Author: Vaidik Mandloi
Translator: Block unicorn
Preface
Nowadays, most people buy Bitcoin and then completely stop using it.
They hold Bitcoin, calling it digital gold, and proudly claim they are "looking at long-term investment." There’s nothing wrong with that, as Bitcoin has indeed earned such a reputation.
However, such a large holding has created one of the largest pools of idle funds in today’s crypto ecosystem. About 61% of Bitcoin has not been moved for over a year, and nearly 14% of Bitcoin has not been moved for more than a decade. Despite Bitcoin's market cap exceeding $2 trillion, currently only 0.8% of Bitcoin is involved in any form of decentralized finance (DeFi) activity.
In other words, Bitcoin is the most valuable asset in cryptocurrency, but it is also the least used asset.
Now, let’s compare this with other aspects of cryptocurrency:
- Stablecoins are used for large-scale settlement payments globally.
- Ethereum supports smart contracts, decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), wallets, and the entire economic system.
- Layer 2 networks (L2) run a complete ecosystem that includes lending, trading, gaming, and thousands of applications.
Meanwhile, Bitcoin, as the largest, most secure, and most widely held asset, fails to achieve any of the above.
In contrast, it has trillions of dollars in value sitting idle, generating neither yield nor liquidity, contributing nothing to the overall economy aside from security and price appreciation.
When people try to solve this problem, various solutions bring new issues. Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC), while once popular, requires trust in custodians. Cross-chain bridges allow you to transfer Bitcoin to another chain, but this also introduces security risks. Bitcoin holders want to use their Bitcoin, but the infrastructure has never provided a secure and native way to do so.
However, this situation has finally changed. In the past few years, a brand new ecosystem has formed around Bitcoin, attempting to unlock all this "sleeping capital" without forcing people to wrap their Bitcoin, trust intermediaries, or transfer it to someone else's custody.
Let’s take a closer look!
Why Bitcoin Has Come to This Point
Bitcoin becoming a passive asset is not a coincidence. Its entire architecture has evolved in this direction. Long before decentralized finance (DeFi) emerged, Bitcoin made a clear trade-off: prioritizing security above all else. This decision shaped its culture, developer environment, and ultimately influenced the types of economic activities that flourished around it.
The result is an extremely immutable blockchain, which is beneficial for fund transfers but severely hinders innovation. Most people only see the surface symptoms: low liquidity, high dormancy rates, and the monopoly of wrapped Bitcoin, but the root of the problem runs much deeper.
The first limitation is Bitcoin's scripting model. It deliberately avoids complexity, keeping the underlying system predictable and difficult to exploit. This means no general-purpose computing capabilities, no native financial logic, and no on-chain automation. Ethereum, Solana, and all modern L1s are built on the assumption that developers will develop. Bitcoin's construction, however, is based on the assumption that developers should not develop.
The second limitation is Bitcoin's upgrade path. Any change, even a minor functional adjustment, requires coordination across the entire ecosystem. Hard forks are nearly impossible to achieve socially, while soft forks take years. Therefore, while other cryptocurrencies iterate and update entire design paradigms (such as automated market makers, account abstraction, layer 2 networks, modular blockchains), Bitcoin has remained almost stagnant. It has become a settlement layer but has never truly become an execution layer.
The third limitation lies in the cultural aspect. The Bitcoin developer ecosystem is inherently conservative. This conservatism protects the network but also stifles the spirit of experimentation. Any proposal that introduces complexity is met with skepticism. This mindset is beneficial for protecting the underlying system but ensures that new financial infrastructure cannot emerge on Bitcoin as it does elsewhere.
Additionally, there is a structural limitation: the rate of Bitcoin's value growth exceeds the growth rate of its surrounding infrastructure. Ethereum had smart contracts from the start; Solana adopted high-throughput design from the beginning. Bitcoin's value ballooned into an asset class before its "usable application scope" expanded. Thus, the entire ecosystem ultimately faced a paradox: you have trillions of dollars in capital, yet almost nowhere to deploy that capital.
The final limitation is interoperability. Bitcoin has a unique isolation, unable to interoperate with other blockchains and lacking native bridging. Until recently, there was no way to connect Bitcoin to external execution environments with minimal trust. Therefore, any attempt to make Bitcoin usable had to completely abandon Bitcoin's security model, such as wrapping, bridging, custodial minting, multi-signature, and federations. For an asset built on a foundation of distrust in intermediaries, this approach can never scale.
The First Workaround: Wrappers, Sidechains, and Cross-Chain Bridges
When it became evident that Bitcoin's underlying system could not support meaningful activity, the industry, as always, developed various workarounds. Initially, these solutions seemed progressive, allowing Bitcoin to enter the thriving realm of DeFi activities. However, upon closer examination, they all share a common flaw: using these solutions requires giving up part of Bitcoin's trust model.
The most notable example is Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC). It once became the default bridge between Bitcoin and Ethereum, and for a time, this model seemed to work. It released liquidity, allowing Bitcoin to be used as collateral, traded in automated market makers (AMMs), lent, cycled, and re-collateralized—essentially achieving everything that Bitcoin itself could not do. But the cost is that the existence of wrapped Bitcoin relies on real Bitcoin being held by others. This means custodianship, reliance on external entities, operational risks, and a guarantee system unrelated to Bitcoin's underlying security mechanism.
Federated systems attempt to alleviate this trust burden by distributing control among multiple entities. Unlike a single custodian, a group collectively holds the Bitcoin backing the wrapped assets. This is an improvement, but it falls far short of completely eliminating trust. Users still rely on a coordinated group of operators, and the strength of the anchoring effect depends solely on their incentive mechanisms and integrity. For communities that prefer trustless systems, this is not a perfect solution.
Cross-chain bridge technology introduces a new set of problems. Users no longer rely on custodians but on a set of external validators, whose security assurances are often weaker than the chain the user is leaving. Cross-chain bridge technology makes it possible to transfer Bitcoin across chains, but it has also become one of the biggest security vulnerabilities in the cryptocurrency space. Multiple analyses indicate that cross-chain bridge vulnerabilities are one of the largest sources of capital loss in the cryptocurrency sector.
The emergence of sidechains adds further complexity. They are chains independent of Bitcoin, connected through various anchoring mechanisms. Some sidechains use multi-signature control, while others use special purpose entities (SPVs) for proof. However, none inherit Bitcoin's security. They operate their own consensus mechanisms, validator sets, and risk assessment systems. The label "Bitcoin sidechain" is often more of a marketing gimmick than a fact. Liquidity may flow, but security assurances do not.
All these methods share a commonality: they push Bitcoin outward, detaching it from its underlying architecture and placing it into an environment governed by rules enforced by others. This temporarily solves the usability issue but creates a larger problem: Bitcoin suddenly begins to operate under a trust model it was designed to avoid.
These flaws are evident:
- Wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) grew simply because people tolerated custodians as a temporary solution.
- Sidechains exist, but due to their failure to inherit Bitcoin's security, they remain limited to niche markets.
- Cross-chain bridges connect Bitcoin to other chains but also introduce entirely new attack vectors.
Each workaround solves one problem but brings another.
Breakthrough Moment: Bitcoin Finally Has New Primitives
For a long time, Bitcoin's limitations were considered irreversible. The underlying architecture would not change, upgrades were slow, and any proposals aimed at enhancing its expressiveness were dismissed as unnecessary risks.
However, in the past few years, this assumption has begun to waver.
1. Bitcoin has gained a "verify without executing" capability: The most significant breakthrough is the emergence of a new verification model that allows Bitcoin to check the results of computations completed elsewhere without running the computations itself.
This breakthrough has made systems like BitVM and later similar systems possible. These systems do not change Bitcoin's functionality but leverage Bitcoin's ability to enforce results through anti-fraud proofs.
This means you can build logic, applications, and even complete execution environments outside of Bitcoin, while Bitcoin can still ensure their correctness. This is in stark contrast to Ethereum's philosophy of "everything executes on L1." Bitcoin can finally adjudicate. This is precisely why it opens the door to:
- Bitcoin-backed rollups
- Trust-minimized cross-chain bridges
- Programmable Bitcoin vaults
- Off-chain computation, on-chain verification
2. Upgrades like Taproot quietly expand Bitcoin's application scope: Taproot was not initially promoted as a DeFi upgrade, but it provided the cryptographic foundation needed for BTCFi: lower-cost multi-signatures, more flexible key path spending, and better privacy protection. More importantly, it enabled architectures like Taproot Assets (for stablecoins) and more advanced vault systems.
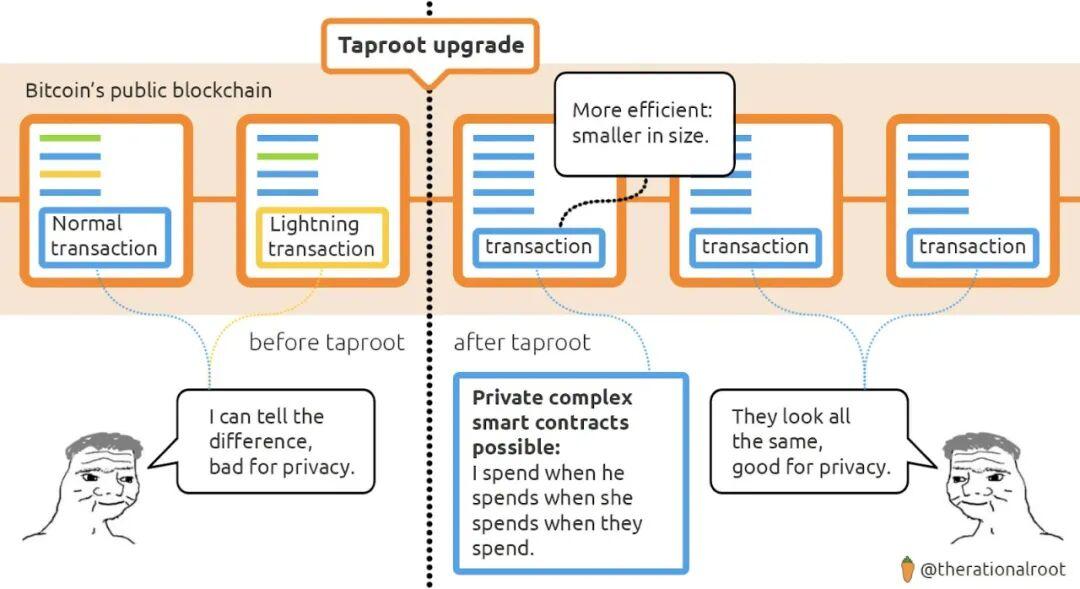
3. The Emergence of Bitcoin Native Assets: With the advent of Taproot and updated proof systems, projects have begun to launch assets based on Bitcoin or secured by Bitcoin without the need to wrap BTC.
Combining Taproot, Schnorr signatures, and new off-chain verification technologies, developers can now build assets directly on Bitcoin itself or assets that inherit Bitcoin's security.
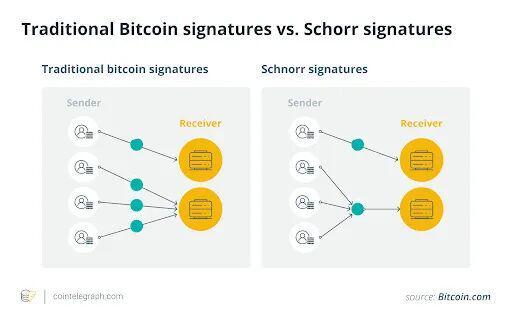
This includes the following:
- Taproot Assets (Tether directly minting USDT on the Bitcoin/Lightning Network stack)
- Bitcoin native stablecoins that do not rely on Ethereum, Solana, or Cosmos
- Synthetic assets that do not depend on custodial-backed BTC
- Programmable vaults and multi-signature structures that were previously unattainable
Assets issued on Bitcoin can now be utilized without leaving Bitcoin. Moreover, assets issued on Bitcoin do not require Bitcoin to leave self-custody.
4. Bitcoin Yield Becomes Possible: Bitcoin itself has never had yield. Historically, the only way to "earn" yield on Bitcoin was to wrap it, send it to custodians, lend it on centralized platforms, or bridge it to other blockchains. All these methods carry risks and completely detach from Bitcoin's security model.
BTCFi introduces a brand new way to earn yield on Bitcoin. How is this achieved? By creating systems that allow Bitcoin to contribute to network security. This gives rise to three types:
- Bitcoin Staking (for other networks): BTC can now secure PoS networks or application chains without leaving the Bitcoin chain.
- Bitcoin Re-staking: Similar to how Ethereum can protect multiple protocols through shared security mechanisms, Bitcoin can now be used as collateral to support external chains, oracles, DA layers, etc.
- Lightning Network-based Yield Systems: Protocols like Stroom allow BTC used in Lightning Network channels to earn yield by providing liquidity, again without wrapping or relying on custodial bridges.
Before the emergence of BTCFi, all of this was impossible.
5. Bitcoin Finally Has an Execution Layer: Recent advancements in off-chain verification enable Bitcoin to enforce computation results that it does not execute itself. This allows developers to build rollups, cross-chain bridges, and contract systems around Bitcoin that rely on Bitcoin for verification rather than computation. The base layer remains unchanged, but the external layer can now run logic and prove its correctness to Bitcoin when needed.
This grants Bitcoin unprecedented capabilities: supporting applications, contract-like behaviors, and new financial primitives without transferring Bitcoin to custodial systems or rewriting protocols. This is not "smart contracts on Bitcoin," but a verification model that maintains Bitcoin's simplicity while allowing for more complex systems to exist around it.
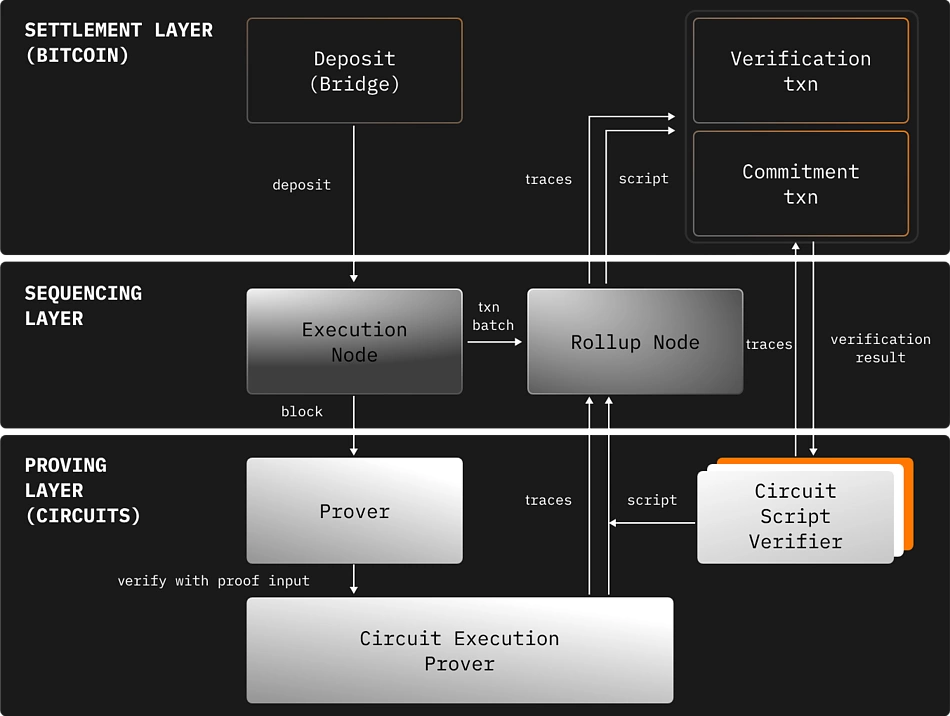
BTCFi Overview: What is Actually Being Built
With the maturation of underlying verification and portability tools, the Bitcoin ecosystem is finally beginning to expand in a way that no longer relies on custodians or wrapped assets. What is emerging today is not a single product or category, but a series of interconnected layers that for the first time provide Bitcoin with a fully functional economic system. The simplest way to understand this is to observe how these components complement each other.

Infrastructure Layer: The first significant change is the emergence of secure execution environments for Bitcoin. These environments are not L1-level competitors nor are they trying to turn Bitcoin into a smart contract platform. They are external systems that handle computation, relying solely on Bitcoin for verification. This separation is crucial. It creates a space where lending, trading, collateral management, and even more complex underlying functions can exist without requiring any changes to Bitcoin's base layer. It also avoids the flaws of the old model, where using Bitcoin meant handing it over to custodians or trusting multi-signatures. Now, Bitcoin itself remains unchanged; computation occurs around it.
Asset and Custody Layer: Meanwhile, a new generation of Bitcoin cross-chain bridges is beginning to form. These are no longer the custodial, trust-heavy bridges of the previous cycle, but bridges built around verifiable results. These systems no longer require users to trust a group of operators; instead, they employ challenge mechanisms and fraud proofs to automatically reject incorrect state transitions. As a result, users can transfer Bitcoin to external environments more securely without relying on the fragile trust assumptions of previous designs. More importantly, these bridges align with Bitcoin holders' inherent understanding of security: minimal trust, minimal reliance.
Protocol Layer: As asset flows become more secure, the next phase of innovation focuses on what role Bitcoin can play in these environments. Yield markets and security markets have emerged in this context. Throughout most of Bitcoin's history, earning any yield on Bitcoin required handing it over to exchanges or wrapping it into other blockchains. Now, staking and re-staking models allow Bitcoin to contribute to the security of external networks without losing control over it. Yield does not come from credit risk or re-staking but from the economic value of maintaining consensus or verifying computation results.
At the same time, Bitcoin native assets are beginning to emerge. Developers are no longer wrapping or migrating Bitcoin to Ethereum; instead, they are starting to issue assets on Bitcoin or anchor assets to Bitcoin's security mechanisms using technologies like Taproot, Schnorr signatures, and off-chain verification. This includes stablecoins minted directly on Bitcoin infrastructure, synthetic assets that do not rely on custodians, and vault structures that allow for more flexible spending conditions. All of these expand Bitcoin's utility without introducing it into different trust models.
These advancements are interesting on their own. Together, they mark the birth of the first coherent Bitcoin financial system. Computation can occur off-chain and be enforced on Bitcoin. Bitcoin can be securely transferred without custodianship. It can earn yield without leaving self-custody. Assets can exist natively without relying on the security guarantees of other ecosystems. Each advancement addresses different aspects of the liquidity trap that has plagued Bitcoin for over a decade.
My Perspective
I believe the simplest way to view BTCFi is that Bitcoin finally has an ecosystem that matches its scale. For years, people have tried to build the Bitcoin ecosystem using tools that could not support trillion-dollar liquidity. Any serious Bitcoin holder would not stake their Bitcoin on custodial anchors, unverified cross-chain bridges, or hastily constructed sidechains, and they indeed have not done so.
This wave is different because it fully embraces Bitcoin on its own terms. The security model remains intact, self-custody is fully preserved, and the surrounding systems are finally robust enough to support meaningful capital. As long as a small portion of dormant BTC begins to flow because the infrastructure finally deserves them, the impact will be profound.
This new wave is different from previous ones because it responds to challenges in a way that is true to Bitcoin itself. The security model remains unchanged, the self-custody mechanism is fully preserved, and the systems surrounding Bitcoin are finally strong enough to support significant capital flows. Even if only a small portion of dormant Bitcoin begins to flow due to the maturity of the infrastructure, its impact will be significant.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



