Author: Kylo@Foresight Ventures
The emergence of blockchain technology and its ecosystem has provided many opportunities for innovators, developers, and users. However, so far, issues related to scalability, transaction speed, and front-running have been hindering Web3 from achieving true mass adoption. Sei has emerged to address these issues.
This article mainly elaborates on the superiority of the Sei mechanism through the description of the basic mechanism of Sei. This report is specifically divided into several parts, including "Introduction to Sei's Mechanism," "The Flourishing Ecosystem of Sei," "Comparison of Sei with other layer1," and "Unique Advantages of Sei in Transactions."
Sei: Mechanism Introduction
Sei is a universal Layer1 network designed to address various common issues in layer1. It operates through the Twin-Turbo consensus mechanism and utilizes transaction parallelization to achieve fast transaction confirmation, high throughput, and scalability. This innovative approach makes Sei a versatile and powerful platform, effectively bridging the gap between decentralization and high performance.
Twin-Turbo Consensus
Sei is a high TPS parallel Layer1, similar to DyDx's Tendermint mechanism at the consensus level but with some differences. To better understand Sei's mechanism, we need to understand the traditional block generation model. Block generation is achieved through consensus reached by validators by packaging transactions from their own mempool and broadcasting them to the entire network. Each network validator has their own mempool. When a transaction occurs, the user submits the relevant information to a full node (which is also a validator), and the full node sends the information to other nodes in the network, a process known as gossip. After receiving and verifying the transaction information, other nodes add the transaction to their mempool. The proposer, who constructs the block, sorts the transactions from their mempool, creates the block, and broadcasts the block information to the entire network for validation by other validators. Once consensus is reached, other validators accept the full block information from the proposer.
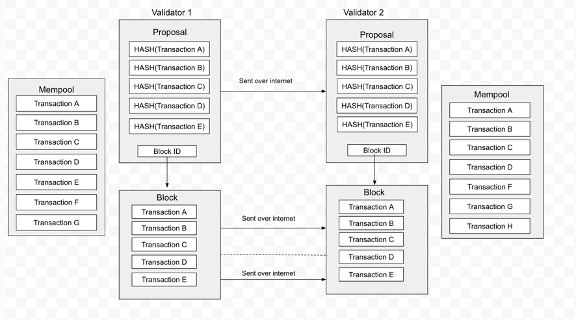
dumb block propagation
From the above mechanism, it can be observed that there are two steps where optimization is possible:
- Since each validator has a mempool, the transaction data in a new block may already exist in their respective mempools. Other validators can create blocks on their own without waiting for the proposer to send detailed block data to them.
- Block confirmation requires sequential processes of block proposal, validator voting, consensus, and block broadcasting. As these steps are carried out sequentially, there is no way to accelerate the process. Parallel processing of these steps can significantly improve block performance.
Based on the above points, Sei has optimized its consensus mechanism. It defines its consensus mechanism as Twin-Turbo Consensus, which is essentially a more intelligent block propagation method and an optimistic block production mechanism.
The first turbo needs to address two issues:
- Ensuring that each validator's mempool contains as much transaction information as possible.
- Allowing other validators to quickly know the transaction information packaged by the block proposer.
Having all mempools contain all transactions is an ideal state but difficult to achieve in reality. Therefore, Sei has implemented a remedy. When proposing a block, the block proposer breaks down the block and sends it to the entire network, while also sending a hash of all transactions within the block. Other validators search for the corresponding transactions in their mempools based on this hash. If some transactions are missing, they retrieve the missing transactions from the block proposer's sent block fragments to reconstruct the block. Through this method, the Sei Network reduces the time required for other validators to synchronize block information.
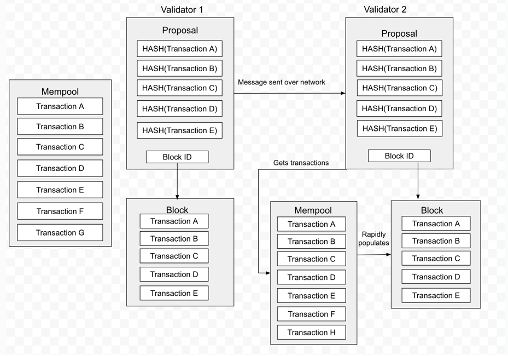
intelligent block propagation
The second turbo of Sei utilizes an optimistic block generation mechanism. "Optimistic" here means assuming that the majority of block proposers will not make mistakes. Under this optimistic assumption, validators can process block data synchronously while conducting prevote and precommit, meaning they can write the block data proposed by the proposer into the cache and directly import the cached data if the block is verified, without waiting serially for prevote and precommit to pass. Through the Twin-Turbo Consensus, Sei Network achieves reduced transaction latency and improved blockchain performance.
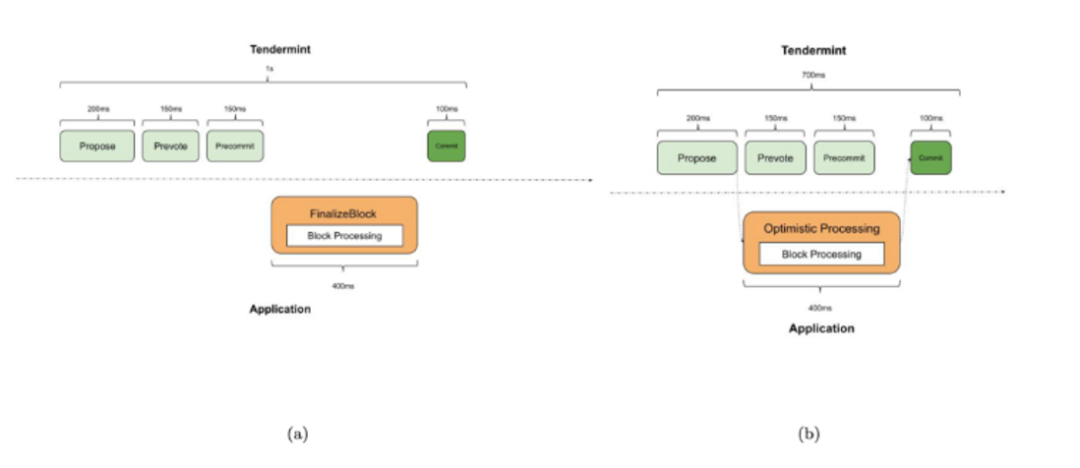
comparison between “normal” and “intelligent”
Transaction Parallelization
Transaction parallelization is a common method used by Layer1 networks such as Solana and Aptos to increase throughput. However, for Sei Network, transaction parallelization has an additional layer of meaning.
Similar to DyDx's V4 version, Sei Network places the order book matching engine on validator nodes, and each validator needs to maintain a mempool. When any validator is selected as a block proposer, they need to directly match transactions through the built-in matching engine and propose a block. For DyDx, this mempool only contains transactions from DyDx, while for Sei Network, due to the nature of its layer1 network, the transactions in the mempool come from various protocols on Sei. Most of these transactions from different protocols are unrelated. If serial processing is still implemented, various order book protocols on Sei will compete for block space, which is not conducive to the overall ecosystem development.
In summary, Sei's parallelization design is intended to allow projects on Sei to operate independently without interference, while also increasing the system's throughput.
One major issue that transaction parallelization will face is the interdependence of transactions, as interdependent transactions can only be processed serially. For example, the minting process of an NFT needs to ensure that the NFT being minted has not been fully minted, thus requiring serial processing. Therefore, distinguishing independent transactions from related transactions is a problem that transaction parallel systems need to address. The UTXO model is one of the commonly used methods to achieve parallel transactions, while Sei adopts DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) technology to achieve this. A DAG can be understood as a line with direction, where the connections represent each transaction, and the two transactions connected to it are the associated transactions. Sei sets up a DAG for all transactions in the entire network to identify associated transactions.
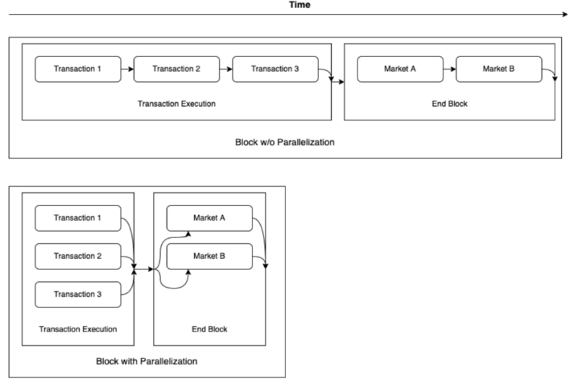
Sei's transaction parallelization
MEV Prevention, Order Bundling, and Oracle Pricing
Sei's MEV Prevention feature is primarily aimed at preventing block proposers from maliciously extracting MEV while matching transactions and constructing blocks, achieved through Batch Auction. Batch Auction is a solution proposed by Cowswap to address the MEV problem faced by AMM transactions. It bundles transactions of the same type over a period of time into a batch and executes them uniformly. All transactions within the batch have no execution order and have the same execution price, thus avoiding the occurrence of frontrunning.
Order Bundling is a mechanism designed for market makers. Market makers can update the state of all order books with a single transaction, rather than individually. This means market makers can quickly adjust their risk exposure across different order books at a low cost.
In terms of oracles, Sei has a built-in oracle system that provides price quoting services for assets within the ecosystem. The main implementation method is to introduce price quoting from oracles into the consensus process. At each block generation, all validators need to provide their own asset price quotes and reach consensus on the quotes. Therefore, the asset prices in the entire Sei are updated at each block time.
Current Development Status of Sei Ecosystem
As of now, the flourishing Sei ecosystem includes over 150 projects across various Web3 domains, including social, NFT, gaming, and DeFi.

Top projects in Sei's ecosystem include Fable, Dagora, and Fuzio. They are exploring gameFi, NFT, and DeFi based on Sei's unique mechanisms. Developers choose Sei mainly for the following reasons:
- Scalability: Sei's high-performance architecture can process thousands of transactions per second, making it suitable for dApps requiring high throughput and low latency.
- Low transaction fees: Sei's low transaction costs will incentivize developers and users to interact actively on Sei.
- Ecosystem resources: Sei provides developers with rich development tools and resources, and an open community forum. It also has support from prominent investors and mature blockchain projects.
- Interoperability and composability: Sei seamlessly interacts with other networks, allowing the combination of various protocols and applications.
- Security: Sei's consensus mechanism ensures transaction security, allowing developers to focus on application development.
- Community: The growing user base and active community of Sei are highly attractive to developers.
- Grants ecosystem fund: The 1.2 billion Sei ecosystem fund can help projects expand faster.
Sei provides developers with a comprehensive platform to explore new possibilities for dApps through its unique mechanisms. Additionally, Sei guides on-chain liquidity flow through the "Liquidity Alliance Program" and provides exposure to various projects for Web3 users through its large community. Currently, Sei has active on-chain users, with over 100 million transactions and over 5 million wallet addresses based on testnet data. The active on-chain user behavior will provide significant development momentum for the Sei ecosystem.
Sei's DEX: Balancing High Performance and Low Cost
Speed and scalability are among Sei's characteristics, along with flexibility and adaptability for developers. Developers can freely build various applications on Sei. With its high throughput, low transaction costs, and fast finality, Sei provides an ideal infrastructure for building the next generation of Web3 applications.
One of Sei's strengths lies in decentralized exchanges (DEX). Generally, DEX is easily affected by blockchain performance issues. When the number of transactions increases within a unit of time, DEX faces more prominent issues due to blockchain congestion. High transaction fees, long transaction execution times, and poor scalability often harm user experience and profitability.
Sei offers an effective solution for this market. It introduces an on-chain matching engine, making on-chain transactions more efficient by leveraging its fast finality, high throughput, and low transaction costs. This means better performance and lower transaction costs for decentralized exchanges, making them competitive alternatives to centralized exchanges.
Compared to Serum and DyDx, Sei's DEX on Sei has several advantages. DyDx's issue is that the entire chain mechanism is designed for a single application, lacking the survival soil for other DeFi protocols, thus losing the space for liquidity sharing and combination between protocols. It must connect with off-chain DeFi applications through some cross-chain means to achieve so-called DeFi composability. Serum faces the problem that, despite its rich liquidity and the ease of combining protocols, its stability is greatly affected by non-trading activities on-chain. However, Sei Network's Layer 1 design can address the issues faced by DyDx and Serum. In short, Sei Network's features of decentralized off-chain matching and DeFi protocol composability give it a strong advantage in terms of trading.
Comparative Analysis with Other Layer1 Platforms
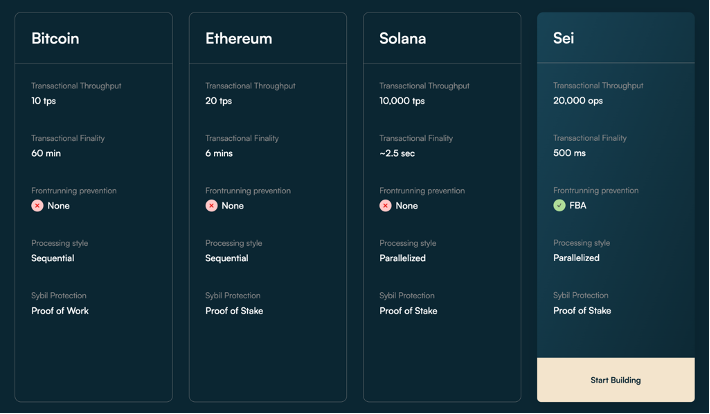
The current Layer1 landscape is diverse, with each platform having its unique features, advantages, and limitations. To better understand Sei's advantages, we will compare Sei with well-known platforms such as Sui, Aptos, Solana, and Ethereum.
Sei
Sei's key advantage lies in its unique network structure, addressing common issues of scalability, transaction speed, and front-running in other blockchains. With its innovative consensus mechanism, Sei achieves high throughput, fast finality (as fast as 0.5 seconds), and scalability. Sei's transaction parallelization design further enhances these capabilities, enabling Sei to handle a large number of transactions.
Sui
While Sui has its unique advantages, compared to Sei, its scalability will face bottlenecks as its transaction speed increases. Although Sui also emphasizes decentralization, its consensus mechanism differs from Sei in terms of flexibility, lacking the freedom of validator selection that Sei possesses.
Solana
Similar to Sei, Solana processes block production in parallel, achieving high transaction speed and low transaction costs through its unique Proof of History (POH) timestamp system. However, its excessive focus on performance requires concessions at the decentralized level. Due to centralization issues, Solana's stability is affected by special circumstances.
Ethereum
Ethereum is currently the most diverse layer1 in the dApp ecosystem. Especially in the DeFi field, it ranks first in both TVL and protocol composability. However, Ethereum currently faces high fees and scalability issues, with its current solution being to offload through rollups. However, the migration of applications and TVL from layer1 to layer2 still takes a long time. In summary, while Sui, Solana, and Ethereum bring unique features and advantages, Sei stands out due to its novel design and powerful performance. Sei's blockchain architecture has been optimized for speed, scalability, and security without compromising decentralization. In the future, it may even surpass mature platforms like Solana in terms of performance.
Future of Sei
The potential of blockchain technology is enormous. By providing a highly scalable, secure, and user-friendly environment, Sei paves the way for mass adoption of blockchain technology. However, in the overall competition between layer1 and layer2, Sei still faces fierce competition from other Layer 1 and Layer 2 platforms. Although Sei's mechanisms and testnet data have set it on the right path, its future prosperity will require continuous nurturing of talent within the ecosystem and promotion within the community.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




