On-chain AI is expanding the crypto space to potentially billions of AI-driven participants.
Author: Jonathan King
Translation: Deep Tide TechFlow
Abstract
The fusion of cryptography and artificial intelligence is giving rise to a thriving on-chain AI economy, an ecosystem of blockchain applications and services driven by autonomous AI agents. Over the past 18 months, decentralized AI projects have received significant funding and rapid growth, but we believe that on-chain AI is rapidly emerging, marking the next wave of innovation in this cross-disciplinary field. The significance of on-chain AI lies in its ability to expand the crypto space to potentially billions of AI-driven participants. Each autonomous AI agent acts like a new "user" on the blockchain, capable of operating around the clock and making complex decisions, thereby significantly driving on-chain activity and growth.
By investing in on-chain AI, Coinbase Ventures is supporting the builders of this future agent-based economy, paving the way for a new "Agentic Web."
Coinbase Ventures portfolio companies mentioned for the first time in the following article will be marked with an asterisk (*).
In October 2024, Coinbase Ventures released a theoretical framework on the fusion of crypto and AI, highlighting the complementary advantages of blockchain and AI—blockchain provides decentralization, censorship resistance, verifiability, and user ownership, while AI brings powerful data processing, reasoning, and automation capabilities. We believe this synergy can fundamentally change the way humans and machines interact in the digital economy, ultimately giving rise to an "Agentic Web," where AI agents operate on cryptographic infrastructure, driving significant economic activity and growth.
A key distinction is between decentralized AI and on-chain AI. Decentralized AI ("Crypto → AI") refers to the construction of general AI infrastructure that inherits the openness and peer-to-peer characteristics of blockchain networks. This includes efforts to democratize the use of computing resources, data, models, and training, avoiding the monopolization of AI development by a few large companies. These decentralized AI resources also support on-chain AI ("AI → Crypto")—on-chain AI is an ecosystem of applications and services that embed AI into new and existing blockchain use cases (e.g., trading agents, on-chain portfolio managers, DeFi abstractions, etc.). While decentralized AI projects have received substantial funding and growth over the past 18 months, we believe that on-chain AI is rapidly emerging, marking the next wave of innovation in this cross-disciplinary field.
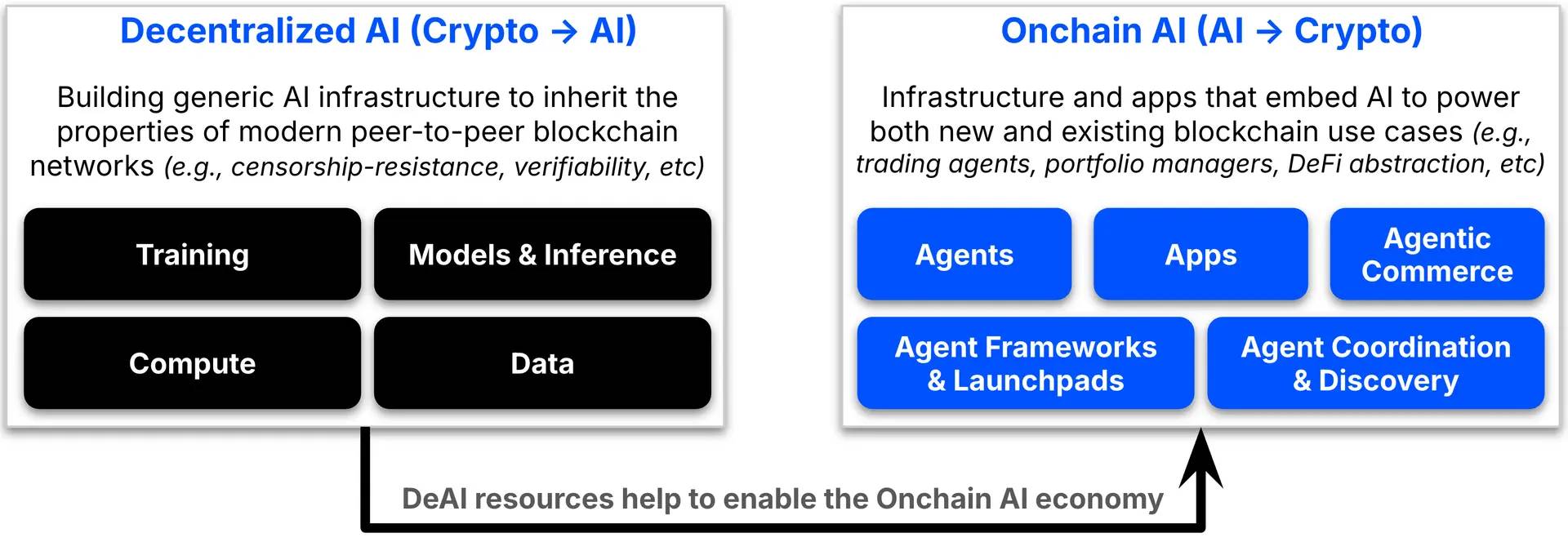
Introduction to On-chain AI
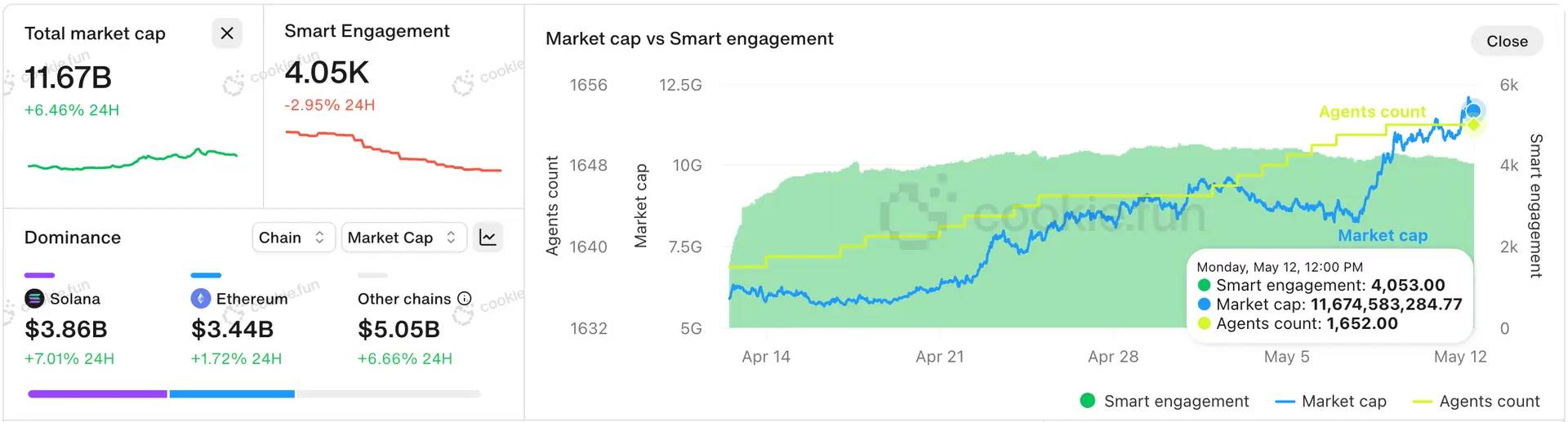
In the past year, we have witnessed an AI agent (such as Truth Terminal) equipped with a self-custody wallet, creating an internet-native religion and launching a meme coin with a market cap exceeding $950 million, becoming the first AI agent "millionaire." According to data from cookie.fun, there are currently around 1,600 AI agents with a total market cap exceeding $11 billion. Overall, we see AI agents (and related "agent tokens") rapidly taking over social channels, some of which have practical utility, transforming on-chain AI from a concept into a thriving reality. In particular, the following three interrelated concepts are increasingly gaining attention: on-chain AI agents, on-chain AI applications, and agentic commerce.
On-chain AI agents are autonomous programs (driven by AI models) capable of executing on-chain operations. AI agents can be viewed as intelligent software robots equipped with a crypto wallet—they can hold tokens, interact with smart contracts, trade assets, and even vote in DAOs, all based on their programming and objectives. Unlike the isolated AI chatbots we commonly see on social platforms today, these agents can learn, reason, and act within the on-chain economy.
On-chain AI applications are blockchain applications that integrate AI into their core functionalities. For example, AI can be embedded into DeFi protocols to optimize yields, into games to control NPC behavior, or into decentralized social networks or consumer applications for highly personalized user content. While we will explore these examples later, the key point is that these applications aim to seamlessly blur the lines between blockchain and AI-driven logic.
Agentic commerce is an emerging business model where AI agents transact via blockchain (including transactions with humans). This represents a paradigm shift from manual, search-based transactions to more automated, intent-driven, and personalized transaction experiences. Agents will become shoppers, negotiators, and service providers, completing transactions at software speed while aligning with human intent. Blockchain provides these agents with identity, wallets, stablecoins as payment currency, and a framework of programmable transactions.
The importance of on-chain AI lies in its ability to expand the crypto space to potentially billions of AI-driven participants. Each autonomous AI agent acts like a new "user" on the blockchain, capable of operating around the clock and making complex decisions, laying the foundation for significant on-chain activity and growth. Next, let’s delve into the thriving on-chain AI ecosystem, exploring its building blocks (new types of infrastructure services and on-chain agent types), emerging on-chain AI applications, and how commerce itself may be reshaped.

Agents
On-chain AI agents are at the core of the "Agentic Web." These are AI-driven entities capable of perceiving, deciding, and acting within the on-chain economy. To understand their rise, we need to break down the infrastructure required to enable on-chain agents and explore the types of agents currently emerging.
Agent Infrastructure and Services
Building a powerful on-chain AI agent is complex—it requires a new set of services and tools based on decentralized AI (DeAI) infrastructure resources (such as computing, data, models, intelligence, etc.) to support an open ecosystem of autonomous agents. These services abstract complexity and provide reusable components, making it easier to create, deploy, discover, and operate autonomous on-chain agents. Here are key emerging categories in agent infrastructure and their roles in the on-chain AI tech stack.
- Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs)
To truly achieve autonomous and secure operation, on-chain AI agents need a tamper-proof, verifiable execution environment independent of any centralized party. Trusted Execution Environments (such as Intel SGX or decentralized alternatives like Eternis, Fleek, or Phala Network) provide a hardware-secure "sandbox" where the agent's code and data can be processed confidentially, even kept secret from the agent's creator. Agents running in TEEs are protected from external interference and can generate cryptographic proofs demonstrating that their behavior aligns with programming instructions. As the agent economy expands, embedding sovereignty into the infrastructure layer will be crucial for gaining user trust and achieving a fully autonomous agent ecosystem.
- Agent Frameworks & Tools
Agent frameworks (such as ElizaOS, G.A.M.E. by Virtuals, RIG, Heurist, REI) are development environments and libraries for building AI agents, allowing developers to avoid starting from scratch. These frameworks provide the architecture for the agent's "core brain"—responsible for memory, decision-making, responding to prompts, and executing tasks. On-chain agent toolkits (such as Coinbase AgentKit, SendAI) package these frameworks for specific use cases and connect agents to smart contracts, wallets, payment channels, and on-chain data. By using these frameworks and tools, developers can quickly create powerful agents with built-in support for advanced multi-platform interactions, long-term memory, and on-chain connectivity.
- Agent Launchpads
This category of platforms helps create, launch, manage, and/or monetize agents by packaging AI agents as on-chain entities (often with their own tokens). For example, agent launchpads (such as Virtuals, auto.fun, ARC) allow creators to deploy new agent instances and build communities or funding support around them. By aligning incentives through tokens or fees, these launchpads enable agent developers to maintain and scale their on-chain agents as independent projects or businesses.
- Multi-agent Coordination
Not all problems can be optimally solved by a single agent. Multi-agent coordination protocols (such as Virtuals ACP, Questflow, Theoriq) can coordinate multiple AI agents (i.e., "agent groups") to work together to accomplish complex tasks. For example, one agent may be responsible for data collection, while another agent evaluates the results, all supervised by an on-chain coordinating agent. This "group" approach can surpass the capabilities of a single agent by leveraging specialization and parallel processing. By supporting collaboration between agents, multi-agent coordination platforms can expand the automation scope of on-chain AI, from multi-step workflows to entire autonomous organizations.
- Model Context Protocols (MCP)
Model Context Protocols sit at the intersection of AI agents and external data, initially created by Anthropic, and are a key service. These protocols help standardize how on-chain agents obtain relevant context, knowledge, or tools from external sources. Instead of customizing integrations for each data source or smart contract, agents integrated with MCP standards can access any compatible context provider (whether on-chain data, off-chain databases, or web services) to retrieve the necessary information or tools. Decentralized MCPs (such as Heurist and DeMCP) provide agents with self-developed and open-source MCP services, enabling them to access mainstream large language models in one place, thereby enhancing the adaptability and capabilities of on-chain agents in practice.
- AI App Stores
AI app stores (such as Alchemist AI, ARC Ryzome) serve as marketplaces and discovery layers for on-chain agents, tools, and experiences. These app stores enable developers to easily publish, monetize, and distribute agents or AI modules while allowing users to browse, summon, or customize agents through familiar interfaces. These app stores are not only distribution centers but also coordination interfaces for the broader on-chain AI economy, facilitating interoperability between agents, tools, and protocols. As the number of on-chain agents and AI-native applications grows, these platforms may become vital ecosystems—curating experiences, guiding users, and capturing a portion of the value flowing from agent interactions.
Types of Agents
With the rapid development of agent infrastructure and service layers, we believe that on-chain AI agents can currently be broadly categorized into the following types:
- Trading / DeFi Agents
These agents focus on financial operations, such as executing trades (e.g., Bankr, Cliza), providing liquidity (e.g., BasisOS), optimizing yields (e.g., ARMA, Mamo), or engaging in arbitrage within DeFi. Additionally, they may participate in prediction markets (e.g., Billy Bets), or even manage entire investment funds or portfolios (e.g., ai16z, aiXCB). These trading agents can react faster than humans, operate 24/7, and may make more informed decisions based on data, thereby improving market efficiency (or potentially surpassing human traders in certain aspects).
- Service Agents
Service agents provide practical services to users or protocols. For example, an agent can offer relevant market analysis research and insights (e.g., aiXBT, BitQuant, Chaos AI). Some agents may handle DAO governance tasks—reading proposals, summarizing content, and even voting based on preset logic. Other service agents may audit smart contracts for vulnerabilities or automatically generate new smart contract code based on natural language input (e.g., AgenTao, Kolwaii). Additionally, there are business-related service agents (like Byte AI), which negotiate deals or pay for goods on behalf of users. These agents essentially act as "autonomous workers" in the crypto space, capable of automating on-chain tasks that typically require human labor or attention.
- Entertainment Agents
These agents focus on interacting with users. In games, AI agents can act as NPCs (non-player characters) that interact naturally with players. Unlike traditional scripted game bots, these AI NPCs can learn and evolve, making the gaming experience more immersive. Beyond gaming, there are social agents: for instance, AI influencers on platforms (like X or Farcaster*) (e.g., Luna) that can post content and interact with users, or AI agents that create art and IP based on community input (e.g., Botto). In the future, you might follow an AI influencer on-chain, managing its own treasury (potentially earning cryptocurrency by creating content on Zora8 or completing tasks for fans). There are also AI companion agents capable of providing highly personalized interactions, some of which even possess very nuanced multimodal expressions and actions (e.g., Nectar AI).
Although still in the early stages, these categories showcase the vast possibilities of on-chain AI agents. From AI fund managers to AI virtual friends, on-chain agents can occupy multiple niches. What unifies them is their foundation in cryptographic technology, utilizing cryptographic primitives as a "playground" and toolbox—holding assets, executing smart contract code, and fully leveraging the transparency and composability of decentralized networks.
Applications
Alongside the rise of autonomous agents, we are also witnessing a wave of AI-driven on-chain applications. These applications and platforms embed AI into user experiences or core functionalities. Here are some areas where on-chain AI applications are taking shape:
- DeFi ("DeFAI")
AI is entering the DeFi space in various ways. One notable trend is AI-assisted trading and portfolio management. Users can leverage AI interfaces to handle complex DeFi protocols without manual operations. For example, HeyElsa is an AI-driven crypto assistant where users simply issue task commands to its agent (e.g., "swap X for Y"), and the agent executes these operations across protocols. Protocols like Giza offer non-custodial agents that can monitor DeFi markets, identify yield optimization opportunities, and dynamically manage positions through real-time market awareness. We believe this AI-driven user experience marks the "Wealthfront moment of crypto" (note: Wealthfront is a well-known robo-advisor in traditional finance), where on-chain AI agents effectively become personal crypto portfolio managers designed for DeFi that anyone can use.
- Gaming & Agentic Metaverses
Gaming is a natural testing ground for AI agents, and when combined with real asset ownership on-chain, it gives rise to the concept of agentic metaverses. These are game worlds or virtual environments composed of AI agents, as well as other agents or human players, creating richer and more dynamic gaming content. These agents can be friendly NPCs, autonomous opponents, or even AI avatars controlled by other players. For example, Youmio is building an autonomous world where AI agents can learn, play, and entertain in real-time, creating an endless on-chain simulation. Additionally, companies like Farcade* are developing AI-driven on-chain game studios where anyone can "improvise code" and distribute on-chain games through natural language prompts.
- Consumer AI
AI is revolutionizing the consumer experience by making applications more personalized, interactive, and intelligent. ChatGPT alternatives like Venice and FreedomGPT allow users to access powerful models in a privacy-protecting and censorship-resistant environment. In on-chain social networks, AI agents can act as influencers, curators, or creators—managing content flows, generating posts, engaging in conversations, and even executing on-chain operations (like Clanker). In on-chain consumer applications (like Zo), AI can help streamline user registration processes, recommend actions based on on-chain behavior, or negotiate on behalf of users in peer-to-peer markets. Finally, AI companion agents (like Nectar) allow users to create and interact with agents that can respond with nuanced multimodal expressions and actions—all of which can be verified on-chain. These agentic experiences are expected to significantly enhance user experiences in the crypto space, bringing them closer to mainstream consumer expectations.
- Commerce
One of the most profound impacts of on-chain AI is how it drives a new form of digital commerce—what Coinbase Ventures refers to as "Agentic Commerce." This business model is driven by transactions between AI agents and humans or other agents. In such an economy, cryptocurrency becomes the preferred payment method for machines and humans alike. The logic behind this is simple: autonomous AI agents operating globally cannot access banks, but they can send and receive cryptocurrency trustlessly on public blockchains. The borderless and programmable nature of cryptocurrency makes it well-suited for machine-to-machine payments, micropayments, and automated contracts. For example, the Coinbase developer platform team recently launched x402, a new open-source payment protocol that allows AI agents and applications to use crypto payments for GPU computing, API access, digital content, and more. Additionally, startups like Payman* and Skyfire* are building infrastructure services that leverage stablecoins like USDC to facilitate payment coordination between agents and humans or agents.
Although agentic commerce is still in its early stages, we believe it has the potential to automate and accelerate commercial transactions in unprecedented ways. Commerce could become as efficient as machines, operating around the clock, with agents negotiating deals, executing contracts, and exchanging value in seconds. Importantly, humans set the goals and parameters, while agents handle the rest. The role of the blockchain is to provide a secure and interoperable "playground" for these agents' transactions—complete with clear rules (smart contracts) and reliable currency (stablecoins).
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the prospects for on-chain AI are full of potential, but its development will unfold in phases. In the short term, we expect ongoing experimentation with on-chain AI agents and AI-driven applications. In the long run, we believe that cryptocurrency will become the factual economic layer for AI, meaning that any advanced AI agent will use cryptocurrency to store value and settle transactions. As AI's capabilities in writing software and smart contract code continue to improve, the pace of innovation in the on-chain economy may accelerate rapidly, leading to a surge of new applications and users.
However, achieving this vision will require overcoming several challenges. Agent technology is still in its early stages, and some expectations may be ahead of reality. Current AI agents are still limited in reliability and functional scope, and it may take time for them to safely handle open-ended tasks. Additionally, if a large number of agents transact simultaneously, the scalability of the blockchain will be tested. Furthermore, there is an urgent need for new trust and governance frameworks. While AI agents can greatly enhance the functionality of on-chain systems, poor governance could also amplify security and trust issues.
From a value capture perspective, we believe that unlocking the potential of the on-chain AI economy requires support in several areas: robust infrastructure to enhance agent intelligence (e.g., data networks and post-training models designed for on-chain agent use cases); services and tools for coordinating agent behavior (e.g., multi-agent coordination, decentralized MCPs, agent identity/payment rails); channels for distributing agents to mainstream consumers (e.g., agent launch platforms, AI app stores, and consumer AI).
In summary, the rise of on-chain AI represents a new frontier of machine-driven intelligence. From autonomous agents executing smart contracts to on-chain applications that adapt in real-time to user needs, this movement could redefine the way humans interact with machines. It is an exciting time—Coinbase Ventures and many in the crypto community believe this could lead to the next significant leap in the evolution of the internet, heralding the arrival of an "Agentic Web" that will drive a more autonomous and intelligent digital economy.
Thanks to Hoolie (Coinbase Ventures), Luca (Base), Lincoln (Coinbase), Vik (Coinbase), Daniel (Variant), Josh (Contango Digital), Anand (Canonical), Teng (Chain of Thought), and EtherMage (Virtuals) for their insightful feedback and discussions on this article.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




