The government's contrasting attitudes towards trading platforms and technological development make the Indonesian Web3 market stand out.
Authored by: Team composed of members from Tiger Research, Xangle, Avarik Saga, and Animoca Brands
Translated by: Babywhale, Foresight News

Research Method
This report was written by a team from Tiger Research, Xangle, Avarik Saga, and Animoca Brands, who spent a week in Indonesia interviewing industry experts and leaders about the Indonesian Web3 market. The main purpose of this report is to gain a broader understanding of the unique and complex dynamics of the Indonesian market. As with any market, the opinions gathered from the interviews sometimes diverge, but these differing viewpoints enrich the data and help us gain a more comprehensive understanding of the Indonesian Web3 market.
Summary
Indonesia's Web3 market has enormous potential. As the world's fourth most populous country, Indonesia has a thriving market, with the majority of its residents being young people, with a median age of 30. The Indonesian government also actively implements favorable policies to support Web3. Currently, there are more Indonesians with cryptocurrency accounts than stock market accounts. Given this momentum, we believe that Indonesia's growth will drive the development of the Web3 industry and local projects in the future.
However, to succeed in Indonesia, it is necessary to have a deep understanding of the country's unique national conditions. The Indonesian market is heavily influenced by major political and economic figures, and trading platforms operate under government supervision. Indonesia's religious and cultural diversity is rich and vibrant. In terms of talent recruitment, companies also face fierce competition from established Web2 companies. Additionally, compared to North America and East Asian countries, the Indonesian population is clearly lacking in Web3 knowledge.
Indonesia, this giant, is awakening, and its potential is enormous. Our report provides a comprehensive overview of Indonesia's Web3 market, aiming to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of this promising market.
Background: Indonesia is composed of numerous islands and is a country where multiple cultures and religions coexist harmoniously. Although Indonesia has historically experienced political turmoil, since 2000, Indonesia has achieved significant democratization and economic growth, and has emerged as one of the leading economies in Southeast Asia. Additionally, as the world's fourth most populous country, a considerable number of Indonesians adhere to Islam. However, Islamic finance practices, which guide Islamic financial regulations, do not seem to be a major obstacle to the Web3 ecosystem.
Regulation: After the Southeast Asian financial crisis, Indonesia implemented strict monetary policies to protect its currency value. The country continues to impose strict restrictions on the use of cryptocurrencies as a means of payment. However, at a higher level, interest in blockchain and cryptocurrency technology is growing. Regulatory authority over cryptocurrencies has been transferred from the Indonesian Commodity Futures Trading Regulatory Agency to the Indonesian Financial Services Authority (OJK), which has established a dedicated blockchain industry committee internally. Additionally, by July 2023, Indonesia is expected to launch a state-owned cryptocurrency exchange system similar to the current stock exchange model. This indicates that commercial cryptocurrency exchanges may be limited to legal securities distribution and brokerage roles, similar to traditional securities firms, while state-owned cryptocurrency exchanges will oversee order book management, among other things.
Infrastructure: Indonesia's Web3 infrastructure ecosystem is still in its early stages, and it is challenging to find significant blockchain infrastructure development projects locally. This is attributed to: 1) a lack of developer communities; 2) limited global experience of startups; 3) immaturity of the Web3 ecosystem. Therefore, like other countries, the main blockchains used are BNB Chain and Ethereum, as well as wallets like MetaMask.
Exchanges: In Indonesia, the activity of the CEX market surpasses other industries. Currently, there are over 30 exchanges in operation, and cryptocurrency users account for about 4% of the total population (approximately 10 million), a number comparable to the registered investors on the Indonesia Stock Exchange (IDX). However, factors such as 1) a high tax rate of 0.21%, 2) lack of product diversity, and 3) concerns about privacy lead most users to prefer global exchanges. These challenges hinder the development of local commercial exchanges.
Gaming: Indonesia's Web3 gaming market is still in its early stages. Nevertheless, with a high smartphone penetration rate (70% as of 2021) and an average of 8.54 hours of gaming per week per resident (ranking fourth globally), Indonesia's gaming market still shows enormous growth potential. Founders of major gaming companies such as Agate and Avarik Saga are expanding their investments in Web3 gaming. Additionally, the Indonesian government is providing various incentives to promote the development of the gaming industry and has shown a positive attitude towards the blockchain industry, raising expectations for future growth in the Web3 gaming market.
NFTs: Due to the recent market downturn, the heat of the Indonesian NFT market is currently at an all-time low. Despite high expectations from many investors, transactions have not met expectations, and the local market has not received significant attention.
Developer Ecosystem: Among Southeast Asian countries, Indonesia's developer ecosystem is relatively small. Therefore, even mature startups often outsource development tasks to countries such as India and Vietnam. As a result, the Indonesian government and private enterprises have shifted their focus to the education and training of developers. However, the number of developers enthusiastic about the blockchain industry in Indonesia is still significantly lacking. Most Indonesian developers tend to work for mature Web 2 startups rather than early-stage Web 3 companies, attracted by generous salaries, job stability, and the opportunity to work for well-known companies.
Background Knowledge
To understand Indonesia's Web3 market, it is necessary to first understand Indonesia's complex history and unique cultural background. Therefore, the following will explain Indonesia's historical and cultural characteristics to help readers gain a deeper understanding of the Indonesian Web3 market.
Brief History of Indonesia
Indonesia is composed of over 17,000 islands stretching 5,000 kilometers from east to west. In addition to geographical factors, Indonesia's culture has long been influenced by numerous external forces. In particular, the successive occupations by the Dutch and Japanese have had profound effects on Indonesian society, culture, and politics. Although Indonesia achieved complete independence in 1945, the country's political situation has been unstable, with military and democratic governments alternating in power. Indonesia established a democratic government in 2000 and has continued to focus on economic development, becoming one of the leading economies in Asia. However, the complex relationship between the economy and politics remains a major challenge.
Dutch Occupation: In the 17th century, the Dutch East India Company (VOC) began occupying various parts of Indonesia. Indonesia remained under Dutch colonial control for over 300 years. During this period, the Dutch utilized Indonesia's abundant resources to consolidate their control over the country.
Japanese Occupation and Independence: In 1942, Japan occupied Indonesia during World War II. After a brief period of Japanese rule, Indonesia declared independence in 1945. However, the Netherlands did not recognize Indonesia's independence, leading to the Indonesian War of Independence, which lasted until 1949 when the Netherlands officially recognized Indonesia's independence.
Post-Independence: Since declaring independence in 1945, Indonesia has experienced several periods of political turmoil. In the early years of independence, the country made efforts to consolidate stability, with democratic and military governments alternating in power. Political turmoil had a negative impact on the economy and foreign investment. After the fall of the military government in 1998, the democratization movement intensified, and in the 21st century, efforts for democratic reform and economic growth continue.
Present: Indonesia's current president, Joko Widodo, was first elected in 2014 and re-elected in 2019. Joko Widodo's election is seen as an important achievement in Indonesia's democratization following the fall of the Suharto dictatorship in 1998. During Joko Widodo's tenure, there has been significant economic growth, but he has rejected the proposal for a third term. Indonesia's new presidential election will be held on February 14, 2024.
Indonesia's Macroeconomic Situation
Indonesia's GDP in 2022 was $1.32 trillion, ranking first in Southeast Asia and nearly 2.7 times that of the second-ranked Thailand. Indonesia's average GDP growth rate over the past decade has also been high, with Indonesia's growth being the strongest in Southeast Asia at 4.4%, compared to 3.4% for Singapore and 2.4% for Thailand. This indicates that Indonesia has greater development potential compared to other countries, and we expect this growth to be a driving force for the future Web3 industry.
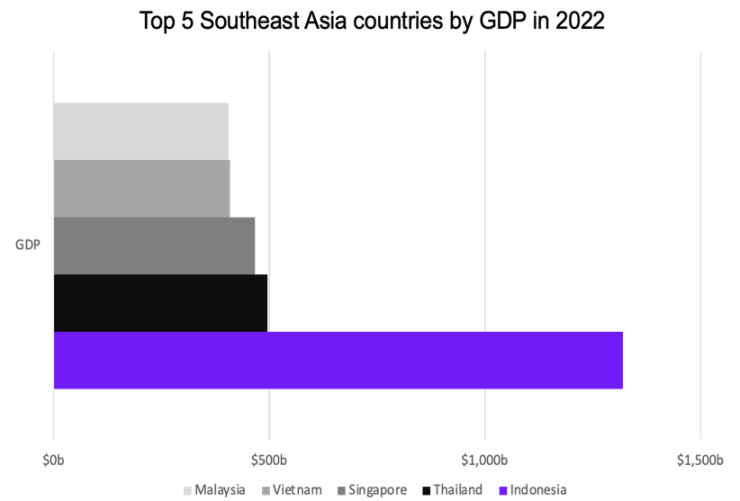
Source: World Bank, Xangle
Multiculturalism
Indonesia is the fourth most populous country in the world. It consists of over 17,000 islands, each with its own unique culture, traditions, and language. The country is also the birthplace of various religions, with Islam being the vast majority (87%) of the population. Many sources indicate that Islamic law, which governs the Muslim community, will have a significant impact on the economy. According to a 2020 government report, the Indonesian government is developing a roadmap to increase the proportion of "Islamic finance" in the total financial amount to 20%. However, in our research, we have not yet seen significant impacts of Islamic financial regulations on the development of the Web3 ecosystem and projects.
Impact of Islamic Law: Islamic law has some religious applications, but its impact on the Web3 market is not significant. Interestingly, some younger generations are reinterpreting Islamic law. For example, while Islamic law restricts usury, it also emphasizes the obligation to provide for one's family, so if cryptocurrency monetization helps provide for one's family, it is not considered illegal.
Bali is a famous tourist destination in Indonesia, and many developers work there. In particular, many Web3 developers from Russia and Ukraine have chosen to move to Bali to escape the conflict, which is an open secret. It has been reported that due to UN financial sanctions, Russians living in Bali cannot use the Russian ruble for financial transactions, so they secretly use cryptocurrency for daily expenses. Additionally, there is strong support for making Bali the center of the Web3 ecosystem, so large-scale Web3-related events (such as Coinfest) are held in Bali rather than the Indonesian capital, Jakarta.
Regulatory History
The Indonesian central bank does not recognize cryptocurrency as a payment method due to concerns about currency devaluation, which may stem from the country's experience of inflation after the 1997 Asian financial crisis. The Indonesian central bank is committed to protecting the value of the national currency and requires proof of purpose for currency exchange and large cash transactions.
However, interest in and investment in blockchain and cryptocurrency technology are growing. Indonesia hopes to use this technology to improve financial services and revitalize high-value industries. Since 2019, the Commodity Futures Trading Regulatory Agency (BAPPEBTI) has been drafting cryptocurrency regulations. Within two years, regulatory authority over cryptocurrencies will be transferred to the Financial Services Authority (OJK).
Currently, over 30 companies have registered as cryptocurrency operators and started operating services. Additionally, the number of cryptocurrency users and trading volume continues to grow. As of July 2023, the number of cryptocurrency users in Indonesia is approximately 18 million, with a monthly trading volume of approximately 8.027 trillion Indonesian rupiahs (60 billion USD).
- In December 2017, the Indonesian central bank banned the use of cryptocurrency for payment of goods and services.
- In February 2019, BAPPEBTI established regulatory rules for cryptocurrency market operations (BAPPEBTI Reg.No.9/2019).
- In November 2019, the Indonesian cryptocurrency exchange TokoCrypto became the first cryptocurrency exchange approved by BAPPEBTI.
- In December 2020, cryptocurrency trading in Indonesia was limited to government-designated exchanges, and a list of 229 approved cryptocurrencies for trading in Indonesia (including Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc.) was released (BAPPEBTI Reg. No.7/2020).
- In February 2021, after cracking down on unauthorized cryptocurrency exchanges, 68 exchange websites, including Binance, were closed and inaccessible in Indonesia.
- In May 2021, the Indonesian central bank officially announced the issuance of a CBDC through its social media accounts.
- In October 2021, detailed regulations for cryptocurrency exchange operations (minimum capital, etc.) were announced (BAPPEBTI Reg. No.).
- In May 2022, the Indonesian government decided to impose value-added tax and income tax on cryptocurrency transactions.
- In November 2022, Indonesia announced the latest list of 383 approved cryptocurrencies for trading in Indonesia (including new cryptocurrencies such as Klaytn and Solana) (BAPPEBTI Regulatory No. 11/2022).
- In December 2022, after the passage of the P2SK law in Indonesia, regulatory authority over cryptocurrencies will be transferred from the Commodity Futures Trading Regulatory Agency (CoFTRA) to the Financial Services Authority (OJK), with an expected grace period of about two years to avoid confusion.
- In June 2023, Indonesia announced the latest list of 501 approved cryptocurrencies for trading in Indonesia (including new cryptocurrencies such as Aptos and Sui) (BAPPEBTI Reg. No.).
- In July 2023, the Indonesian national cryptocurrency exchange was launched.
Main Findings
Indonesia's Web3 market is growing rapidly. However, we have found that the actual situation of the Indonesian Web3 market is more complex than what has been covered in previous articles and reports. This report will provide an in-depth analysis of the Indonesian market by focusing on six key areas: 1) regulation; 2) infrastructure; 3) exchanges; 4) gaming; 5) NFTs; 6) developer ecosystem. We hope to provide an accurate and comprehensive understanding of the Indonesian Web3 market through this analysis.
Regulation
Overall, Indonesia's regulatory environment is evolving into a unique structure that is difficult to find in other countries. From a macro perspective, the Indonesian government is taking a proactive stance towards the Web3 market and integrating it into the legal financial market, which is commendable, but the way and details of its development are worth noting.
Cryptocurrency Exchange Registration, Licensing, and Derivatives Authorization System: First, Indonesian regulatory agencies implement a system of 1) registration and 2) licensing for cryptocurrency exchanges:
Cryptocurrency Exchange Registration and Licensing System: In Indonesia, the Ministry of Trade's BAPPEBTI implements a system of registration and licensing for cryptocurrency exchanges. Apart from initial capital, there are no apparent differences in the requirements for registration and licensing of cryptocurrency exchanges, but the specific conditions for licensing have not been formally disclosed. Currently, over 30 exchanges have registered with BAPPEBTI as legal exchanges, but none have obtained final approval from BAPPEBTI. It is expected that the self-regulatory organization (SRO) under the Indonesian government-supported cryptocurrency exchange system will become the ultimate license holder, which will be discussed later.
Pledges and Other Derivatives Authorization System: Although many Indonesian exchanges currently offer cryptocurrency pledging services, they seem to require written authorization from BAPPEBTI to operate formal legal pledging services. The Indonesian cryptocurrency exchange Reku reports that its pledging service has been approved by BAPPEBTI. However, despite the formal authorization system by BAPPEBTI, the definition of industry derivatives remains unclear. Therefore, lack of authorization from BAPPEBTI does not seem to result in any sanctions.
Regulation of Cryptocurrency Exchanges: After the passage of the Law on the Development and Strengthening of the Financial Industry (RUU P2SK) on December 15, 2022, securities regulation was transferred to the OJK. Therefore, the regulatory authority of BAPPEBTI, a regulatory agency under the Ministry of Trade, will also be transferred to the OJK through inter-agency consultations, with a grace period of about two years until 2025.
Indonesian Web3 market experts generally hold a positive attitude towards the transfer of regulatory authority. This is because they expect the transfer of regulatory authority to the OJK, which is responsible for supervising and managing traditional financial markets such as banks and securities companies. This will 1) facilitate the entry of cryptocurrency operators into traditional financial services, and 2) make it easier for them to conduct business with traditional financial companies (such as stablecoins). Some believe that, unlike the lenient approach of BAPPEBETI, the OJK will maintain a stricter regulatory stance. Therefore, many cryptocurrency operators, especially exchanges, are looking to establish more comprehensive investor protection and anti-money laundering measures.
Currently, the OJK has a financial regulatory commissioner responsible for overseeing the cryptocurrency and digital asset industry. Indonesia is currently the only country that has established a specialized blockchain industry committee under the highest decision-making body for national financial policies. This is a positive signal for the importance and prospects of the blockchain and digital asset industry in Indonesia. Additionally, in September 2023, the OJK launched the first carbon credit exchange using a consortium blockchain and is collaborating with the Indonesian central bank to develop a CBDC project using a consortium blockchain.
State-Supported Cryptocurrency Trading System: In July 2023, Indonesia announced the launch of a state-supported cryptocurrency trading system. This is a unique event not seen in other countries and is an important factor in understanding the cryptocurrency trading environment in Indonesia. Market experts state that its purpose is to make Indonesia's cryptocurrency market more stable and transparent.
OJK has designed a cryptocurrency trading model that mimics Indonesia's existing securities trading model. This model is completely different from the existing systems of private cryptocurrency exchanges such as Binance and Coinbase, which manage and monitor their own order books. The overall liquidity of the cryptocurrency market is centrally managed by the central regulatory authority.
The state-supported cryptocurrency trading system consists of the following roles: 1) Custodian; 2) Clearing House; 3) Centralized cryptocurrency exchange; 4) Nationally authorized private cryptocurrency exchanges:
The custodian is responsible for custody (management and storage) of cryptocurrencies on Indonesian exchanges, with a maximum custody of 70% of the cryptocurrency volume on the exchange (based on public-private negotiations).
The clearing house will be responsible for safeguarding and managing the Indonesian rupiah (IDR) deposited into the exchange and will safeguard up to 100% of the legal currency (based on public-private negotiations).
The state-supported cryptocurrency exchange is responsible for managing the order book and liquidity of private cryptocurrency exchanges, including trading volume.
The role of private cryptocurrency exchanges seems to be somewhat diminished, similar to the legitimate securities distribution and brokerage business of traditional securities companies.
Unlike private cryptocurrency exchanges, the custodian, clearing house, and central cryptocurrency exchange in the new system will operate as self-regulatory organizations (SRO), similar to the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE).
Currently, Indonesia has granted a license to a custodian, a clearing manager, and a state-supported cryptocurrency exchange as self-regulatory organizations. The license for the national cryptocurrency exchange implies significant power and information in the Indonesian cryptocurrency trading business. Intense competition and some scandals and court cases have emerged between local and foreign companies to obtain this license.
Restrictions on Cryptocurrency Payments: Although cryptocurrencies have been recognized as assets (Bappebti No. 8, 2021), their use as legal tender or in electronic payment systems is still strictly limited. For example, Bali once had a cryptocurrency electronic payment business with the slogan "Bit Island." However, after over 100 participating merchants became targets of the Indonesian National Tax Office and OJK, the business was suspended. Therefore, Indonesian Web3 officials believe that it is unlikely for Indonesia to use any legal settlement currency other than the Indonesian rupiah (IDR) in the near future.
National Efforts to Join the Financial Action Task Force (FATF): It is reported that Indonesian financial authorities are working to join the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) at the national level. Joining the FATF will have a positive impact on the international recognition of Indonesia's anti-money laundering system and enhance the international credibility of financial institutions. This may lead to increased foreign investment and expansion, benefiting the Indonesian Web3 market.
Infrastructure
We found that Indonesia's Web3 infrastructure ecosystem is still in its early stages. In particular, we found that Indonesia lags significantly in infrastructure (such as local team Layer1/2 and wallets). In the past, Indonesian blockchain projects like Vexanium have not achieved significant results. This is due to several factors, including 1) limited developer community; 2) lack of global project experience for startups; 3) immaturity of the Web3 ecosystem. Therefore, globally popular blockchains (such as BNB Chain and Ethereum) and wallets (such as MetaMask) have become the preferred choice:
Layer 1/2: According to a survey by the crypto infrastructure provider Chainstack, BNB Chain dominates the use of node infrastructure in Asia, accounting for 72.1%, while Ethereum accounts for 25.4%. Similarly, most projects from Indonesia use Ethereum and BNB Chain. The Polygon, Base, Near, Algorand, and Tezos platforms also have some community activity. In particular, Base, known for expanding its activities in Indonesia by recruiting local staff. These teams have been hosting events and projects, interacting with the local cryptocurrency community.
Wallets: In Indonesia, apart from custodial wallets provided by exchanges, we could not find other significant participants. However, similar to other countries, MetaMask is the most recognized. Some DeFi users are also using the Crystal Wallet developed in Singapore. In Indonesia, many people still store their cryptocurrencies in centralized exchanges (CEX), possibly due to: 1) low adoption of DeFi applications; 2) ease of use and security of centralized exchanges.
Consortium Blockchain: The consortium blockchain market for Indonesian enterprises is still in its early stages but is expected to become more active. Currently, some public organizations are preparing pilot projects using consortium blockchains. For example, the carbon trading project and CBDC project led by the Indonesian government have applied consortium blockchain technology. It is expected that major companies in the financial sector and other industries will also announce various projects using consortium blockchain technology. Local startups focused on consortium blockchains, such as D3 Labs, have recently successfully completed fundraising. This trend is expected to further promote the adoption of blockchain technology in Indonesia.
Exchanges (CEX, DeFi)
Indonesia is one of the most active markets in the world centered around cryptocurrency exchanges. From 2014 to 2018, the cryptocurrency market was in its early stages, and many cryptocurrency exchanges emerged, with over 30 exchanges still in operation. The number of customers using them exceeds 17 million. Excluding duplicate accounts, it is estimated to be around 10 million, accounting for about 4% of the total population. Considering that there are 11.8 million retail investors registered on the Indonesian stock exchange, it is clear that cryptocurrency as an investment asset is highly attractive in the Indonesian market.
However, due to: 1) high tax rates for local exchanges (total tax rate for buying and selling is 0.21%); 2) lack of product diversity; 3) inability to trade anonymously, reportedly, 50% to 70% of users in the low market value market use global exchanges such as Binance. This situation limits the development of local cryptocurrency exchanges.
In the CEX field, Indodax and Tokocrypto seem to dominate the market, but it is believed that many Indonesian retail investors use global unlicensed exchanges, accounting for an estimated market share of over 50-70%. The Indonesian government has blocked access to unauthorized exchanges on the internet, but many users can bypass this ban by using VPNs.
- Indodax: Founded in 2014, Indodax has maintained a high market share in the Indonesian cryptocurrency market, with a notable market share of 42.0% in 2023.
- Tokocrypto: After being acquired by Binance in 2022, Tokocrypto has collaborated extensively with Binance, leading with a market share of 43.0% in 2023.
- Upbit Indonesia: Upbit Indonesia briefly led the market in 2022 but gradually lost its advantage in 2023.
- Reku: Reku is the first exchange authorized to conduct staking operations in Indonesia and has been expanding its market share with user-friendly UI/UX.
- NOBI: In addition to being an exchange, NOBI also offers high net worth asset management and over-the-counter trading, with a focus on staking. Apart from retail clients, NOBI is also dedicated to managing institutional client assets.
Currently, Indonesia imposes a purchase tax (0.11%) and a sales tax (0.10%) on each transaction. This has led users to frequently migrate from exchanges registered with BAPPEBTI to external platforms such as Binance. Some believe that this tax system is suppressing legitimate Indonesian exchanges, and it is reported that the Indonesian Blockchain Association and other organizations are discussing this issue with the government. Under the new state-supported exchange system, the burden on investors is expected to increase due to stricter SRO supervision and corresponding fees. The Indonesian Tax Office has disclosed plans for public-private negotiations on this issue starting this year, with expected improvements.
Although Indonesia has a publicly tradable cryptocurrency list, there are currently no specific standards or general criteria for listing and delisting cryptocurrencies on exchanges. Additionally, it is widely known that exchange officials and BAPPEBTI can directly intervene in the listing of new projects, making it difficult to establish transparency and trust in the cryptocurrency market. More transparent regulatory supervision is needed to ensure investor protection.
In Indonesia, exchanges do not have direct deposits and withdrawals but use payment aggregators. This is similar to the typical structure of payment gateway (PG) companies. Payment aggregator companies work with various banks and other financial institutions to ensure efficient payment processes. Through them, users can securely deposit funds and then easily trade cryptocurrencies.
Indonesia's largest tech company, GoTo Group, acquired the Indonesian cryptocurrency exchange PT Crypto Maksima Koin in 2022, entering the cryptocurrency field. However, we cannot confirm any significant collaborations or achievements by GoTo Group in the cryptocurrency field.
Gaming
The Indonesian gaming market has been steadily growing due to its mobile-friendly environment. As of 2011, the smartphone penetration rate in Indonesia was approximately 70%. According to Limelight Networks' global market research, Indonesians spend an average of 8.54 hours per week playing games, ranking fourth globally, behind China, Vietnam, and India.
Despite high market expectations, the Web3 gaming market is still in its early stages. The main obstacles are: 1) limited experience and capabilities of developers; 2) lack of awareness of Web3 among gamers. Additionally, compared to developed countries, the low average revenue per user (ARPU) also hinders the development of the gaming industry. Therefore, the number of Web3 gaming companies in Indonesia is limited, and the same is true for Web2 gaming companies.
However, some talented founders are working to develop new games and improve the ecosystem. Among them, two companies are seen as the twin stars of the Indonesian Web3 gaming industry: 1) "Mythic Protocol," developed by Arief, the founder of the renowned Indonesian game company Agate; 2) "Avairk Saga," developed by Indonesian expatriates.
Furthermore, the Indonesian government is actively promoting the gaming industry as the next important driver of industrial growth. According to the "2023 Indonesian Content Industry Development Trends" report released by the Korea Creative Content Agency, the Indonesian government is actively involved in the gaming industry and provides incentives for investors in the gaming industry. Capital-intensive enterprises with over 500 billion Indonesian rupiahs (approximately $32 million) are exempt from 100% of corporate taxes for up to 20 years, while enterprises with investments ranging from 100 billion to 500 billion Indonesian rupiahs (approximately $6.4 to $32 million) are exempt from 50% of corporate taxes. Therefore, it is expected that the future gaming ecosystem will be more active. Additionally, the government's friendly attitude towards the blockchain industry is expected to drive explosive growth in the Web3 gaming market.
In the areas where major engineering universities in Indonesia are located, such as Bandung and Yogyakarta, there are over 20 gaming companies, but most of them mainly develop outsourced games rather than creating their own IP. This limits the industry's development into a high-value-added industry, even in the gaming sector. This structure also limits the ability of companies to attract investment and grow. The historical reliance on outsourcing rather than creating proprietary intellectual property has been a major obstacle to the continued growth and technological development of the gaming business.
The Web3 gaming ecosystem in Indonesia is just getting started, with "Avarik Saga" and "Mythic Protocol" at the forefront. "Avarik Saga" is a JRPG game developed by Kevin Cahya, former director of the leading venture capital firm East Ventures, and a group of experienced professionals in the gaming industry with overseas experience. The game's team consists of approximately 50 employees and is expected to be launched next year.
"Mythic Protocol" was developed by the founder of the leading game company Agate, which recently secured a $6.5 million seed funding round from the crypto venture capital firms Shima Capital and Alpha Ventures. Agate has over 200 employees and has released popular games on Steam such as "Juragan Terminal" and "Valthirian Arc: Hero School Story." Given the success of P2E games such as "Axie Infinity," "Thetan Arena," and "Splinterlands" in Indonesia, there are high hopes for the future of the Indonesian Web3 gaming industry.
NFT
In recent months, Indonesia's NFT market has remained consistently weak, with multiple data points hitting historic lows. Many investors have high expectations for significant profits, but due to the global market downturn, the NFT market has not rebounded. Most Indonesians prefer to use global markets rather than local ones. Looking at the 2022 market share of the Indonesian NFT market, OpenSea accounted for 95%, Blur accounted for 4%, and other markets accounted for the remaining 1%. Art collection NFT projects such as Karafuru and Mindblown were once popular but have seemingly lost their momentum.
Developer Ecosystem
In comparison to other Southeast Asian countries, Indonesia does not have a large developer ecosystem. The reality is that many Indonesian unicorn companies such as Tokopedia and Gojek outsource their development to countries like Vietnam to address the shortage of development talent. To improve this situation, the Indonesian government and businesses are heavily investing in educating and training developers, especially in education and training programs. However, there is still a shortage of developers willing to work in this emerging industry. Many Indonesian developers prefer to work for Indonesian unicorn companies because these companies can provide: 1) higher salaries and better job security; 2) greater visibility, rather than working for early-stage Web3 startups. According to data published by Github, due to these efforts, the number of new developers in Indonesia increased by 36% in 2022, showing significant results.
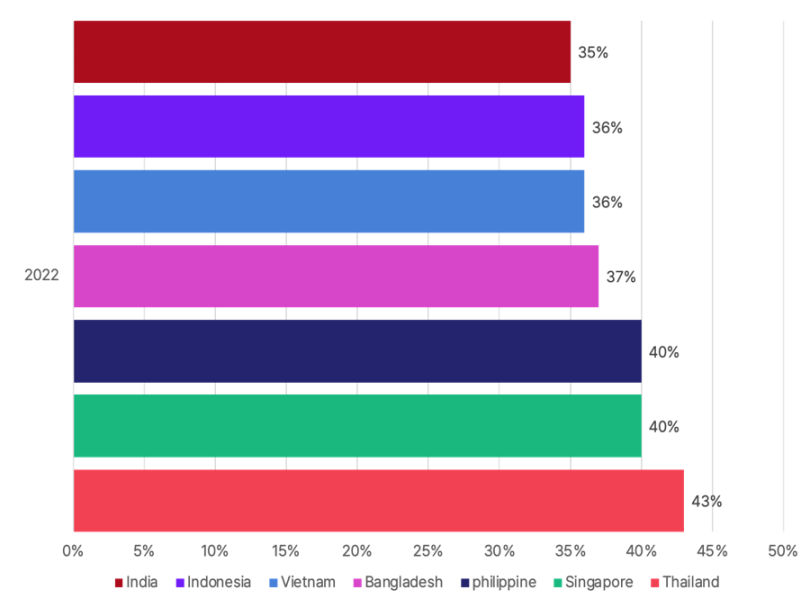
Blockchain developers growth by country, Source: Github
Blockdev.id is the largest and most active blockchain developer community in Indonesia. Currently, the community's Telegram group has over 1400 members and supports the growth of blockchain developers through various training and events. Meanwhile, some companies have also set up WhatsApp groups to help nurture the developer community.
Educational institutions in various countries have recognized the importance of blockchain education. Starting from the first semester of 2024, BINUS University plans to launch a project related to blockchain mining. In addition, Professor Andry Alamsyah of Telkom University is leading research on the Indonesian CBDC Garuda project. Furthermore, Bandung Institute of Technology (ITB), the University of Indonesia, and Gadjah Mada University are continuously nurturing excellent developers in the blockchain field. It is expected that the efforts of these schools will greatly support the development of Indonesia's blockchain and technology industry.
References
- 2022 Indonesia Population by Religion: Statista
- Vexanium
- Ethereum Dominates Web3 Developer Activity in the US, BNB Chain Dominates in Europe and Asia: Chainstack
- 2023 Q4 Indonesia Media Development Report
- 2023 Indonesia Content Industry Development Trends
- Global Tech Talent, Github
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



