In the past, people were accustomed to the "hacker breaching a major project, news trending for a few days" type of singular explosive incidents. However, this year, risks have gradually permeated every seemingly ordinary on-chain operation: for example, the convenience brought by on-chain protocol upgrades has also become a new phishing entry point; fake websites are disguised down to the pixel level; malicious apps on mobile phones can quietly monitor the clipboard in the background; phishing links after social media hijacking are more "official" than the official ones; and those old contracts that were once authorized may be awakened by hackers one night.
A Chainalysis report indicates that by mid-2025, the amount stolen from crypto platform services, including exchanges, wallets, and custodial services, has exceeded $2.17 billion, and if the trend of disclosed incidents continues, it may rise throughout the year. The core issue in 2025 is no longer "Is there a risk?" but rather how an ordinary user can obtain real security protection in a risky environment.
Increasing amounts of data and events have repeatedly proven that only by blocking risks beforehand, combined with user-friendly self-service tools (such as batch revocation and device scanning) that have low operational thresholds, can personal losses be truly reduced, allowing users to genuinely feel that "security is in their own hands." This is also the moment in 2025 when OKX brings users a sense of "security." In the past year (2025.01 - 2025.11), OKX Wallet has helped users recover losses totaling over $500 million, with an average response time of just 3 seconds for tracking black addresses, and has cumulatively marked and intercepted over 70 million pieces of risk information.
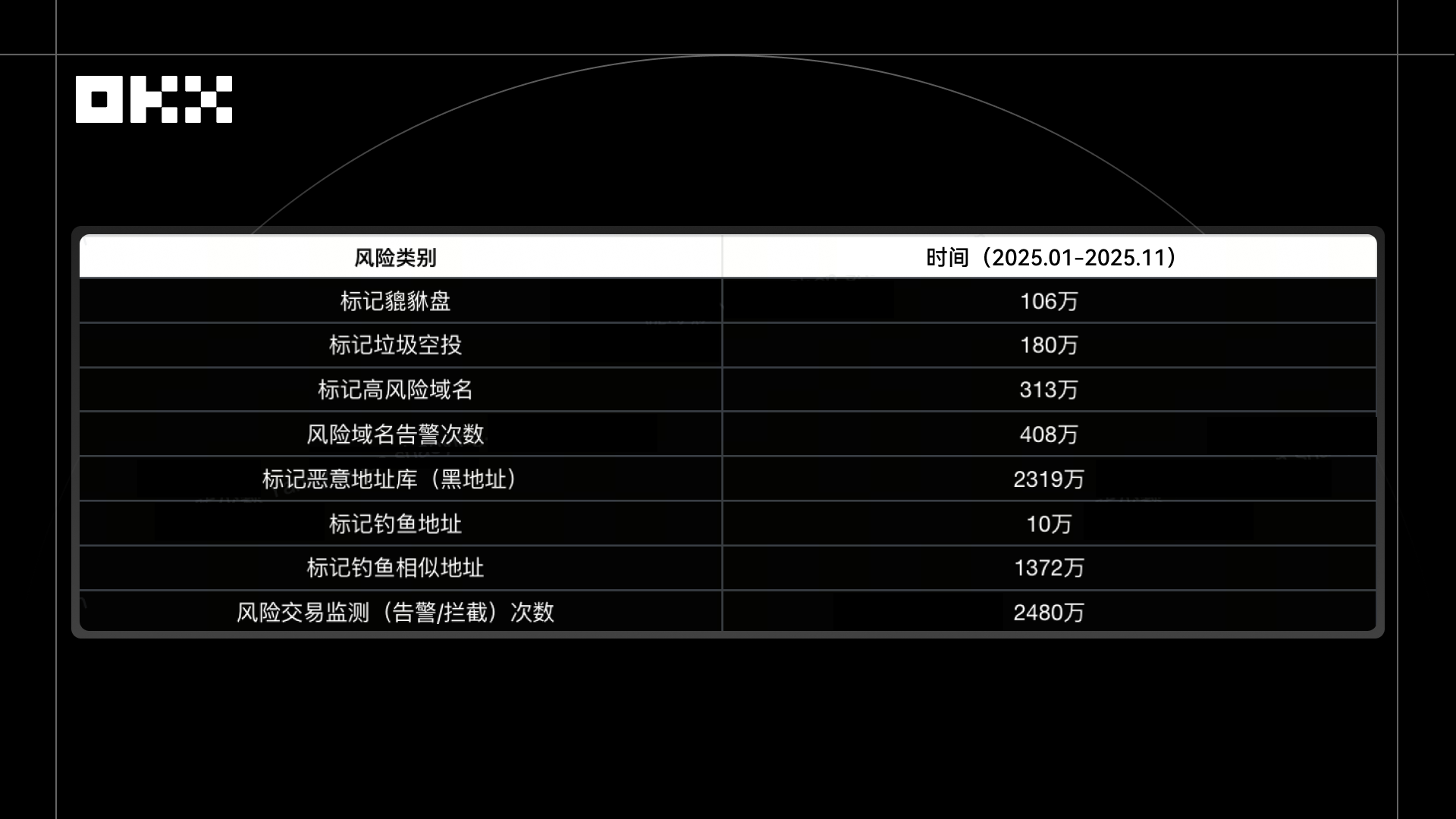
Image: OKX Wallet covers full-chain security protection
1. "Deformed" Security Risks
According to a report from CertiK, the total loss of crypto assets in the first half of 2025, including wallet theft, phishing, scams, and server attacks, is approximately $2.47–2.5 billion.
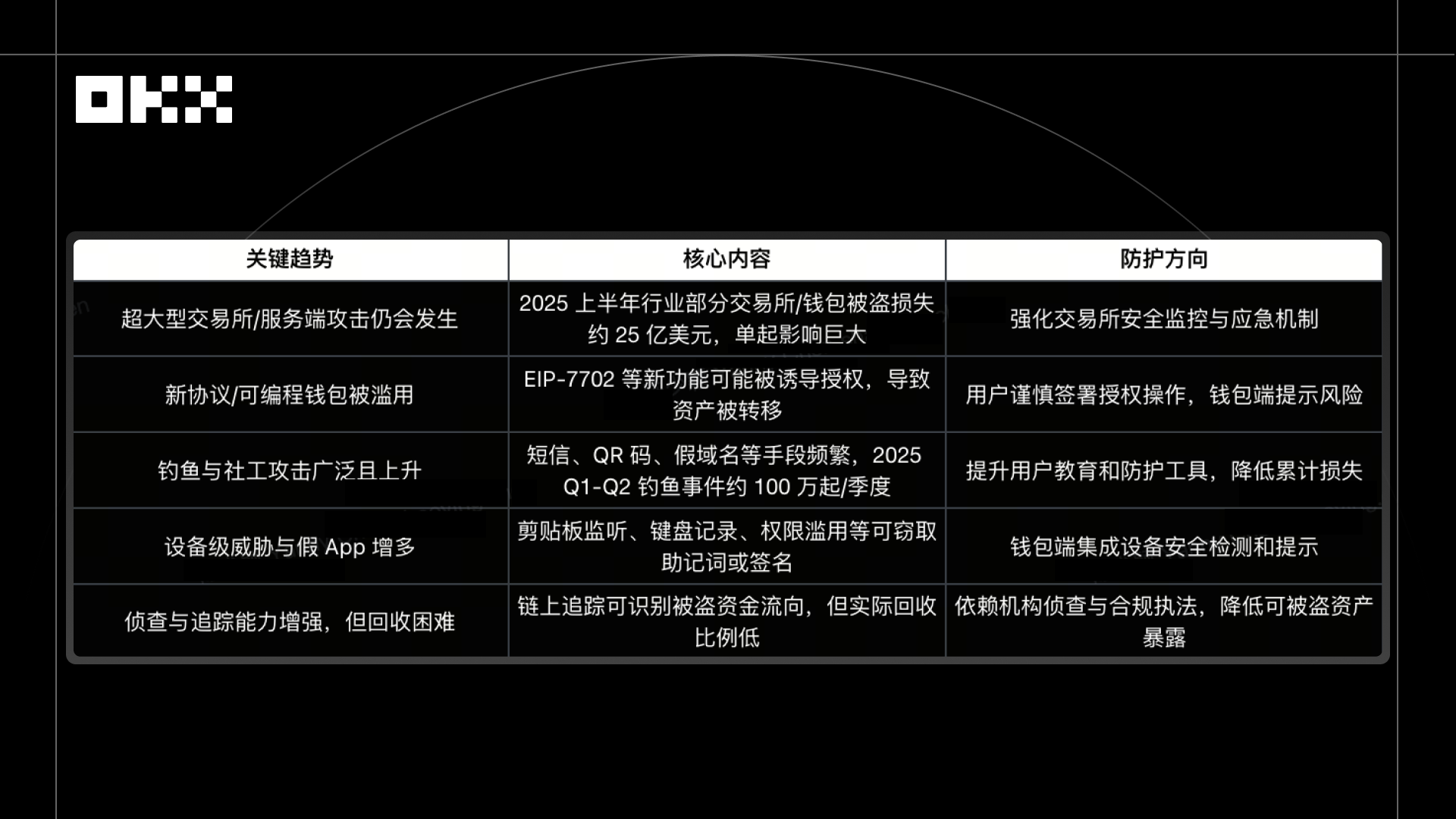
From 2024 to 2025, the industry's security situation has manifested in two parallel forms: a few large exchanges or servers have been breached, resulting in significant losses; at the same time, individual users are continuously facing phishing, malware, and social engineering scams, leading to frequent small losses. The coexistence of high-concentration losses (platforms) and high-frequency small losses (users) puts dual pressure on the entire industry's security.
Among these, phishing and social engineering attacks remained prevalent in the first half of 2025. APWG data shows that there were over 2.13 million attack incidents from Q1 to Q2, with Q2 seeing a 13% increase compared to Q1. The widespread security incidents are not due to users being "too inexperienced," but rather because risks have "deformed" into forms that ordinary people find difficult to distinguish:
- An address that seems normal may be a highly similar fake address, easily leading to misdirected funds.
- A familiar official website link may be a hijacked or disguised phishing mirror, hard to discern.
- An on-chain operation that appears safe may hide malicious upgrade requests, inducing multi-signature or authorization operations, leading to fund theft.
- A seemingly harmless plugin may record mnemonic phrases or signature operations in the background.
- A commonly used wallet or contract may also be abused during authorization or upgrades, with risks hidden, causing users to lose assets without triggering vulnerabilities.
Security incidents in 2025 show that hacker attacks have shifted from directly exploiting code vulnerabilities to leveraging user psychology and operational habits. Annual reports from multiple security agencies, including CertiK, Chainalysis, Ledger, and Kroll, indicate that such attacks account for over 70% of total losses. Although the individual amounts may not be large, they are almost impossible to defend against because users often "did nothing wrong and are already victims." Unlike past major project explosions that were clear-cut, these "deformed" risks are hidden, widespread, have low triggering conditions, do not rely on vulnerabilities, and can cause losses with just one authorization, signature, or click. Even experienced users can fall victim. Therefore, relying solely on contract audits or on-chain monitoring is no longer sufficient; protection must also combine local wallet security, contract whitelists, reputation systems, and visual anti-phishing mechanisms.
2. The "Sense of Security" Moments Brought by OKX
Moment 01: The "Insider" on the Phone Was Caught
In 2025, an NFT collector downloaded an app called "Purchase Assistant (pseudonym)" on their Android phone to participate in a popular NFT project. After downloading, they noticed abnormal wallet operations, but initial checks found no unauthorized transactions. On the surface, this app seemed like an ordinary auxiliary tool, but in reality, it exhibited high-risk behaviors such as stealing clipboard content, monitoring keyboard input, and abusing accessibility permissions. Once activated, it could lead to the theft of mnemonic phrases and private keys, jeopardizing the user's asset security.
After enabling the "Device Security Scan" feature in OKX Wallet, the system conducted a real-time proactive scan of the Android device, accurately identifying that the plugin was attempting to monitor clipboard and keyboard input. OKX's device-level protection covers Windows systems, browser plugins, and mobile devices, detecting potential local malware and assessing its threat level to mnemonic phrases, private keys, and transaction security. The scan report indicated high-risk behavior from the plugin, and the system clearly warned the user of the risk. Prompted by the warning, the user immediately uninstalled the plugin, eliminating the potential threat.

Moment 02: Clicked on a Fake Website? Already Intercepted in Advance
In 2025, a user prepared to participate in a new project activity and entered the project party's page through a social platform, not noticing that the official account of the project had been hijacked and was posting a phishing link pointing to a disguised staking platform. As the user clicked in, before the page fully loaded, the OKX Wallet proactively popped up a red warning box, indicating that the URL had been marked as a high-risk phishing site, advising the user not to connect their wallet or perform any signature operations.
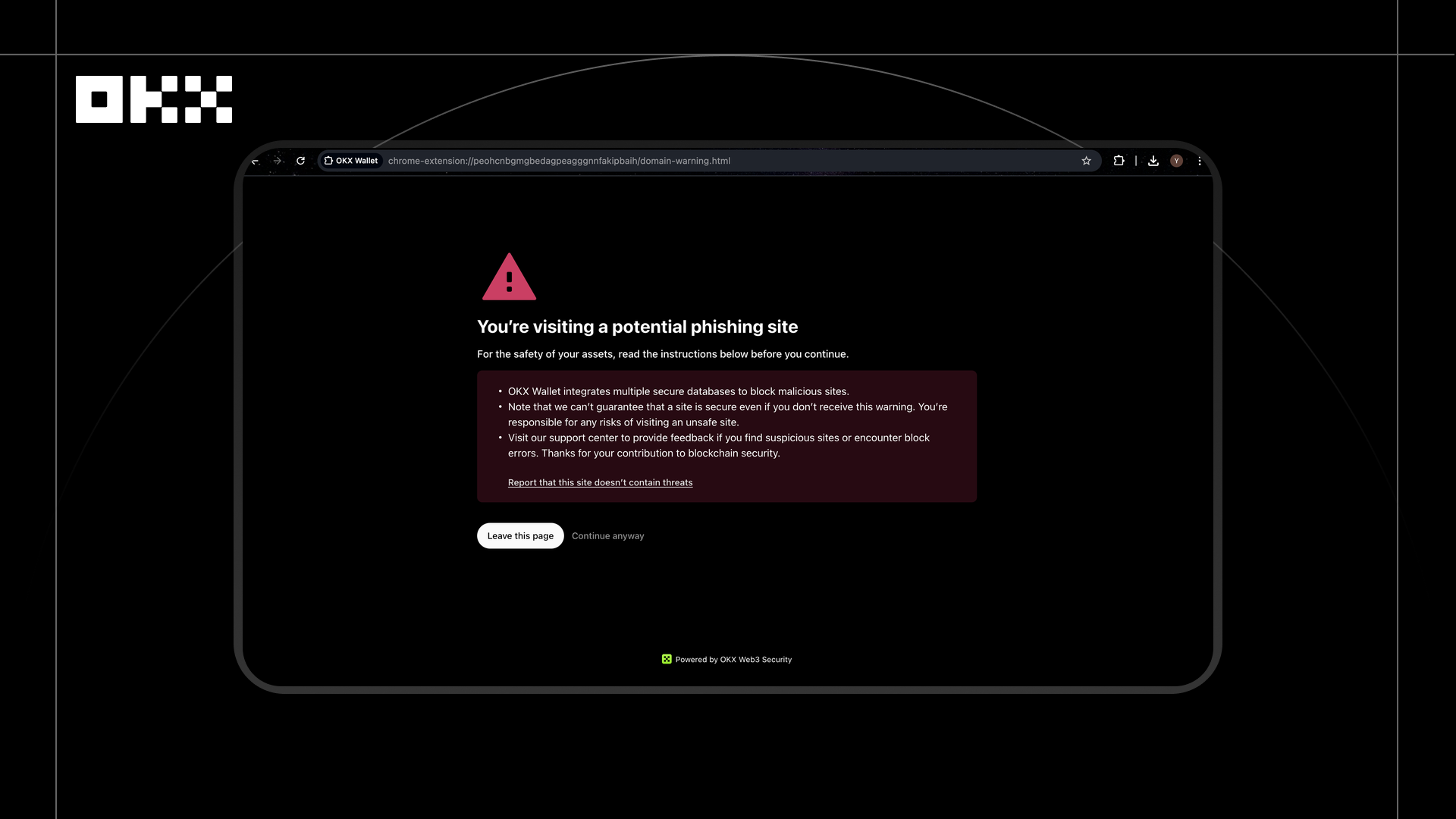
This interception is based on OKX's malicious DApp and URL detection system. The system performs static and dynamic security scans of links and DApp pages before the user accesses them, identifying page disguise features, malicious redirection behaviors, high-risk contract calls, and abnormal script activities, relying on a real-time updated URL risk database for graded judgment. When a phishing website or fraudulent content is detected, the system immediately blocks access before the user interacts with the page, preventing asset theft due to erroneous authorization.
Moment 03: One-Click Revocation of Risk Authorization
In 2025, a user who had long participated in various on-chain projects discovered while reviewing their history that a contract from an early project they had used was reported to have a risk of authorization theft. Due to frequent participation in airdrops, DeFi, and NFT projects over the years, the user had accumulated a large number of idle authorizations that needed to be cleaned up quickly to avoid potential asset misuse. For example, a protocol you once authorized may stop operating at any time, taking away the funds you authorized, or may be attacked by hackers, also transferring your funds. Therefore, canceling idle authorizations is very necessary. However, revoking them one by one is not only time-consuming but also incurs high Gas costs, making processing efficiency very low.
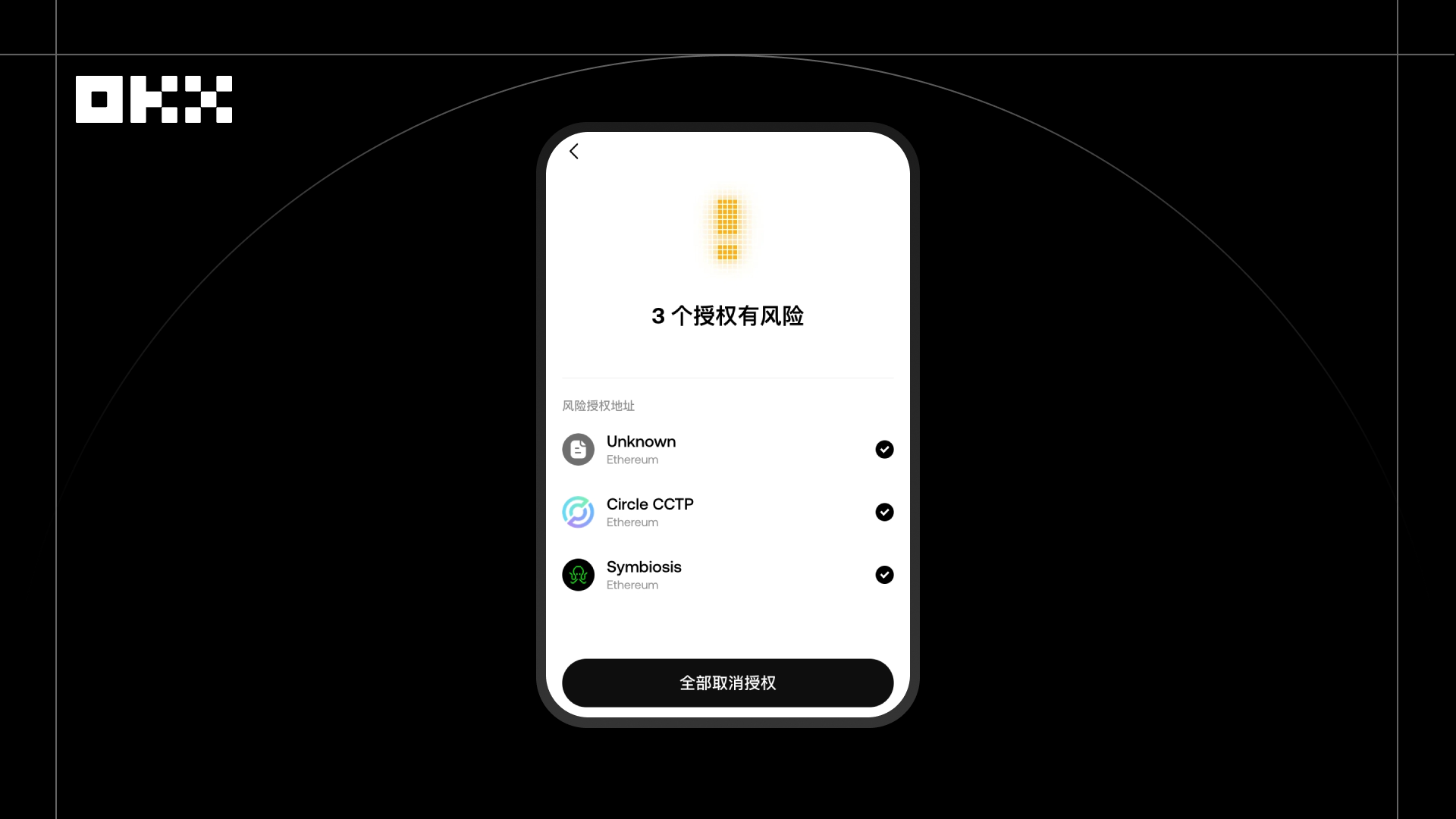
After using the authorization management tool in OKX Wallet, the system automatically scanned the user's historical authorization list and provided batch revocation capabilities. After selecting multiple risky authorizations, the user could complete all revocations with just one on-chain operation. For users who have upgraded to support EIP-7702 delegated contracts, this feature allows for the free cancellation of all authorizations without needing to process them one by one. Compared to traditional single revocation methods, batch revocation not only significantly improves processing efficiency but also reduces Gas costs by over 30% on average.
Moment 04: Before Paying Gas Fees, the Wallet Says "Stop"
EIP-7702 phishing attack interception incident. In 2025, during the launch of EIP-7702, a user saw someone "generously" sharing a mnemonic phrase on a social platform and, out of curiosity, imported it into their EVM address wallet, attempting to transfer a small amount of Gas fees to that address to extract USDT assets. On the surface, the address appeared to be an ordinary EVM wallet, and the user believed it was safe. However, in reality, the address disguised itself as an ordinary payment address using the EIP-7702 standard, and the deployer of the delegated contract had advanced permissions. Once the user sent Gas fees, the funds could be immediately transferred away.
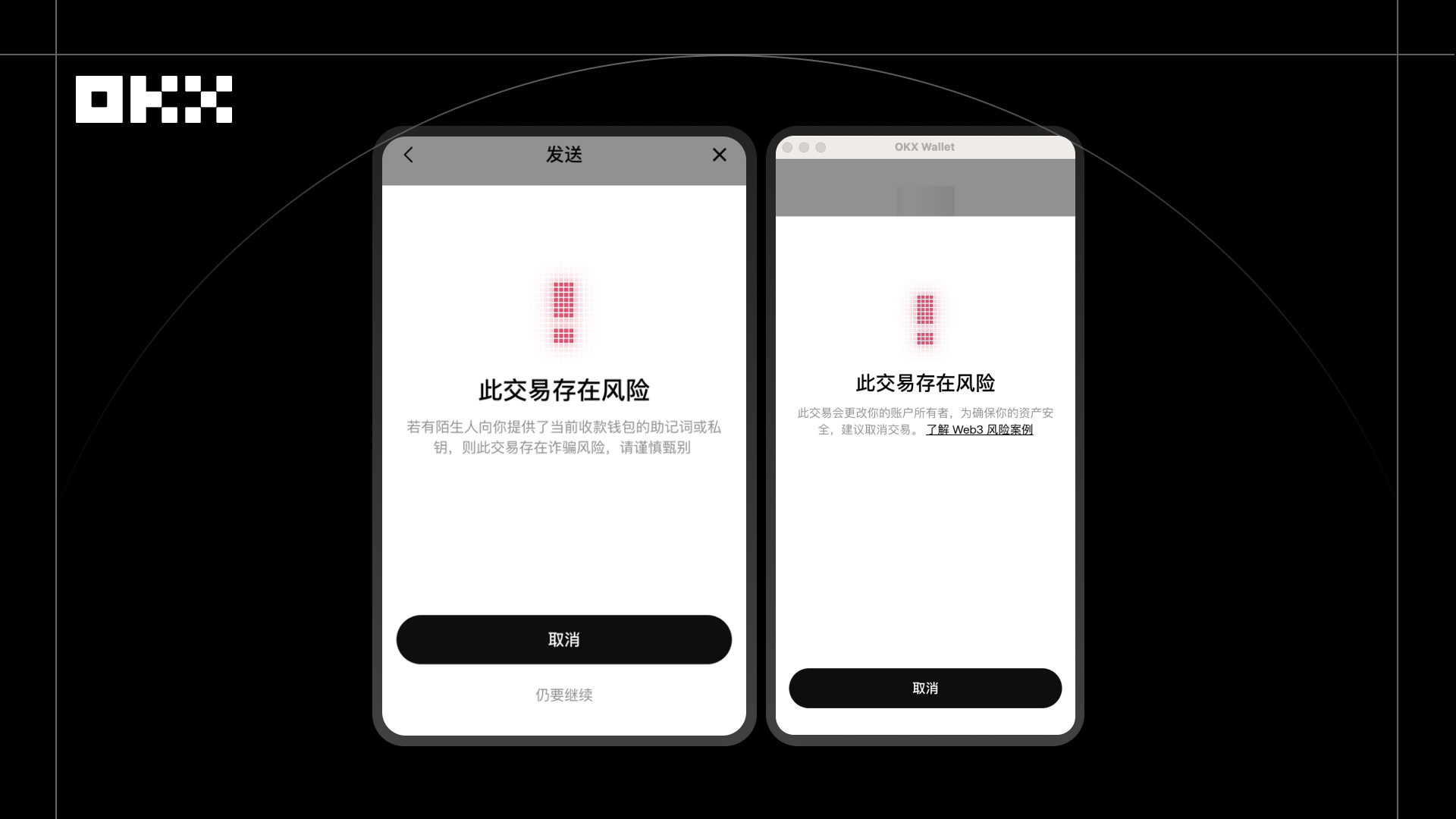
When the user attempted to make the transfer, OKX Wallet's real-time risk control system immediately recognized that the transaction belonged to a high-risk mode and triggered an interception. The system accurately identified potential risks through on-chain behavior analysis, transaction history, and smart contract logic detection, including the contract disguising as a normal address, inducing the user to authorize or pay Gas fees in the EIP-7702 phishing attack, as well as abnormal contract interaction behaviors inconsistent with user operational habits. At the same time, with the rise of Move series public chains like Aptos, targeting funds theft through tampering with public-private key mapping relationships, OKX Wallet can analyze MoveVM interaction behaviors in real-time, actively interrupting transactions when identifying key tampering risks to prevent asset theft. The transaction was blocked at the confirmation stage, with the interface clearly prompting the user that "the payment address is a high-risk address, and your transfer funds may be transferred away," effectively preventing financial loss. After the incident, the user not only avoided economic loss but also learned about the attack principles and risk patterns through the prompt, enhancing their awareness of cutting-edge on-chain threats.
Moment 05: Address Tampered, Withdrawal Stopped!
Beyond OKX Wallet, this sense of "security" is also reflected in the OKX exchange.
In 2025, a user received an on-chain payment address sent by a friend in a social application, not realizing that a malicious program lurking in their phone had quietly tampered with the message content. The address that the friend should have sent was ABC123**456DEF, but the user saw it tampered to ABC234**567DEF. When the user attempted to transfer to the incorrect address, the OKX system timely recognized the anomaly and, with OKX's persistent reminders, guided the user to discover the address discrepancy, thus helping the user avoid losses and increasing their awareness of on-chain scam tactics.
To combat the highly covert tampering attacks, the OKX platform has launched a dedicated address tampering protection strategy. Before a user initiates a withdrawal, the system conducts real-time detection of the receiving address through on-chain behavior analysis and risk modeling, accurately identifying address tampering risks. Once an anomaly is detected, the platform temporarily restricts the withdrawal and guides the user through a risk notification process, informing them of the source of the risk and how to investigate it, assisting them in verifying and correcting the address to prevent assets from mistakenly entering a hacker's account.
Moment 06: Account Compromised? Transfer Restrictions and Security Checks Implemented
In 2025, a user's account was identified by the system as "suspected to be in a fraudulent chain" before any abnormal transactions occurred. The account's fund flow, behavioral characteristics, and device associations exhibited a typical pattern of a victim of cross-border e-commerce scams. The OKX system immediately executed a protective freeze and customer service proactively contacted the user to verify the risk.
Such scams have become frequent in recent years. Scammers use "cross-border e-commerce entrepreneurship" as bait, attracting users through advertisements and guiding them to register on OKX, claiming that "operating a store requires using an overseas wallet," and then requesting verification codes and other key security information under the guise of custodial operations. Once the user completes the recharge, the scammers immediately take over the account and transfer all the funds away. In response to the characteristics of such scams, OKX has established relevant risk identification models and deployed automated handling strategies. When external manipulation of a user is detected, key account functions are immediately restricted, potential transfers are blocked, and users are simultaneously notified to complete risk confirmation and security checks. In this incident, the user was included in the protection process on the same day they were identified. Customer service confirmed that they were being induced to entrust their account to the scammers, and the system's interception helped them stop losses before the funds were transferred.
3. Evolving Security Services from "Post-Event Remediation" to "Pre-Event Interception"
The blockchain world resembles a fast-moving city, where assets, permissions, contracts, DApps, and addresses are constantly flowing, and risks are becoming smarter and more covert, lurking in every click, every confirmation, and every moment of hesitation. A sense of security does not lie in the halo of technology or functionality, but in those moments that can be felt at your fingertips—confidence when operations are error-free, reassurance when potential threats are quietly intercepted, and peace when complex systems silently protect.
In the past year, OKX Wallet has continuously strengthened security protection and proactive defense, covering full-chain monitoring from high-risk domains, spam airdrops to phishing addresses and blacklisted addresses. It has not only developed scalable capabilities in real-time monitoring and risk identification but also, through multi-dimensional and multi-strategy protective mechanisms, intercepted potential losses and scam risks before they could affect user assets, realizing the security concept of "protecting before anomalies occur."
Recently, OKX Wallet has also launched a new security landing page audit report and made its security protection system public: https://web3.okx.com/zh-hans/security; allowing users to view it anytime and anywhere.
In this world, protection is no longer an occasional reminder but a normalized capability: real-time risk identification, layered threat blocking, and early interception of potential losses, making security a perceivable and reliable presence. In 2026, perhaps more users will pause in this charming yet complex city, not out of fear, but because of visible protection, to explore the infinite possibilities of the on-chain world.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




