Introduction
This week, developers from around the world are gathering in Buenos Aires to attend the annual Ethereum developer conference. Additionally, Ethereum is set to undergo a significant upgrade codenamed "Fusaka" in December, which will increase data throughput by eight times, enhance network security, and introduce new development tools. At the same time, increased institutional participation is bringing strong capital inflows, and the RWA market is expected to provide a new growth engine for Ethereum.
However, due to the uncertainty in the macro environment, Ethereum's price has fallen into a downward channel since early October, dropping from a new high of $4,900. Especially after the "10·11 crash" black swan event, the price of ETH has struggled, hovering around $3,000 recently, down over 30% from its peak. The funds that previously supported ETH's rise are now withdrawing: shares of the Ethereum Treasury Company (DAT) have plummeted, turning from profit to loss, with some shareholders selling off to cash out; multiple ETH spot ETFs globally are experiencing continuous net outflows, and traditional institutional funds are becoming more cautious. Meanwhile, the Ethereum ecosystem is facing a chill: the total locked value has decreased by over 20% since October, on-chain stablecoins have faced consecutive depegging events, and DeFi protocols have encountered setbacks one after another.
This article will review Ethereum's recent performance, deeply analyze the current favorable and unfavorable factors facing Ethereum, and look ahead to Ethereum's prospects and trends by the end of the year, next year, and even in the medium to long term. It aims to help ordinary investors clarify the fog, grasp trends, and provide some reference for making more rational judgments during this critical turning point.
Recent Performance Analysis of Ethereum
In the third quarter of this year, Ethereum's price surged alongside rising market sentiment, climbing from about $2,500 at the end of June to nearly $4,950, the year's peak, in late August. However, entering October, a combination of macro and endogenous market risks triggered an "epic crash." On October 11, the unexpected announcement by the U.S. to impose additional tariffs on China acted as a catalyst, leading to a global sell-off of risk assets, with the crypto market experiencing a sharp decline, and Ethereum's price plummeting over 20% to around $3,380. Although the market rebounded afterward, liquidity gradually diminished, and overall it has been trending downward. As of now, the ETH price is approximately $3,000, down more than 30% from the August high.
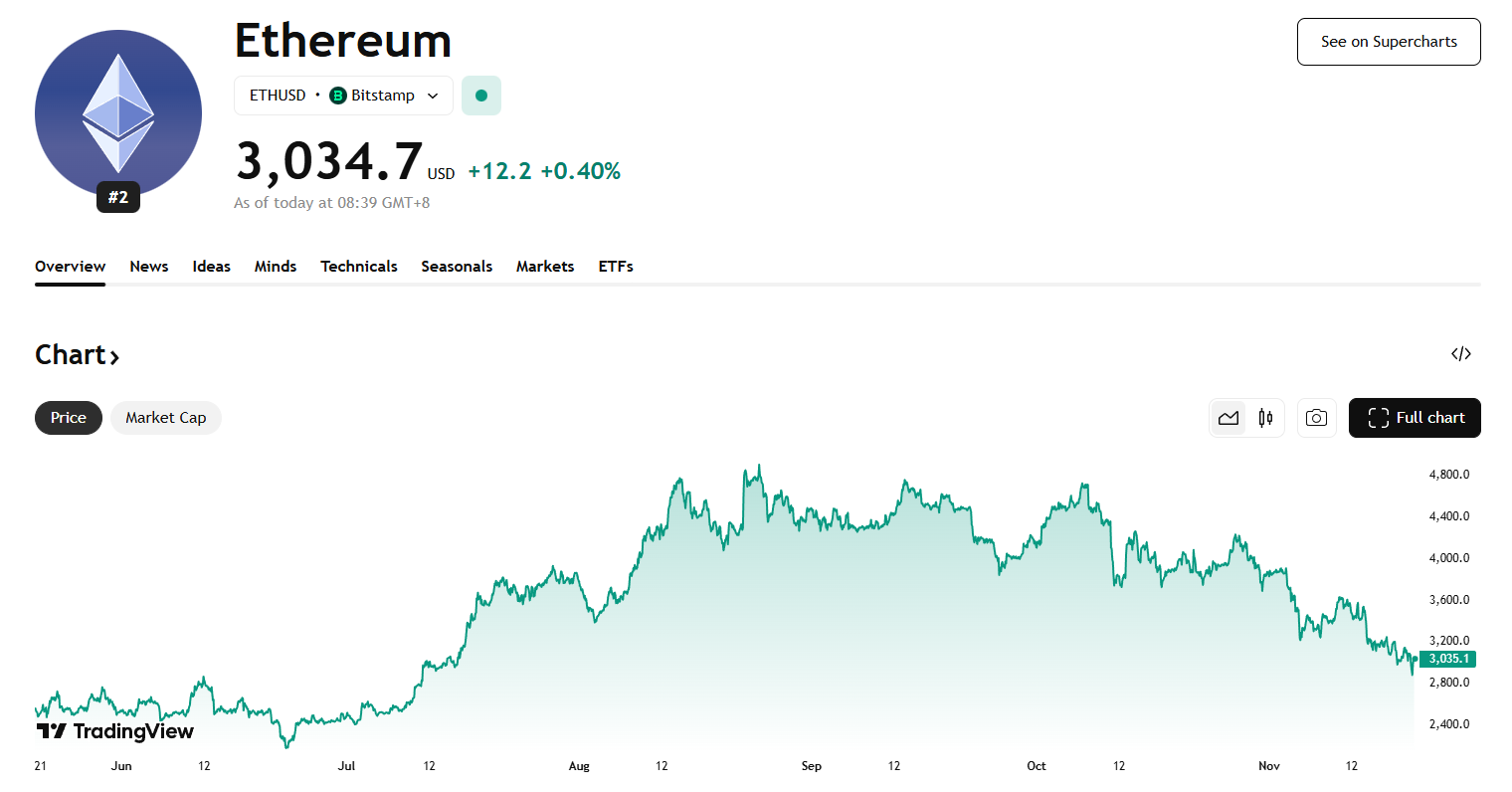
Source: https://www.tradingview.com/symbols/ETHUSD
1. Tightening Macro Environment: Behind this round of adjustment, tightening macro liquidity and a shift in interest rate expectations are significant factors. The Federal Reserve sent a strong signal in November, cooling market expectations for a rate cut in December, leading to a notable decline in risk appetite. The prosperity of the crypto market in the third quarter was largely due to institutional funds "speculating on new assets"—multiple Ethereum spot ETFs were launched in the summer, attracting traditional investors, coupled with several listed companies announcing substantial coin purchase plans, creating strong buying support. However, entering October, the uncertainty in the macro environment increased, with safe-haven funds flowing back into the dollar and U.S. Treasuries, rapidly depleting the marginal increment in the crypto market.
2. ETF Fund Outflows: According to SoSoValue data, by mid-November, the total holdings of Ethereum spot ETFs were approximately 6.34 million coins (worth $192.8 billion), accounting for 5.19% of ETH's supply. However, this month, the funds have shifted from net inflows to net outflows, with the scale of withdrawals significantly exceeding new inflows, and the maximum daily outflow reaching as high as $180 million. This contrasts sharply with the steady capital inflow seen in July and August. ETF investors are primarily long-term holders, and consecutive days of net redemptions indicate that the demand for ETH from traditional financial channels is weakening. Their withdrawal not only directly reduces buying pressure but may also amplify short-term volatility.
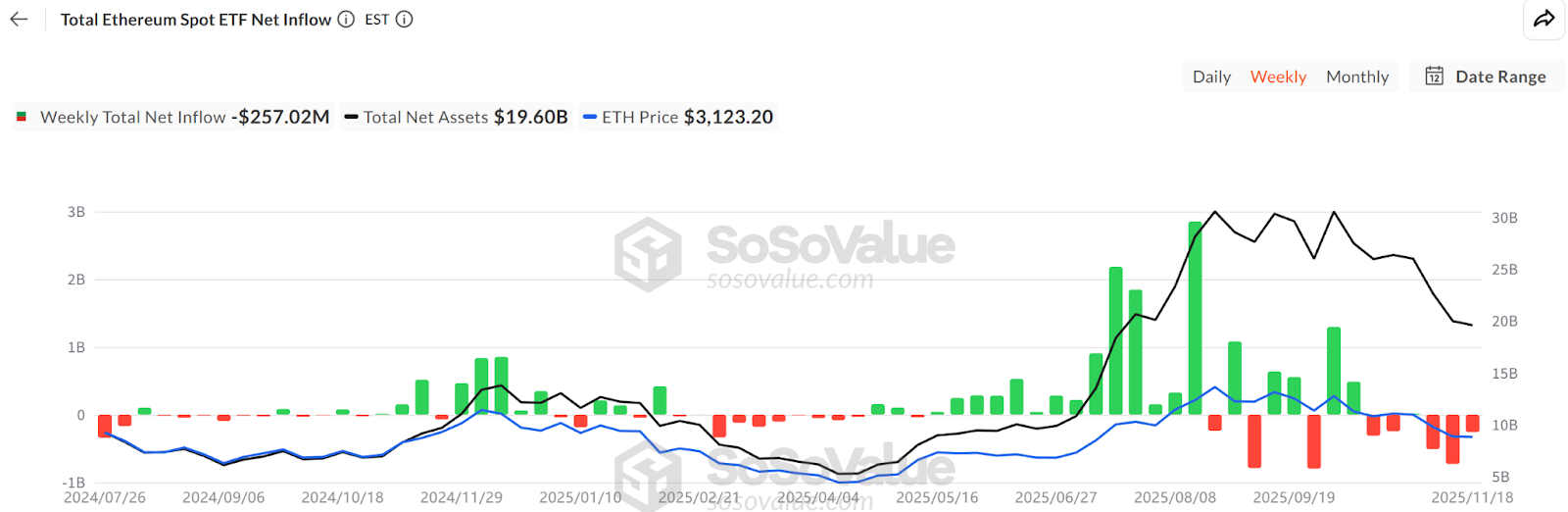
Source: https://sosovalue.com/assets/etf/us-eth-spot
3. DAT Company Incremental Contraction: There is also differentiation within the sector. As of mid-November, the overall strategic reserve of Ethereum held by DAT was approximately 6.24 million coins, accounting for 5.15% of the supply, with the pace of accumulation noticeably slowing in recent months. Among the "whales," the pioneer BitMine has become almost the only major player still aggressively buying ETH, having added 67,000 coins in the past week. In contrast, another leading company, SharpLink, has ceased its buying activities after acquiring 19,300 coins in mid-October, with an average holding cost of about $3,609, now showing a paper loss. Furthermore, some small and medium treasury companies have been forced to sell off to survive: for example, "ETHZilla" sold approximately 40,000 ETH at the end of October to repurchase its own stock, hoping to narrow the price discount. The treasury industry has shifted from previous broad expansion to polarization: capable giants can still maintain buying pressure, while smaller players are trapped in liquidity constraints and debt pressures, forced to reduce positions to stop losses.

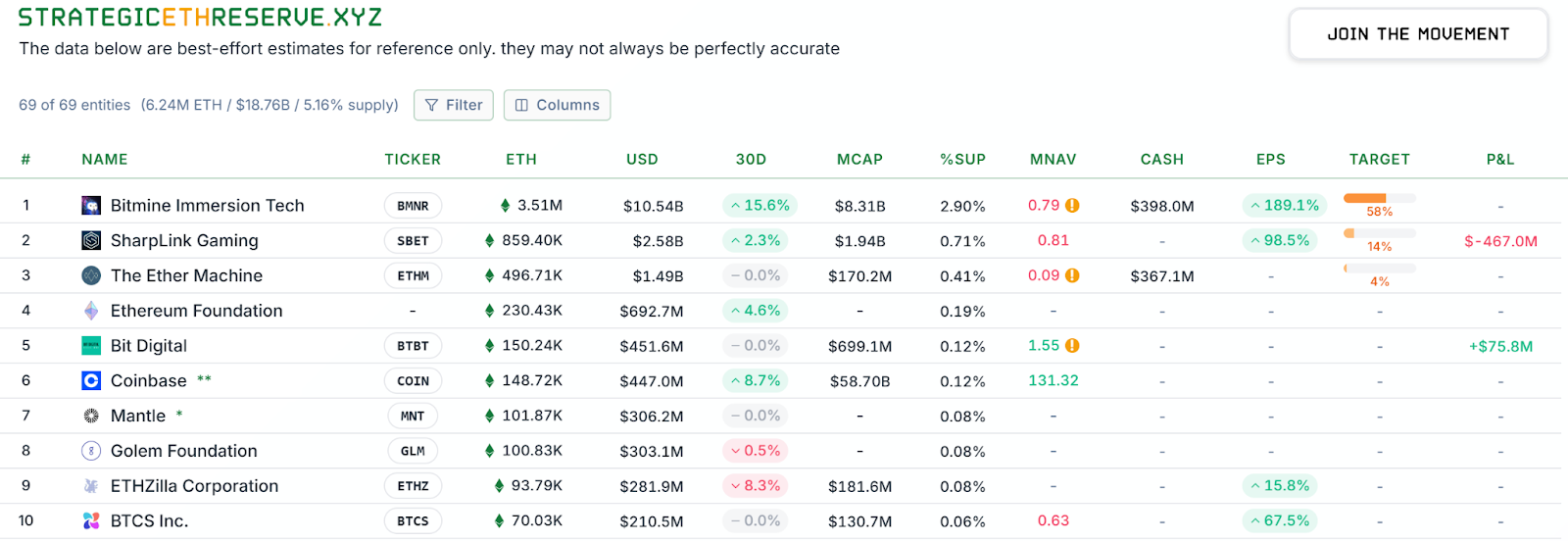
Source: https://www.strategicethreserve.xyz/
4. Leverage Cleansing and Selling Pressure Emergence: In the secondary market, the rapid retreat of leveraged funds has further intensified the selling pressure on ETH. During the October crash, the positions of whales like "Brother Ma Ji" who had been continuously long were forcibly liquidated, spreading panic in the market and somewhat undermining bullish confidence. According to Coinglass statistics, the open interest of ETH contracts has plummeted nearly 50% since the August peak, indicating that leveraged funds are rapidly deleveraging, which means both speculative enthusiasm and liquidity in the market are cooling. Not only are leveraged longs retreating, but long-term holders are also beginning to adjust their positions. On-chain analysis firm Glassnode reported that long-term holders who have held coins for over 155 days are recently selling about 45,000 ETH (approximately $14 million) daily, the highest selling level since 2021, indicating that some older holders are choosing to cash out at high prices. This series of signs shows that the bullish momentum within the market has significantly weakened.
5. Ethereum Staking Retreat: Data from the Beacon chain shows that the number of active Ethereum validators has decreased by about 10% since July, marking the first significant decline in the validator scale since the transition to POS in 2022. The main reasons are that in the first half of this year, the significant rise in ETH led many node operators to choose to exit staking to realize profits, with a surge in validator exit queues in late July, reaching a historical high for daily ETH exits; secondly, the recent annualized staking yield has dropped to about 2.9%, while on-chain lending rates have risen, squeezing the arbitrage space, and the price support for ETH from staking has correspondingly weakened.
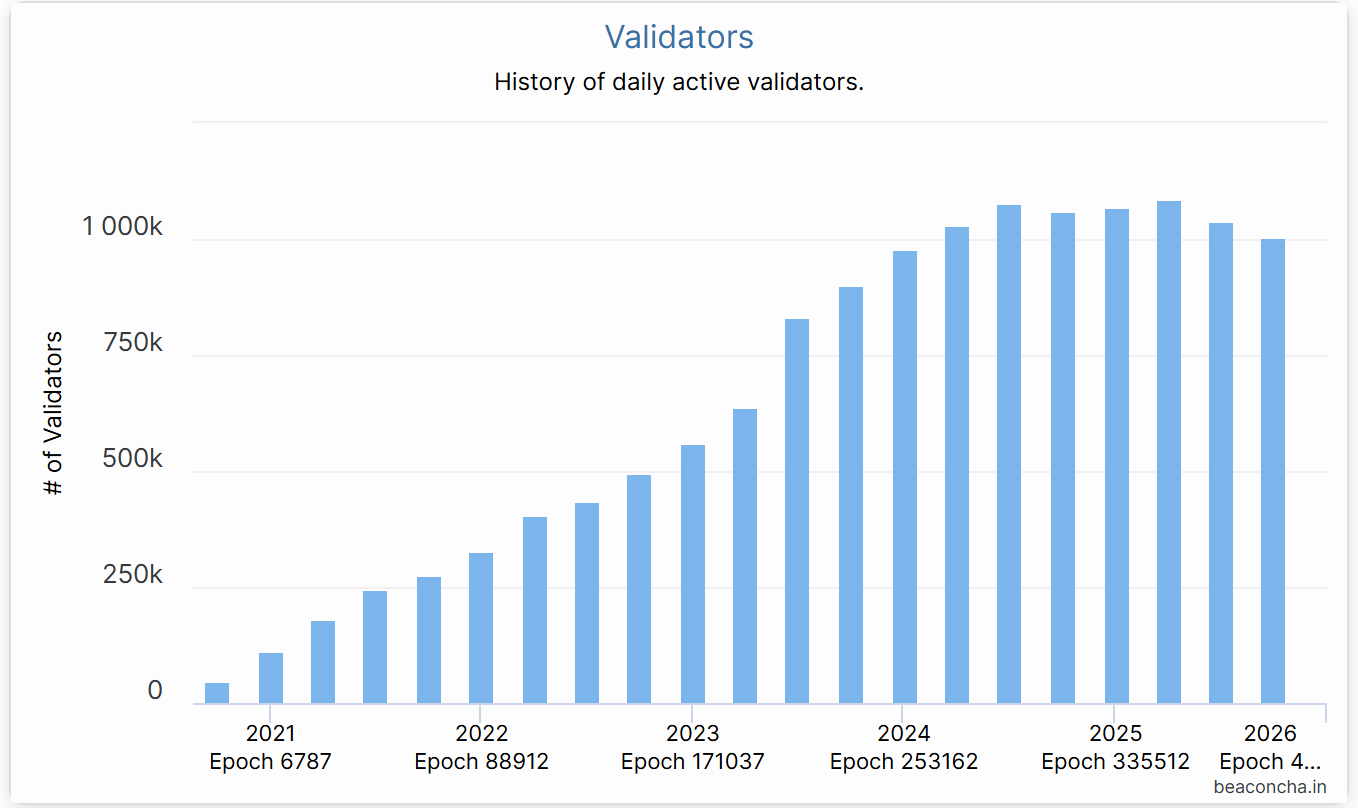
Source: https://beaconcha.in/
6. Stablecoin and DeFi Turmoil: Issues within the Ethereum ecosystem itself have also been exposed, further undermining investor confidence. On the day of the October 11 crash, USDe collapsed due to a failure in its circular lending arbitrage mechanism, dropping to as low as $0.65. Although it quickly recovered to near $1, it triggered a chain reaction. Subsequently, several risk events re-emerged in the decentralized stablecoin sector: the xUSD issued by the Stream protocol severely depegged due to the underlying hedge fund's collapse, and then the USDC also fell to $0.38 during a liquidity crisis, facing risks of not being redeemable at a 1:1 ratio; another algorithmic stablecoin, deUSD, also failed to maintain its peg, all dropping below their pegged prices. These newly minted stablecoins, once highly anticipated, faltered in extreme market conditions, exposing the vulnerabilities and black-box risks of "delta-neutral" stablecoin models in such scenarios. The consecutive failures of stablecoins have dealt a heavy blow to DeFi. Since mid-October, several lending and yield aggregation protocols have reported bad debts and a sharp decline in TVL: the Morpho protocol's USDC treasury lost value due to the associated Elixir stablecoin pool going to zero, forcing it to delist related strategies, resulting in a loss of about 3.6% of the treasury's assets; the established lending protocol Compound also faced bad debt pressure due to the collapse of some long-tail stablecoins, triggering a liquidation crisis. The Balancer protocol suffered a hacker attack at the end of October, resulting in losses exceeding $100 million. These events have led to a continuous outflow of funds from DeFi. By early November, the on-chain TVL of Ethereum had dropped from a peak of $97.5 billion to about $69.5 billion, evaporating over $30 billion in assets in just over a month.
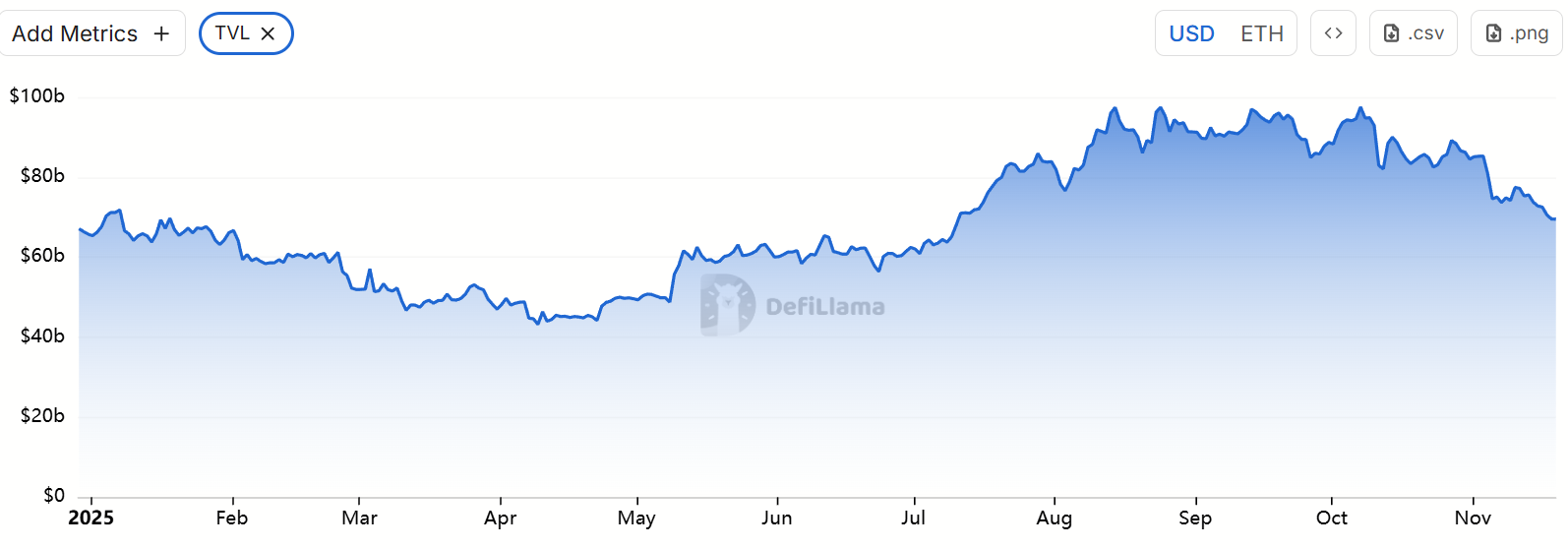
Source: https://defillama.com/chain/
Overall, Ethereum has undergone a "double whammy" test over the past two months, facing external macro tightening and simultaneous pressure on the three main buying forces (ETFs, treasury, on-chain funds), while its internal ecosystem has encountered turmoil in stablecoins and security. Amidst skepticism, both the price and market capitalization of Ethereum are under pressure.
Negative Factors: Macro Clouds and Potential Concerns
It is undeniable that the negative clouds currently hanging over Ethereum may continue to exert pressure on ETH prices and ecological development in the medium to short term.
1. Macro Tightening and Capital Withdrawal
The biggest unfavorable factor comes from the macro environment. Major central banks around the world are maintaining cautious interest rate policies amid unstable inflation, and expectations for a rate cut in December have been thwarted, leading to heightened market risk aversion. Several forces that drove ETH's rise in the first half of this year (ETF purchases, DAT buying, on-chain leverage accumulation) have now become potential sources of selling pressure. If the macro environment remains cold over the next six months, it is possible that more institutions will indirectly reduce their ETH positions by redeeming ETFs or selling treasury company stocks, resulting in sustained capital outflows. Particularly, the treasury model itself has certain vulnerabilities: companies like BitMine are currently trading at a significant discount, and shareholder confidence is low. If their financing chains break or they face repayment pressures, the risk of being forced to sell ETH for cash cannot be ignored. In summary, until a turning point in global liquidity is observed, the headwinds in the capital market may continue to overshadow Ethereum.
2. Competition and Diversion Effects
Other public chains like Solana and BSC have diverted speculative funds to some extent. Additionally, the rise of cross-chain protocols and application chains like Plasma, Stable, and Arc has weakened Ethereum's appeal to project teams and users. With the rise of modular blockchain concepts, some projects are even building their own sovereign Rollups, no longer relying on Ethereum's security. Moreover, within the Layer 2 space, there is competition among various Rollups: Arbitrum and Optimism are offering high incentives or airdrops to compete for users and traffic, which may lead to an "L2 war." The success of L2 does not directly equate to an increase in the price of the main chain ETH, and may instead dilute some value. For instance, some L2s have issued independent tokens for fee payments, which could impact the long-term demand for ETH as gas. Of course, ETH remains the primary settlement asset for now, and short-term competitive impacts are limited, but it is a concern for the long term.
3. Regulatory and Policy Uncertainty
The regulatory environment is also a Damocles sword hanging overhead. Although SEC Chairman Paul Atkins has stated that Ethereum should not be considered a security, if the regulatory stance changes in the future, Ethereum's compliance status may be called into question, which could affect institutional participation enthusiasm. Additionally, discussions on DeFi regulation are underway in various countries, and features like decentralized stablecoins and anonymous transactions may face stricter restrictions or even crackdowns. These policy uncertainties could become constraints on the development of the Ethereum ecosystem. For example, if certain countries prohibit banks from participating in staking or restrict retail investors from buying and selling crypto assets, it would directly reduce potential capital inflows. Furthermore, the MiCA regulations in Europe impose requirements on stablecoin issuance and DeFi services, which may increase compliance costs for Ethereum projects.
4. Internal Ecological Risks and Trust Rebuilding
After a series of upheavals, the trust deficit in the Ethereum ecosystem will take time to mend. On one hand, the frequent depegging events of stablecoins have left DeFi users wary of high-yield products. Currently, the overall market risk appetite has decreased, and conservative strategies are prevalent, with users favoring centralized platforms or mainstream stablecoins like USDT/USDC. This will likely lead to liquidity shortages and limited growth for many innovative protocols on Ethereum in the near term. On the other hand, frequent security incidents (such as hacks and vulnerabilities) have raised doubts about the security of Ethereum's application layer. Each major attack or collapse is often accompanied by users of related protocols selling ETH or withdrawing funds. It can be expected that in the near term, risk governance will become a key focus for the Ethereum community, and project teams may strengthen reserves and insurance measures to restore user trust. However, once a bearish market psychology takes hold, investors often require more positive stimuli (such as price rebounds or new application breakthroughs) to be willing to reinvest.
In summary, Ethereum is currently in a phase of bottoming out amid internal and external challenges. The retreat of macro capital, industry competition and regulatory pressures, as well as issues within its own ecosystem, may continue to suppress ETH performance in the short term. These unfavorable conditions will require time and sufficient positive stimuli to resolve. During this process, the market may still experience pain and fluctuations.
Positive Factors: Upgrade Drivers and Fundamental Support
Despite the recent turmoil, Ethereum's foundational position as the largest public chain ecosystem remains solid, with its network effects, technical foundation, and value consensus demonstrating resilience over the long term.
1. Network Effects and Ecological Resilience
Active Development and Innovation: The number of active developers and projects on Ethereum remains the highest in the industry, with a continuous emergence of new applications and standards. During the DevConnect conference, several important developments drew community attention: Vitalik reiterated Ethereum's principles of "trustworthy neutrality and self-custody"; topics such as account abstraction and privacy protection became focal points.
Layer 2 Ecosystem Thriving: Although total TVL has recently faced setbacks, user activity and transaction volume on Layer 2 networks like Arbitrum, Optimism, and Base remain relatively high, indicating that there is still potential demand on-chain in a low-cost environment. After the Fusaka upgrade, as the cost of data publishing decreases further, the economic model of Rollups will become more sustainable, attracting more users and projects to deploy on Ethereum's Layer 2, thereby benefiting the main chain's value.
Security and Decentralization of the Ethereum Network: The total amount of staked ETH on-chain still exceeds 35 million coins, accounting for about 20% of the supply, providing solid POS security assurance. Even though the number of validators has slightly declined recently, new institutional node operators are filling the gaps. In the future, more traditional institutions will hold and stake ETH to obtain stable returns, creating a continuous "reservoir" of funds for Ethereum.
Fee Burning Maintains ETH Deflation: The EIP-1559 fee burning mechanism maintains a deflationary attribute, which is expected to amplify ETH price elasticity, giving it characteristics similar to "digital asset inflation hedging."
It is evident that Ethereum's strong network effects (developers + users + capital network) and increasingly refined economic model form the underlying logic that continues to attract long-term investors.
2. Major Upgrades and Improvements
Fusaka Upgrade Expands Capacity and Reduces Costs: The Fusaka upgrade is regarded as the boldest scaling attempt in Ethereum's history. According to the plan, this upgrade will be activated on the mainnet on December 4. The highlight of Fusaka is the introduction of Peer Data Sampling (PeerDAS) technology, which allows each node to store only about 1/8 of the total transaction data, with the rest verified through random sampling and reconstruction, significantly reducing the storage bandwidth requirements for each node. This change is expected to increase the number of data blobs that Ethereum can accommodate per block by eight times, greatly reducing the cost of submitting transaction data for L2 Rollups. In other words, Fusaka will further expand data capacity and lower gas fees, directly benefiting Layer 2 networks and users like Arbitrum and Optimism.
Other Key Improvements: In addition to the core PeerDAS, this upgrade includes several key improvements: adjustments to the blob economic model, enhanced DoS resistance to limit extreme transactions and block sizes, and new tools for users and developers; EIP-7951 natively supports P-256 elliptic curve signatures, improving compatibility with hardware wallets and mobile devices, and optimizations for contract algorithms with CLZ instructions.
If all goes well, Fusaka may become another milestone in Ethereum's journey toward its vision of a global settlement layer, following the 2022 merge and the 2023 Shanghai upgrade, laying the technical foundation for the next growth cycle.
3. New Application Trends and Value Consensus
Enhancement of On-Chain Practical Value: With improvements in Ethereum's performance and reduced fees, some application areas that were once promising but struggled to scale due to cost issues are expected to regain vitality. For example, platforms requiring high-frequency small transactions, such as blockchain games, social networks, and supply chain finance, will be more willing to choose the upgraded Ethereum or its L2 as the underlying architecture.
Continuous Innovation in DeFi: Represented by Sky (formerly MakerDAO), DeFi protocols are actively introducing compliant assets: through sub-projects like Spark, Grove, and Keel, expanding into areas such as stablecoin loans, government bond investments, and inter-protocol settlements. The leading DEX Uniswap recently activated a fee switch through community voting, charging a 0.15% protocol fee on certain pools to accumulate treasury funds. This marks the beginning of DeFi protocols exploring sustainable profit models, empowering governance tokens, and indirectly revitalizing the Ethereum network. Additionally, Aave plans to launch version V4, introducing cross-chain functionality and more refined risk management. Once the market environment improves, the more powerful and better risk-controlled DeFi 2.0 is expected to attract a new wave of returning users.
Increased Recognition and Gradual Policy Clarity: The approval of U.S. ETFs, the opening of retail trading in places like Hong Kong, and strong demand for stablecoins in emerging markets all present growth opportunities for Ethereum. Especially in high-inflation countries (such as Argentina and Turkey), stablecoins and payment applications on the Ethereum network are becoming important tools for residents to combat inflation and facilitate cross-border remittances, reflecting real-world utility and subtly promoting a global value consensus for ETH.
In summary, despite short-term fluctuations, Ethereum's long-term value support remains intact, and its core position in the global blockchain landscape has not been shaken. These positive factors may not immediately reverse the market trend, but they are like seeds buried under snow, which may quickly sprout and grow once the spring breeze blows.
# Outlook and Conclusion
Based on the above analysis, we make the following judgments and outlooks for Ethereum's future trajectory:
Short-term (by the end of this year): Ethereum is likely to maintain a weak oscillating tone, showing signs of bottoming out within a range, but a significant rebound is unlikely. The Fusaka upgrade itself is a favorable factor that was anticipated, and the market has largely digested it, so it is unlikely to reverse the trend solely based on upgrade news. However, considering that ETH prices have fallen more than 30% from their highs, there is technical overselling, and the pressure for short sellers to take profits is also increasing, leaving relatively limited space for further declines before the end of the year. If no new major negative macro factors emerge (such as an unexpected interest rate hike), investor confidence is expected to recover slightly, and ETH may slowly rise above $3,500 for consolidation before the end of the year. It should be noted that as the year-end approaches, liquidity may tighten, and the height of any rebound lacking volume support may be limited, with the $3,500 level being an important resistance.
Medium-term (2024 throughout to the first half of 2025): It is expected that in the first half of 2024, Ethereum will undergo a bottoming and accumulation phase, with a gradual strengthening anticipated in the second half of the year. Specifically, in the first quarter of next year, ETH may continue to oscillate, and factors such as tax selling pressure and institutional earnings report season adjustments may also disrupt the market in January. However, around the middle of the year, the situation may turn: if inflation decreases and drives the Federal Reserve to cut interest rates, the marginal improvement in the global liquidity environment will benefit risk assets, including ETH, leading to a rebound. At that time, combined with a warming risk appetite ahead of the U.S. midterm elections, ETH may have the opportunity to start a new upward trend, rising to the $4,500-$5,000 range.
Long-term (end of 2025 and beyond): Looking further ahead, Ethereum is still expected to reach new highs in the next complete bull market cycle, solidifying its position as the "global value settlement layer." From the second half of 2025 to 2026, if the macro environment becomes more accommodative alongside the large-scale application of blockchain, ETH prices have the potential to move towards the $6,000-$8,000 range. This judgment is based on the following logic: First, after the Fusaka upgrade, Ethereum's continuous upgrades, such as Verkle trees, PBS proposals, and full sharding, will continuously improve performance and reduce costs, with technological dividends attracting a massive influx of new applications and users, providing solid support for value enhancement. Second, Ethereum's network effects are accelerating in a snowball effect, where more users attract more developers, leading to more assets and applications, creating a virtuous cycle. In the long run, Ethereum is highly likely to become the foundational network supporting trillions of dollars in economic activity, at which point the demand for ETH (for gas payments, collateral, and value storage) will far exceed current expectations. Additionally, the property of ETH as a productive asset (which can be staked for returns) is uniquely attractive to institutions. Once the institutional environment matures, large pension funds and sovereign funds allocating ETH may become a trend, similar to current allocations in real estate and equities. This will bring in a new wave of massive incremental capital, pushing ETH towards a higher value center.
Conclusion: As an important cornerstone of the crypto world, Ethereum has experienced several rounds of bull and bear cycles, each time being reborn amidst skepticism. The interplay of positive and negative factors will eventually become clear, and time will favor technology and value. After completing self-renewal and weathering market trials, a stronger Ethereum may once again stand at the center of the stage in the coming years, continuing to write a new glorious chapter.
About Us
Hotcoin Research, as the core research institution of Hotcoin Exchange, is dedicated to transforming professional analysis into your practical tools. Through our "Weekly Insights" and "In-Depth Reports," we analyze market trends for you; leveraging our exclusive column "Hotcoin Selection" (AI + expert dual screening), we help you identify potential assets and reduce trial-and-error costs. Each week, our researchers also engage with you through live broadcasts, interpreting hot topics and predicting trends. We believe that warm companionship and professional guidance can help more investors navigate cycles and seize value opportunities in Web3.
Risk Warning
The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile, and investment carries risks. We strongly recommend that investors conduct investments based on a full understanding of these risks and within a strict risk management framework to ensure the safety of their funds.
Website: https://lite.hotcoingex.cc/r/Hotcoinresearch
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




