On October 31, 2023, the price of BTC is 34,000 US dollars per coin.
Fifteen years ago today, on October 31, 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto released the white paper for Bitcoin.
In just 15 years, Bitcoin has created a myth with a 20 million-fold increase and a market value of 5 trillion.
Such an increase is unparalleled in any financial product in human history.
If a novice in the cryptocurrency circle is asked to explain what Bitcoin and blockchain are,
they will probably tell you that it is a decentralized, peer-to-peer electronic cash system.
Then the novice will leave, and the experienced individual, despite hearing these words for many years, may not understand the meaning of this statement.
So today, Jin Guixu is here to explain Bitcoin to everyone again.
As a Chinese person, the most commonly used payment software for everyone is WeChat.
Today, the boss paid Zhang San 5,000 yuan, and Zhang San transferred 4,800 yuan to his wife. His wife took this 4,800 yuan to KTV and gave it as a tip to a male model.
The above information involves three transactions with a large amount of information and a sad story.
Now, every second, WeChat has to process 14,000 such transactions.

The reason Zhang San can make normal transfers is because WeChat knows how much money Zhang San has, and this money is recorded in a special account at the People's Bank of China.
Zhang San also trusts that WeChat and the banking system's countless employees will not make a mistake with his balance.
But if there are no trusted third parties, how can Zhang San send money to his wife in a completely anonymous and decentralized network?
On October 31, 2008, an ID named Satoshi Nakamoto solved this problem with a nine-page paper.

Now we know that this mysterious person known as Satoshi Nakamoto and this nine-page paper created Bitcoin, equivalent to 5 trillion RMB, and the technology that supports the operation of Bitcoin, blockchain.
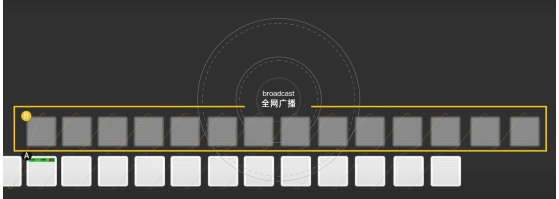
After the absence of trusted third parties, the biggest problem is that none of us can trust each other, so in the world of blockchain, transfers have to be broadcasted to let everyone know the origin and destination of every penny in the network.
Let's put this story back into the context of blockchain. Zhang San transferred 4,800 yuan to his wife, and this is Zhang San's electronic signature 859c362.
Everyone will verify the electronic signature and record this transfer in the ledger, proving that Zhang San has lost 4,800 yuan and his wife has gained 4,800 yuan.
But how do we know if Zhang San really has this money?
Zhang San's ledger will help him confirm. This ledger is the block, and connecting the blocks forms the blockchain.
And these ledgers record all the transaction records of Bitcoin from its inception to today.
There are approximately 800,000 blocks now, with two to three thousand transactions recorded in each block, including the amount of money in every account, where it came from, where it went, all recorded clearly, transparently and openly.
In the blockchain network, everyone holds an identical and real-time updated ledger.
So when Zhang San wants to transfer money to his wife, everyone's ledger will start to backtrack, checking if he really has that 4,800 yuan. If not, the transfer is invalid.
It is not difficult to see that the reliability of the ledger is the cornerstone of digital currency. If the ledger has a problem, no currency will work.
But this leads to two new problems.
Who will keep the ledger for everyone? How can we ensure that the ledger is not tampered with?
If everyone can keep the ledger, then the transactions and transaction order in each block may be different. If there are intentional false accounts, it will be even more chaotic, and it will not be possible to obtain a ledger that everyone can accept.
So the person keeping the ledger must be acceptable to everyone, which is also known as the consensus mechanism.
Today's various blockchains have different consensus mechanisms.

And Satoshi Nakamoto's solution is to solve a puzzle. Whoever solves the puzzle first has the right to keep the ledger.
This mechanism is called proof-of-work.

The essence of proof-of-work is exhaustive search. The stronger your device's computing power, the higher the probability of finding the answer.
To achieve this, hash encryption is used.
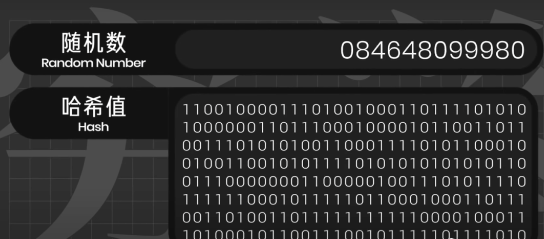
Taking the SHA256 algorithm as an example, any string of characters encrypted with it will produce a unique 256-bit binary number.
And as long as there is any slight change in the original input, the hashed number will be completely different.
Opening a block, we can see the number of transactions recorded in this block, transaction details, block headers, and other information.
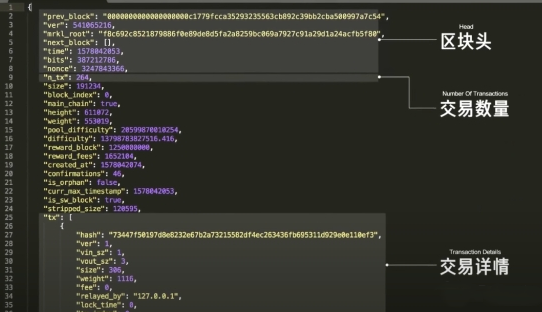
The block header is a label for a block, containing a timestamp, Merkle root, hash value, random number, and the hash value of the previous block.
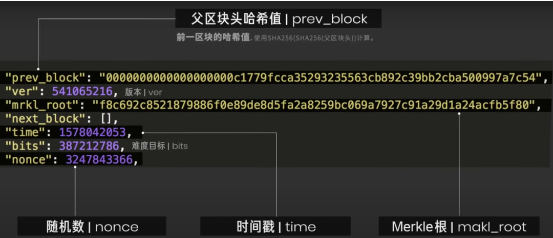
And by performing a second SHA256 calculation on the block header, we can obtain the hash value of this block.
To keep the ledger, the various information in the block needs to be packaged, and then the random number in the block header needs to be modified so that the input value can produce a hash value with the first n digits being zeros after the hash calculation.

In fact, each digit has only two possibilities, 1 and 0.
So the probability of success for each change in the random number is one in two to the power of n.
Assuming n is 1, meaning only the first digit needs to be zero, the success rate is 1 in 2.
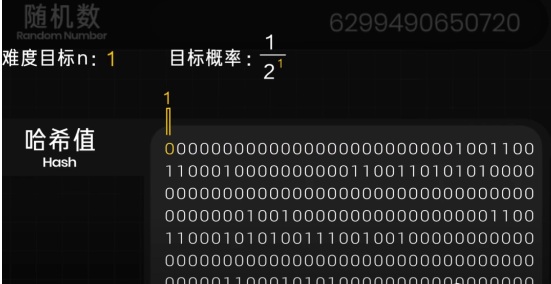
As the computing power in the network increases, the more zeros are required, and the difficulty of the proof-of-work also increases.
Today, the value of n in the Bitcoin network is approximately 76, so the success rate is about 1 in 2 to the power of 76, which is roughly 755 trillion trillion to one.
It would take about 1,000 years with an RTX 4090 graphics card to find the answer.
So it is not easy to find the answer, but once you do, everyone can verify it instantly.
If there are no issues, everyone will add this block to the ledger and start packaging and calculating the next block.
This way, everyone in the network has an identical and real-time updated ledger.
To motivate everyone to keep the ledger, the first node to completely package a block will receive a system reward.
The current reward for a block is 6.25 bitcoins, roughly 1.5 million RMB, and this process is also known as mining.

On the other hand, to prevent the ledger from being tampered with, each newly added block needs to record the hash value of the previous block in the block header, also known as a hash pointer.

This continuous pointer will eventually point to the first founding block, connecting all the blocks tightly together.
If you modify any character in any block, it will change the hash value of that block, making the hash pointer of the next block invalid.
So you must modify the hash pointer of the next block, but this will affect the hash value of that block, so you need to recalculate the random number.
After completing the calculation, you need to continue modifying the next block of this block until you have modified all the blocks after this block, which is very troublesome. ```
This way, even if the bookkeeper wants to falsify, it is impossible, because there are electronic signatures, and the bookkeeper cannot forge a transfer from someone else to themselves. And because of the existence of historical ledgers, money cannot be created out of thin air.
But this leads to a new problem, if two people complete the calculation at the same time and package a new block, whose block should be followed?
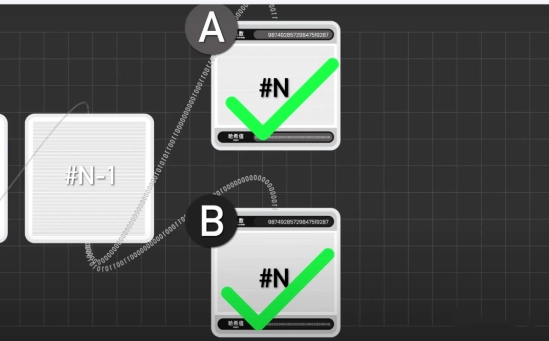
The answer is to follow the longer chain.

Now everyone can continue to package behind these two blocks. For example, if the next person to complete the calculation in the next round chooses to record on chain B, then the B chain becomes longer.
Next, others will also be willing to follow behind B. In general, the winner can be determined within six blocks. Transactions on the abandoned chain will be withdrawn and placed back into the transaction pool for repackaging.
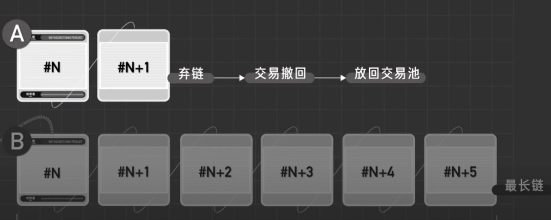
But since it follows the longer chain, as long as you can calculate better than everyone else, with computing power greater than 51%, you can calculate the longest chain and thus control the ledger.
So the stronger the mining power in the Bitcoin world, the more zeros need to be calculated, ensuring that no one can control the right to keep the ledger.
But it's hard to say for other blockchains with fewer participants.
For example, on May 15, 2018, a digital currency called Bitcoin Gold suffered a 51% attack.

The attacker first transferred $10 million worth of Bitcoin Gold to an exchange, and this transaction was recorded in block A.
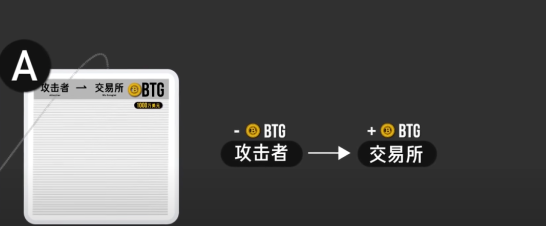
At the same time, the attacker secretly prepared a block B where this transaction did not occur, and then calculated new blocks after block B.

After the transfer on chain A is confirmed, the attacker can withdraw the Bitcoin Gold from the exchange. But because the attacker's computing power is greater than 51% of the entire network, the length of chain B will always be greater than that of chain A.
At this point, as long as the longer chain B is broadcast to the entire network, history will be rewritten, and chain B will replace chain A as the true main chain, and the transfer to the exchange in block A will be withdrawn, allowing the attacker to profit by $10 million.
Today, for ordinary people without mining power, the simplest way to obtain digital currency is to buy it from an exchange.
After buying, you can withdraw it to a wallet address, which comes from your private key. The private key, when encrypted, produces a public key, and the public key, when encrypted, produces an address.
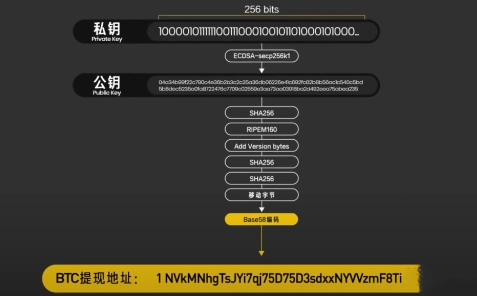
In an anonymous network like blockchain, only the private key can prove that you are you. As long as you attach the electronic signature generated by your private key during a transfer, everyone can confirm that the transfer is valid.
If the private key is leaked, anyone can impersonate you and transfer the money.
For example, in 2013, a man named Adam received Bitcoin worth 10,000 RMB in today's value on live TV, and after happily showing his private key to the camera, the money was stolen on the spot.

In the encryption industry, if you want to seize the opportunity of the next bull market, you need to have a high-quality circle, where everyone can band together and stay insightful. If you are alone and find that there is no one around, it is actually very difficult to persist in this industry.
If you want to band together or have doubts, feel free to join us, the public account "Hao (Guanguan Shuo Bi)"! 
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



