Author: Fu Shaoqing, SatoshiLab, Everything Island BTC Studio
This article has a total of 12,306 words, estimated reading time: 45 minutes.
Table of Contents
- The Anticipated 2025 Feels So Empty
1.1. Everyone is Full of Expectations for the "Four-Year Cycle"
1.2. The Heavy Blow of October 11
- The Glamour Fades, the Main Characters Appear, the Turbulent BTC Undercurrent
2.1. Key Players in the BTC Ecosystem
2.1.1. The Striking RGB
2.1.2. The Low-Key and Steady TAP (Taproot Assets Protocol)
2.1.3. From Ambitious to a Bit Disheartened BitVM
2.1.4. The Restless Spark
2.2. Are Other Blockchains Really Just Testnets?
- A Future Full of Expectations
3.1. Different Understandings of "All Chains Return to One"
3.2. The Foundation of Large-Scale Applications in Web 3.0 and the Future Price of Bitcoin
References
Main Text
0 1 The Anticipated 2025 Feels So Empty
1.1. Everyone is Full of Expectations for the "Four-Year Cycle"
Since the Bitcoin block reward halving in 2024, throughout 2025, the Web3/Crypto field has been filled with high optimism regarding the "four-year cycle," anticipating new highs for cryptocurrencies. This expectation is supported by several seemingly logical viewpoints and endorsed by some well-known figures in the industry. Some of the most famous supporting logics are as follows:
1. Bitcoin Halving Cycle Theory
This is the most classic and fundamental theory. The core logic of this theory is: Bitcoin's block reward is halved every four years, with the most recent halving occurring on April 20, 2024, reducing the block reward to 3.125 BTC. With demand remaining constant or increasing, supply shocks will drive up prices. This also marks the first time Bitcoin's inflation rate is lower than that of fiat currencies. Historical data shows that in the 6-18 months following the first three halvings (2012, 2016, 2020), Bitcoin experienced significant price increases, leading the entire crypto market into a bull market.
Prediction Basis: According to historical patterns, the effects of the 2024 halving will fully manifest in 2025, reaching the peak of the cycle. This is considered a "cyclical law encoded in the protocol."
Representative Views: Although this is a market consensus, anonymous analyst PlanB (creator of the S2F model), Tone Vays, and others have repeatedly predicted that a new high will occur in 2025 based on this model. Many KOLs in the Chinese Twitter community also generally predict new highs.
2. Monetary Policy Shift and Liquidity Return Theory
This is the strongest argument in the macro context. The core logic is that the crypto market is a "sponge for global liquidity," highly sensitive to changes in U.S. dollar liquidity. The Federal Reserve's aggressive interest rate hikes and quantitative tightening (QT) from 2022 to 2023 drained market liquidity, which is a core macro reason for the bear market. The market generally expects the Federal Reserve to begin cutting interest rates in the second half of 2024 or in 2025 and possibly restart quantitative easing (QE). In fact, the Federal Reserve did cut rates several times in 2025.
Prediction Basis: Once global dollar liquidity becomes abundant again, risk assets (including cryptocurrencies) will gain tremendous upward momentum. 2025 is seen as a "perfect storm" moment for a full recovery of liquidity, combined with the effects of the Bitcoin halving.
Representative Figures:
Arthur Hayes (Co-founder of BitMEX): He has repeatedly articulated that the shift in Federal Reserve policy will be the most important catalyst for this bull market, pinpointing 2024-2025 as a critical time window.
Raoul Pal (CEO of Real Vision): His "Everything Code" theory posits that global liquidity cycles drive all asset classes and explicitly predicts that as liquidity improves after 2024, cryptocurrencies will experience an explosion.
3. Technological Maturity and Large-Scale Application Inflection Point Theory
This argument suggests that the mainstream technologies of web3 have gradually matured and are entering the early stages of large-scale application.
Core Logic: Institutional Infrastructure Improvement: Giants like BlackRock and Fidelity have launched Bitcoin spot ETFs (approved in early 2024), providing compliant and convenient entry points for traditional capital. This is likened to the Coinbase effect of 2017 or the Grayscale Trust effect of 2020, but on a larger scale.
Mature Technology Stack: Ethereum has completed its merge (transitioning to PoS), and Layer 2 solutions (like Arbitrum, Optimism, zkSync) have significantly reduced transaction costs and delays, making truly usable DApps possible. The ecosystems of public chains like Solana and Avalanche are also thriving.
New Narratives and User Entry Points: New narratives such as DeFi 2.0, NFT financialization, RWA (Real World Assets), DePIN (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure), SocialFi, and full-chain gaming may incubate blockbuster applications in 2024-2025, attracting tens of millions of new users.
Prediction Basis: The improvement of infrastructure has fueled the "bull market engine," just waiting for the spark of liquidity (argument 2) and cycles (argument 1) to ignite it. 2025 is seen as the year when these technological accumulations and institutional layouts will produce synergistic effects, achieving a leap in network effects.
This article will also enhance this viewpoint from the perspective of the improvement of Bitcoin's native ecosystem.
Representative Figures:
Michael Saylor (Founder of MicroStrategy): He continually emphasizes Bitcoin's attributes as "digital gold" and the ultimate asset repository, believing that institutional adoption is just beginning and will continue for many years.
Vitalik Buterin (Founder of Ethereum): Although he does not directly predict prices, he has repeatedly stated that Ethereum's scaling (through Layer 2) and account abstraction will bring the next "100 million users," which is often interpreted by the market as a prerequisite for a flourishing ecosystem.
4. Market Sentiment and Cycle Model Theory
Based on historical experience and human psychology.
Core Logic: Market sentiment follows the classic cycle of "hope-surrender-optimism-ecstasy." After the deep bear market and panic of 2022-2023, the market is rebuilding. Various long-cycle models (such as Bitcoin's 200-week moving average, rainbow chart, Mayer multiple, etc.) all point to 2025 being in the "ecstasy" or "bubble" region at the top of the cycle.
Famous Model: PlanB's Stock-to-Flow model: Although it deviated in 2021, many believers still consider its long-term predictions valid, pointing to extremely high prices in 2025.
Cryptocurrency Total Market Cap Logarithmic Growth Curve: This model shows that the total market cap has been rising along a stable exponential channel, currently positioned in the lower-middle part of the channel, indicating significant upward potential.
All these logics and arguments weave together a "triple overlap" bullish narrative:
Internal Drivers: Bitcoin halving (supply shock).
External Catalysts: Global liquidity shift (demand-driven).
Fundamental Support: Technology and institutional adoption maturity (value foundation).
However, by the end of 2025, none of this happened, and on October 11, 2025, a severe downturn occurred, with record liquidations.
1.2. The Heavy Blow of October 11
At a time when most retail investors and the market were filled with expectations, unexpected events often arise inadvertently, and such surprises in a high-value market may be inevitable.
According to Coinglass data, the October 11 event saw $19.141 billion in liquidations across the network within 24 hours, setting a new historical record and marking the largest wave of forced liquidations since early April 2025, with a total of 1.62 million people liquidated globally. Among them, long positions faced liquidations of $16.686 billion, while short positions faced $2.455 billion. The largest single liquidation occurred in the ETH-USDT contract trading pair on the Hyperliquid platform, valued at $203 million.
The impact on users and the market is reflected in: On the user level, 1.62 million people were liquidated, with long positions losing $16.686 billion and short positions losing $2.455 billion. Some market makers suffered losses exceeding 50% or even went bankrupt, while ordinary users faced delays in trading interfaces and failed orders. On the market level, Bitcoin liquidations totaled $5.317 billion, Ethereum liquidations totaled $4.378 billion, and SOL liquidations totaled $1.995 billion. Binance later compensated $283 million, while OKX accused market manipulation, and platforms like Hyperliquid saw whales accurately shorting for profit, exposing systemic risks.
Numerous OG-level individuals were reported to have been liquidated on Twitter.

This crash also led many users to question and criticize certain exchanges. To this day, there are doubts about some exchanges modifying candlestick charts, system outages that could not respond, and price spikes. They continue to assert their rights on Twitter.
0 2 The Glamour Fades, the Main Characters Appear, the Turbulent BTC Undercurrent
From being filled with expectations for 2025 to the painful blow of October 11 and the massive losses, and then to the continued slump by the end of the year, retail investors and some small to medium-sized institutions are filled with anger. The anticipated new highs in Crypto did not materialize, leaving many deeply affected. Has the glamour of this cycle ended with 2025?
Regardless of how the market performs, we, as industry practitioners, especially those in technology, are feeling a surge of undercurrents. Particularly in the BTC ecosystem, Bitcoin's value not only occupies 60% of the Crypto market share but is also accumulating strong power in technological and ecological development. The important technological accumulation began in 2017, and detailed content can be found in my previous article "Summary of New Technological Developments Leading to Bitcoin's Resurgence."
As we reach the end of 2025, after 6 to 7 years of continuous development, what new changes have occurred in Bitcoin's ecological technology? Let's take a look at several important driving forces in the BTC ecosystem.
2.1. Key Players in the BTC Ecosystem
This article mainly focuses on the native technology field of Bitcoin, introducing RGB, TAP (Taproot Assets Protocol), BitVM, and Spark (though not entirely native, it has also achieved significant results). The reason for selecting native technologies is: how to achieve scalable, private, and powerful smart contracts without sacrificing the decentralization and security of Bitcoin's core protocol.
Note: My team develops a series of products based on TAP and RGB, and we have a relatively in-depth understanding and development experience of these two protocols. I have limited usage and research on some products of Spark and have only read documents and discussions from some individuals regarding BitVM, without in-depth research or usage.
2.1.1. The Striking RGB
Bitcoin's performance and its non-Turing completeness have long been criticized. While the Lightning Network offers a solution for performance, the solution to the Turing completeness issue has garnered significant attention. Among various solutions, the RGB protocol is an important extension for achieving Turing completeness in Bitcoin, and its development potential has attracted widespread attention and high hopes.
With the explosion of the market due to Ordinals inscriptions, the Runes protocol, and others in 2023-2024, interest in building complex applications on the Bitcoin chain has been reignited. Given the design shortcomings of protocols like Ordinals, particularly the obvious limitations in programming capabilities, smart contract solutions like RGB have garnered significant attention in 2025. RGB employs off-chain computation and client verification models, seen as a potential technological path to address Bitcoin network congestion and high fees.
Core Potential and Advantages of the RGB Protocol
Based on Bitcoin's native technology, RGB ensures applications possess the complete characteristics of the Bitcoin mainnet through one-time sealing and client verification.
Scalability and Privacy: Transaction data and smart contract logic are primarily stored off-chain, with commitments made only through the Bitcoin blockchain, theoretically allowing for more complex applications while keeping transaction details hidden from the public. Basic technical protocols and elements such as tokens (RGB20), NFTs (RGB21), DeFi, and DIDs (RGB22) have been initially established.
Asset Security: Asset ownership is directly secured by Bitcoin UTXOs, inheriting the security model of the Bitcoin mainnet.
Avoiding On-Chain Congestion: Unlike Ordinals, RGB does not directly compete for block space with regular Bitcoin transactions.
Despite its immense potential, RGB is still in a very early development stage, and market reactions are polarized. There is much technical work needed to improve its architecture and design, and the fragmentation within the RGB organization, along with its pursuit of perfection, presents significant challenges to its development and maturation.
Important Milestones for RGB:
2016: Concept proposed, with Bitcoin core developer Peter Todd introducing the core ideas of client verification and one-time sealing. Giacomo Zucco envisioned RGB as a better asset protocol on Bitcoin and the Lightning Network (improving Colored Coins).
2017-2018: Early prototype development, initially called BHB Network, supported by the Poseidon Group.
2019: Official development begins, led by Maxim Orlovsky, evolving it into a complete smart contract system. Co-founded the LNP/BP Standards Association (a non-profit organization) with Giacomo Zucco to establish RGB standards. Secured funding from Bitfinex, Fulgur Ventures, and others, initiating community participation in development.
2020-2021: Demonstrated AluVM (RGB's Turing-complete virtual machine). RGB begins running on the Lightning Network. Enters beta testing phase, supporting tokenization and basic smart contracts.
2022: Launched the Contractum language for writing RGB smart contracts. New official website goes live, with documentation and tools gradually improving.
April 2023: Major milestone - RGB v0.10 released, the first stable version supporting full smart contract functionality. Complex contracts and asset issuance are realized on Bitcoin and the Lightning Network. This marks RGB's entry into the practical stage, allowing developers to build real applications.
2024: Core library frozen and standardized, with the RGB core library (rgb-core) completing major design (led by Maxim Orlovsky from 2019-2024). The protocol matures, emphasizing consensus fixation (ossification, only accepting bug fixes).
2025: Significant achievements, RGB v0.11.1 released. Tether announces plans to issue USDT on RGB. Numerous product teams release early products, such as Bitlight, BitMask, Lnfi, Bihelix, and other ecosystem products. Some application development teams have created wallets, order book trading markets, swaps, NFTs, and other applications based on these RGB products. Initial products for infrastructure like bridges and oracles also begin to emerge.
Theoretically, any web3 application can be completed based on RGB technology, and various popular financial applications can be migrated to RGB with higher security and reliability. Many people are enthusiastic and expectant about this technology. This has led to any related products and news stirring market excitement. By the end of 2025, some products in the RGB ecosystem began early user trials, with representative products like Bitlight not only completing approximately $1.6 million in RGB token issuance (based on RGB technology) but also securing significant funding (publicly reported at $9.6 million), with the Light token (non-RGB asset) launching on Binance Alpha. The subsequent crash of the Light token by the end of 2025 also indicates that products in the RGB ecosystem are still in their early stages and carry significant risks. Other products, such as kaleidoswap and other RGB concept products, have also received considerable attention.
In 2025, RGB, with its ambitious goals (a Turing-complete system on Bitcoin supporting all web3 applications), strong features (higher security, better scalability), and initially experienceable products, gives the impression that a superhero within the Bitcoin ecosystem is starting to "strut their stuff."
I personally believe that RGB will one day become very powerful, capable of shouldering the burden of mainstream web3 construction. However, its growth currently faces numerous issues. These shortcomings will be compared with TAP in the next section.
2.1.2. The Low-Key and Steady TAP (Taproot Assets Protocol)
The Taproot Assets Protocol (TAP, formerly known as Taro, and sometimes referred to as Taproot Assets in some articles) is a protocol developed by Lightning Labs that utilizes the Bitcoin Taproot upgrade (activated in 2021). It allows for the issuance and management of various assets (such as stablecoins, NFTs, real-world assets) on the Bitcoin blockchain and enables instant, high-throughput, low-fee transfers through the Lightning Network. It transforms Bitcoin into a "multi-asset network," anchoring asset issuance in Bitcoin's security, with transfers primarily conducted off-chain to avoid main chain congestion. (During our team's development process based on TAP, we found that the name TAP can be quite misleading, as it may seem like a simple asset protocol, but its TAP-VM can accomplish more BTCFi functions.)
Important Development Milestones for TAP:
April 2022: Lightning Labs first announces the Taro protocol (later renamed Taproot Assets), aiming to bring asset issuance and management to Bitcoin and the Lightning Network.
October 2023: Alpha version of the mainnet goes live (v0.3), achieving the first mainnet asset issuance and management, supporting developers in testing stablecoins, etc.
July 2024: Release of v0.4, gradually improving Lightning integration and supporting larger-scale transfers.
February 2025: Tether (issuer of USDT) announces plans to natively issue USDT on Taproot Assets, supporting instant transfers on the Bitcoin main chain and Lightning Network (as of the end of 2025, it has not yet been officially issued).
June 2025: v0.6 released, introducing group_key identifiers (simplifying stablecoin management) and multi-path payment support (larger, more reliable transactions), marking the protocol as a "decentralized foreign exchange network."
December 2025: v0.7 released, adding reusable addresses, fully auditable asset supply, and greater transaction reliability; further optimizing large payments and supply verification.
Core Features and Advantages of TAP
Issuance Mechanism: Utilizes the same UTXO model as the Bitcoin mainnet, referred to as vUTXO, inheriting Bitcoin's virtual machine functionality and architecturally separating it from BTC-VM, providing a solid foundation for the further development of TAP-VM virtual machine functions. It embeds asset metadata in Taproot transactions and uses external Universe storage for vUTXO-related data. It supports fungible assets (like stablecoins) and non-fungible assets (like NFTs).
TAP's assets can be transferred not only on the Bitcoin main chain (on-chain) but also through off-chain transfers via the Lightning Network, achieving fast, low-fee, and high-privacy transactions (transactions do not directly touch the main chain). It uses Taproot technology to verify Bitcoin mainnet transactions and stores vUTXO in an external sparse Merkle tree, with data primarily stored off-chain (locally or in Universe repositories), submitting only small commitments in Bitcoin UTXOs to enhance scalability and privacy. It supports multi-asset channels that can coexist with BTC channels; introduces an RFQ quoting mechanism to achieve decentralized foreign exchange.
TAP inherits almost all characteristics of the Bitcoin mainnet and expands the data space that Bitcoin can use to infinity. If needed, TAP could theoretically develop into a Turing-complete system. The specific details related to TAP's development into Turing completeness are detailed in my article "Will the Third Isolation Witness TAP's Development Bring Bitcoin into Stage 2.0." The main development diagram of TAP is as follows.
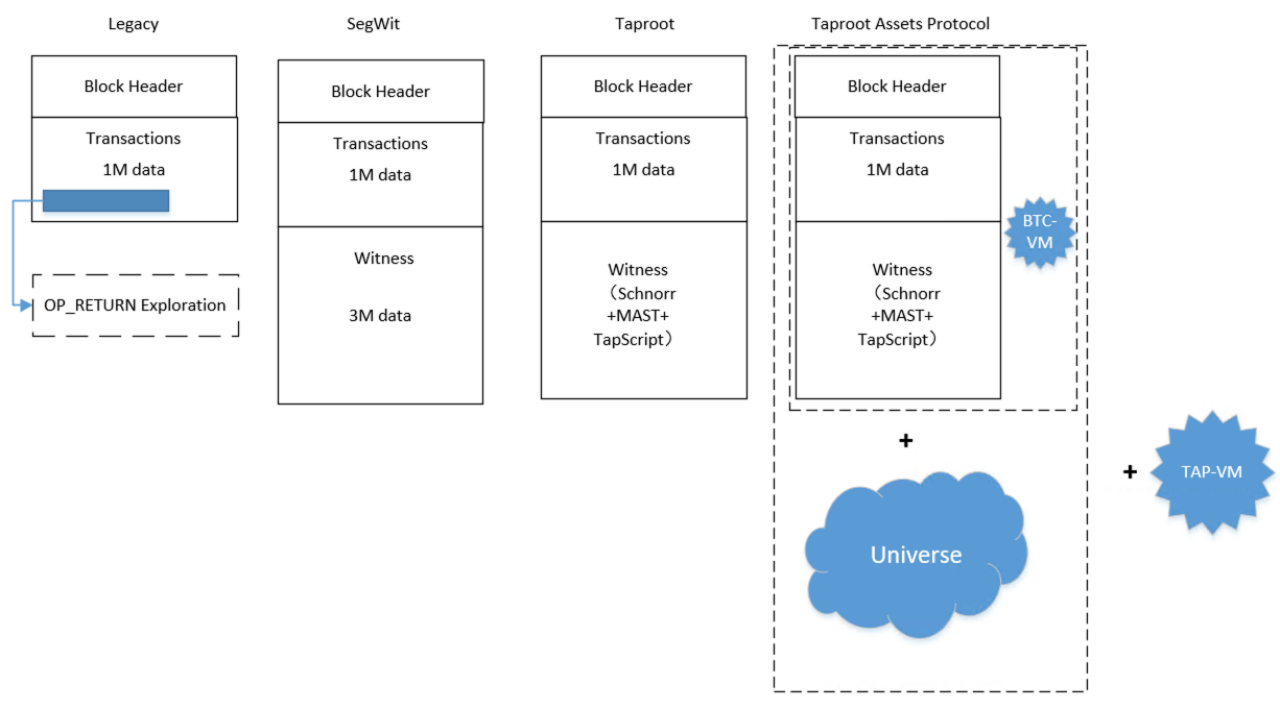
Main Comparison Between TAP and RGB
Many people believe that TAP's non-Turing completeness is a significant issue, generally considering TAP to be much weaker than RGB and not as powerful. Through theoretical analysis and practical experience with my team's products, I have found that this is not the case, reflected in the following points:
Business Model Comparison: TAP uses the UTXO model, inheriting the main characteristics of the Bitcoin mainnet, making it suitable for issuing and managing cash-type assets. RGB uses an account model, similar to EVM and other account model systems, which is closer to user-level logic and suitable for business logic based on accounts.
Virtual Machine Maturity Comparison: TAP-VM is based on the BTC-VM script stack virtual machine and has architecturally separated from BTC-VM. It currently implements simple incremental instructions for TAP, and this virtual machine has been tested against the rich scenarios of Bitcoin mainnet scripts. This progressive increase in instructions enhances security and functionality, making it more controllable. This bottom-up innovation offers better security and maturity, making it more suitable for BTC financial applications with high security requirements. In my product design and engineering implementation, almost all major BTCFi functions can be completed through TAP-VM, and functions that cannot be completed can also be gradually achieved by incrementally adding TAP instructions. This indicates that whether to achieve Turing completeness is a design choice rather than a technical flaw.
RGB, as a Turing-complete virtual machine, is completely redeveloped, and its functionality, stability, and security have many issues that need to be resolved. This top-down innovation (integrating a Turing-complete system with Bitcoin's non-Turing complete mainnet) is also referred to in the industry as radical innovation, requiring many scenarios to test and validate related functions. For BTC financial applications with high security requirements, it is currently not suitable for large-scale applications on RGB.
- Comparison of Organizational Structure: TAP is a protocol developed by the Lightning Labs team, which has been operating for many years. The collaboration among team members, especially between CTO Olaoluwa (the main designer of the TAP protocol) and CEO Elizabeth Stark, has been well-coordinated, allowing TAP to develop and progress step by step according to plan.
In contrast, the RGB organization currently exhibits a fragmented state, with multiple offshoots and the key technical figure Maxim lacking suitable partners to help him with organizational management beyond technical aspects. This indicates that there are still many issues to resolve within the RGB organization regarding protocol design, architectural design, and organizational implementation.
Personally, I am more optimistic about the development of TAP and the applications being developed on it. Its strengths in protocol definition, organizational management, development iteration, incremental innovation, and maximum support for BTC characteristics have allowed TAP to enter the early stages of mature applications. However, there has not been much publicity or reporting in the industry, including from Lightning Labs itself. It gives the impression of being "low-key and steady," but perhaps in 2026, TAP will no longer be low-key and will offer more product experiences and surprises.
2.1.3. From Ambitious to a Bit Disheartened: BitVM
BitVM (Bitcoin Virtual Machine) is an optimistic computation paradigm proposed by Robin Linus in 2023, aimed at verifying any complex computation (Turing complete) on Bitcoin without modifying Bitcoin's consensus rules (no soft forks), thereby enabling richer smart contracts, sidechains, rollups, and trust-minimized bridging functionalities. It is similar to Ethereum's optimistic rollup: computations are primarily executed off-chain, with on-chain verification through fraud proofs only in case of disputes, inheriting Bitcoin's security. The core mechanism and working principles involve the Prover claiming that a certain function produces a specific output for given inputs, while the Verifier can challenge this claim. If the challenge is successful, the Prover's funds are forfeited. It utilizes technologies like Taproot scripts, hash chains, and garbled circuits to break down computations into bit-level operations.
Advantages of BitVM:
- No need for soft forks, compatible with existing Bitcoin.
- Supports verification of arbitrary computations, including SNARK/STARK verifiers, sidechain light clients, etc.
- Trust assumption: 1-of-n (only one operator needs to be honest).
- Main applications: trust-minimized Bitcoin bridges, ZK-rollups, DeFi, sidechain scaling.
Comparison with similar technologies: Similar to client verification in RGB/TAP, but with a greater focus on general computation and bridging; it does not directly compete but rather complements the Bitcoin Layer 2 ecosystem.
Important Development Milestones
October 2023: Robin Linus releases the original BitVM white paper (BitVM1), proving the concept: using NAND gates to simulate arbitrary computations, sparking a wave of interest in Bitcoin programmability.
2024: Development of BitVM1 is paused, shifting towards a more practical design. BitVM2 is released: introducing SNARK verifiers, single challenge protocols, and permissionless challenges (anyone can challenge), significantly reducing dispute costs and supporting trust-minimized bridges. The BitVMX white paper is released: developed by Rootstock Labs and others, designing a general-purpose CPU (supporting RISC-V/MIPS), simplifying verification (no Merkle trees, signature equivalence), and providing a more efficient alternative to BitVM2.
2025: BitVM3 white paper (July): achieving a 1000x efficiency improvement using garbled circuits, focusing on complex computations like RSA. Extensions like Glock further optimize bridging security. The BitVM Alliance is established, with Robin Linus and others promoting standardization and implementation.
By 2025, BitVM has transitioned from theoretical exploration to practical production: standards are published, mainnet bridges are launched, and parts of the ecosystem mature, driving Bitcoin's transformation from "digital gold" to a programmable settlement layer. Projects like Bitlayer, Rootstock's BitVMX, Fairgate, etc., continue to iterate, focusing on multi-verifier support, SDK toolchains, and hackathons. BitVM is one of the core foundations of Bitcoin Layer 2 innovation, alongside the Lightning Network, Ark, Ordinals, etc. The technology is still rapidly evolving, with potential risks including script complexity and fee volatility.
From the title of the BitVM white paper, "Compute Anything on Bitcoin," it is evident that the designers of BitVM are ambitious. However, by 2025, the main supported application, the token issuance of Bitlayer, has been quiet, and the lack of other heavyweight product releases makes the entire BitVM ecosystem appear somewhat disheartened, lacking the initial ambition. Nevertheless, if BitVM can realize the vision it was designed for, there is still much expectation for the richness and diversity it could bring to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
2.1.4. The Restless Spark
Spark Technology Summary (Bitcoin Layer 2 Protocol): Spark is an open-source Bitcoin Layer 2 protocol developed by Lightspark (CEO David Marcus, former head of PayPal and Meta's Libra project), focusing on instant, low-fee, self-custodial payments and support for Bitcoin-native stablecoins. It is based on statechain technology, combining atomic swaps, threshold signatures (like FROST), and elements of the Ark protocol to achieve off-chain ownership transfer of Bitcoin UTXOs without the need for channel management or bridging. Spark is fully compatible with the Lightning Network, aiming to address Lightning's pain points (such as inbound liquidity, complex channel management, and scaling difficulties), making Bitcoin more suitable for everyday payments and global settlements.
Core Features and Advantages
Mechanism: Users delegate their Bitcoin UTXOs to entities composed of Spark Operators, achieving off-chain transfers through coordinated signatures. Operators "forget" old keys to ensure security. Supports splitting/aggregating UTXOs and has no absolute time locks.
Self-Custody: Users always control their funds and can unilaterally exit to the Bitcoin main chain.
Asset Support: Native issuance and transfer of Bitcoin, stablecoins, and tokens (supporting the LRC20 standard, compatible with Taproot Assets and RGB bridging).
Integration with Lightning: Seamless sending/receiving of Lightning payments without channel management; supports UMA (Universal Money Address) addresses.
Fees and Speed: Near-zero fees for internal transfers on Spark, with instant settlement; only on-chain deposits and withdrawals incur fees.
Advantages: Simplified user experience (no need for online liquidity guidance), high scalability, native stablecoins (no wrapping/bridging), inheriting Bitcoin's security.
Limitations: Reliance on operators for joint signatures (trust is required that they do not collude to steal); privacy issues inherited from the Bitcoin main chain; still in beta phase, with ecosystem development ongoing.
Comparison with Other Technologies: Easier to scale and support stablecoins than Lightning; focuses more on payment UX and stablecoins than Ark; complements RGB/Taproot Assets but is more focused on payments rather than complex contracts.
Important Development Milestones
October 2024: Lightspark officially announces the Spark protocol (alpha version), open-sourcing the code, positioning it as a high-performance L2 compatible with Lightning, supporting stablecoins.
April-May 2025: Mainnet goes live (mainnet beta), launching Wallet-as-a-Service and stablecoin issuance platform; supports LRC20 token standard.
May 2025: Breez SDK integrates Spark, allowing developers to easily build Lightning-compatible applications.
July 2025: Wallet of Satoshi integrates, providing a true self-custodial Lightning experience; multiple wallets and tools support Spark addresses (sprt1…).
Throughout 2025: The ecosystem grows rapidly, including integration with Theya multi-signature wallet; SDK improves, supporting developers in building payment applications, stablecoins, and cross-chain functionalities.
Current Status: Spark is now operational on the mainnet, with an ecosystem that includes multiple wallets (Wallet of Satoshi, Breez, Theya), SDKs, and an operator network. The focus is on promoting Bitcoin as an "internet currency protocol," especially for stablecoin global payments and adoption in emerging markets. Lightspark provides infrastructure (like Flashnet) to facilitate institutional integration. Spark is an emerging force in the Bitcoin Layer 2 ecosystem, running parallel to Lightning, Ark, BitVM, etc., driving the "Bitcoin payment renaissance." The protocol is still rapidly iterating, with potential risks including operator trust and regulation.
With its support for Bitcoin and the Lightning Network, Spark has gained many users in the Bitcoin space. Among them, my experience with the BitBit wallet and SparkSat has been quite surprising.
2.2. Are Other Blockchains Really Just Testnets?
If the current development of the BTC ecosystem is indeed full of undercurrents, does it have a brighter future? Firstly, in terms of market capitalization, Bitcoin is undoubtedly dominant. With so much technological development, will its applications also monopolize the market like its market cap? This reminds me of a controversial topic: "Apart from Bitcoin, all other blockchains are testnets." This statement originates from the viewpoint of Bitcoin maximalists and has long been a highly "insightful" and controversial perspective in the blockchain and web3 space.
Bitcoin is the only super blockchain pursuing "ultimate security and trust," while other blockchains explore and "test" different goals (such as scalability, programmability, and privacy) along the path it has pioneered. Almost all current blockchains were born out of the need to solve certain problems on the Bitcoin mainnet when there were no good solutions available. This essentially means that other blockchains are localized experiments on the paradigm established by Bitcoin.
Due to its consensus algorithm characteristics, Bitcoin has become the most decentralized, secure, and censorship-resistant blockchain network, currently possessing uniqueness, with no substitutes found. Other existing blockchain systems can find or create substitutes, lacking uniqueness.
From some cases, we can see examples of this functional specialization and experimental grounds:
Ethereum: Testing the feasibility of a "world computer," exploring Turing-complete smart contracts and decentralized applications. Ethereum has validated many concepts: smart contracts, DeFi, NFTs, rollup technology, etc.
Solana, Avalanche, etc.: Testing the limits of high-throughput consensus mechanisms, exploring the possibilities of large-scale Web3 applications.
Monero, Zcash, etc.: Testing the feasibility of stronger privacy protection technologies and their acceptance by regulators.
Numerous PoS Chains: Testing whether the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism can achieve higher energy efficiency and scalability while ensuring sufficient security.
In these explorations of functionality, certain experimental features have led to significant pattern innovations, such as Ethereum's account model, which is completely different from Bitcoin's UTXO-based cash model.
After these validations are completed, actual deployments often choose more secure and decentralized platforms. If the results of these "test chains" can be implemented on the Bitcoin mainnet, or combined in some way, then the Bitcoin ecosystem will undoubtedly have a brilliant future. This raises another topic: "The Convergence of All Chains."
0 3 An Anticipated Future
The year 2025 has passed, and the transition from high expectations to disappointment and confusion (some even despair) is now a thing of the past. What will the future look like? Instead of broadly stating that the web3 industry is full of potential, I will discuss two important topics related to Bitcoin, allowing readers to judge the future development trends for themselves.
3.1. Different Understandings of "The Convergence of All Chains"
"The Convergence of All Chains" is a common narrative viewpoint in the blockchain community (especially in the Chinese circle), suggesting that the blockchain ecosystem will ultimately trend towards unity or convergence, rather than a permanent coexistence of multiple chains and fragmentation. This viewpoint posits that the current multi-chain landscape (Ethereum, Solana, various L1/L2s, etc.) is a transitional phase, which will eventually converge towards a dominant chain or unified settlement layer, achieving seamless interconnection, efficient liquidity, and a globally unified financial system. Personally, I believe that if a unified financial system were to form, it would not lead to a clear "convergence of all chains." However, if large-scale applications enter web3.0, this phenomenon is likely to occur. Many current viewpoints argue from the perspective of a globally unified financial layer, which I believe is insufficiently substantiated and has many limitations in its observational angles. We should analyze whether "the convergence of all chains" will occur from the perspective that the entire world will enter web3.0.
During our classes on the Island of All Things, Dr. Xiao Feng taught us many lessons, and I was particularly impressed by one of them, which defined the broad concept of web3.0. I strongly agree with this definition of web3.0, and its main ideas are reflected in the following diagram:
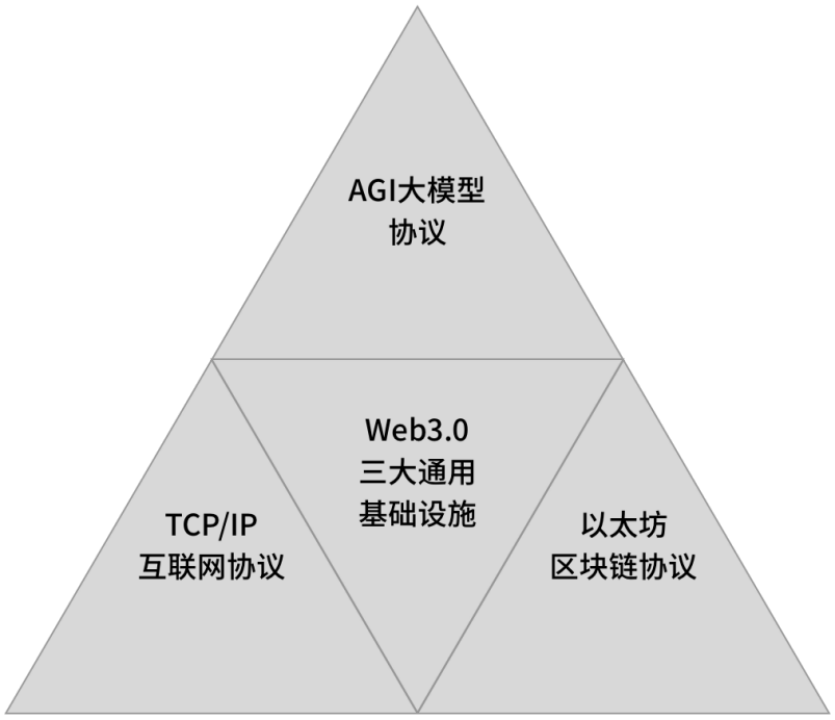
A simple summary of this definition is that the future web 3.0 will have three major universal infrastructures: Internet protocols, AGI large model protocols, and blockchain protocols. The Internet protocol is responsible for connecting people and things globally; the AGI large model protocol is responsible for enhancing productivity, and the blockchain protocol is responsible for managing production relationships. In Dr. Xiao Feng's course, the implementation of the blockchain protocol was considered to be Ethereum, rather than Bitcoin. In discussions on this topic, those who believe that "the convergence of all chains" will occur either think it will converge to Ethereum or to Bitcoin, with no third voice heard.
What is the true convergence of all chains? We can refer to the well-established case of the Internet protocol TCP/IP among the three major infrastructures for analysis. The notable characteristics of the TCP/IP protocol are: (1) it is a layered architecture design; (2) it enables end-to-end connections and data exchanges; (3) it has open standards and protocols; (4) it is technically compatible and can operate over various underlying hardware networks such as Ethernet, Wi-Fi, fiber optics, and satellite links; (5) it separates applications from the network, allowing application layer protocols (HTTP, SMTP, FTP, DNS, etc.) to develop freely above the transport layer (TCP/UDP). The network is only responsible for delivering data, while how the data is interpreted and what services it is used for is entirely determined by the applications on the terminal hosts. This has given rise to endless innovations in applications such as the World Wide Web and email.
If the blockchain protocol is to become a universal infrastructure for the future web3.0, then a single blockchain system cannot fulfill this function, as the future web3.0 will accommodate not only the global population of 8 billion but also various smart devices and agents, creating a world far beyond the current web2.0. Therefore, as a major foundational blockchain protocol, it is likely to be a layered protocol similar to TCP/IP. Bitcoin serves as a layer with the highest security and decentralization commitment, adopting a minimalist and conservative development philosophy, where all innovations should occur at more flexible higher-level protocols. The value of the foundational layer lies not in the richness of its functions but in the strength of its security. Bitcoin has an undisputed advantage in this regard. Similarly, could AGI also be a layered protocol? Layered design is a methodology for humans to handle complex systems by dividing the system into multiple hierarchical structures and defining the relationships and functions between layers, thereby achieving modularity, maintainability, and scalability, which enhances the design efficiency and reliability of the system.
Currently, Ethereum's development has also evolved into Layer 2 and even Layer 3, indicating that Ethereum may also become a major infrastructure in web3.0. The development of Bitcoin ecosystem technologies discussed in this article represents a higher-level expansion beyond the Bitcoin mainnet, and the Bitcoin mainnet also has diverse Layer 2 solutions, suggesting that Bitcoin could also become a major infrastructure in web3.0. Other networks may also evolve into layered structures, and how to determine the convergence of all chains requires additional dimensions.
If layered protocols are an inevitable state, do we need multiple Layer 1 networks as consensus layers (or commitment layers)? What is the fundamental requirement for a consensus layer?
In a layered protocol, blockchain systems suitable as Layer 1 networks need to have excellent indicators in decentralization, security, and stability. This ensures that the system is resilient to attacks, accommodates the addition and reduction of any nodes, and maintains good stability under various conditions. Are these requirements not very similar to those of the TCP/IP network? Therefore, all Turing-complete systems should not be suitable as Layer 1 networks, as rich functionality does not guarantee simplicity and reliability, leading to inherent risks in stability. In a layered protocol system, from the perspective of network and application, there should not be a large number of applications built on a Layer 1 network. In terms of decentralization, it should allow any nodes to join and leave at any time, which can only be achieved with asynchronous consensus algorithms like PoW. After this simple analysis, it becomes clear that only systems like Bitcoin are suitable as Layer 1 networks in a layered protocol.
Although the Bitcoin network is suitable as a Layer 1 network, if it cannot support the establishment of Layer 2 networks and even higher-level applications, the convergence of all chains will still not occur. The turbulent undercurrents in the BTC ecosystem discussed in this article are strong evidence of the vigorous development of this layer. I increasingly believe that the situation of the convergence of all chains will emerge.
Note: The convergence of all chains does not mean that other blockchain systems will disappear, leaving Bitcoin as the sole dominant player. Instead, it suggests that at the higher levels of the layered protocol, numerous blockchain systems will support the application layer, supplementing the deficiencies of Bitcoin in the higher layers. However, the entire system's decentralization capability, security, and stability are guaranteed by the foundational Bitcoin system.
3.2. The Foundations of Large-Scale Web 3.0 Applications and the Future Price of Bitcoin
For web3.0 to truly enter the lives of the masses, it will not be an event of "instant explosion," but rather a gradual process. One day, when users no longer perceive the existence of "blockchain" and can enjoy the new value, experiences, and rights it brings, then web3.0 will have truly arrived.
To genuinely enter the web3.0 era, some foundational infrastructures need to be improved, which can generally include the following aspects:
Scalability and performance (making the network faster and cheaper). A hallmark of improvement would be that the experience and cost of a user performing an on-chain interaction (such as a transfer or a like) would be no different from the current web2 methods, and the experience might even be better.
User experience and entry points (making usage seamless and secure). A hallmark of improvement would be the absence of technical concepts such as mnemonic phrases, public and private keys, gas fees, and cross-chain operations.
Identity and privacy systems (building a trustworthy digital persona). Decentralized identity and user privacy will be better addressed. A hallmark of improvement would be that individuals or entities possess a self-sovereign digital identity, allowing seamless login to all applications and selective disclosure of information, fully controlling their privacy.
Legal, regulatory, and interoperability frameworks (enabling trustworthy value flow). A hallmark of improvement would be the formation of a relatively unified and stable regulatory consensus globally, allowing assets to flow freely and securely across different chains and applications, with smooth connections to real-world laws.
With the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem, the foundational infrastructure of scalability and performance (point 1) will see good progress, while points 2 and 3 will still require a certain construction period. Point 4 will also accelerate its maturity under the condition of fully developed financial services.
What will the future price of Bitcoin be? If the phenomena analyzed in this article align with reality and are logically sound, then there is no need to worry about the price of Bitcoin. Because Bitcoin, in addition to its traditional financial attributes, has also gained technological attributes from its recent developments, the future application growth will continue to increase Bitcoin's consumption. I conclude with the global Bitcoin price predictions for 2026 published by Wu Shuo; these predictions, while uncertain in timing, will certainly be realized in terms of price in the future.
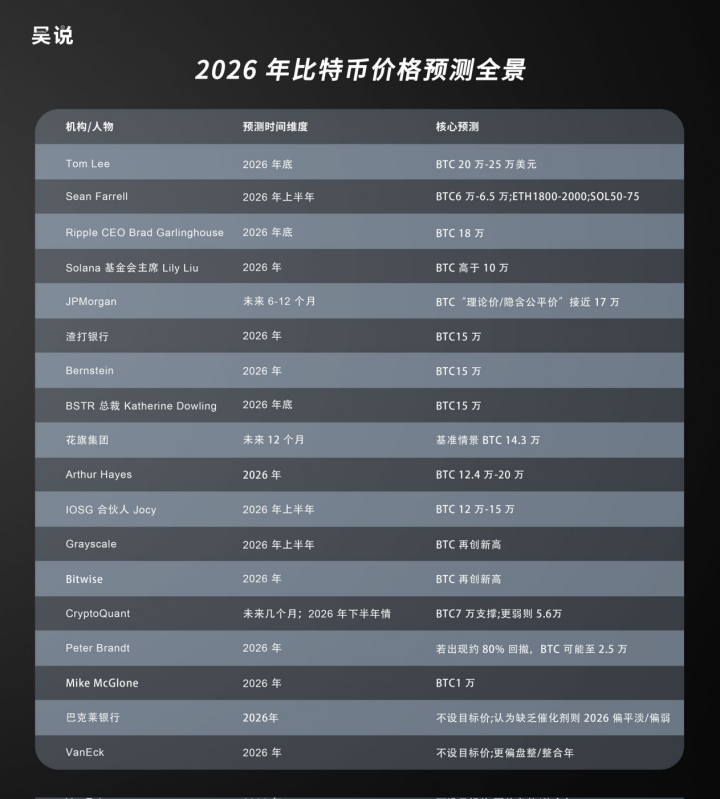
Regardless of the gains, losses, or setbacks in 2025, they are all temporary and have already become part of the past. The future will hold more opportunities, and web 3.0 will undoubtedly have a brilliant future. We need to continue participating in and building it.
References:
1. The supporting logic of the four-year cycle mainly refers to related articles in the industry and daily exchanges. I have selected what I consider to be four main logical points, not reflecting the content of any single article.
2. Global Network. Plummeting! Over 1.6 million people liquidated, some lament: My trading career is over. 2025.10.11
3. RGB Protocol Comprehensive Technical Report: Architecture, Analysis, and Ecosystem Trajectory.
4. Fu Shaoqing. The Third Isolation Witness: Will TAP Lead Bitcoin into the 2.0 Phase?. 2025.12.2
6. Robin Linus. BitVM: Compute Anything on Bitcoin. December 12, 2023
7. Aaron Zhang. Is Ethereum Really a Test Chain for Bitcoin?2025.8.20.
9. Wu Shuo Blockchain. What Predictions Have Institutions and Influencers Made for Bitcoin Prices in 2026?2025.12.29
I sincerely thank all the contributors and participants who have enriched my knowledge system.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



