CoW Swap adopts MEV minimization method instead of MEV maximization method.
Guest: Anna (@AnnaMSGeorge)
Host: Stephanie (@stephaniiee_eth)
If you are interested in DeFi and MEV, you may have heard of intent-based trading, frequent batch auction, solver model, order flow auctions (OFAs), etc. CoW Swap can be said to be an example of the above innovations, organically integrating them into DEX products, providing users with the most favorable prices, finding the best routes, and avoiding MEV attacks.
In this episode, Stephanie and CoW Swap co-founder Anna discussed in detail the design of CoW Swap, including the difference between the trading cycle starting from collecting user transaction intentions in CoW Swap and the traditional trading lifecycle; how to ensure the security of user funds when outsourcing trading execution to mature solvers; how to guide effective competition among solvers, which is a key component of elevating intent-based trading to a new level; and how to continuously incentivize solvers while avoiding malicious behavior.
They also discussed broader topics, such as how newcomers view Uniswap's first-mover advantage, why CoW Swap adopts MEV minimization method instead of MEV maximization method, and why dapp-level MEV mitigation measures make sense.
"CoW Swap's Trading Cycle and Its Design"
 (src: https://docs.cow.fi/overview/introduction)
(src: https://docs.cow.fi/overview/introduction)
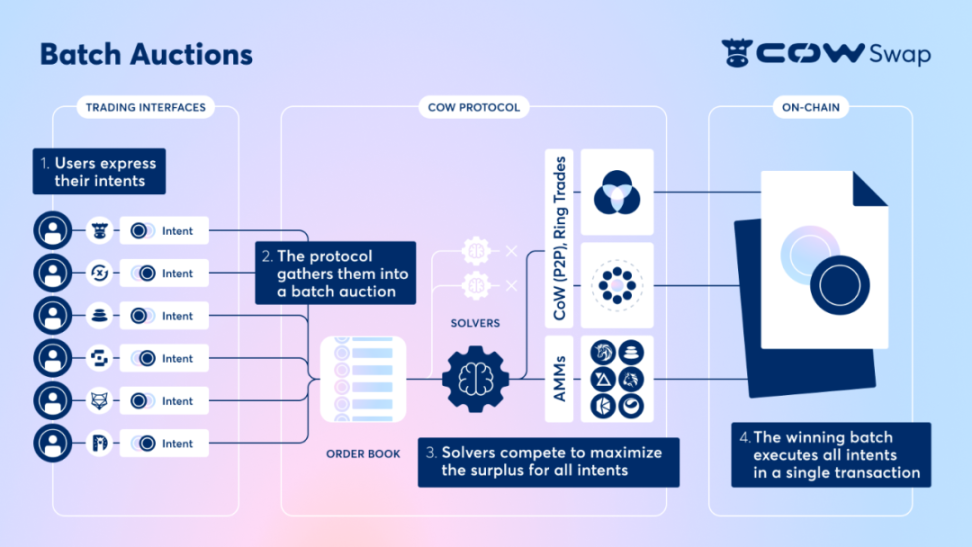
CoW Swap's trading cycle is mainly divided into four steps
Users express their intentions through signed messages, including the tokens to buy or sell, the quantity of the transaction, and the validity period of the transaction execution.
The CoW protocol collects user intentions and puts them into an off-chain order book for batch auctions.
Third-party transaction executors (solvers) access the order book. They are good at mathematics and can quickly find the optimal execution path (including all on-chain liquidity, demand coincidences, circular trading) and the best price. They compete with each other, and the protocol ranks the value they can provide to users. The winning solver in the auction can execute the batch of transactions.
The winning batch is executed on-chain at a unified price to fulfill all intentions.
How CoW Swap initiates competition among solvers
CoW Swap is able to elevate intent-based trading to a new level by introducing competition at the execution layer, rather than just a simple on-chain execution model. To ensure that this competition is effective and that user transactions receive better execution, CoW Swap's nurturing work mainly went through three stages:
Gnosis initially ran some solvers internally, which were relatively simple, collecting some aggregator API endpoints, such as paraswap, 1inch, and 0x, comparing their return values, and then deciding to submit transactions to the API that could provide the best transaction return.
At last year's Amsterdam Devconnect, they encountered a very smart and mathematically adept team that was very interested in running solvers. They started developing their own algorithms and successfully won in the API competition.
Liquidity providers became interested in solvers, integrating their own liquidity with existing solvers. Private liquidity allowed them to gain an advantage.
Currently, CoW Swap's solver set consists of 16 solvers, each with their own expertise.
Design with both incentives and constraints
CoW Swap distributes incentives to solvers every week, which are divided into two parts: one part is about continuity, as they want solvers to continuously participate in the competition, rather than only bidding when they think they can win in a particular competition. At the same time, when some solvers are offline or engage in malicious behavior, there are still solvers bidding. The other part is based on how much more the winning solution found by the solver is worth compared to the second best, to ensure that they do not only focus on providing a path that is only 1 cent better than the second best. The more value they find compared to the second best, the more incentives they receive.
The current source of incentives is 2% of the CoW tokens distributed annually. In January, they will introduce a small fee, which is actually taken from the value they provide to users. These fees are received by solvers, but they must use them to repurchase CoW tokens and return them to the CoW treasury.
Currently, the solver set is theoretically permissionless, but in practice, there are some elements that require permission. Since solvers theoretically still have the potential to exploit user slippage tolerance, CoW Swap requires solvers participating in the competition to provide collateral. This mechanism does not have to be centralized. Currently, there is a centralized factor because the CoW DAO is also managing the collateral pool to lower the entry barrier. However, in 2024, solvers will be able to build their own collateral pools, and smart contracts will automatically check whether solvers have private keys, provide access permissions, and have established collateral pools. This way, solvers can automatically join the competition.
"MEV Maximization vs. MEV Minimization"
CoW Swap focuses on MEV minimization because the MEV maximization method has some risks.
First, from the start of maximizing MEV, you need to extract value from users. To extract value, you need multiple participants, and then you need to reward their efforts, meaning users cannot get back 100% of MEV. In the best case, users can receive a small rebate, but in CoW Swap's view, the initial MEV value is created by users, and they should not incur losses.
Second, because of the need to redistribute value, it becomes inefficient, as it requires the rebate transactions to be included in blocks, meaning more block space is needed.
Finally, MEV maximization brings more complexity, now requiring the introduction of PBS (proposer/builder separation). Flashbots initially brought MEV to the forefront of discussions and advocated for the democratization of MEV, allowing everyone to extract MEV rather than only benefiting one party, which is good. But the downside is that it allows more players to enter the game, and makes MEV extraction truly professional, making the MEV problem more serious today. Of course, we do not know what would happen now without these discussions, but now it has indeed become a big problem.
CoW Swap believes that most MEV opportunities occur at the application layer, where users initiate transactions, so the occurrence of MEV should be minimized as much as possible. CoW Swap ensures that there is no possibility of capturing value from these transactions or reordering them by collecting user transaction intentions and clearing each batch of transactions in a block at a unified price.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




