptime as mining power recovered from regulatory shocks.
Also read: Satoshi Nakamoto to Martti Malmi: The Correspondence That Shaped Bitcoin’s Early Days
The following year tested Bitcoin’s separation from broader crypto failures. While centralized firms like FTX collapsed and prices retreated, Bitcoin’s hashrate reached new highs, another country adopted it as legal tender, and regulators began crafting clearer frameworks that increasingly distinguished Bitcoin from riskier experiments.
Innovation returned to the spotlight in 2023 with Ordinals and renewed optimism around spot bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs). By 2024, that optimism became reality as U.S. regulators approved spot ETFs and Bitcoin’s fourth halving coincided with a move into six-figure prices, pushing market capitalization into rarefied territory.
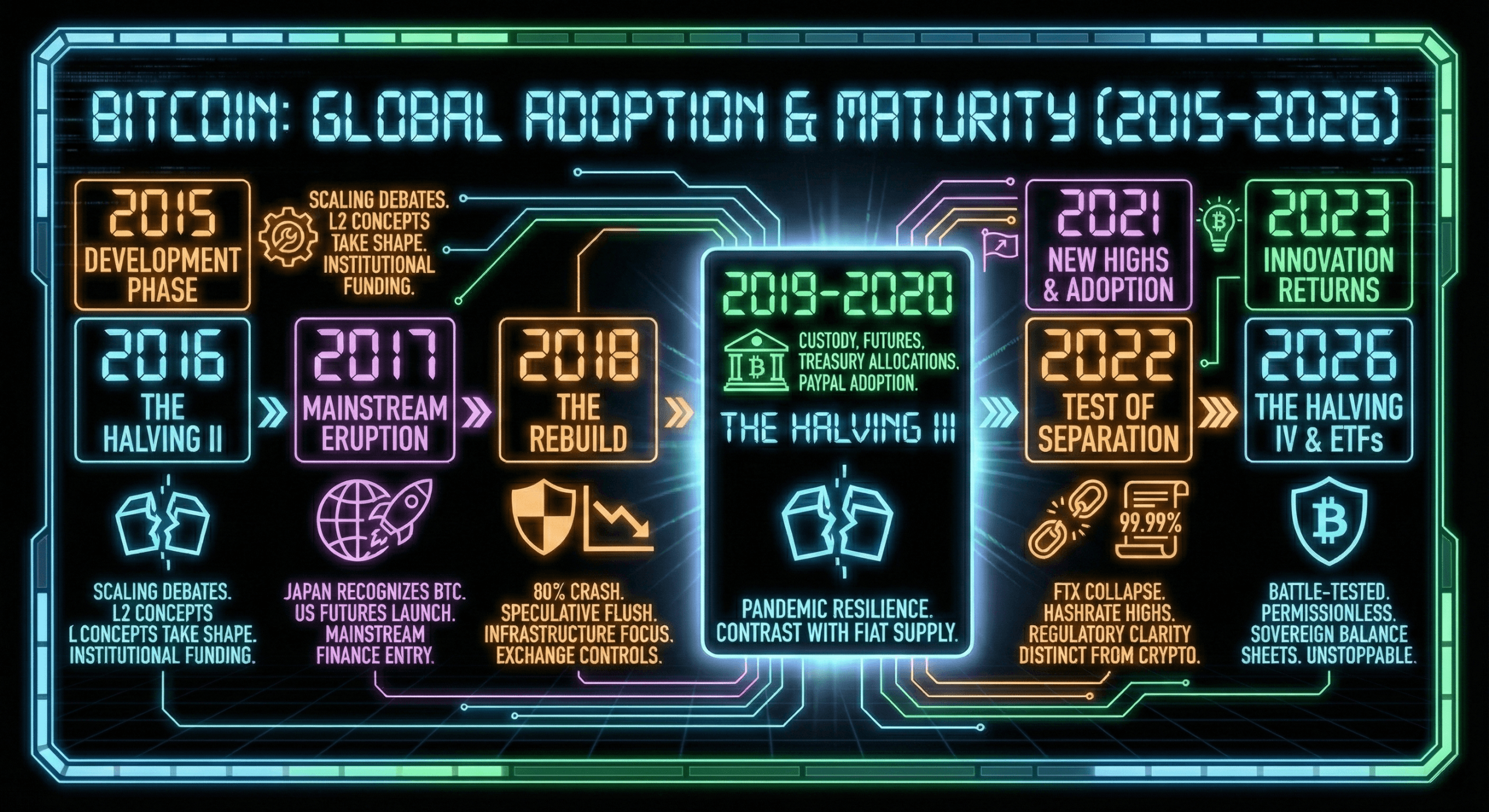
Throughout 2025, Bitcoin settled into a phase that once seemed impossible: relative stability. Institutional participation deepened, adoption expanded, and the network’s lifetime uptime hovered around 99.99%, rivaling critical internet infrastructure. What began as an outsider system had become embedded in global finance.
Now, on its 17th anniversary, Bitcoin stands as one of the most battle-tested monetary networks ever built. It has weathered hacks, forks, bans, bubbles, and busts — and kept producing blocks. From pennies to six figures, from mailing lists to sovereign balance sheets, Bitcoin has come a long way without asking anyone’s permission.
- What happened on Jan. 3, 2009?
Bitcoin’s genesis block was mined, officially launching the network and embedding a message about bank bailouts. - Why is Bitcoin’s 17th anniversary important?
It marks nearly two decades of continuous operation for a decentralized financial network. - How reliable has the Bitcoin network been?
Bitcoin has maintained roughly 99.99% uptime across its entire history. - What role do institutions play in Bitcoin today?
ETFs, corporate treasuries, and asset managers now hold and offer bitcoin at scale.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




