Written by: @BlazingKevin_, the Researcher at Movemaker
Introduction: A Historic Turning Point in Regulation
The cryptocurrency industry reached a historic turning point in the U.S. regulatory environment in 2025. After a long period of "enforcement as regulation" that led to significant legal uncertainty, the new SEC Chair, Paul Atkins, launched the "Crypto Project" initiative in July 2025, aimed at modernizing securities regulation and supporting the administration's vision of positioning the U.S. as the "global crypto capital."
One of the core initiatives of this new regulatory paradigm is the introduction of the "Innovation Exemption" policy. This exemption is designed as a time-limited regulatory relief, intended to allow emerging crypto technologies and products to enter the market quickly while alleviating initial compliance burdens before the SEC finalizes permanent rules for digital assets. Atkins has confirmed that the exemption rule is expected to officially take effect in January 2026. The release of this policy signal marks a shift in U.S. regulatory agencies from passive response to proactive construction, seeking a more flexible balance between investor protection and industry innovation.
This article will delve into the core mechanisms of the SEC's Innovation Exemption, its strategic positioning within the overall U.S. crypto regulatory framework, assess the market's controversies and opportunities it has sparked, and compare it globally, especially in relation to the EU's MiCA regulations, providing strategic advice for industry participants.
1. Core Mechanisms and Objectives of the Innovation Exemption
The core of the SEC's Innovation Exemption is to provide a temporary "safe harbor" pathway, allowing digital asset companies to operate without immediately bearing the full burden of traditional securities law registration and disclosure.
1.1 Scope and Duration of the Exemption
The scope of the Innovation Exemption is broad; any business entity developing or operating in relation to crypto assets can apply, including trading platforms, DeFi protocols, stablecoin issuers, and even DAOs.
Duration Design: The exemption period is typically set for 12 to 24 months, aimed at providing project teams with sufficient "incubation time" to achieve "maturity" or "full decentralization."
Simplified Registration: During the exemption period, projects only need to submit simplified information disclosures, without the need to complete complex and time-consuming S-1 registration documents. This mechanism is similar to the "on-ramp" design in the CLARITY Act being advanced by Congress, which allows startups to raise up to $75 million from the public each year, provided they meet disclosure requirements, without fully complying with SEC registration regulations.
1.2 Principle-Based Compliance Conditions
Atkins emphasized that the exemption will be principle-based rather than rigidly rule-based. Companies using the exemption will still need to meet basic compliance standards and investor protection measures, such as:
Regular Reporting and Review: They may be required to submit quarterly operational reports and undergo regular reviews by the SEC.
Investor Protection: For projects aimed at retail investors, risk warnings and investment limits must be established.
Technical Standards: Conditions may include requiring projects to use whitelists or certified participant pools, or even adhere to standards-based restrictions like ERC-3643.
1.3 Token Classification and "Decentralization" Testing
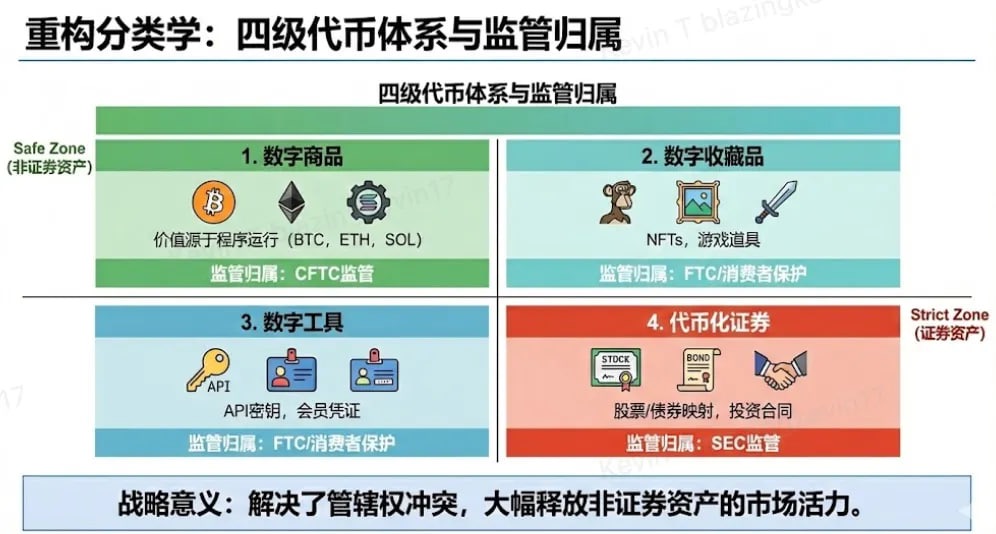
The operation of the Innovation Exemption relies on the SEC's emerging token classification system, which aims to determine which digital assets qualify as securities based on the principles of the Howey test.
Classification System: The SEC categorizes digital assets into four main types: Commodity/Network Tokens (e.g., BTC), Utility Tokens, Collectibles (NFTs), and Tokenized Securities.
Exit Path: If the first three types of assets meet the conditions of "sufficient decentralization" or "functional integrity," they can **exit the securities regulatory framework. Once an investment contract is deemed "terminated," subsequent transactions of the token, even if initially issued as a security, will not automatically be considered "securities transactions." This model of *control transfer* provides projects with a clear regulatory exit path.
Significance of the Exemption: Within this framework, the SEC instructs staff to clarify when digital assets constitute securities and emphasizes that most crypto assets are not securities, and even if they are, regulation should encourage rather than hinder their development.
2. Strategic Context of the Innovation Exemption: Synergy with Congressional Legislation
The SEC's Innovation Exemption is not an isolated administrative action; it forms part of a new U.S. crypto regulatory system alongside two major legislative pillars being advanced by Congress: the CLARITY Act and the GENIUS Act.
2.1 Clarifying Jurisdiction: The Complement of the CLARITY Act
The CLARITY Act aims to address the long-standing jurisdictional conflicts between the SEC and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC).
Core Division of Labor: The CLARITY Act places primary issuance/fundraising activities under the jurisdiction of the SEC while explicitly granting regulatory authority over digital commodity spot trading to the CFTC.
Mature Blockchain Testing: The CLARITY Act introduces a "mature blockchain" test to determine when a project reaches a sufficient level of decentralization to qualify for more lenient regulatory treatment (i.e., being considered a digital commodity). This test includes standards such as decentralized token ownership, governance participation, and functional independence from any single controlling group.
Coordination of Exemptions: The Innovation Exemption provides a temporary transition period for startups in a "maturity intent" state. It allows these projects to conduct limited fundraising and product testing through simplified disclosures while striving for full decentralization. This means that the delineation between administrative exemptions and legislative proposals is highly coordinated: the exemption is a temporary administrative "trial run" permit, while the CLARITY Act provides permanent legislative "graduation" standards.
2.2 Isolation of Stablecoin Framework: The Effectiveness of the GENIUS Act
The GENIUS Act was signed into law in July 2025, becoming the first comprehensive federal digital asset legislation in the U.S.
Status of Stablecoins: The GENIUS Act explicitly excludes payment stablecoins from the definitions of "securities" or "commodities" under federal securities and commodity trading laws, placing them under the regulation of banking regulators (such as the OCC).
Issuance Requirements: The legislation requires approved stablecoin issuers to maintain reserves in a 1:1 ratio with highly liquid assets (only including U.S. dollars, treasury bills, etc.) and prohibits the payment of interest or returns.
Regulatory Impact: Since the GENIUS Act has clarified the regulatory framework for payment stablecoins and the qualifications for issuers, the SEC's Innovation Exemption will primarily focus on more innovative areas outside of stablecoins, such as DeFi protocols and new network tokens, avoiding duplication or conflicting regulation in the stablecoin space.
2.3 Institutional Cooperation and Market Oversight
The SEC and CFTC announced that they will enhance regulatory coordination through joint statements and joint roundtable discussions to address uncertainties in cross-agency jurisdiction.
Spot Trading: The joint statement clarifies that exchanges registered with both the SEC and CFTC are allowed to facilitate the trading of certain spot crypto asset products, reflecting the regulators' willingness to encourage market participants to freely choose trading venues.
Coordination of Exemptions: One of the discussion topics for the joint roundtable is the regulation of "Innovation Exemptions" and DeFi. This coordination is crucial for reducing compliance gaps for market participants.
3. The "Traditionalization" Risk of DeFi
The introduction of the SEC's Innovation Exemption has sparked strong polarized reactions within the crypto industry.
3.1 Opportunities for Innovators and Compliers
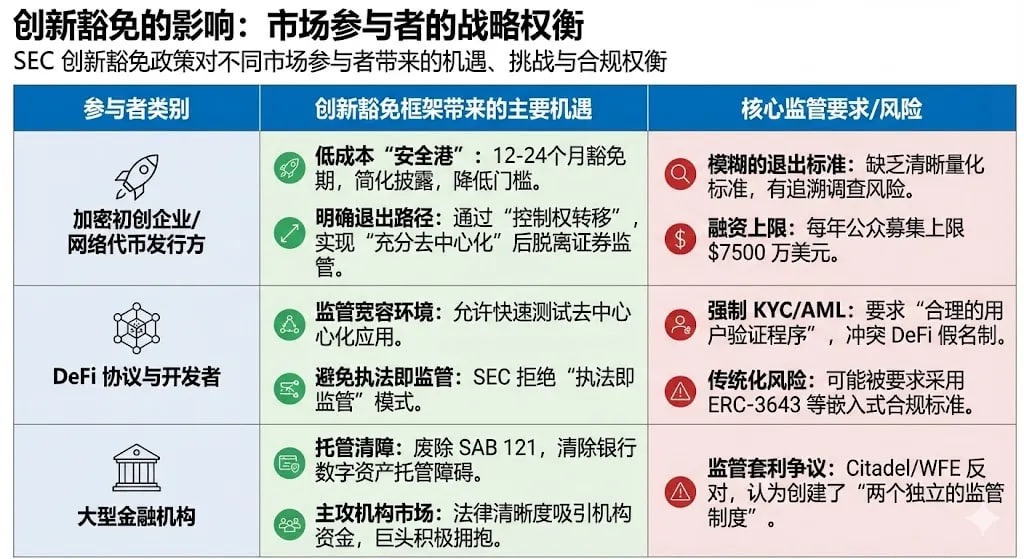
For startups and existing platforms seeking to operate compliantly in the U.S., the Innovation Exemption brings tangible benefits:
Lower Entry Costs: In the past, a crypto project wishing to operate compliantly in the U.S. might have needed to spend millions of dollars in legal fees and take over a year. The Innovation Exemption significantly lowers the compliance threshold and time costs for startup teams by simplifying disclosure processes and providing a clear transition framework.
Attracting Venture Capital: A clear regulatory path will lead projects that previously chose to "exit" or establish themselves overseas due to regulatory ambiguity to reconsider the U.S. market. Policy certainty helps attract institutional investors and venture capital, as they value the ability to invest within a clear framework.
Promoting Product Innovation: The exemption period allows a range of new crypto concepts to be tested under the new framework, especially in the emerging DeFi and Web3 ecosystems. For example, companies like ConsenSys thrive in a regulatory tolerant environment, enabling rapid testing of decentralized applications.
Beneficial for Large Institutions: Traditional financial giants (like JPMorgan, Morgan Stanley) are actively embracing digital assets. The SEC's removal of SAB 121 (an accounting standard that previously forced custodians to record client crypto assets as on-balance-sheet liabilities) has removed significant barriers for banks and trust companies to scale digital asset custody services. Coupled with the administrative flexibility brought by the Innovation Exemption, these institutions can enter the crypto space with lower regulatory capital costs and clearer legal pathways.
3.2 Concerns of the DeFi Community and "Traditionalization" Risks
The core controversy of the exemption policy lies in its impact on the decentralization principle:
Mandatory User Verification (KYC/AML): The new regulations require all projects participating in the exemption to implement "reasonable user verification procedures," which means DeFi protocols need to enforce KYC/AML procedures.
Splitting and Control of Protocols: To comply, DeFi protocols may need to split liquidity pools into "permitted pools" and "public pools," and be required to adopt compliant token standards such as ERC-3643. ERC-3643 aims to embed identity verification and transfer restrictions into smart contracts. If every transaction requires a whitelist check and tokens can be frozen by centralized entities, then whether DeFi is still truly DeFi is called into question. Industry leaders, including the founder of Uniswap, argue that regulating software developers as financial intermediaries will harm U.S. competitiveness and stifle innovation.
3.3 Opposition from Traditional Financial Institutions
The traditional financial industry has also expressed opposition to the "Innovation Exemption," fearing it could create "regulatory arbitrage."
Same Assets, Different Rules: The World Federation of Exchanges (WFE) and companies like Citadel Securities have written to the SEC urging it to abandon the "Innovation Exemption" plan, arguing that broad exemptions for tokenized securities would create two separate regulatory regimes for the same asset.
Upholding Traditional Protections: The Securities Industry and Financial Markets Association (SIFMA) emphasizes that tokenized securities must adhere to the same fundamental investor protection rules as traditional financial assets. They believe that loosening regulations will increase market risks and fraud.
4. Global Regulatory Comparison: Strategic Divergence between the U.S. and Europe

The SEC's Innovation Exemption and the more flexible U.S. model stand in contrast to the ex-ante coordinated and unified model represented by the EU's MiCA, forming two poles in global digital asset regulation, with significant differences in philosophy and operation.
The U.S. Innovation Exemption and the "control transfer" concept of the CLARITY Act sharply contrast with MiCA's "ex-ante authorization" model. The U.S. model tolerates initial uncertainty and higher risk exposure in exchange for the speed and flexibility of innovation, which is most attractive to small and medium-sized fintech companies and startups. In contrast, MiCA provides large established financial institutions (like JPMorgan) with a stable and predictable market across the EU through structural safeguards and unified rules.
This regulatory divergence forces global companies to adopt a "market-to-market" dual compliance strategy to address the differing classifications and operational requirements for the same product (e.g., dollar-pegged stablecoins) in the two major jurisdictions.
5. Market Outlook and Conclusion
The formal implementation of the SEC's Innovation Exemption policy is a key step toward the maturation of the U.S. crypto regulatory system. It not only provides an administrative "safe harbor" but also profoundly influences the geographical direction of global digital asset innovation in the coming years, marking 2026 as the "year of compliant innovation." With the unprecedented legal certainty afforded by the Innovation Exemption and the CLARITY Act, the U.S. crypto industry is set to attract significant institutional capital, accelerating the transition of crypto assets from the fringes of traditional finance to a "structured asset class."
For industry participants eager to seize this policy dividend, the strategic focus must be clear: startups should view the exemption period (12 to 24 months) as a window for low-cost, rapid entry into the U.S. market, but must regard "sufficient decentralization" as the ultimate operational goal. This means teams must design a clear decentralization roadmap based on "control," rather than relying on vague "continuous effort" standards. Projects that fail to achieve verifiable decentralization on time will face high retroactive compliance risks. Additionally, given the ongoing controversy regarding the implementation of KYC/AML requirements for DeFi protocols under the exemption policy, projects that cannot achieve complete technical decentralization and are unwilling to adopt compliant standards like ERC-3643 may need to consider abandoning the U.S. retail market after the exemption period.
Despite breakthroughs at the administrative and legislative levels in the U.S., the challenge of global regulatory fragmentation remains severe. The divergence between the flexible U.S. model and the strict, ex-ante authorized model of the EU's MiCA will continue to lead companies to engage in "regulatory arbitrage" globally. To create a fair competitive environment and ensure consumer protection is not affected by geographical location, the future development of the industry urgently requires international coordination. In the long term, a possible prediction is that by 2030, major jurisdictions may trend toward adopting a common foundational framework, including unified AML/KYC standards and stablecoin reserve requirements, which will promote interoperability and institutional adoption globally.
The SEC's Innovation Exemption policy marks a milestone in the U.S. regulatory system's shift from "ambiguous suppression" to "clear regulation," attempting to compensate for legislative lag with administrative flexibility, providing a transitional path for digital assets to achieve compliance while maintaining vitality. For the crypto industry, the opening of this exploratory door signifies the end of the era of rampant growth, where "compliant innovation" will become the core competitiveness across cycles. The next phase of crypto will no longer be solely based on code but will increasingly rely on clear asset allocation and regulatory frameworks. The key to a company's success lies in its ability to steadfastly move toward verifiable decentralization and robust compliance baselines while enjoying the speed advantages brought by the exemption, thereby transforming the complexity of regulation into a competitive advantage in the global market.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



