The walls of traditional systems are gradually crumbling, and the era of blockchain has already set sail.
Author: blocmates.
Translated by: ShenChao techFlow
If history can serve as a reference, freedom will always find a way to prevail. In this field, betting on privacy ultimately means betting on freedom.
Hey! Let me tell you, if you have on-chain investigation capabilities at the level of ZachXBT (plus a bit of patience), crypto transactions can be tracked—though you already knew that, right?
Nowadays, we can find out whether it was your 78-year-old grandma who emptied your wallet or a hacker group linked to North Korea threatening every protocol.

Yes, these so-called "bad" cases do exist, but their emergence is merely because on-chain activities are publicly visible to everyone. Surprised? Public chain ledgers are indeed public.
Crypto and Privacy
Perhaps today's young people do not understand, but those seasoned players (Uncs) know that the journey of Bitcoin and the entire cryptocurrency landscape today began with the vision of the Cypherpunks—to build an open society based on privacy.
It is this idea that gave birth to David Chaum's privacy digital currency Digicash (based on blind signature technology) and Wei Dai's proposed anonymous decentralized payment system b-money (sounds like a rapper's name, right?).
Satoshi Nakamoto took it a step further by embedding a degree of privacy protection within a completely transparent ledger. The design of Bitcoin relies on pseudonymous addresses and cryptographic hash values rather than real names or identities, creating an illusion of anonymity.
However, this illusion of anonymity did not last long. With the rise of smart contracts, attention gradually shifted from privacy to on-chain programmability.
Now, as the popularity of cryptocurrencies accelerates once again, we have returned to the starting point of it all—the primary principle of privacy.
In the crypto space, privacy is becoming an important topic, encompassing not only the sending and receiving of funds on public chains but also the privacy protection of on-chain applications.
In today's article, we will explore what privacy means in the crypto space, its various aspects, products built around privacy, points to pay attention to, and our views on the future of crypto privacy.
Please fasten your seatbelts and get ready to take off!
What Does Privacy Mean in Cryptocurrency?
The best way to understand privacy is to examine it from the perspective of traditional finance (TradFi).
In traditional finance, the meaning of privacy is simple: personal data is protected and not made public, visible only to authorized entities. This includes users' personal information, such as biometric data, transaction history, account balances, etc.
When we bring this concept into the crypto space, the core of privacy lies in protecting personal data in on-chain transactions. True privacy means that only the user themselves or designated recipients as authorized entities can view or understand their own data.
In the crypto space, people often confuse privacy with anonymity. While the culture of anonymity stems from the concept of privacy, the two technically differ.
For example, the focus of privacy is on hiding the details of transactions, such as the amount transferred from one person to another, the counterparties, and other information; whereas anonymity is more concerned with hiding the identity of users in transactions.
A clear distinction between privacy and anonymity can be seen in Zcash and Monero. The former primarily relies on cryptographic technology, using zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Arguments of Knowledge) to hide transaction amounts; while the latter obfuscates addresses and uses ring signature technology to pseudo-anonymize user identities.
However, for the purposes of this article, we will consider privacy as an overarching phenomenon that includes anonymity.
Why is Privacy an Important Topic in the Crypto Space?
As mentioned earlier, the foundation of the crypto industry stems from the spirit of the Cypherpunks, which pursues privacy and decentralization to achieve freedom from state-level control.
However, with the rapid expansion of private surveillance companies and their powerful influence in the financial sector, coupled with concerns over data misuse brought about by AI technology, the alarm bells are ringing louder than ever.

Without privacy, data on the blockchain could expose users' spending habits, wealth distribution, political donations, and counterparty relationships. If this data falls into the wrong hands, it could be used for extreme control or exploitation.
Another crucial reason why privacy is vital in the crypto space is that without the support of privacy technologies, cryptocurrencies cannot truly achieve censorship resistance. Privacy can protect individuals and organizations from coercion, enabling genuine permissionless participation in on-chain financial systems.
Moreover, privacy can ensure the safety of users in real life and the security of assets on-chain. Especially in a public transaction graph, high-value targets are easily susceptible to hacker attacks, extortion, or even personal threats—many such cases have occurred recently.
Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs)
There are various implementations of privacy-enhancing technologies, each designed for specific use cases, but their ultimate goal is consistent: to provide privacy and security guarantees for end users.
Different technological paths have their own advantages, disadvantages, and applicable scopes. Below, we will introduce several major privacy-enhancing technologies and their working principles in non-technical language.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZK)
As the name suggests, the core of this technology is to prove that something is true without revealing the underlying details or data.
Zero-knowledge proofs involve two key participants:
Prover: Proves that a statement is true.
Verifier: Confirms the truth of the statement without accessing the underlying data.
As a privacy-enhancing technology in the crypto space, there are two main forms of zero-knowledge proofs:
zkSNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Arguments of Knowledge)
zkSTARKs (Zero-Knowledge Scalable Transparent Arguments of Knowledge)
Zero-knowledge proofs support various privacy-protecting applications, including but not limited to:
Confidential Transactions: Hiding transaction amounts to protect financial privacy.
Asset Proofs: Proving solvency without exposing addresses or sensitive data.
Privacy-Preserving Authentication: Applicable to decentralized identity systems (DID).
Private Smart Contracts: Enabling privacy-protected on-chain contract interactions.
Ring Signatures and Ring Confidential Transactions: A Strong Backbone for Anonymity
If you've heard of privacy coins with built-in or default privacy features, most of them utilize ring signature technology. A typical example is Monero, a cryptocurrency known as a "veteran in the privacy coin space."
The working principle of ring signatures allows users to sign transactions within a group without revealing the specific identity of the signer. By obfuscating the source of transactions, ring signatures effectively hide the identity of the sender.
This technology is particularly useful for anonymity, allowing users to transact on-chain without worrying about being tracked by on-chain analysts like ZachXBT.
From this perspective, it is not hard to understand why Monero faces so many compliance challenges, such as being delisted from exchanges or encountering other regulatory issues.
In contrast, Zcash offers two options: transparent addresses (t-address) and privacy-protecting addresses (z-address). Centralized exchanges can choose to support only fully transparent ZEC transactions to meet compliance requirements.
Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE): The Ultimate Weapon for Privacy Protection
Remember the scene in school where you secretly passed notes? If you conveyed information using a mix of letters and numbers in an encrypted note that only your friend could decrypt, you were already exposed to the concept of fully homomorphic encryption.
FHE is a cryptographic privacy-enhancing technology that allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without decrypting it. This means users can securely transmit sensitive information without worrying about the verifier seeing the data.
While FHE leans more towards privacy protection rather than solving anonymity issues, it is undoubtedly one of the most powerful technologies for on-chain privacy protection.
Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs)
If you are a loyal reader of blocmates, you may already be familiar with TEEs. If needed, you can revisit our previous article dedicated to discussing TEEs.
In simple terms, a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) is a hardware-based privacy-enhancing technology (PET) that protects the confidentiality and integrity of data within a secure area (also known as a secure enclave) in a processor or network through encryption keys.
A common example is the facial recognition feature on smartphones. When you set up facial recognition, the device captures your facial features through the camera, encrypts the data, and securely transmits it to the TEE for processing. The captured biometric data never leaves the TEE unprotected.
Within the TEE, the raw facial data is converted into a template, which is a mathematical representation of your unique facial features, and is securely stored in the secure enclave for future authentication.
Multi-Party Computation (MPC)
In the crypto space, certain activities require collaborative computation, and Multi-Party Computation (MPC) is a cryptographic privacy-enhancing technology specifically designed for such scenarios.
For example:
An AI product that relies on multiple AI inferences to optimize output.
A decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) conducting governance voting without wanting to disclose individual decisions.
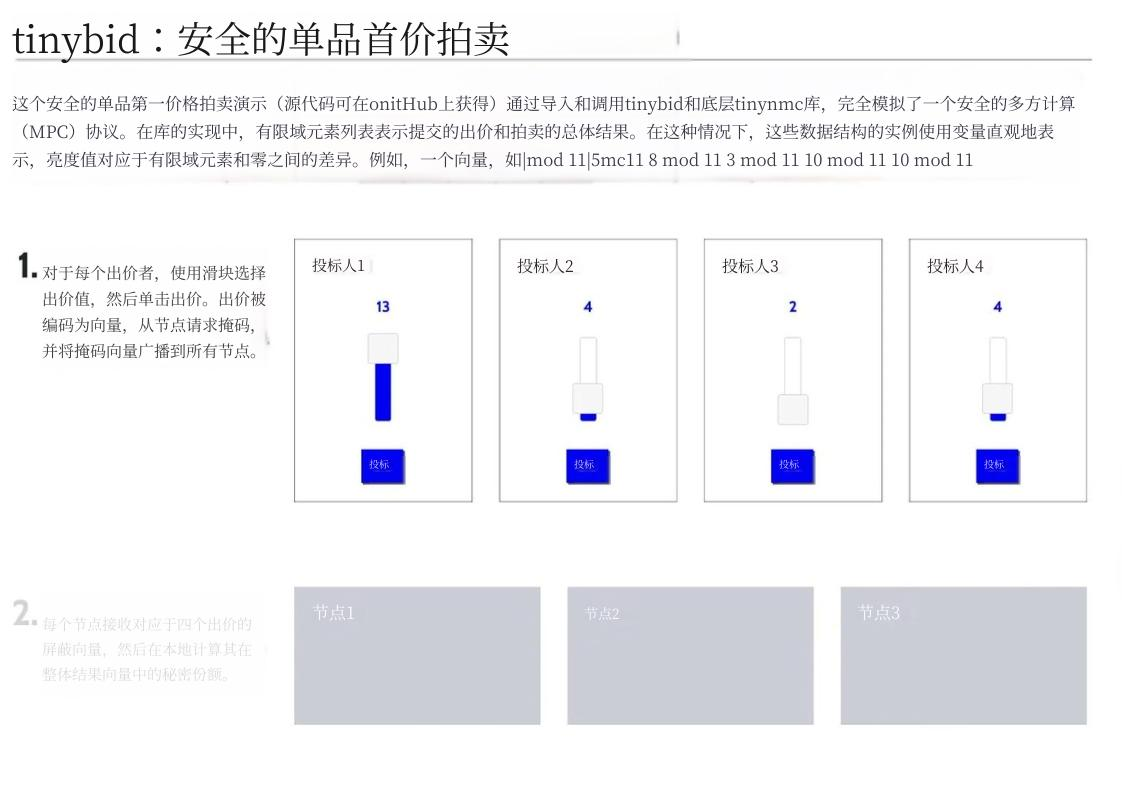
An on-chain auction activity, such as the experimental case of Nillion.
MPC allows multiple parties to collaboratively compute a function (such as signing a transaction or verifying a balance) without revealing their individual inputs. This technology ensures the privacy of each party's data while achieving collaborative computation goals.
In addition to the privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs) we have already mentioned, there are other technical means, such as coin mixers, homomorphic encryption, and composable privacy. These technologies provide stronger protection by combining various privacy tools.
In the crypto space, some projects focus on directly developing products based on these cryptographic technologies, while others are dedicated to building underlying privacy infrastructure that supports crypto applications.
Key Projects in Building Privacy Infrastructure
In the crypto space, privacy protection is not a "one-size-fits-all" solution. Different projects and teams often focus on specific aspects of PETs to support particular application scenarios and needs.
Here are some noteworthy projects in the field of privacy infrastructure.
Nillion
We previously discussed Nillion's technology and its application scenarios in detail; if you want to learn more, you can refer to related articles.
In short, @nillion's infrastructure focuses on achieving decentralized trust for sensitive data.
Nillion's core technology—"Blind Computer"—protects sensitive data through various privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs), specifically including:
Multi-Party Computation (MPC): Used for its NilDB database.
Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs): Used for AI inference (such as NilAI and NilCC).
Additionally, Nillion has developed several innovative consumer applications based on its infrastructure, which we will detail in the following sections.
Succinct
@SuccinctLabs' airdrop event brought joy to some and disappointment to others, but its technology is definitely worth paying attention to.
Succinct Labs is dedicated to promoting zero-knowledge proofs (ZK Proofs) through its technology and has built a technical framework that can verify any software. Although this technology is not entirely privacy-centric, its flagship product—SP1 ZK Virtual Machine—can be used to provide client-side privacy protection. For example, in the case of Hibachi, the public order flow is hidden, but the central operator (Hibachi) can still see everything.
Zama
@zama_fhe is at the forefront of technology based on Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE), dedicated to supporting the development of confidential applications.
Zama has built a technology that supports confidential blockchain protocols, capable of integrating with Solidity-based networks to enable the following privacy applications:
Privacy-based decentralized exchanges (DEX) for token swaps.
Confidential lending protocols.
Asset tokenization with embedded privacy features.
Zcash
To be honest, Mert could run for the annual opinion leader (KoL) award for his successful promotion of @Zcash (ZEC).
As an OG project in the privacy space, Zcash is a pioneer in peer-to-peer private payments using zero-knowledge encryption (ZK Encryption).
Zcash utilizes zkSNARKs technology to achieve optional transparent privacy transactions. While the technology appears relatively simple, combined with its imitation of Bitcoin's token economic model, it is easy to understand why it has become an alternative to Bitcoin for those who still believe in the spirit of the Cypherpunks against the backdrop of renewed privacy demand.
Monero
In addition to attracting a fervent following due to its token (XMR), @monero is also a privacy technology project worth noting.
Monero achieves complete transaction privacy through three cryptographic technologies:
Ring Signatures: Hides the true sender's identity by mixing the real sender's signature with a set of decoy signatures extracted from the blockchain.
Stealth Addresses: Generates a unique one-time public key address for each incoming transaction, preventing any association between the receiving wallet and the payment.
Ring Confidential Transactions (RingCT): Uses cryptographic commitments and range proofs to hide transaction amounts while allowing the network to verify that inputs equal outputs, ensuring no tokens are created out of thin air.
Unlike Zcash, Monero's privacy features are not optional but mandatory. This means that all transactions on Monero are completely hidden, with no concept of "selective privacy" or "shielded transactions."
However, this enforced privacy has also provoked hostility from regulators, leading to Monero being delisted from many compliant centralized exchanges.
Arcium
Remember we mentioned that some products understand privacy is not a "one-size-fits-all" approach, especially at the infrastructure level?
Yes, @Arcium is a great example.
Arcium is a multi-party computation network that has built several protocols on top of it, including:
Cerberus Protocol: A general-purpose protocol with a unique security model.
Cerberus adopts a "dishonest majority" trust model, equipped with cheat detection and identifiable abort mechanisms.
This means that as long as one node is honest, privacy can be guaranteed.
If a node is found to be dishonest, it will be identified, kicked out of the network, and penalized (reduced stake).
Notably, protocols like Cerberus typically operate under an "honest majority" trust model, requiring 51% or more nodes to be honest, while Cerberus's model is more flexible and reliable.
Manticore Protocol: Designed specifically to support AI use cases.
Although Manticore's security assumptions are not as unique and robust as Cerberus, it still plays an important role in specific scenarios.
Manticore is suitable for permissioned environments, supporting AI training in trusted settings to meet specific needs.
Similar to Nillion, Arcium's technology has also supported some impressive consumer applications, which we will further explore in the following sections.
Core Consumer Projects Driven by Privacy Technology
The allure of crypto privacy lies in the fact that we do not need to abstractly discuss those complex technical backends, especially since we cannot "play around" with these underlying technologies like developers do.
But the final products—the consumer products built on these infrastructures—are what we can directly experience. Here are some applications built on privacy technology:
Hibachi: Privacy-Supporting Perpetual Contract Trading
Not everyone wants their positions or liquidation records to be public.
If you remember the incident involving James Wynn (whether as a pawn in a larger conspiracy or a genuine event), he was "hunted" and liquidated due to his publicly visible position on Hyperliquid. This situation indicates that privacy is indeed necessary in on-chain perpetual contract trading.
@hibachi_xyz is addressing this issue by using Succinct's zero-knowledge proof technology (SP-1) and Celestia's data availability (DA). It employs a novel architecture that integrates on-chain and off-chain components, where Succinct verifies the central limit order book (CLOBs) in Celestia's Blob data.
As an application in the privacy space, Hibachi also optimizes trading execution speed, with latency as low as 5 milliseconds. There is currently no token issuance, making it a project worth watching.
NilGPT: Privacy-Supporting AI Chatbot
To be honest, sometimes AI can feel "creepy," especially when it refers to itself using personal pronouns.
However, AI technology itself is indeed very cool, particularly with the various innovative attempts people make in prompting.
Yet, many people tend to overshare when interacting with AI chatbots, forgetting that centralized software may be lurking behind those inferences, such as products like ChatGPT, Gemini, and even Grok.

@nilgpt_ is a privacy-focused AI chatbot built on Nillion's confidential computing infrastructure, designed to ensure the security of users' conversations and data without collecting or exposing personal information.
NilGPT utilizes Nillion's Blind Compute layer to encrypt and process data on distributed nodes, ensuring that no single entity can access plaintext input or output data, thus achieving true privacy protection.
Railgun: On-Chain Ecosystem Based on Privacy Technology
If you wish to achieve anonymity on the blockchain, @RAILGUN_Project is a project worth paying attention to (just a whisper, this is a privacy solution supported by Vitalik).
Railgun is an on-chain ecosystem based on zero-knowledge (ZK) privacy, serving as a smart contract system compatible with Ethereum chains, allowing users to conduct private transactions and DeFi interactions without sacrificing security and composability.
Railgun is fully decentralized, governed by the Railgun DAO, and uses zk-SNARKs technology to implement on-chain encrypted balances, transactions, and smart contract executions, supporting multiple chains including Ethereum, Polygon, BSC, and Arbitrum.
It is important to note that, unlike traditional coin mixers, Railgun provides complete anonymity through zero-knowledge cryptography while seamlessly integrating with existing decentralized applications (dApps) and liquidity protocols.
Privy Home: Wallet Infrastructure
To be honest, Privy can be considered one of the most market-demand-driven products in the crypto space. Its product Privy Home is a secure control layer and unified management center for managing embedded wallets in crypto applications. Developed by @privy_io, Privy Home serves as wallet infrastructure, providing robust support for on-chain experiences, helping users easily and securely manage multiple wallets and applications.

Privy enables users to track, manage, and oversee assets from multiple applications on a single platform. By providing security through key sharding and Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs), Privy achieves enhanced self-custody and interoperability, making wallet management more convenient while avoiding exposing keys to applications.
Umbra
This year, Solana has become the de facto home for on-chain entertainment, where users have earned substantial profits while attracting more attention and scrutiny.
Therefore, products like @UmbraPrivacy are particularly important.
Umbra is a privacy protocol that provides "stealth mode" for Solana transactions, enabling on-chain private transfers through Arcium's confidential network, bringing true financial privacy to users.
Currently, Umbra has launched private transfer features and plans to continue building a more complete Solana privacy DeFi hub. Future plans include private swaps, Solana-Zcash bridging, and an SDK for native integration of privacy features for wallets and other applications.
If you are an "observer" who enjoys peeking into wallets, you might find Umbra off-putting; but if you are a crypto player yourself, Umbra may excite you.
Zashi App
If you have been "enlightened" to start purchasing $ZEC and privacy issues are becoming increasingly important, what’s next?
Why not download and use @zashi_app directly! This is a mobile wallet designed specifically for Zcash, developed by Electric Coin Co. (ECC)—the very team behind the launch of Zcash in 2016. Zashi focuses on shielded, privacy-protecting transactions.
Zashi is a self-custodial application that allows users to send, receive, and use $ZEC without intermediary, government, or corporate surveillance.
By default, Zashi's transactions are shielded, utilizing Zcash's zero-knowledge encryption technology to achieve end-to-end privacy protection, providing the most convenient entry for peer-to-peer payments.
To be honest, I downloaded this app myself, and it feels very smooth. So, maybe you can give it a try?
While there are many consumer products based on privacy technology worth exploring, we will pause here to accommodate our readers with shorter attention spans. Next, we will share our thoughts on all of this.
Conclusion
The walls of traditional systems are gradually crumbling, and the era of on-chain has already begun.
Although the pace of adoption seems slow, the process of going from nothing to something is always the hardest, and the leap from "one" to "ten" often happens much faster.
What I mean is, as on-chain technology continues to advance, even your grandmother might start using on-chain services, making privacy issues—whether hers or yours—critically important.
We firmly believe that privacy is not just a "nice-to-have" feature but an indispensable core. It should not be treated as an afterthought but should become an important cornerstone of your short-term and long-term planning.
The infrastructure is already being built, with some already online, and as applications emerge, these products are proving the potential of privacy.
To keep up with this trend, you need to pay attention to solutions that can achieve deep integration, finding an "ultimate fix" like AWS, or at least enabling you to be a truly "anonymous John Doe" on-chain.
If history serves as a reference, the power of the pursuit of freedom will always prevail. In the blockchain space, betting on privacy is betting on freedom.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




