Original Author: Alfred, LD Capital

On the morning of October 7, 2023, the armed organization led by Hamas, known as the Islamic Resistance Movement, launched the operation codenamed "Aqsa Flood," and within a short period of time, more than 5,000 rockets were launched into Israeli territory. Thousands of armed militants entered Israeli territory from the Gaza Strip and engaged in conflict with the Israeli military. On the same day, Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu issued a public statement on the event, stating that the country was in a state of war and had begun to retaliate. The conflict has been ongoing for a week and is showing signs of further escalation, resulting in over 4,700 deaths. This conflict has once again shifted the focus of global politics and economy back to the Middle East. This article will analyze the logic of the conflict and its impact on the financial market.
I. The Formation of the Century-old Grudge between Israel and Palestine
The history of Palestine and Israel in the present-day Palestinian region can be traced back to two or three thousand years ago. The true formation of the grudge and conflict occurred after the 1917 Balfour Declaration and the "two-state solution" proposed by the United Nations in 1947. The conflict has now lasted for about a hundred years, during which there have been five Middle East wars and countless conflict events. The root of the conflict lies in the firm and differing views of the two sides on land ownership, as well as the historical ambiguity left by countries such as Britain and the United States in their past dealings in the Middle East.
In the view of the Jewish people in Israel, the present-day Palestinian region is the promised land given to the Jewish people by God, as recorded in their religious book, the Tanakh. Before 1600 BC, the Israelites lived in the land of Canaan (now Palestine). Later, there was a famine in Canaan, and the Israelites sought refuge in Egypt, where they were enslaved. Around 1250 BC, Moses led the Israelites back to Canaan to rebuild their homeland, a period of history known as the "Exodus." Around 1000 BC, the 12 tribes of Israel united to establish the Kingdom of Israel. The northern part of Israel was later conquered by the Assyrians, while the southern Kingdom of Judah remained, later known as the Jewish people. Subsequently, the Jewish people were successively conquered and ruled by the Babylonians and then the Romans. Around 70 AD, the Jewish people waged war against the Romans and suffered a disastrous defeat, leading to the expulsion of all Jewish people. Since then, the Jewish people have left the land of Palestine and embarked on a two-thousand-year exile. A small number of people remained in the Middle East, while the majority migrated to Europe and other regions to live. However, the Jewish people have always considered the land of Palestine to be the place where their ancestors lived and the promised land given to them by God.
In the view of the Palestinian Arabs, around 337 AD, during the time when Palestine was still under Roman rule, some Arabs began to live in the land of Palestine. After 630 AD, Islam began to emerge and gave birth to its religious book, the Quran. In the following hundred years, Islam rapidly expanded. The Middle East, including Palestine, became a region dominated by Arab people and the mainstream religion became Islam. Palestine was subsequently ruled by the Turks, Franks, Mamluks of Egypt, Mongols, and the Ottoman Turkish Empire. However, most of the subsequent rulers also began to embrace Islam, and the region remained predominantly Muslim. Before 1882, the Jewish population in Palestine accounted for only 8% of the total, making them a minority.
Around 1800, the idea of Zionism, also known as Jewish nationalism, was proposed among the Jewish people, calling for Jews from around the world to return to Palestine to establish a homeland. At first, the idea of Zionism did not receive widespread support because Jews had their own lives in various places and information spread slowly, making it difficult to form a consensus. However, in 1881, a large number of anti-Jewish riots occurred in southern Russia, which prompted the spread of Zionism and led to two waves of Jewish immigration. By 1914, the proportion of Jews in Palestine had risen to 13.6%, leading to conflicts between the newly arrived Jewish population and the existing Arab population. In 1915, the British government, in order to overthrow the Ottoman Empire's rule in the Middle East and to support the establishment of an independent Arab state, reached an agreement with Hussein and gave support for the ownership of Palestine. However, the British later reached a different agreement with France, leaving behind a potential conflict. In 1917, the British government publicly supported the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine through the Balfour Declaration, for the purpose of lobbying and its interests in the Middle East. By 1939, the proportion of Jews in the region had exceeded 30%. After the outbreak of World War II, Nazi Germany began the extermination of Jews. After the war, a large number of Jews went to the United States and Palestine, and pushed for the establishment of an independent state. In 1947, the United Nations proposed the "two-state solution," dividing Palestine into two parts: the State of Israel, predominantly Jewish, and the State of Palestine, predominantly Arab, with Jerusalem as an international public area under the jurisdiction of the United Nations.
The Jewish people declared the establishment of Israel in 1948, but Arab countries believed that Palestine had been predominantly Arab territory since the 7th century, and that the international agreements that followed were different from the previous promises made by Britain. They strongly opposed the establishment of a Jewish state in a region predominantly inhabited by Arabs. On the second day of Israel's establishment, neighboring Arab countries gathered to attack Israel, leading to the outbreak of the first Arab-Israeli war. Israel emerged victorious, but local wars, conflicts, and disputes over the ownership of the Palestinian territories have continued to this day.
II. Overview and Projection of the Current Israeli-Palestinian Conflict
1. The Underlying Logic of the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict
After the fifth Middle East war, the first peace agreement, the Oslo Accords, was signed by both Israel and Palestine in 1993, allowing the Palestinian side to establish a temporary autonomous authority for subsequent negotiations and discussions with Israel on the transfer of territories. In 1995, the leader of the Palestinian Liberation Organization, Yasser Arafat, and the Israeli Prime Minister, Yitzhak Rabin, signed the Oslo II Accord, for which they were awarded the Nobel Peace Prize. However, the progress of the agreement was not smooth, and various factions within each side were dissatisfied with the specific content of the agreement. After the signing of the Oslo II Accord, Rabin was assassinated by right-wing extremists in Israel, and the Palestinian Liberation Organization was mainly divided into two factions: Fatah, which pursued a peaceful path, and Hamas, which sought to further fight for its rights. Subsequent peace processes under the Oslo Accords did not make effective progress. After 2000, large-scale conflicts broke out again in Palestine, leading to a deterioration of relations between the two sides. Subsequently, the Gaza Strip came under the control of Hamas, while the West Bank came under the control of Fatah.
The current Prime Minister of Israel is from the right-wing Likud party, Benjamin Netanyahu. He has served as the Prime Minister of Israel three times, from 1996 to 1999, from 2009 to 2021, and from 2022 to the present, with a total tenure of over 15 years, making him the longest-serving Prime Minister since the establishment of Israel in 1948. On December 29, 2022, Netanyahu was reappointed as Prime Minister for the third time and formed the most right-wing cabinet in Israeli history. Netanyahu's right-wing stance is evident in both domestic and foreign policies. Externally, he has continuously compressed the living space of the Palestinians through policies and practical actions, leading to increasingly hostile sentiments from Palestinians and some Arab countries. Internally, on the basis of the increasingly fierce confrontation between secular Israelis and ultra-Orthodox factions within Israel, the Netanyahu government insisted on promoting a judicial reform in early 2023 to weaken the power of the Supreme Court and strengthen the Prime Minister's power. The Supreme Court is the only institution in Israel that can check the ruling party, and this move has aroused fear among left-wing individuals and secular Israelis, as well as dissatisfaction from the United States, which has just shifted its global strategy away from the Middle East. This has led to 29 consecutive weeks of strikes and protests, and Netanyahu continues to face pressure from both domestic and international governance.
In the case of Hamas in Palestine, there may be two main reasons for the initiation of the current Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Firstly, it is based on a long-standing resentment over living space and resource accumulation. The Gaza Strip is currently referred to as the "largest open-air prison in the world," with 3 million people living on 365 square kilometers of land, surrounded by border walls with limited access to water and electricity from Israel. They are unable to develop beyond basic survival. The Palestinian territories in the West Bank are also continuously encroached upon by Israeli settlements, and various policies make it difficult to achieve normal economic and industrial development. Essentially, Palestine is slowly dying, and Gaza is in an extremely difficult situation, becoming a powder keg ready to explode. Secondly, Hamas is able to continue its resistance in the confined space of Gaza, with support from some Arab interest groups. The motivation behind the initiation of the conflict also considers the instructions and actual support from these interest groups. Since September, there have been reports that the United States and Saudi Arabia are advancing a joint defense mechanism, in which Saudi Arabia needs to support Israel's legitimate status for normalization of relations and increase oil production in 2024 according to U.S. demands in exchange for U.S. military support. It is possible that the conflict is being used to hinder the achievement of this agreement.
2. Current Development of the Conflict
Hamas has demonstrated unprecedented levels of preparation and organization in the current conflict, indicating thorough preparation for escalation and sustained conflict. They have also received significant support from several Arab countries and organizations. In addition to Iran, Lebanon, Syria, Iraq, and Egypt, the Saudi Crown Prince has expressed continued support for Palestine, and some countries have begun supplying materials to the Gaza Strip. The support from resistance organizations in various regions is more direct and radical. The second-in-command of Hezbollah in Lebanon, Qassem, has stated that the organization is closely monitoring the situation between Israel and Palestine and is prepared to act when the time is right to confront Israel, even if other countries advise against it. The Badr Organization in Iraq, the Fatah Alliance, Hezbollah Brigades, and the Houthi armed forces in Yemen have also warned that if the United States directly intervenes in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, it could escalate into a regional war.
The ruling party in Israel has taken an extremely right-wing stance, indicating a willingness to eliminate Hamas. The Israeli parliament has approved Netanyahu's proposal to form an emergency interim government and activate the provisions in the Basic Law regarding "declaring war or taking significant military action," in order to empower an emergency cabinet consisting of Netanyahu, Defense Minister Yoav Galant, and Benny Gantz. Netanyahu has recently expressed a strong stance that Israel will "crush and destroy Hamas," and every member of Hamas will be "dead." At the same time, Israel has received extensive support from European and American countries and their important media. The National Security Council has stated that the United States can support both Ukraine and Israel simultaneously and has begun providing military supplies to Israel. The USS Ford aircraft carrier has arrived in the eastern Mediterranean, and a second aircraft carrier is on its way to provide deterrence and support. The Secretary of State and the Secretary of Defense have visited Israel to meet with Netanyahu. The UK has announced the deployment of reconnaissance aircraft and two Royal Navy ships to the eastern Mediterranean near Israel to support Israel.
The current conflict has the potential for large-scale escalation and further spillover risks, with the highest number of casualties in years on both sides. Israel has begun engaging in actual combat with Hezbollah in northern Israel and with Syria in the northeast, conducting airstrikes on Aleppo and Damascus International Airport in Syria. Israel has also cut off water and electricity supplies to the Gaza Strip, effectively besieging it. Over 400,000 reserve soldiers have been called up, and Israeli armored vehicles and ground forces have been assembled along the Gaza border, preparing to enter the Gaza Strip. In a phone call with Putin, Netanyahu stated that Israel will not stop its actions in the Gaza Strip until Hamas is destroyed. Since the destruction of hospitals in the Gaza Strip on October 17, the conflict has shown further signs of escalation.
3. Future Projection of the Conflict
There are three possible directions for the future of the conflict:
First, both sides are willing to negotiate after several weeks of sustained conflict, or Hamas is quickly defeated, leading to discussions on a new peace plan under the advocacy of major powers. On October 10, senior Hamas official Moussa Abu Marzouk stated in a phone interview with Al Jazeera that Hamas is open to discussing a possible ceasefire and all political dialogues. If the goal of Hamas in this conflict is to hinder the recent US-Saudi agreement, there may be a motivation for negotiations. Israel may be willing to accept indirect negotiations through mediation from various countries when it has a significant advantage over Hamas in terms of casualties, to explore possible peace plans. Alternatively, if Hamas is quickly defeated, the Palestinian people will face a ceasefire plan dominated by Israel.
Second, the conflict between the two sides evolves into a proxy war and continues for several months. As the conflict escalates, armed organizations from various Arab regions intervene to support Hamas in order to balance the situation, while major powers maintain their respective interests and refrain from direct involvement. This could lead to support for various organizations, dynamic developments towards negotiations, or further escalation.
Third, the conflict between the two sides escalates to the extreme and evolves into a regional war. After the second scenario occurs, there is an increased risk of further escalation of the conflict. The more forces and resources are involved, the more likely it is for misjudgments to occur, leading to radical decisions by one side. If any major power intervenes in the conflict, it will escalate into a regional war.
Due to the significant disparity in negotiation resources between Hamas and the armed forces of Israel, the key to whether the conflict escalates lies with Israel. If Israel gains the upper hand in the conflict for a period of time, and is willing to expand the living space for the Palestinian people, or even willing to accept the 1947 two-state solution advocated by the United Nations and mainstream countries, there may be a better resolution to the Israeli-Palestinian issue. The implementation of the two-state solution would greatly improve the current situation for Palestine, and Israel could fundamentally resolve regional issues through concessions. However, the current government in Israel is extremely right-wing, and the Netanyahu government needs to establish a common external enemy and take longer to resolve domestic issues. The current statements and actions are extremely radical, and if Israel launches a destructive strike against Hamas and the Gaza Strip, the conflict will escalate to the extreme. Currently, the second possibility seems more likely.
III. Historical Review of the Impact of War on Financial Markets
(1) Conflict between Russia and Ukraine
In the one-month period following the outbreak of the conflict between Russia and Ukraine in February 2022, the prices of gold, crude oil, and Bitcoin rose to varying degrees. The price of Brent crude oil rose to a high of $137, the price of gold rose to a high of $2068, and the price of Bitcoin rose to a high of $47,888. Russian stock prices significantly declined, and the ruble's exchange rate also dropped significantly due to sanctions, such as Russia being removed from the SWIFT system and its foreign exchange reserves being frozen by Western countries. On March 15, the Federal Reserve began raising interest rates, and the price of Bitcoin began to decline continuously, showing a high sensitivity to interest rates and liquidity. The prices of crude oil and gold remained high for several months, while the ruble's exchange rate rebounded significantly due to Russia's issuance of a ruble settlement order, requiring "unfriendly" countries and regions conducting natural gas trade with Russia to open ruble accounts in Russian banks for settlement, or else Russia would consider it a default, leading to a V-shaped rebound in the ruble exchange rate after a significant decline.
(2) Iraq War
In October 2002, the US Congress authorized then-President George W. Bush to use military force against Iraq. Bush issued a final ultimatum to Iraqi President Saddam Hussein, and the financial markets captured the brewing conflict, with the prices of crude oil and gold initially rising and then falling. On March 20, 2003, the United States, along with the United Kingdom, Australia, and Poland, launched a bombing campaign against Iraq, officially starting the Iraq War. This nearly decade-long war led to continuous conflicts in the Middle East and a sustained rise in crude oil prices, until the 2008 financial crisis.
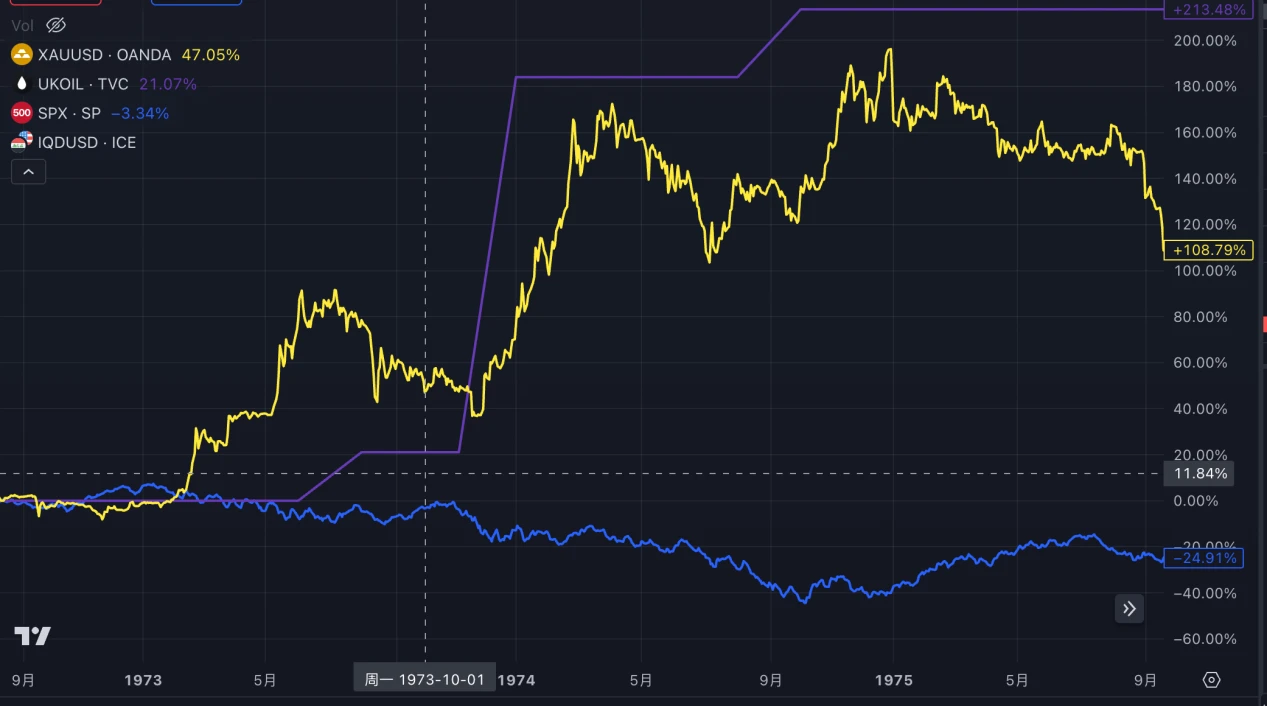
(3) The Fourth Middle East War
In the six months following the outbreak of the Fourth Middle East War in 1973, the prices of crude oil and gold rose significantly. This war led to an oil embargo implemented by Middle Eastern oil-producing countries led by Saudi Arabia, as a protest against the United States' support for Israel. Over the next three months, oil prices nearly doubled, and even after the conflict was resolved, they remained at high levels. The stock market in the United States, far from the war, experienced a certain degree of decline in prices, but the overall impact was limited.
IV. Fluctuations in the International Crude Oil Market in the Current Conflict
The geopolitical risk of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict in the oil-producing region of the Middle East, which accounts for more than one-fifth of the oil supply, is the most significant factor affecting oil prices. Since the Palestinian territories are not traditional oil-producing regions, the impact on oil prices will not be significant if the regional conflict does not escalate. However, if the conflict expands to OPEC member countries, it will significantly push up oil prices.
1. Pre-Conflict Crude Oil Market Situation
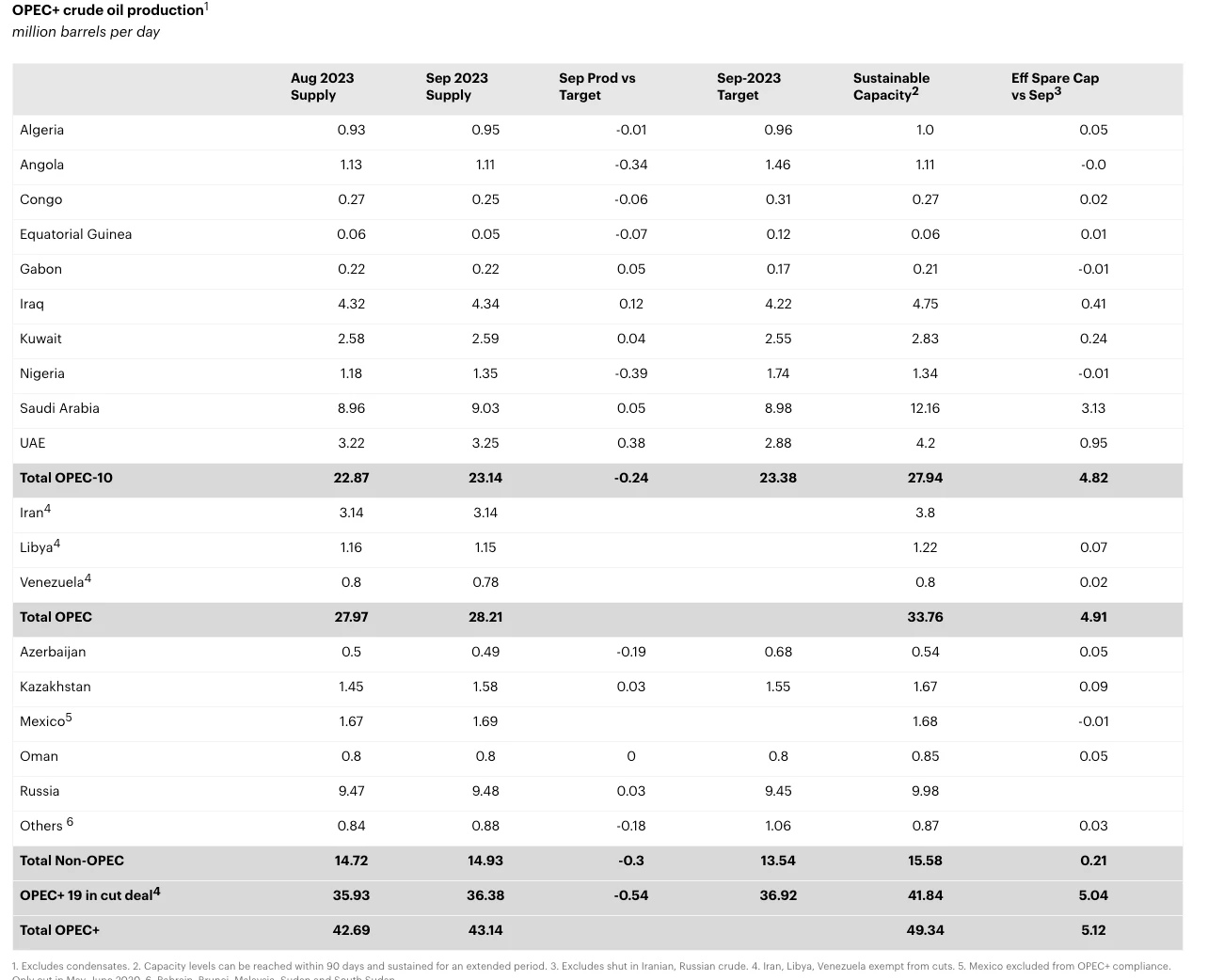
On September 5, 2023, Saudi Arabia and Russia extended their previous oil production reduction plan. Saudi Arabia voluntarily extended its additional 1 million barrels per day of production cut for three months until the fourth quarter of 2023, and Russia also decided to extend the 300,000 barrels per day reduction in oil exports until the end of the year.
According to IEA data, the OPEC+ production cuts continued to be implemented, with the total crude oil production of OPEC+ countries in September 2023 at 36.38 million barrels per day, lower than the target of 36.92 million barrels per day. Non-OPEC countries supplied 14.94 million barrels per day in September, lower than the target of 13.54 million barrels per day. The demand growth forecast for 2023 was revised from 2.2 million barrels per day to 2.3 million barrels per day.
Overall, global crude oil supply in September 2023 was 101.34 million barrels per day, while global crude oil demand was 101.63 million barrels per day, resulting in a supply shortage in the global crude oil market for the month. Looking at the forecast for the fourth quarter of 2023, global oil supply is expected to be 101.56 million barrels per day, and global oil demand is expected to be 101.62 million barrels per day, resulting in an expected supply shortage in the fourth quarter. The current supply shortage may worsen with the escalation of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, leading to higher oil prices.
2. Key Variables Currently Affecting Oil Prices
The suspension of the US-Saudi joint defense agreement. Previously, Saudi Arabia expressed its intention to increase oil production to the White House, stating that it was willing to increase oil production to facilitate the "US-Saudi joint defense agreement." Saudi Arabia stated that its oil production actions would depend on market conditions. If oil prices are high, Saudi Arabia is willing to take action at the beginning of 2024. Saudi and US officials stated that this move aims to promote the normalization of relations between Saudi Arabia and Israel. According to the agreement, Saudi Arabia will recognize Israel, and in return, the United States will sign a joint defense agreement with Saudi Arabia. For the United States, this move would help alleviate high inflation by lowering oil prices and aid in Biden's re-election campaign. However, the outbreak of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict makes it impossible for Saudi Arabia to proceed with the normalization of relations with Israel, and the US-Saudi joint agreement will be temporarily suspended.
Uncertainty in Iran's oil production. Since the end of 2022, in contrast to the production cuts by Saudi Arabia and Russia, Iran's oil production has continued to increase this year. According to previous forecasts, Iran could become the world's second-largest source of crude oil after the United States in 2023. However, with the outbreak of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, Iran is certain to firmly support Palestine in this event and may face oil export sanctions from the United States.
Potential reduction in oil production by Gulf countries in the event of an escalation. The Gulf oil-producing countries are mainly Arab countries, most of which support Palestine. If the conflict escalates to the third scenario and draws Gulf countries into the war, it will inevitably push global oil prices above $100 per barrel, although the probability of this event is currently low.
3. Current Oil Price Situation
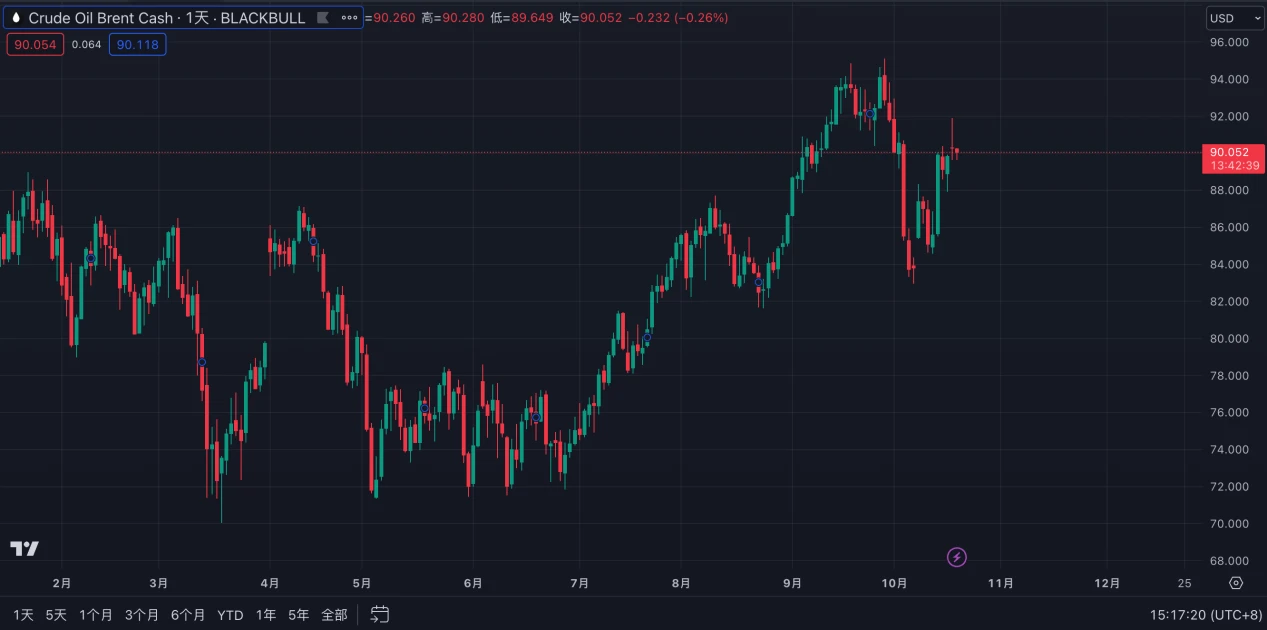
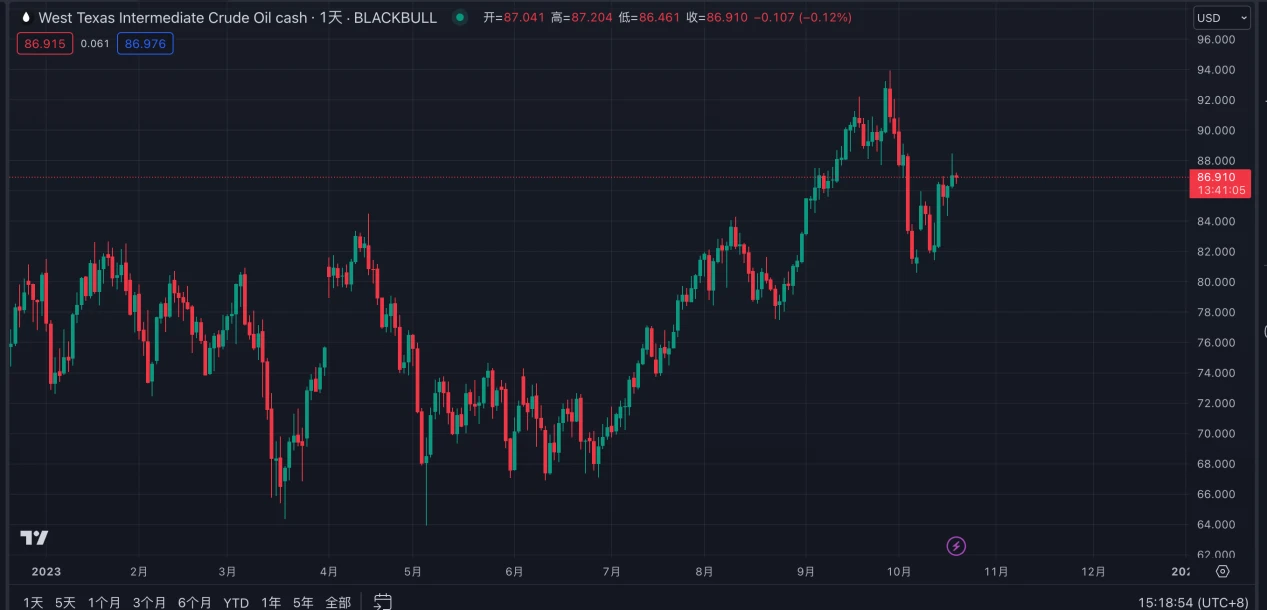
On the day the conflict broke out on October 7, Brent crude oil and WTI crude oil jumped at the opening, and market sentiment over the next two days was relatively optimistic, with the belief that the event would not have a significant impact on other oil-producing countries, leading to a slight decline in oil prices. However, on October 13, as the conflict continued to escalate, the market reassessed the situation, leading to a significant increase in oil prices, recovering from the price decline at the beginning of October. Currently, the prices of both types of oil are around $90 and $86 per barrel.
IV. Impact of the Conflict on Israel and the International Financial Markets
The recent Israeli-Palestinian conflict has had varying degrees of negative impact on the stock markets in Israel and the Middle East, with the currency exchange rate in Israel experiencing a significant negative impact. The markets in Europe and the United States have not been significantly affected as long as the conflict does not escalate further.
1. Stock Market
Since the outbreak of the conflict on October 7, the Israeli TA35 index has experienced the largest decline, falling by approximately 8% to date. The Egyptian EGX30 index initially declined but rebounded to a level higher than before the conflict. Major stock indices in Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Lebanon, and other neighboring countries have experienced varying degrees of decline. The major stock indices in the United States and the European Union have not been significantly affected. The negative impact of the conflict on the stock market is mainly in Israel and some Middle Eastern countries.
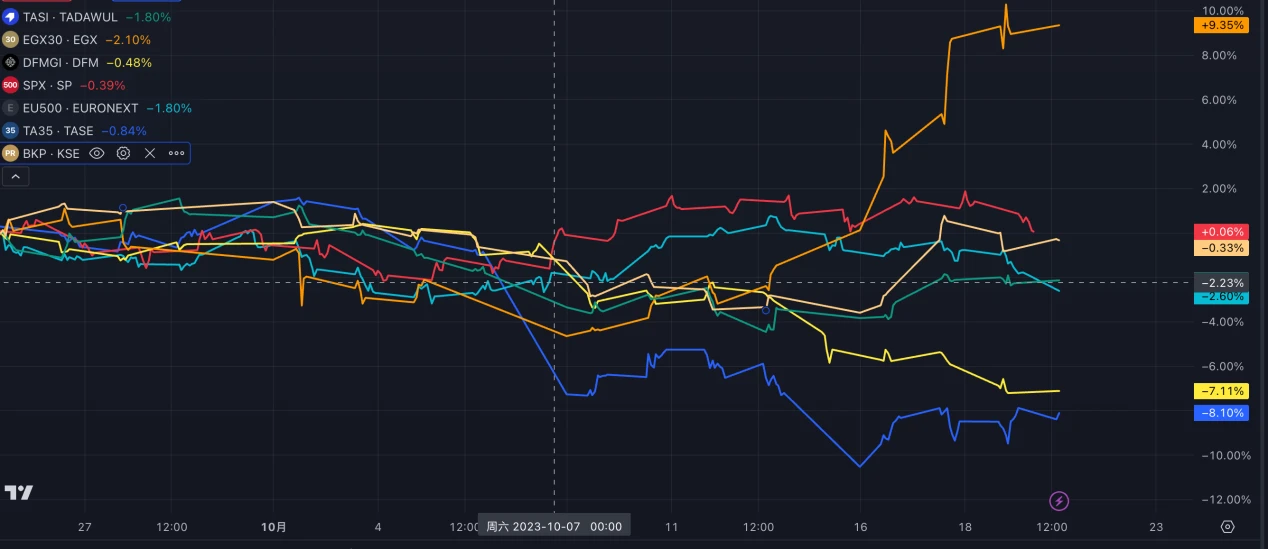
2. Exchange Rate Market
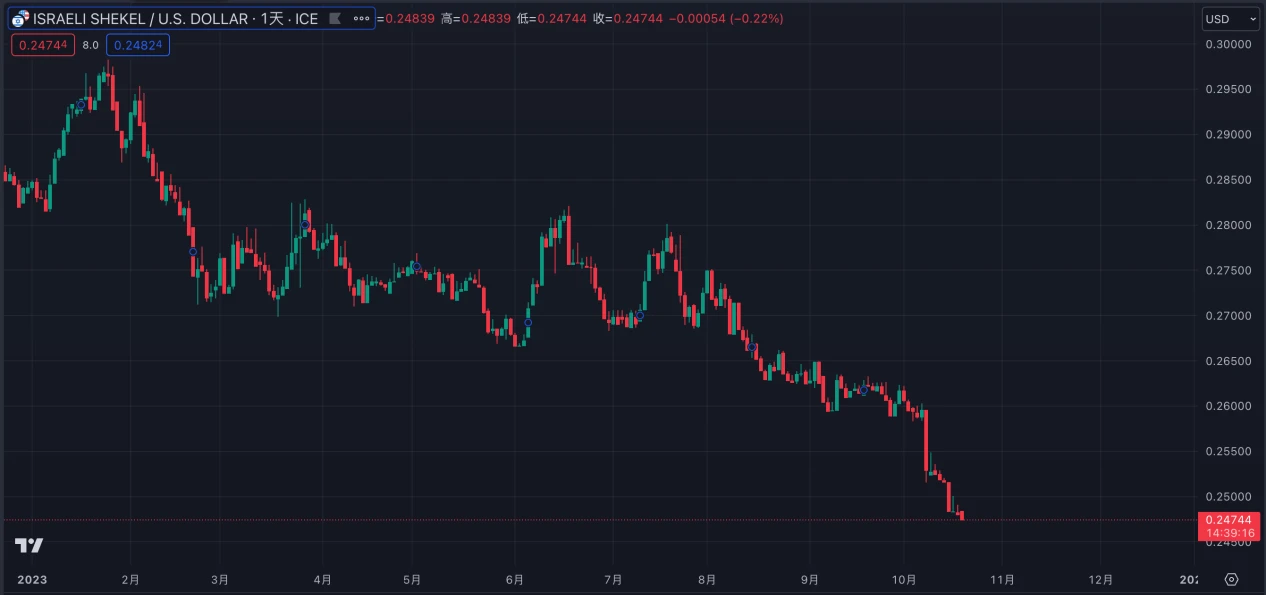
The main currency in Israel is the New Israeli Shekel, and the Palestinian territories do not have their own independent currency, using the Israeli New Shekel and the Jordanian Dinar for daily transactions. Since the outbreak of the conflict, the exchange rate of the Israeli New Shekel has experienced a significant decline, with a decrease of approximately 4%. The Bank of Israel recently stated that it would not defend any specific exchange rate level for the Israeli New Shekel.
3. Other
The city of Tel Aviv in Israel, known as the "Silicon Valley of the Middle East" and the "City of Innovation," has attracted a large number of research talents and technology companies. However, after the outbreak of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, many talents have enlisted, and many business activities of technology companies have been negatively affected. Recently, NVIDIA announced the cancellation of the offline conference for its annual AI summit scheduled to be held in Tel Aviv from October 15 to 16. According to the original plan, NVIDIA was to showcase its latest developments in the field of artificial intelligence during the AI summit, and NVIDIA's CEO, Jensen Huang, was scheduled to deliver a keynote speech at the summit.
In addition, on October 12, S&P Global Market Intelligence reported that Israel's 5-year credit default swap rose to 103 basis points, the highest level in nearly 10 years.
V. Changes in Gold, Bitcoin, and Cryptocurrency Markets
1. Gold
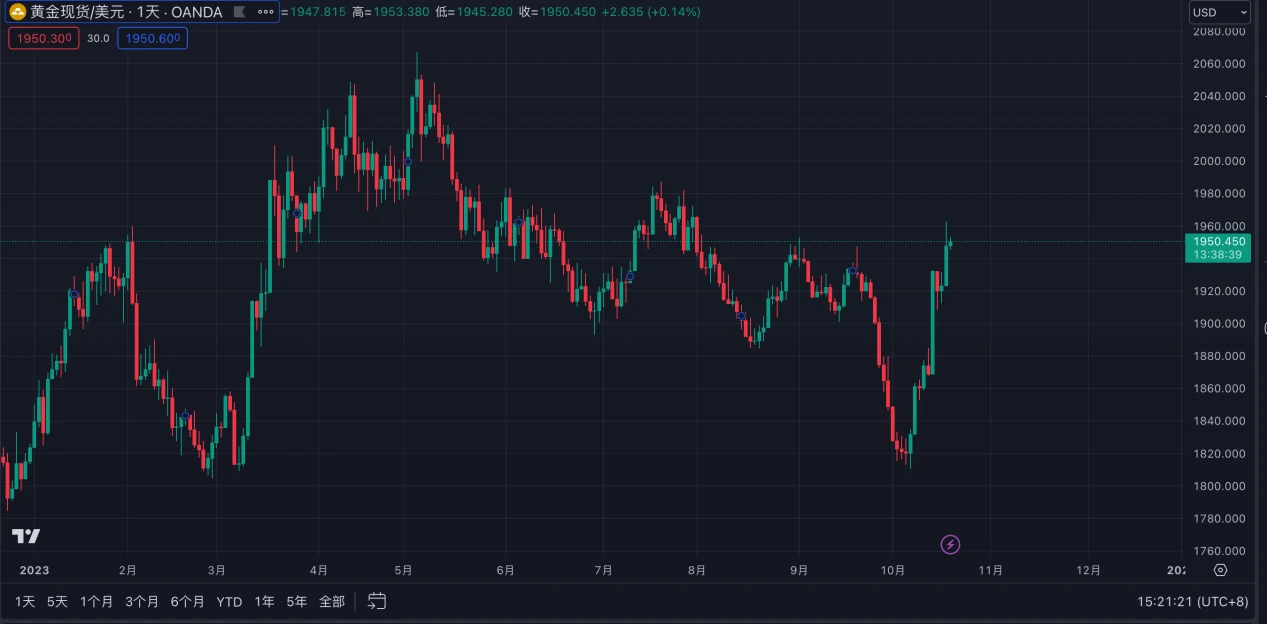
Gold, as a traditional safe-haven asset, tends to rise in price during significant wars and conflicts. Since the outbreak of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the price of gold has continued to rise, with a nearly 3.4% increase at the close on October 13, marking the largest increase in recent times. It has seen a small decline at the beginning of this week, but has accumulated a 5.5% increase, making it the most significantly affected asset by the conflict.
2. Cryptocurrency Market
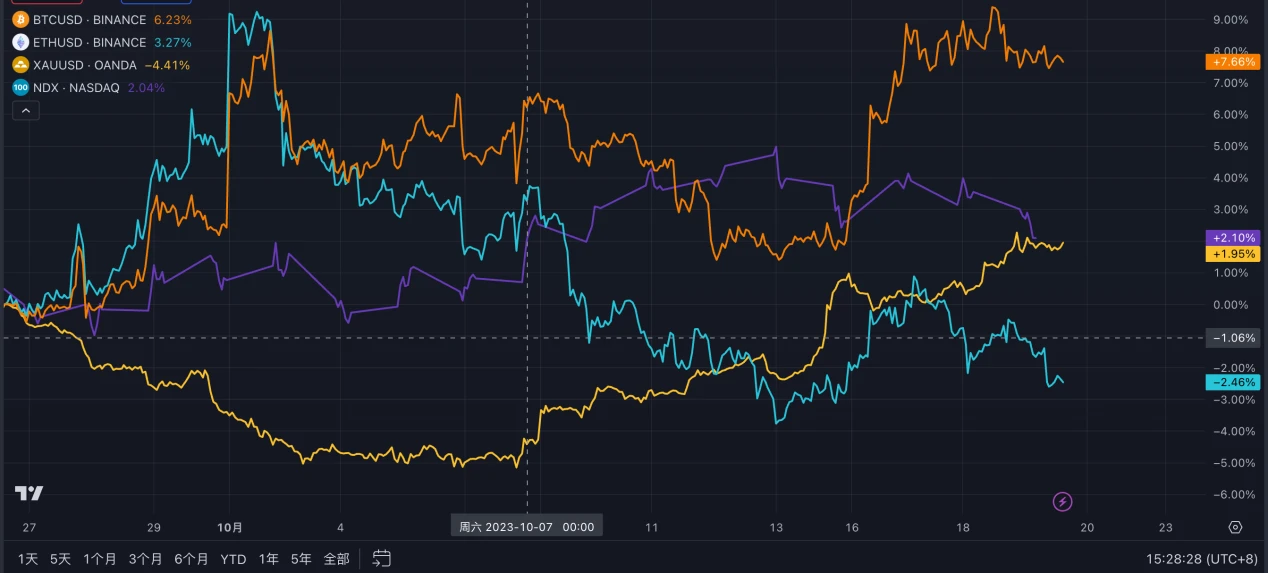
BTC was previously considered digital gold and to a large extent had a safe-haven property. However, since the outbreak of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, it has not shown a significant price increase like gold. It has even exhibited a relatively independent trend of continuous decline. Later, due to the fake news about the approval of a Bitcoin spot ETF this week, it experienced a sharp rise followed by a decline, reflecting BTC's inclination towards risk assets during a period of interest rate hikes.
3. Israeli and Islamic Cryptocurrency Projects
Israel has a high density of high-tech talents and companies, accounting for 0.1% of the global population, but it has some of the most successful startups in the world, ranking seventh in the number of unicorns. This advantage is not only evident in high-tech manufacturing and the internet but also in the Web3 field. Israel is home to leading academics such as Eli Ben Sasson, Shaffi Goldwasser, Yehuda Lindell, Aviv Zohar, Eran Tromer, and many revolutionary technologies such as MPC and ZKP. Well-known cryptocurrency projects include Starkware, Fireblocks, Kaspa, Secret Network, Bancor, and SSV Network.
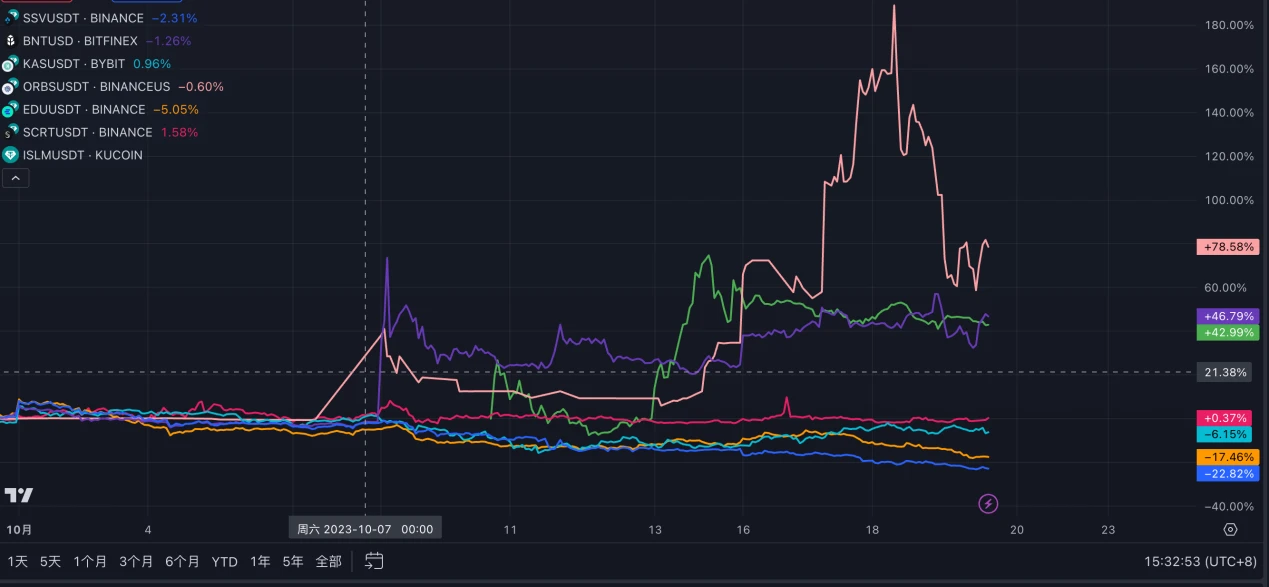
Since the outbreak of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, some Israeli cryptocurrency projects have been negatively affected, with price declines. For example, SSV, the Israeli founder of the Ethereum staking infrastructure SSV Network, Alon Muroch, announced on October 11 that he had been called up for military service. Although the team stated that operations were still normal, the SSV token price has significantly declined, falling by approximately 15% since the conflict began. BNT and ORBS recently experienced sharp price fluctuations due to significant market maker and whale activities, while most other token projects have experienced varying degrees of decline. Due to Israel's conscription system, many members of technology companies and projects may become reservists and directly or indirectly participate in military actions as the conflict intensifies. This may pose further downside risks for cryptocurrency projects headquartered in Israel.
It is worth mentioning that on October 10, the Islamic cryptocurrency project, Islamic Coin, announced the launch of the ISLM token and distributed community airdrop rewards. The project claims to operate an ecosystem on the HaqqNetwork blockchain that is compliant with Islamic principles. Its mission is to allow over 1.8 billion Muslims to enter digital finance without compromising their values and beliefs. The token price experienced a high and then a decline after opening, but has remained at high levels in recent days. If the conflict continues to escalate and more members of the Islamic world become involved, it may have a positive or negative impact on the token price.
4. Hamas and Cryptocurrency Financing
A recent report from TRM Labs shows that Hamas is the first Middle Eastern armed organization to use cryptocurrency financing. According to analysis by the cryptocurrency research firm Elliptic, digital wallets associated with the Palestinian Islamic Jihad organization received $93 million in cryptocurrency from August 2021 to June of last year. The BitOK research report also indicated that approximately $41 million flowed into wallets associated with Hamas during the same period, but it has not been confirmed whether these funds were used to fund the recent Israeli attacks. However, Ari Redbord, Director of Legal and Government Affairs at the blockchain intelligence company TRM Labs, revealed that cryptocurrency is only a small part of Hamas' fundraising strategy, as Hamas is primarily funded by states. Previously, Israeli law enforcement agencies and teams had cooperated with Binance to locate and seize funds from certain accounts, and the seized funds will flow into the Israeli treasury.
VI. Conclusion
Three Scenarios for the Development of the Israeli-Palestinian Conflict. In the first scenario, if both sides are willing to negotiate after several weeks of conflict or if Hamas is quickly defeated, there may be a new peace plan discussed in the future, leading to a quick return of oil, gold, and stock prices affected by the conflict to pre-conflict levels, and even further positive effects, pushing up the prices of equity assets in the Middle East. In the second scenario, if the conflict between the two sides evolves into an expanded proxy war and lasts for several months, with armed organizations from various Arab regions intervening to support Hamas to balance the situation that is leaning towards Israel, and major powers can maintain their respective interests in the region and refrain from direct involvement, the price of oil may be in the range of $85-100, and gold may be in the range of $1900-2000, with short-term trading opportunities following conflict news. Middle Eastern stock markets and the exchange rates of participating countries may remain at current low levels, and the overall impact on the cryptocurrency market may not be significant, but BTC is currently the most volatile asset among global assets in the short term. In the third scenario, if the conflict escalates significantly, with oil prices significantly rising above $100, even $150, and gold breaking through $2000, the stock markets and exchange rates of participating countries in the Middle East will experience significant declines, and the cryptocurrency market may see some increase due to the large outflow of funds from the Middle East to other markets, while the token prices of cryptocurrency projects headquartered in Israel will decline.
The key to the escalation of the conflict lies in the attitude of the Netanyahu government in Israel towards Hamas. Although the current conflict is limited to the Palestinian territories, Israel has shown extreme right-wing attitudes and behaviors. Various forces such as the United States and Iran have begun to make necessary preparations and support for Israel's attack on the Gaza Strip. The United States has deployed an aircraft carrier and a 2,000-strong force in the Mediterranean to support Israel. Lebanon and Syria have engaged in direct border clashes with Israel. The probability of the conflict escalating is increasing, and it may evolve into the second or even the third scenario.
Financial Market Impact under the Three Scenarios. In the first scenario, the prices of oil, gold, and stocks affected by the Israeli-Palestinian conflict will quickly return to pre-conflict levels, and if a ceasefire solution is appropriate, there may even be further positive effects, pushing up the prices of equity assets in the Middle East. In the second scenario, the price of oil may be in the range of $85-100, and gold may be in the range of $1900-2000, with short-term trading opportunities following conflict news. Middle Eastern stock markets and the exchange rates of participating countries may remain at current low levels, and the overall impact on the cryptocurrency market may not be significant, but BTC is currently the most volatile asset among global assets in the short term. In the third scenario, if the conflict escalates significantly, with oil prices significantly rising above $100, even $150, and gold breaking through $2000, the stock markets and exchange rates of participating countries in the Middle East will experience significant declines, and the cryptocurrency market may see some increase due to the large outflow of funds from the Middle East to other markets, while the token prices of cryptocurrency projects headquartered in Israel will decline.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



