The discussion about modular blockchain narrative originates from Celestia and its token TIA's outstanding performance. In fact, modularity is the main development direction and trend of future blockchain design. Modular blockchain, like LEGO bricks, breaks down the blockchain system into reusable modules, and different blockchain networks with different functions can be achieved through customized combinations. This flexibility and customizability provide a new way of thinking and solutions for the development and deployment of blockchain applications.
I. Overview of Modular Blockchain
Traditional monolithic blockchains integrate core functions (execution, settlement, consensus, data availability) into the same network, leading to the system's lack of scalability. For example, Ethereum and Solana require each node to store complete blockchain data and verify and record each transaction. Although this design ensures the security and decentralization of the network, it also leads to performance bottlenecks. Over time, as the size of the blockchain continues to grow, the amount of data that nodes need to process rapidly expands, leading many blockchain networks to face insufficient processing capacity, thereby affecting their scalability and performance.
Introduction of Modular Blockchain
The initial concept of modular blockchain was based on research and exploration of the Ethereum network. In 2018, Mustafa Albasan, co-founder of Celestia, and Vitalik Buterin, the founder of Ethereum, co-authored a paper titled "Data Availability Sampling and Fraud Proofs," which provided a new approach to solving the scalability problem of blockchain, namely modular blockchain. The paper mainly focuses on how to improve the scalability of the Ethereum network without sacrificing its security and decentralization.
Definition of Modular Blockchain
Modular blockchain is a design paradigm that decomposes the blockchain system into multiple independent modules and realizes communication and collaboration between modules through well-defined interfaces and protocols. Modular blockchain adopts a separation strategy, splitting core functions such as execution, settlement, consensus, and data availability into independent modules, each responsible for handling specific functions or business requirements. Through modular design, a mutually dependent stack structure can be built, allowing selective deployment and updating of different modules based on actual needs, thereby improving the system's flexibility and customizability.
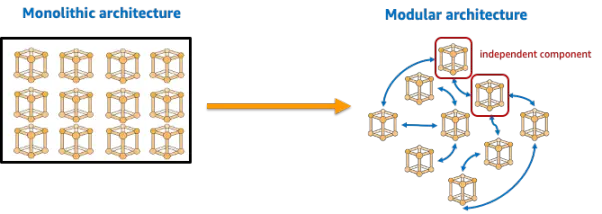
Characteristics of Modular Blockchain
Scalability: Modular blockchain adopts a distributed architecture, splitting the system into multiple modules that can be independently deployed and expanded, thereby achieving horizontal scalability. When the system needs to process more transactions or data, the throughput and performance of the system can be increased by adding corresponding modules without the need for a comprehensive upgrade of the entire system.
Flexibility: Modular blockchain allows selective deployment and updating of different modules based on actual needs, thereby achieving flexible configuration of the system. For example, in the financial field, specialized payment modules can be deployed, while in the supply chain field, specialized logistics modules can be deployed, customizing the blockchain system according to different business needs.
Composability: Modular blockchain achieves efficient communication and collaboration between modules through well-defined interfaces and protocols, allowing different modules to interact and combine with each other to achieve more complex business logic and functionality. For example, identity verification modules can be combined with smart contract execution modules to achieve identity-based permission management, thereby enhancing the security and trustworthiness of the system.
Ease of Maintenance: Due to the decomposition of the system into multiple independent modules, each responsible for handling specific functions or business requirements, it is easier to maintain and update the modules, reducing the maintenance cost and risk of the system.
II. Classification and Principles of Modular Blockchain
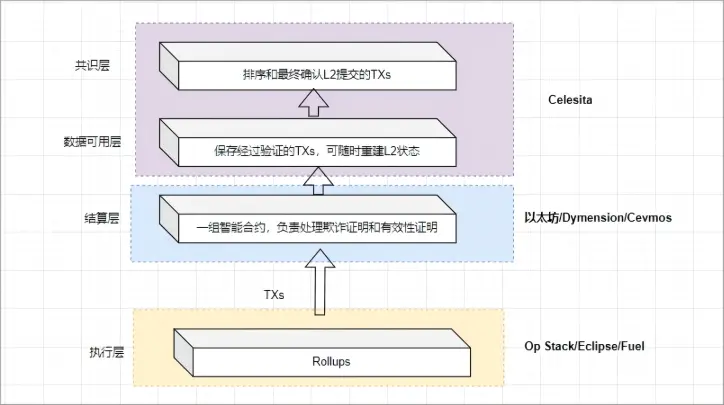
Modular blockchain focuses on handling a few responsibilities and outsourcing the rest to one or more independent layers of the blockchain. The core of modular blockchain lies in the modular design concept, which decomposes the blockchain system into multiple independent modules, each responsible for specific functions, and achieves the combination and extension of functions through interfaces between modules. To understand the working principle of modular blockchain, it is necessary to understand the functional layered structure of the blockchain system, including the consensus layer, data availability layer, execution layer, and settlement layer.
Consensus Layer
The consensus layer is one of the foundational layers of modular blockchain, responsible for ensuring the consistency of full nodes and adding new blocks effectively and determining the order of transactions. In the consensus layer, different consensus algorithms are designed to solve double-spending problems in the network and ensure consistency. For example, Syscoin has a unique ecosystem design, using Bitcoin's PoW as the consensus method while fully compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
Data Availability Layer (DA Layer)
The data availability layer is responsible for ensuring the availability of data, allowing the execution layer and settlement layer to run separately. In this layer, all original transactions of the execution layer must be stored, and the settlement layer verifies the validity of transactions through the data availability layer. For example, Celestia, Avail, EigenDA, and others are representative projects of modular blockchain that focus on data availability, ensuring the availability and integrity of data in the network through different technical means.
Execution Layer
The execution layer is responsible for executing smart contracts, processing transactions, and deploying various user applications. In the execution layer, the execution results of smart contracts are provided to the settlement layer in the form of proofs to update user and chain states. For example, the modular Rollup solution Manta Pacific solves the data availability problem through modular infrastructure design, allowing seamless integration of modular DA and zkEVM. As an Ethereum Layer2, Mantle, built with a modular architecture, cooperates with EigenDA to provide low-cost and high-security solutions while relying on the security of Ethereum.
Settlement Layer
The settlement layer is responsible for providing global consensus and security in modular blockchain, verifying the correctness of execution results from the execution layer, and updating user and chain states. They ensure the security and reliability of the entire blockchain network through different consensus mechanisms. Increasing the number of nodes can enhance the security of the settlement layer. For example, dYmension is a modular platform for the settlement layer, providing all the tools and infrastructure needed for Cosmos ecosystem Rollups.
III. Current Development and Representative Projects of Modular Blockchain
As of May 8th, RootData has recorded a total of 50 modular blockchain projects, with 10 of them having issued tokens. According to public financing data, the financing amount for modular blockchain projects from 2024 to the present has exceeded 350 million USD.
In addition, according to CoinGecko data, as of May 8th, the market value of tokens for modular blockchain projects exceeds 3 billion USD, with a 24-hour trading volume exceeding 230 million USD.
Top 10 Modular Blockchain Token Market Cap Ranking:

Furthermore, key modular blockchain projects that have not issued tokens but are worth paying attention to include Fuel, Avail, Eclipse, etc.
Fuel: Fuel is a UTXO-based modular execution layer that brings global accessibility to Ethereum. As a modular execution layer, Fuel can achieve global throughput in a way that a single-chain cannot, while inheriting the security of Ethereum. John Adler, co-founder and Chief Research Officer of Celestia, is also a co-founder and former CTO of Fuel. According to the official announcement, the mainnet of the modular execution layer Fuel is expected to be officially launched in the third quarter of 2024. In the coming weeks, the Fuel team will share more detailed information about Fuel's unique architecture, product roadmap, and release plans.
Avail: Avail is a modular blockchain focused on data availability: sorting and recording blockchain transactions without the need to download the entire block to prove the availability of block data. This allows it to scale in a way that a single-blockchain cannot achieve. Avail was spun out of Polygon in March 2023, led by Polygon co-founder Anurag Arjun. On February 26, 2024, Avail announced the completion of a $27 million seed round of financing, led by Founders Fund and Dragonfly, with participation from SevenX Ventures, Figment, Nomad Capital, and angel investors including former Coinbase CTO Balaji Srinivasan, Osmosis co-founder Sunny Aggarwal, Polygon Chief Information Security Officer Mudit Gupta, and AltLayer COO Amrit Kumar.
Eclipse: Eclipse is a customizable rollup provider compatible with multiple Layer 1 blockchains. The platform allows developers to deploy their own Solana-operated rollup, supported by any chain for security or data storage. Neel Somani is the founder of Eclipse, having previously worked at Airbnb, Two Sigma, and Oasis Labs. Neel Somani graduated from the University of California, Berkeley. In March 2024, Eclipse completed a $50 million Series A financing round, co-led by Placeholder and Hack VC, bringing its total financing to $65 million. Additionally, Polychain Capital, Delphi Digital, Maven 11, DBA, and Fenbushi Capital also participated in this round of financing. Eclipse has announced that the mainnet is scheduled to be launched in the second quarter of 2024, and has already released the development network and test network versions of its protocol.
IV. Analysis of Risks and Challenges in Modular Blockchain
As a new architectural design concept, modular blockchain is still in its early stages of development and faces a series of risks and challenges.
1. Lack of Unified Standards Affect Compatibility and Interoperability
The development of modular blockchain lacks unified standards, which may affect the compatibility and interoperability between different platforms. Due to the lack of unified standards, the interaction between different platforms may be limited, restricting the overall efficiency and scalability of the system. Additionally, the lack of unified standards may also lead to more technical challenges and obstacles for developers.
2. Functional Fragmentation Increases Systemic Risks
Modular blockchain layers various functional modules in the blockchain network, giving each module independent functions and responsibilities. However, this functional independence may increase systemic and security risks. The independence of each module means that they may have single points of failure, and if a module encounters issues, it can affect the stability and security of the entire system.
3. Updates and Maintenance May Introduce New Risks
Modular blockchain systems require continuous updates and maintenance to adapt to evolving market demands and technological advancements. However, the process of updates and maintenance may introduce new risks and issues, affecting the normal operation of the system. For example, updates may lead to system instability or introduce new security vulnerabilities and privacy issues, thereby posing risks and challenges to the blockchain network.
4. Conflicts of Interest with Monolithic Blockchains
Modular blockchain may have conflicting interests with monolithic blockchain networks such as Ethereum. For example, as one of the most influential and user-based public chains, the emergence of modular blockchain may impact the ecosystem of Ethereum, leading to conflicts of interest and increased competition.
V. Prospects for the Development of Modular Blockchain
As a new architectural design concept, modular blockchain is expected to make breakthroughs and progress in multiple aspects, with significant significance and broad development prospects.
1. Enhancing Flexibility and Scalability of Blockchain Networks
Modular blockchain decomposes various functional modules in the blockchain network, making the network more flexible and scalable. In the future, with the continuous improvement and application of modular blockchain technology, we can expect blockchain networks to become more flexible, allowing for customized configurations based on different needs and scenarios, better meeting the requirements of various application scenarios, and enabling larger-scale application deployments.
2. Reducing the Threshold and Cost of Application Development
The development of modular blockchain will promote the flourishing of the blockchain ecosystem. Through modular design, blockchain networks can better support developers in application development and deployment, reducing the threshold and cost of application development, thereby attracting more developers and innovators to join the blockchain ecosystem. In the future, as the blockchain ecosystem continues to grow, we can expect to see more innovative applications emerging, providing users with richer and more convenient blockchain services and experiences.
3. Accelerating Standardization and Normalization Processes
With the development of modular blockchain, we can expect the acceleration of the standardization and normalization processes of blockchain. By establishing unified standards and specifications, not only can the compatibility and interoperability between different platforms be improved, but the cost of system development and maintenance can also be reduced, promoting the widespread application and promotion of blockchain technology.
4. Promoting Cross-Integration and Innovation
The development of modular blockchain will promote the cross-integration and innovation of blockchain technology with other cutting-edge technologies. Through modular design, blockchain networks can better integrate with technologies such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and big data, forming more powerful and complex application scenarios. In the future, with the cross-integration and innovation of blockchain technology, we can expect to see more new application scenarios emerging.
As an emerging design paradigm, modular blockchain, by improving the scalability, flexibility, composability, and ease of maintenance of systems, has opened up new possibilities for the further development and application expansion of blockchain technology, providing a more powerful and flexible infrastructure for the construction of the digital economy and blockchain networks, bringing new possibilities for future innovation, and demonstrating its enormous potential in a wider range of fields.
Hotcoin pays close attention to the development dynamics of modular blockchain narrative and has launched high-quality assets such as MNT, TIA, OSMO, DYM, MANTA, SKL, ALT, SAGA, CHR, and OMNI. For cryptocurrency investments, come to Hotcoin, where the hottest high-quality assets are reached first, staying one step ahead!
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




