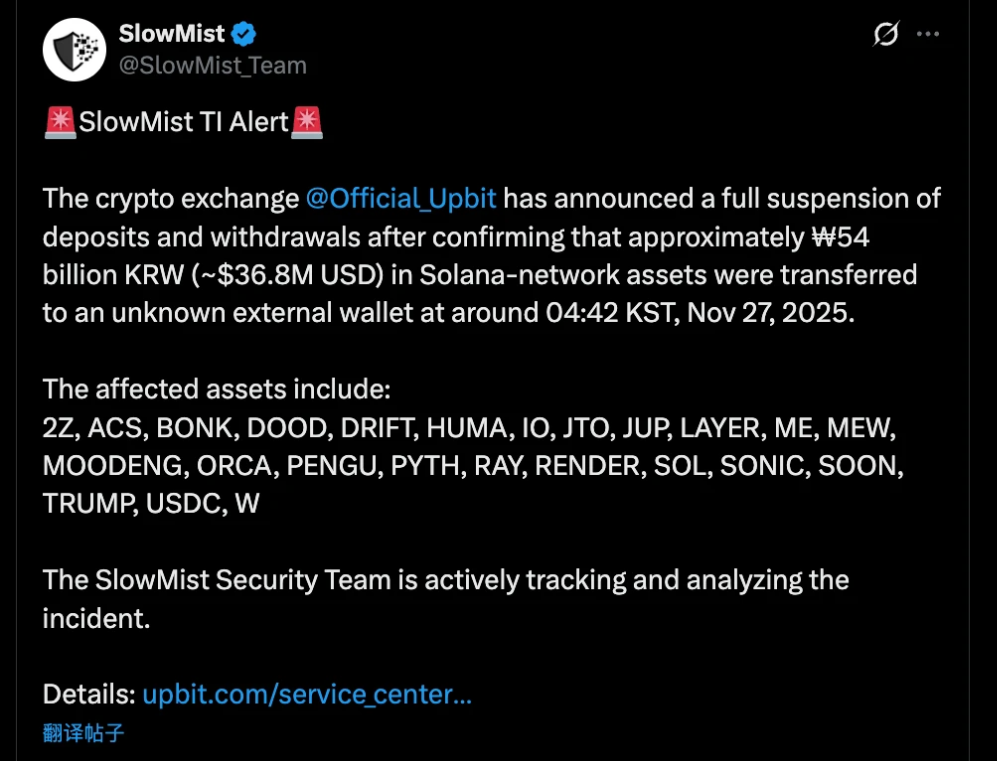
South Korea's largest cryptocurrency exchange, Upbit, has encountered a significant security vulnerability on the Solana chain, resulting in the theft of cryptocurrency assets worth 54 billion KRW (approximately 36 million USD) within minutes. This marks the second major security incident for the exchange in six years.
At 4:42 AM local time on November 27, while most South Koreans were still asleep, a transaction worth 54 billion KRW (approximately 36 million USD) rapidly transferred cryptocurrency assets from Upbit's Solana hot wallet to an unknown external wallet.
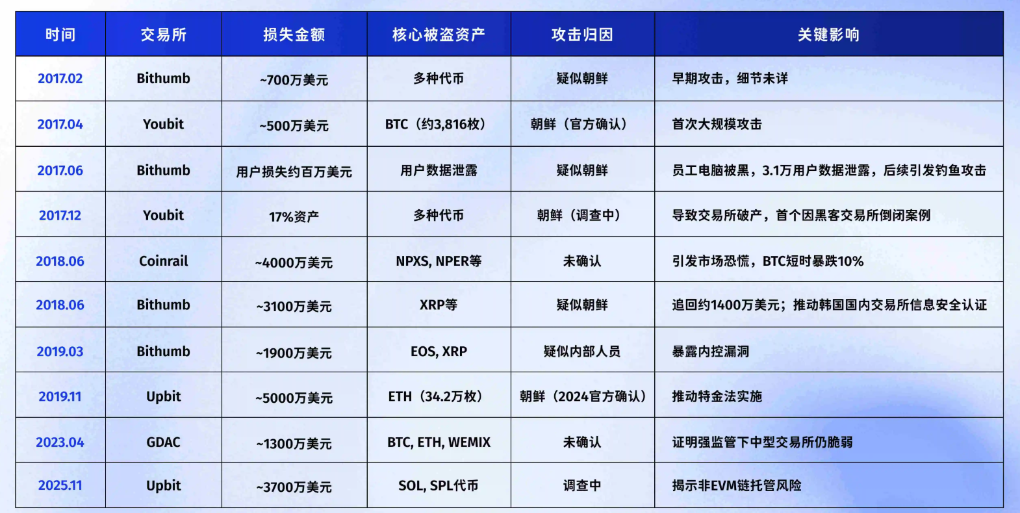
As the largest cryptocurrency exchange in South Korea, Upbit controls over 80% of the country's cryptocurrency trading market. This incident not only recalls the exchange's experience in 2019 when it lost nearly 50 million USD due to an attack orchestrated by the North Korean hacker group Lazarus, but coincidentally, this hacking attack occurred the day after Upbit's parent company Dunamu reached a 10.3 billion USD acquisition agreement with Naver.

1. Hot Wallet Private Key Leakage
The management of hot wallet private keys has become the weakest link in digital asset security. The 2025 theft of Upbit's Solana hot wallet has once again exposed this long-standing security risk.
● Security experts analyze that the "all at once" nature of the attack indicates that the attackers likely gained access to the private key permissions of Upbit's Solana ecosystem hot wallet or that the signing server was directly compromised.
● This is not the first time hot wallets have been targeted by hackers. In 2020, KuCoin also lost approximately 281 million USD due to hot wallet private key leakage. This incident stemmed from a hacker infiltrating an employee's computer, leading to the theft of private keys. After arduous asset recovery efforts, KuCoin ultimately recovered most of the stolen funds, but the vulnerabilities exposed in hot wallets were shocking.
● The 2018 hack of Japanese exchange Coincheck, which resulted in a loss of 530 million USD, serves as a painful lesson. The exchange stored private keys on unencrypted servers and did not implement multi-signature protection, leading to one of the largest cryptocurrency thefts in history.
● The security risks associated with hot wallet private keys mainly stem from two aspects:
Technical level storage issues, such as storing private keys on connected servers without encryption;
Management level process vulnerabilities, including employees falling victim to phishing attacks and chaotic internal permission management.
2. Internal Management and Process Vulnerabilities
● The 2025 Bybit exchange cold wallet anomaly shocked the entire cryptocurrency industry. Surprisingly, the security issue involving the cold wallet was not a traditional external hacker attack but exposed serious flaws in the exchange's internal management.
● Security audit reports revealed that a senior manager at Bybit became a target of a social engineering attack. The attacker, disguised as a company executive through a carefully crafted phishing email, tricked the employee into executing unauthorized cold wallet operations.
● Even more concerning, in the 2018 loss of 170 million USD at BitGrail, the exchange's founder Francesco Firano was accused of possible embezzlement. An Italian court later ruled that Firano had grossly mismanaged the exchange's funds, leading to significant losses for thousands of users.
● Internal process vulnerabilities typically manifest as: unclear permission allocation, allowing employees to unilaterally complete large asset transfers; lack of effective dual-review mechanisms, where key operations do not require multiple authorizations; insufficient social engineering defense capabilities, with employees lacking vigilance against new types of online scams.
● Blockchain security expert Zhang Kai pointed out: "Many exchanges invest substantial resources in technical defenses but neglect the most basic internal control management. In fact, over 40% of cryptocurrency security incidents are related to internal management vulnerabilities."
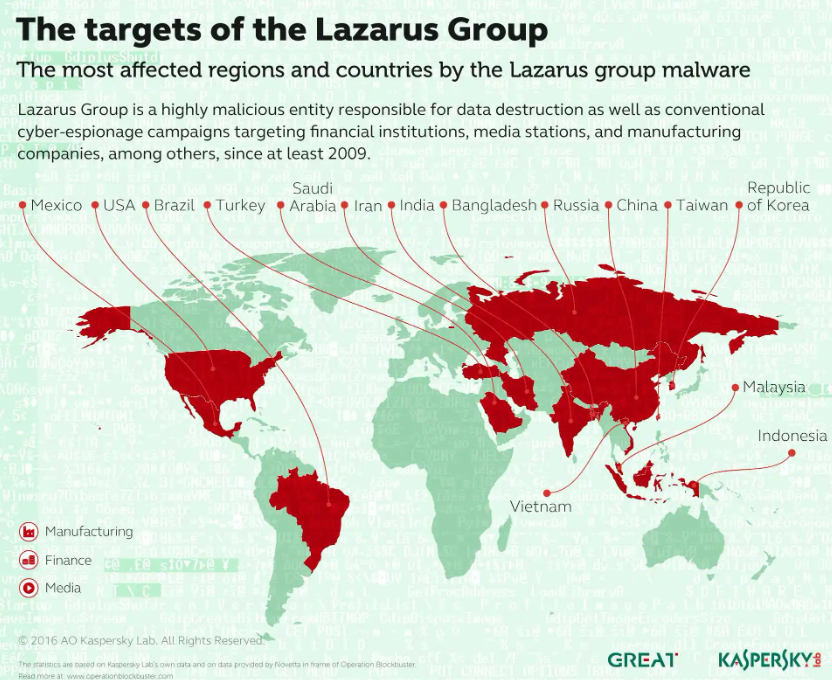
3. Attacks by State-Sponsored Hacker Organizations
The security threats faced by cryptocurrency exchanges have evolved from isolated hacking incidents to organized, state-sponsored systematic attacks.
● The 2025 attack on Bybit has been identified by multiple security agencies as possibly being the work of North Korea's Lazarus group. This assessment is based on the specific tools and tactics used in the attack, which closely align with known Lazarus attack patterns. This organization is known for its high level of organization and persistence, often combining social engineering, zero-day exploits, and customized malware in its attacks.
● Upbit is no stranger to state-sponsored hacker organizations. In the 2019 attack, the North Korean Lazarus group successfully obtained key credentials from Upbit employees through carefully designed phishing emails, subsequently using these credentials to initiate an asset transfer of nearly 50 million USD. This incident prompted Upbit to undertake comprehensive security upgrades, but clearly, the attackers' tactics are continually evolving.
● The 2023 theft of 120 million USD from Poloniex was also attributed to a state-sponsored hacker organization. On-chain analysis revealed that after the attack, the perpetrators employed highly complex money laundering techniques, including the use of cross-chain bridges and decentralized exchanges, making it exceptionally difficult to trace the funds.
● The characteristics of attacks by state-sponsored hacker organizations are very distinct: high levels of organization and persistence, with attack activities often lasting months or even years; multi-stage, multi-method combined attacks, forming a complete attack chain from intelligence gathering to exploit utilization; clear strategic objectives, primarily aimed at acquiring funds to support national economic activities.
4. Vulnerabilities in DeFi and Cross-Chain Bridges
With the rapid development of DeFi and cross-chain ecosystems, new security threats have emerged. The 2022 attack on Binance's cross-chain bridge resulted in a loss of 570 million USD, shocking the entire industry.
● This incident stemmed from hackers exploiting a flaw in the verification logic of the cross-chain bridge's smart contract, forging asset proofs to steal substantial funds. This vulnerability was not a traditional coding error but a system design-level logical flaw, allowing attackers to bypass normal security checks.
● As a hub connecting different blockchains, the security of cross-chain bridges directly impacts the stability of the entire ecosystem. Current major security threats to cross-chain bridges include: smart contract vulnerabilities, especially those in new projects that have not been thoroughly audited; control of validation nodes, leading to false transactions being confirmed; deficiencies in economic model design, which may be exploited for arbitrage or attacks.
● DeFi security expert Li Mingxia stated: "Cross-chain bridges have become a new 'ATM' for hackers. In 2023 alone, losses related to cross-chain bridges exceeded 800 million USD, and this figure may continue to rise in 2024."
5. Inherent Vulnerabilities in Exchange Systems
● Systemic vulnerabilities in cryptocurrency exchanges are a long-standing industry problem. From the 2014 collapse of Mt. Gox, which resulted in an 8.5 billion USD loss, to recent multiple security incidents at Bithumb, similar types of vulnerabilities have been repeatedly exploited.
● The Mt. Gox incident is the most severe security disaster in cryptocurrency history, fundamentally caused by complete mismanagement of private keys and long-term unaddressed system vulnerabilities. Subsequent investigations revealed that the exchange did not even have a dedicated security team, and basic cybersecurity measures were not implemented.
● The South Korean exchange Bithumb has historically suffered multiple hacker attacks, with the most recent occurring in 2023, resulting in a loss of approximately 7 million USD. Security audits found that the exchange had fundamental security issues, such as insufficient network isolation and weak monitoring systems.
● The main manifestations of inherent vulnerabilities in exchange systems include: lack of infrastructure security, such as not deploying firewalls or intrusion detection systems; insufficient security monitoring capabilities, failing to detect abnormal trading behavior in a timely manner; inadequate emergency response mechanisms, unable to quickly address issues once identified.

In the blockchain industry, there is no myth of "absolute security." Upbit, as South Korea's largest exchange, was compromised by hackers due to security vulnerabilities at a critical moment in the 10.3 billion USD acquisition case, once again proving this point. From hot wallet private key leakage to state-sponsored hacker attacks, from internal management vulnerabilities to inherent system flaws, every aspect of exchange security protection faces severe challenges.
In the world of digital currency, security is always a shared responsibility for everyone.
Join our community to discuss and become stronger together!
Official Telegram community: https://t.me/aicoincn
AiCoin Chinese Twitter: https://x.com/AiCoinzh
OKX benefits group: https://aicoin.com/link/chat?cid=l61eM4owQ
Binance benefits group: https://aicoin.com/link/chat?cid=ynr7d1P6Z
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




