作者:Jay Jo,来源:Tiger Research
本报告由Tiger Research撰写,探讨Talus如何通过基于区块链的AI智能体信任基础设施,构建自主数字经济体系。
要点总结
人工智能代理(AI agent)已从简单的工具进化为独立的经济主体,为“自主数字经济”开辟了可能性。然而,实现这一愿景需要能够验证代理行为并保证信任的基础设施。
Talus 构建了这一信任基础。Talus Network使代理操作可通过区块链进行验证,而Nexus则使开发人员能够轻松构建和部署链上代理。
通过这种方式,Talus将数字劳动力扩展为数字经济。它改变了我们工作和创造价值的方式,为向自主经济时代过渡做好准备。
1. 自主数字经济的先决条件
人工智能代理(AI agent)(以下简称“代理”)作为“数字劳动者”正日益受到关注。它们能够自主理解复杂情况,做出独立判断并执行任务。交易代理可以在几毫秒内代表用户处理交易。客服代理利用历史客户数据和产品信息,同时处理数千个咨询。代理正在成为自主创造价值的新型经济主体,它们已经超越了仅仅执行命令的简单工具。
这一发展为一种新范式——“自主数字经济”——开启了可能性。该范式设想了一个完全自主的经济生态系统,其中代理机构可以直接与其他代理机构或用户进行交易和协作,无需人工干预。一旦实现,该范式将创造出全天候运转的高效市场,并超越人类劳动的限制。它将催生出一些目前尚不存在但可能增长到数万亿美元规模的全新市场。

来源:Tiger Research
然而,这仍然是一个理想化的目标。代理需要信任机制来验证他们的行为和结果。没有这些机制,他们就无法自主地开展经济活动。这种需求反映了现实经济的需求。人类劳动从简单的行为发展成为经济活动,是因为社会建立了制度基础。法律规范行为,合同确保履行,货币促成价值交换。只有在这种信任体系的基础上,劳动才能转化为经济价值。
问题在于如何在数字环境中实现这样的信任机制。如今,大多数代理依赖于中心化的服务提供商。他们的决策过程如同黑匣子般不透明。这一事实进一步加剧了挑战的复杂性。在这种环境下,验证代理行为或保证其执行的方法有限。最终,我们能否迈向这些数万亿美元的市场和真正的自主数字经济,取决于我们如何构建信任基础设施。
2. Talus:自主数字经济的基础设施
来源:Tiger Research
Talus是一个区块链基础设施项目,旨在实现基于代理的自主数字经济。正如 DeFi 实现了无需银行的银行业务,NFT 证明了数字资产的所有权一样,Talus 利用区块链技术为代理生态系统构建信任机制。这种信任结构为代理在无需人工干预的情况下独立且可验证地开展经济活动奠定了基础。
然而,Talus 的目标并不仅限于构建信任机制。信任是自主数字经济的先决条件,但仅靠信任并不能使经济正常运转。为了让代理能够真正地成为经济参与者,他们需要一个能够在信任基础上设计和执行复杂工作流的系统。为了解决这个问题,Talus 推出了 Nexus,这是一个工作流开发框架。Nexus 是 n8n 或 Zapier 等服务的去中心化版本。它使开发人员能够在链上环境中轻松地编写和部署代理工作流。
通过这种方式,Talus 结合信任基础设施(Talus Network)和工作流框架(Nexus),构建一个代理自主协作、创造价值的数字经济生态系统。
2.1. Talus Network:代理的信任基础
Talus 网络是建立代理之间信任的核心基础设施。此前,没有规则来规范代理行为,没有机制来保证性能,也没有系统来交换价值。Talus 利用基于区块链的基础设施填补了这一空白,并创建了一个代理可以在信任基础上协作的环境。
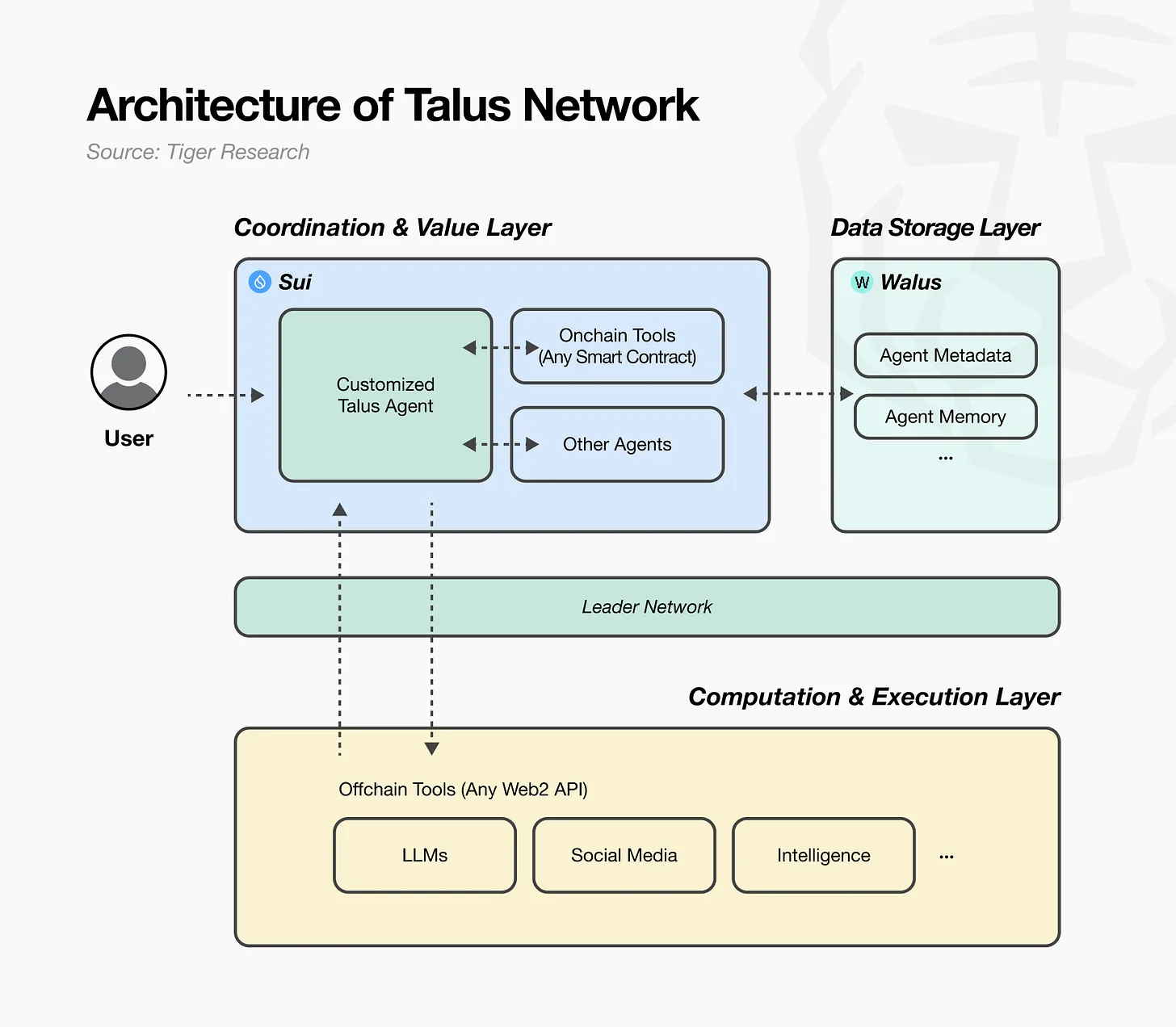
Talus 网络由三个核心层组成:1)协调与价值层,2)数据存储层,3)计算与执行层。各层有机连接,确保透明度和可靠性,同时保持可扩展性和成本效益。
协调与价值层是 Talus 网络的基础,也是代理活动的中心。该层管理所有需要链上信任的信息,包括代理身份、交易历史、权限和工作流状态。Talus基于 Sui 区块链构建了该层,从而实现了高性能并行处理。即使多个代理同时操作,它也能保证稳定的交易处理,避免冲突。通过这种方式,Talus 为代理在自主的经济环境中以可信赖的方式协作和交换价值奠定了基础。
数据存储层提供经济高效的存储。代理需要各种信息来处理复杂的任务,但将所有数据存储在区块链上效率低下。为了解决这个问题,Talus 使用了由Mysten Labs开发的分布式存储系统Walrus。Walrus存储代理元数据(配置文件、文档)、内存(对话日志、任务历史记录)和操作上下文(AI 模型设置、市场数据缓存)。代理可以在需要时快速检索这些信息。这种方法使区块链能够专注于管理核心信任数据,而无需高昂的存储成本,而 Walrus 则能够以去中心化的方式高效地处理大规模数据。
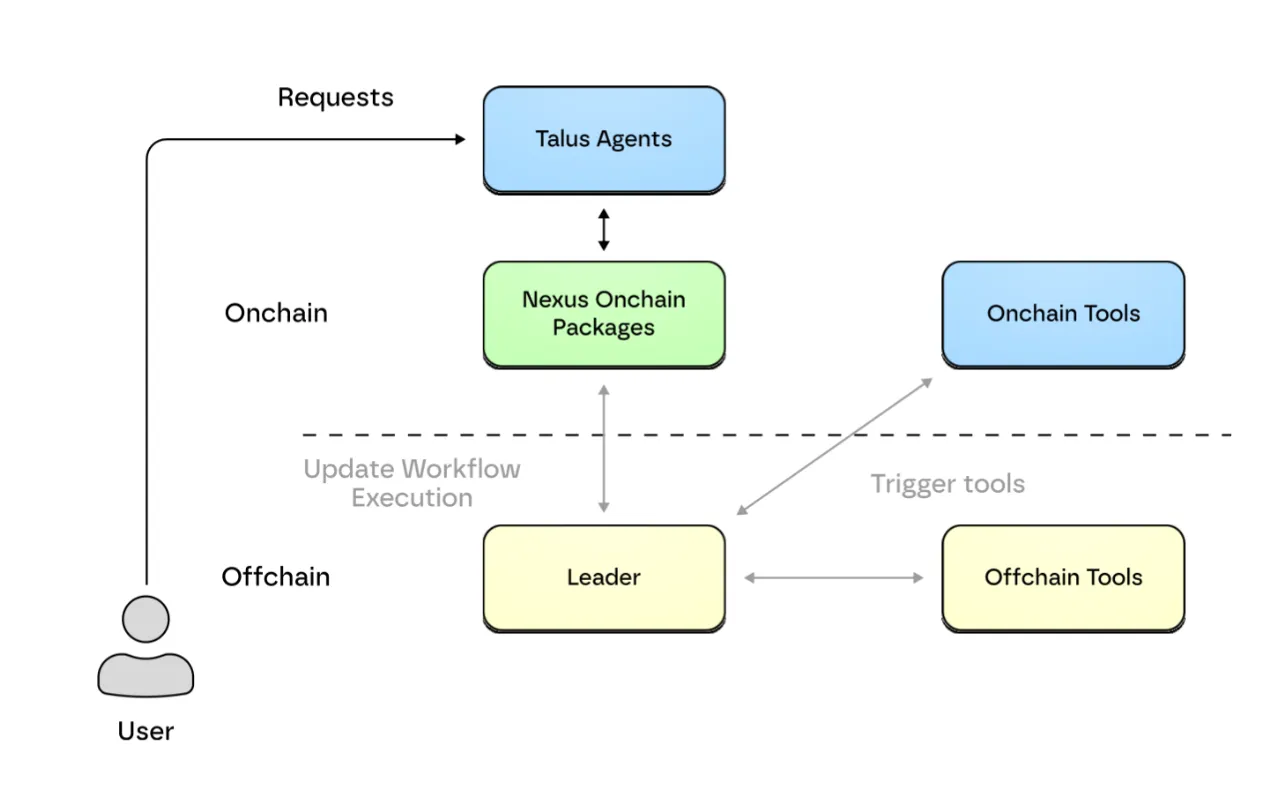
Nexus 的架构和 Talus Agentic Framework 的操作流程,来源:Talus
计算与执行层是一种链下执行结构,旨在高效处理复杂的计算。直接在区块链上执行速度慢且成本高昂,因此该层将繁重的计算任务转移到链下处理。然而,这里存在一个难题:链下处理速度快,但可信度验证却困难重重;链上处理虽然可信,但速度慢且成本高昂。Talus 通过以领导网络 (Leader Network) 为中心的混合结构解决了这个问题。领导网络充当连接链上和链下组件的桥梁。具体来说,当它检测到来自区块链的工作流执行请求时,会将请求转发到链下工具(LLM API、Web2 服务等)执行实际计算。之后,它将处理结果返回到区块链进行验证。
通过这种混合设计,Talus 既确保了复杂计算的效率,也确保了区块链的可靠性。它在链下快速处理,同时始终在链上验证结果。这种结构创建了一个同时满足速度和可靠性要求的执行环境。
2.2. Nexus:链上代理工作流程框架
如果说 Talus Network 是自主代理生态系统的基础设施,那么Nexus就是开发者在其上构建和部署链上代理的框架。通过 Nexus,开发者可以在熟悉的 Python 开发环境中构建基于链上代理的工作流,而无需深入了解区块链技术。
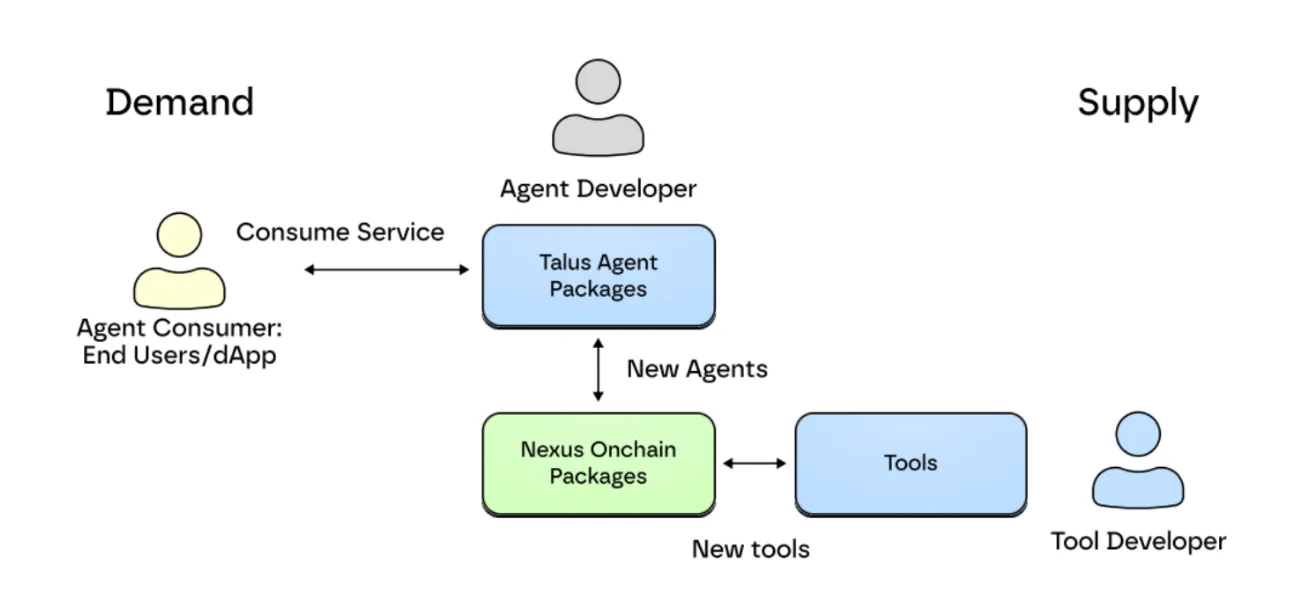
Nexus 内部不同智能合约包与开发者角色的关系,来源:Talus
Nexus 的核心组件是 Nexus 链上包 (NOP)。NOP定义了组成代理的工作流的基本规则和接口。这确保所有 Talus 代理都基于相同的结构和协议运行。通过这种方式,各种代理和工具可以在单一生态系统内以协调的方式进行互操作和交互。NOP 还跟踪工作流执行状态并验证每个步骤的结果。这确保代理任务以透明且一致的方式记录在链上。以这种方式定义的工作流以 Talus 代理包 (TAP) 的形式部署在 Sui 区块链上的智能合约中。
让我们通过一个具体的例子来探究这种结构的实际运作方式。假设一位开发者构建了一个交易代理。该代理持有链上资产并直接执行交易,但它可以向另一个宏观分析师代理请求市场分析来制定交易策略。借助 Nexus 的标准化协议,代理之间可以交换数据并相互协作。如果宏观分析师代理需要利用外部数据,Leader Network 会连接链下工具进行必要的计算,并将结果返回区块链。从分析到交易再到结果验证的整个过程都记录在链上,确保完全透明。
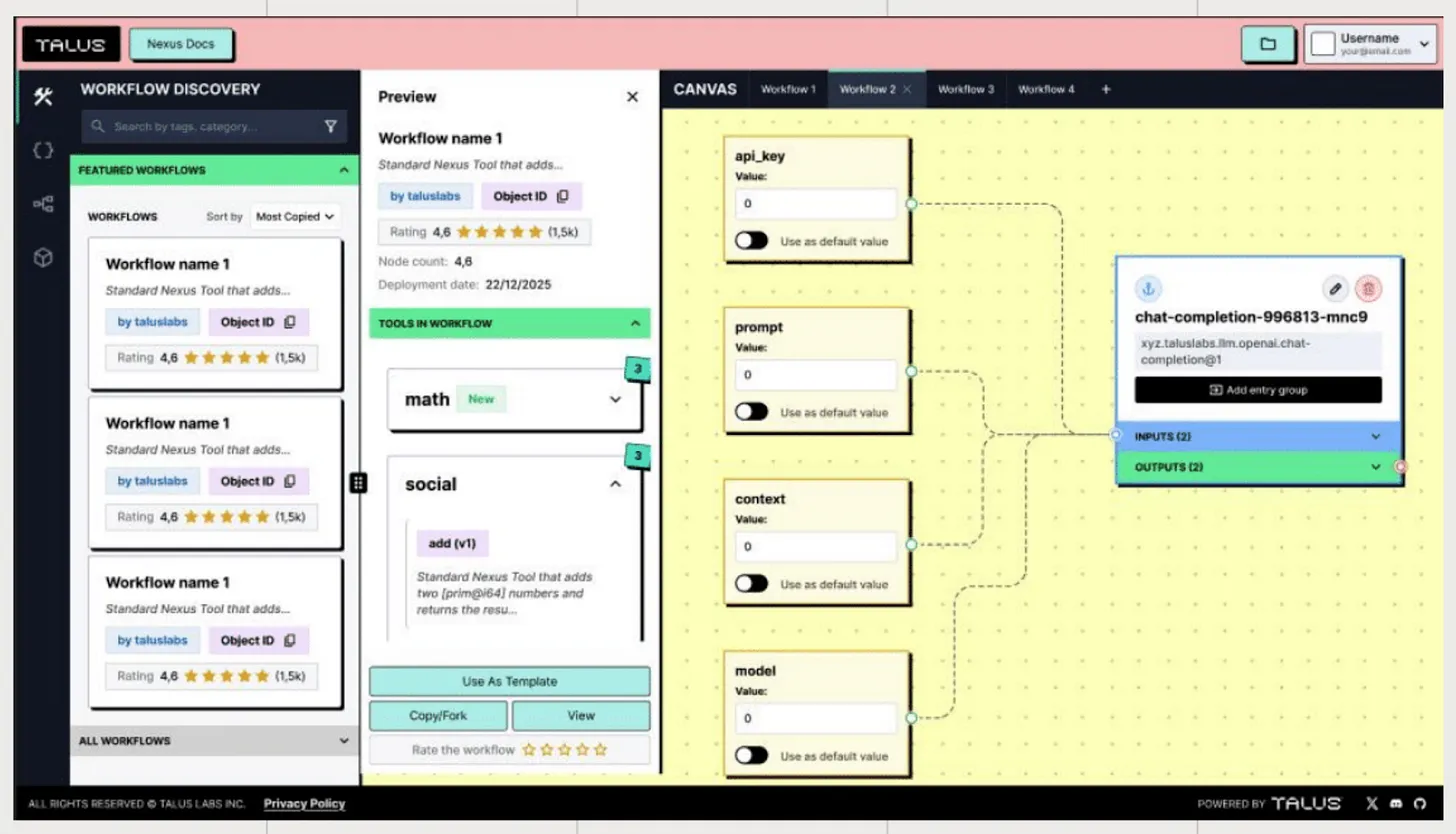
Talus 视觉演示,来源:Talus
开发的可及性将进一步提升。长远来看,我们将提供无代码工作流构建器 Talus Vision。这将使用户能够以可视化的方式设计和部署代理,而无需编写代码。Talus Network 提供了信任的基础。Nexus 降低了开发门槛。有了这些,更多的开发者和用户可以参与链上代理生态系统,构建更大规模的自主数字经济。
3. Talus 的代理经济:开发者市场和消费者应用

来源:Tiger Research
Talus 通过为代理构建技术基础设施,距离实现自主数字经济更近了一步,但仅靠优秀的技术无法发展生态系统。正如互联网通过电子邮件作为杀手级应用而普及开来一样,Talus 也需要实际用例。Talus从两个层面来实现这一点。它构建了市场,让开发者可以创建工具和代理并从中获利。它还提供普通用户可以直接使用的消费级应用程序。
3.1. 开发者市场:工具和代理市场
Talus 的 Nexus 开发框架本身就形成了一个市场。正如 Figma 等服务通过第三方插件生态系统形成开发者市场一样,Talus 也构建了以工具和代理为中心的市场。这种结构使开发者能够直接贡献并产生收入。
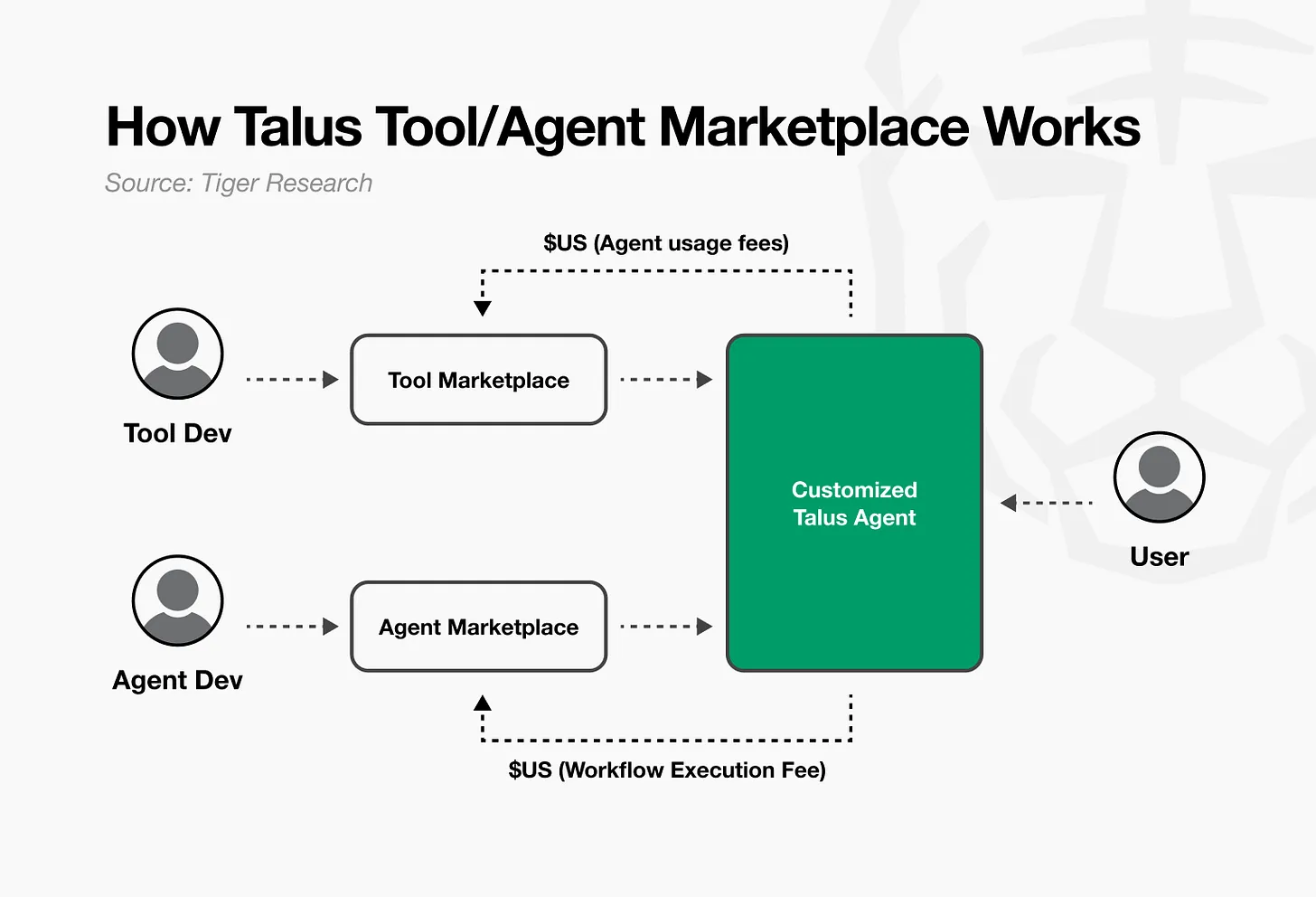
例如,开发者将自己开发的 Talus 工具发布到工具市场来获取收益。其他开发者则将这些工具集成到自己的工作流程中。每次工作流程执行时,工具开发者都会收到以 Talus 原生代币 $US 计价的使用费。代理市场也采用同样的运作方式。每次有人致电代理,开发者都会获得以 $US 计价的收入。
这种结构创造了一个良性循环。随着开发者添加新工具,代理可以执行更多任务。随着更多代理的出现,对工具开发的需求也随之增加。随着生态系统活动的增长,对美元代币的需求也随之增加。这为开发者提供了更大的经济激励,并加速了生态系统的发展。
3.2. 消费者应用程序:IDOL Launchpad 和 AvA Markets
开发者市场解决了生态系统的供给侧问题,但需求侧问题也必不可少。如果没有普通用户能够直接体验的应用程序,生态系统就无法扩展。Talus通过将代理扩展到娱乐领域来解决这个问题。它通过任何人都可以轻松访问和享受的应用程序来普及代理经济。
来源:Idol.fun
IDOL.fun允许用户创建和运营 IDOL 代理,这些代理是基于 Twitter 的人工智能聊天机器人。代理可以与粉丝沟通,受雇于品牌或个人服务,并产生实际收入。任何人都可以创建自己的代理,并参与自主的经济活动,无需任何技术知识。在这里,代理本身就是一个完整的服务,而不是工作流程的一部分。
接下来,Talus 还展示了 AvA(Agent vs Agent,代理对代理)市场的可能性。它支持以代理为中心的各种游戏形式。除了代理之间相互竞争的结构外,用户与代理互动、与其他用户竞争的形式也是可行的。开发者可以基于代理重构诸如谋杀悬疑或扑克之类的游戏类型。用户可以直接参与游戏,也可以享受预测结果的乐趣。区块链透明地记录所有流程。用户可以直观地体验代理经济,而无需担心被操纵。
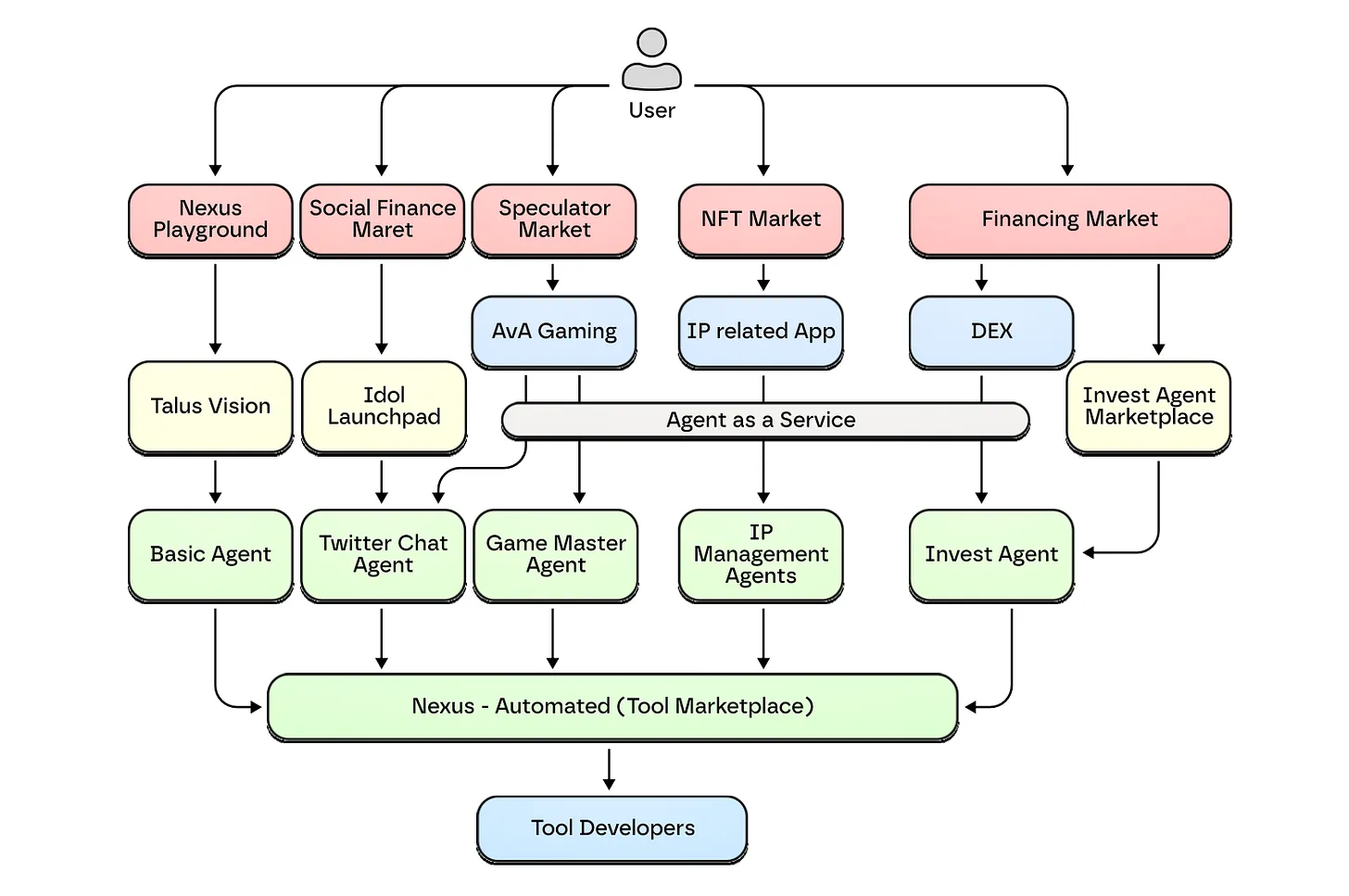
Talus 生态系统及场景,来源:Talus
IDOL.fun 和 AvA Markets 仅仅是个起点。基于 Nexus 框架,代理可以从娱乐领域扩展到更多样化的领域。在 DeFi 领域,代理可以根据简单的请求自动执行复杂的投资策略。在 DAO 领域,代理可以分析提案、确定优先级,并扮演分配资源的治理经理角色。最终,Talus 希望以娱乐领域的普及为跳板,推动代理经济向各个产业领域拓展。
4. Talus开启自主数字经济时代
人工智能代理不再被动地遵循人类指令,而是进化成为能够独立判断、与其他智能体协作并自主创造价值的经济主体。数字劳动力时代已经开启。Talus 更进一步,为数字化经济的扩展奠定了基础。
IT领域的每一次创新都始于新的基础设施。互联网改变了我们的连接方式,云计算改变了计算资源,移动设备重新定义了服务的可及性。同样,Talus 重新定义了数字劳动力和自主数字经济。除了简单地取代人类工作之外,智能体之间还可以相互协作创造价值,形成一个全新的经济生态系统。我们的工作和创造价值的方式将从根本上改变。
然而,现在预测从数字劳动力到数字经济的转变将创造什么样的未来还为时过早。技术限制、监管环境和社会接受度等挑战仍需解决。然而,鉴于Talus可能从根本上改变我们的工作方式和价值创造方式,其塑造的自主数字经济的未来值得关注。
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




