JD predicts that in 2024, every L2 will be labeled with "Parallel EVM," and Georgios believes that 2024 will be the "year of Parallel EVM," and indicates that Paradigm is also exploring and designing related technologies internally.
Authored by: Hotcoin Research Institute
In the wave of the crypto world, a new technical narrative—Parallel EVM (Parallel Ethereum Virtual Machine)—is rapidly becoming a hot topic. Multiple projects such as Monad and Sei are already exploring the implementation of Parallel EVM. Industry figures such as JD, co-founder of Polygon, and Georgios, CTO of Paradigm, have expressed their attention and expectations for Parallel EVM. JD predicts that in 2024, every L2 will be labeled with "Parallel EVM," and Georgios believes that 2024 will be the "year of Parallel EVM," and indicates that Paradigm is also exploring and designing related technologies internally.
I. Overview of Parallel EVM
In addition to the exacerbation of EVM's chain performance burden, optimizing EVM is a continuous theme in the crypto world—new public chains, OP-based L2, ZK-based L2, etc., all derive narratives and projects from optimizing EVM, and the market will value them more. However, these narratives are relatively mature, and related projects no longer have much hype space. Therefore, the new method of optimizing EVM, Parallel EVM, is easily attracting market attention during the bull market.
Parallel EVM (Parallel Ethereum Virtual Machine) is an innovative concept aimed at improving the performance and efficiency of traditional EVM. Traditional EVM, as the core execution environment of Ethereum, is responsible for processing smart contracts and transactions, but its limitations in serial processing have led to slow processing speeds and low efficiency. Parallel EVM greatly increases the throughput and efficiency of the blockchain by identifying and simultaneously processing multiple non-conflicting transactions.
The core of Parallel EVM lies in its parallel processing capability. This can be likened to a restaurant kitchen adding more chefs working simultaneously to improve overall efficiency. Technically, this includes partitioning or sharding processing, optimizing algorithms, as well as ensuring security and consistency. This design not only improves transaction processing speed but also maintains network security and data consistency.
II. Principles and Characteristics of Parallel EVM
Parallel EVM is an innovative optimization of traditional EVM. Traditional EVM is the core of the Ethereum blockchain, responsible for sequentially processing smart contracts and transactions. This sequential processing method can lead to low efficiency and network congestion under high loads. The core idea of Parallel EVM is to change this serial processing mode to achieve simultaneous parallel processing of multiple transactions. Specifically, it allows these transactions to be executed simultaneously on different processing units by identifying non-conflicting transactions. This is similar to parallel processing in multi-threaded programming, where different processing units can execute multiple tasks simultaneously, thereby improving overall processing speed and efficiency.
Improving processing efficiency: By parallel processing multiple transactions, the throughput of the blockchain is significantly increased, reducing transaction waiting times and effectively solving network congestion issues.
- Resource optimization: Parallel EVM allows for more efficient use of network resources. In traditional serial EVM, resources may only be used by a single transaction at a given time, while in parallel EVM, multiple transactions can share and fully utilize these resources.
- Maintaining compatibility: Although Parallel EVM innovates at the execution level, it still maintains compatibility with traditional smart contracts and EVM, ensuring seamless migration and operation of existing Ethereum applications.
- Complexity management: Implementing parallel processing requires significant modifications to the EVM architecture, including enhancing transaction scheduling systems, optimizing memory management, etc., to maintain transaction correctness and order, while ensuring system security and consistency.
- Scalability improvement: Parallel EVM provides better scalability for the blockchain, enabling it to handle more transactions to meet the growing demands of users and applications.
- Potential application scenario expansion: Efficient parallel processing capabilities provide possibilities for complex application scenarios, such as DeFi, large-scale NFT transactions, etc., which may be limited by processing speed and costs on traditional EVM.
III. Current Development Status of Parallel EVM
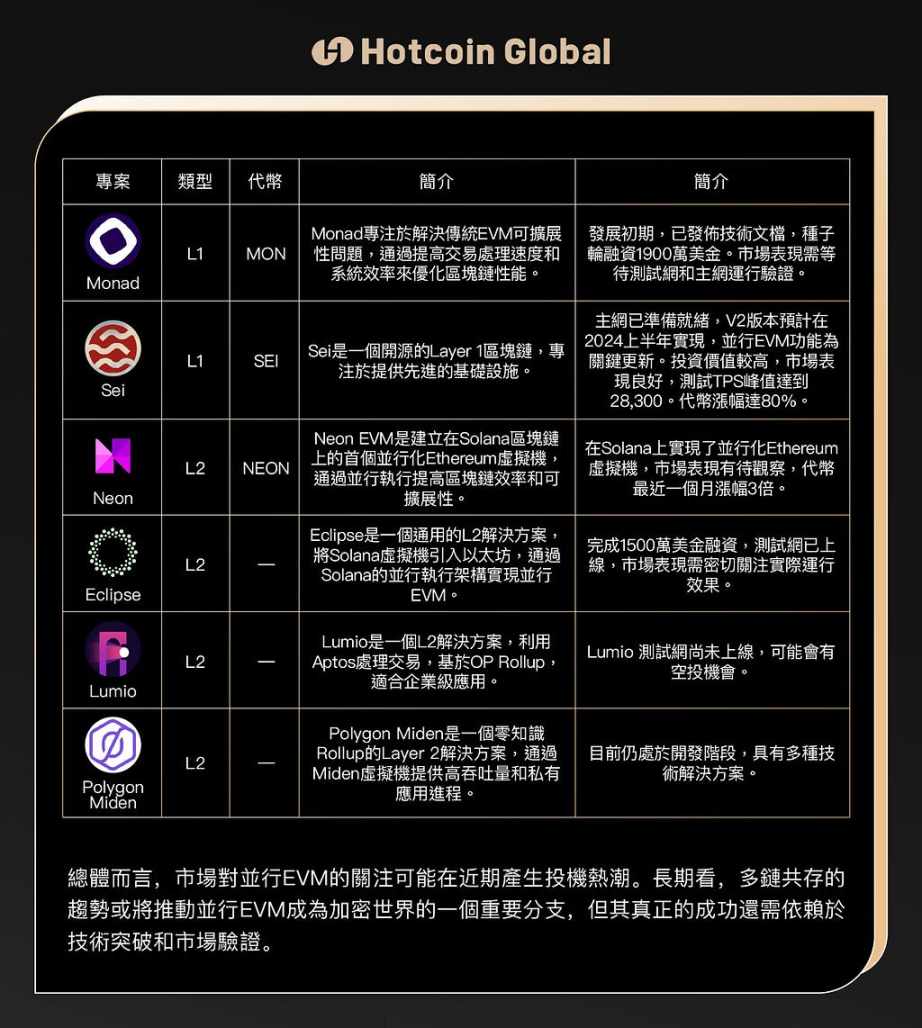
1. Monad:
Monad is a blockchain project focused on solving the scalability issues of traditional EVM, aiming to optimize blockchain performance by increasing transaction processing speed and system efficiency. Monad is expected to make breakthroughs in solving Ethereum transaction congestion issues, and its parallel execution strategy provides a potential solution to increase transaction throughput and solve network congestion issues.
- Project progress: Currently in the early stages of development, it has released technical documents and completed a seed round financing, raising as much as $19 million.
- Market performance: As part of the Parallel EVM narrative, Monad has received significant attention on social media, with impressive financing, but its actual market performance still needs to be verified after testing on the testnet and mainnet.
2. Sei:
Sei is an open-source Layer 1 blockchain focused on providing advanced infrastructure for various transaction applications, including DeFi, NFT markets, and game DEX. The latest V2 version has put Parallel EVM on the agenda. Sei aims to improve blockchain efficiency and transaction speed through optimistic parallelization strategies and other technical optimizations.
- Project progress: The mainnet was ready in August 2023, and the V2 version is expected to implement Parallel EVM functionality in the first half of 2024.
- Investment value: Sei aims to improve blockchain efficiency and transaction speed through optimistic parallelization strategies and other technical optimizations. It has high performance and a secure execution layer, potentially becoming the preferred choice in multiple application areas.
- Market performance: Sei has performed well in the testing phase, with a peak TPS of around 28,300, and the token has seen an 80% increase in the past month.
3. Neon:
Neon EVM is the first parallelized Ethereum virtual machine built on the Solana blockchain, aiming to improve blockchain efficiency and scalability through parallel execution, and is expected to attract attention in the revival of the Solana ecosystem and token frenzy.
- Project progress: Neon has implemented a parallelized Ethereum virtual machine on Solana, allowing developers to extend Ethereum dApps using Solana's parallel execution architecture.
- Market performance: The NEON token has tripled in value in the past month, but its total market value is relatively low. As a Parallel EVM project in the Solana ecosystem, its market performance is still to be observed.
4. Eclipse:
Eclipse is a universal L2 solution that introduces the Solana Virtual Machine (SVM) to Ethereum, achieving Parallel EVM through Solana's parallel execution architecture. Eclipse's design logic aims to improve processing speed and network throughput through Solana's SVM, while reducing congestion and transaction costs, with high performance and compatibility.
- Project progress: Completed a $15 million financing in 2022, with support from multiple well-known investors, including Polychain and Polygon Ventures.
- Market performance: With a strong background, the testnet has been launched, and investors need to closely monitor its actual operational effects.
5. Lumio:
Lumio is an L2 solution that uses Aptos to process transactions and is based on OP Rollup. Compared to other L2 solutions, Lumio has a significant performance advantage. Lumio provides low gas costs and high TPS performance, making it suitable for enterprise-level applications. Investors should pay attention to its development in the multi-chain ecosystem.
- Project progress: Led by Pontem, focusing on building Move and EVM-compatible products, with some integration with Parallel EVM in product design.
- Market performance: Recently experienced an 80% increase, and may be influenced by capital overflow in the future.
Polygon Miden:
Polygon Miden is a zero-knowledge (zk) Rollup Layer 2 (L2) solution running on Miden VM. Unlike zkEVM, Polygon Miden does not rely on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Instead, it uses the Miden Virtual Machine (MVM) written in Rust. This unique approach allows developers to build high-throughput and private applications using modern smart contract languages like Rust, aiming for enhanced security at minimal cost while benefiting from the security of the Ethereum network.
- Project progress: Polygon Miden is still in the development stage.
- Market performance: Polygon has various technical solutions such as sidechains, zk-STARK, and SDK on the Polygon network. While Polygon is recognized as a successful Layer 2 solution, the uniqueness and market acceptance of Miden are still unpredictable.
IV. Risk Analysis of Parallel EVM Narrative
As a technology aimed at improving blockchain processing efficiency and performance, Parallel EVM shows tremendous potential but also faces a series of issues and risks in practical applications and investment.
- Synchronization and consistency issues: Maintaining data consistency and order while parallel processing multiple transactions is a significant challenge. Complex synchronization mechanisms are needed to ensure that all parallel-processed transactions can eventually merge into a consistent state.
- Security challenges: Due to the complexity and novelty of Parallel EVM technology, related projects may face technical risks in implementation, such as new attack vectors or security vulnerabilities resulting from parallel processing.
- Smart contract compatibility: While compatibility with traditional EVM is considered in design, compatibility issues may arise in practical applications, especially for complex or specific-assumption smart contracts.
- Project execution risk: The project team's execution capability and resource allocation are key factors in determining project success. Due to the technical complexity of Parallel EVM projects, the team's technical capabilities and management standards have a significant impact on the project.
- Long-term sustainability: As an emerging technology, the long-term prospects and sustainability of Parallel EVM are still uncertain, especially in the increasingly competitive blockchain technology field.
V. Development Prospects of Parallel EVM
With mainstream public chains such as Ethereum facing performance bottlenecks, optimizing EVM continues to be a recurring theme in the crypto world. As an optimization solution, Parallel EVM is expected to attract more project participation and technological innovation.
- Technological development and optimization: As Parallel EVM technology continues to mature, it can be expected that there will be more innovation and optimization to address existing technical challenges such as data consistency, security, and compatibility issues.
- Market application expansion: The high processing capabilities of Parallel EVM may drive the emergence of more complex and innovative applications, especially in DeFi, NFT markets, and gaming, where these applications may have been hindered by the performance limitations of traditional EVM.
- Enhanced blockchain competitiveness: The development of Parallel EVM may intensify competition between blockchain platforms, especially for those seeking to improve performance and scalability. This may lead to new market dynamics and investment opportunities.
- Wider industry impact: The development of Parallel EVM may have a broader impact on the entire cryptocurrency and blockchain industry, including potential regulatory changes, strategic adjustments by market participants, and new collaboration opportunities.
Overall, market attention to Parallel EVM may lead to speculative fervor in the near term. In the long run, the trend of multi-chain coexistence may drive Parallel EVM to become an important branch of the crypto world, but its true success will depend on technological breakthroughs and market validation.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




