Date: January 11, 2024
Source:
https://www.forbes.com/sites/digital-assets/2024/01/11/how-the-irs-will-tax-bitcoin-etfs/?sh=1a86cf5759ed
As the long-awaited Bitcoin exchange-traded fund (ETF) in the cryptocurrency industry has been approved and investors are excited, they must understand how the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) will tax these products.
What is a Bitcoin ETF?
An ETF is a financial instrument that allows investors to invest in various assets and industries through a single share. A Bitcoin ETF allows investors to invest in Bitcoin without directly holding it.
The launch of an ETF involves multiple parties. In the case of a Bitcoin ETF, authorized participants (APs), typically market makers or large banks, provide cash to the grantor trust established by sponsors such as Ark Invest or Blackrock. The trust then uses the provided cash to purchase Bitcoin and issues trust shares representing the underlying Bitcoin to the APs. These ETF shares are subsequently sold to retail investors through public exchanges such as the New York Stock Exchange or Nasdaq. ETF sponsors typically charge an annual fee (expense ratio) to cover their operating and management costs. As of December 31, 2022, the industry average expense ratio was 0.47%. Lastly, but equally important, regulatory approval from the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is required for the sponsor's application before the ETF can be traded.
Futures-based Bitcoin (or any other cryptocurrency) ETFs track the price of Bitcoin through futures contracts. Several futures-based Bitcoin ETFs have been approved for trading since October 2021, such as ProShares Bitcoin Strategy ETF (BITO), ProShares Short Bitcoin ETF (BITI), VanEck Bitcoin Strategy ETF (XBTF), and others. BITO, as a market leader, manages $2 billion in assets.
How are Bitcoin ETFs taxed?
The taxation of ETFs begins with the assessment of capital gains, but it does not end there.
If you sell Bitcoin ETF assets within less than a year of holding them, the resulting short-term capital gains will be subject to ordinary income tax. The tax rate may range from 10% to 37% depending on your overall taxable income and filing status.
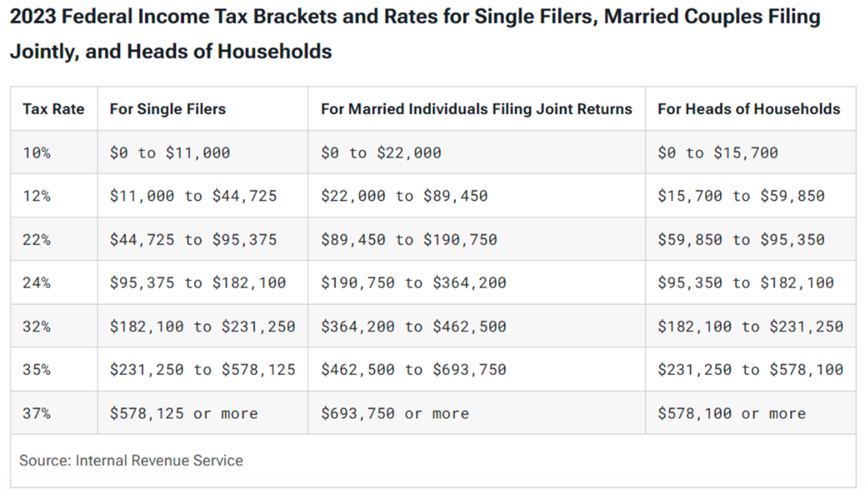
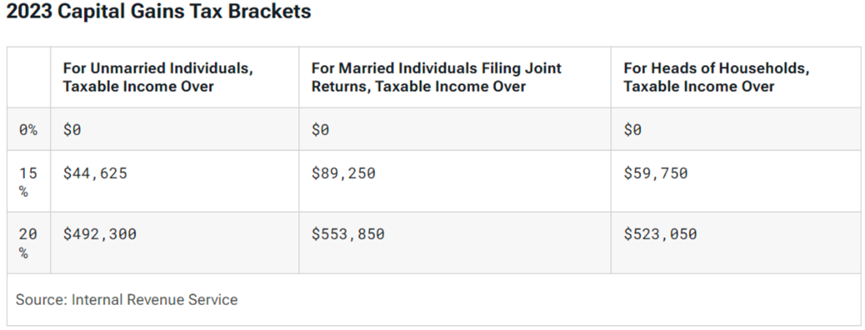
If you sell ETF assets after holding them for more than 12 months, the resulting long-term capital gains will be subject to capital gains tax. The tax rate may be 0%, 15%, or 20%, depending on your overall taxable income and filing status.
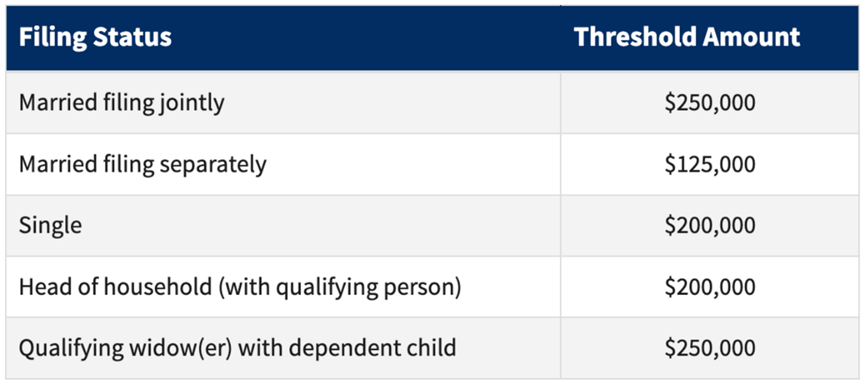
In addition, if your income exceeds certain thresholds, in addition to the above capital gains tax, you may also be required to pay a 3.8% tax.
However, this is not the only way to assess capital gains tax. Bitcoin ETFs spend a small portion of Bitcoin throughout the year to pay management fees. These transactions result in capital gains and losses due to the difference between the cost basis of the spent Bitcoin and its market value at the time of spending. For example, if a fund sells Bitcoin at a profit of $40,000 to pay management fees, these gains will be taxed proportionally based on each investor's holdings in the fund.
Before the passage of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act in 2018, investors could deduct their proportionate share of fund expenses as miscellaneous itemized deductions on Schedule A. Unfortunately, due to restrictions introduced by the act, these expenses are no longer deductible and will be deductible again after December 31, 2025.
Compared to spot ETFs, the tax impact on holders of futures-based Bitcoin ETFs (such as BITO) may be slightly different. The specific details depend on the structure of these funds, particularly whether they are exposed to regulated or unregulated (as defined in IRC§1256) underlying futures contracts. If the fund holds regulated futures contracts (which are typically traded on the dominant platform for Bitcoin futures, the Chicago Mercantile Exchange), then under IRC§1256, 60% of the gains are treated as long-term capital gains, regardless of the holding period, and 40% of the gains are treated as short-term capital gains.
If the fund is exposed to unregulated contract exposure, the gains must comply with normal capital gains rules similar to stocks. Please note that the taxation of futures contracts can be very complex and depends on the facts and circumstances of the contracts, as well as certain tax elections made by the fund and you. These factors can have a significant impact on when and how much tax a taxpayer owes.
Additionally, if you trade in cryptocurrency futures ETFs, fund expenses are typically paid in cash, which does not result in the same capital gains or basis adjustments as spot ETFs.
Key Tax Considerations for Bitcoin ETFs
ETF holders may need to file two types of tax compliance reports at the end of the year, namely Form 1099-B and a trust tax information statement, to fulfill their tax obligations.
Brokers may issue Form 1099-B to report the gains and losses resulting from the disposal of ETF units. This form will report the cost basis, sale price, and resulting gains or losses from the ETF units. (According to proposed broker regulations, starting from the 2025 tax year, this information may be reported on a new form, 1099-DA, dedicated to digital asset transactions).
At the same time, the trust tax information statement will show the amount of Bitcoin used throughout the year to pay management fees. Using Bitcoin to pay fund expenses may result in capital gains (or losses). This document will explain how to calculate your proportionate share of the capital gains or losses generated in these transactions. You will need to manually calculate this information using the trust tax information statement, as this information will not be reported on Form 1099-B. These statements are specific to ETFs established as trusts and may be unfamiliar to most investors.
Finally, in the year you sell the ETF, you will need to adjust the basis reported on Form 1099-B based on the information reported in the trust tax information statement to arrive at the correct gains or losses. This may make tax compliance cumbersome for ordinary taxpayers. This is why it is important to continue monitoring the progress of the next approved spot BTC ETF.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



