Written by: Lacie Zhang, Bitget Wallet Researcher
1. Introduction: From the Hot Debate on x402 to the Emergence of ERC-8004
Recently, the x402 protocol, designed for automatic micropayments between AI agents, has become a market hotspot, sparking ongoing discussions about its early potential. However, beneath the spotlight of x402, a more foundational standard—ERC-8004—is quietly entering the view of keen observers.
A new question arises: since x402 is already focused on solving payment issues, what is the positioning of ERC-8004? Are they in competition with each other?
The answer seems to be negative. They are more like a pair of intricately designed, complementary components in the commercial landscape of AI agents.

Source: X post by Davide Crapis, AI lead at the Ethereum Foundation
A noteworthy detail is that Erik Reppel, the creator of x402 from Coinbase, is also one of the final signatories of the ERC-8004 protocol. Alongside him are core representatives from MetaMask, Google, and the Ethereum Foundation. This heavyweight lineup and the high degree of personnel overlap strongly suggest that the two are not in competition but are collaboratively building a grander blueprint.
The logic of this blueprint is quite clear: if the emergence of x402 validates the immense demand for AI agent payments, then ERC-8004 represents another foundational core element necessary for constructing this vast machine economy. It precisely targets the core problem that x402 cannot solve alone—where does trust come from in an economy of autonomous AI agents? The Bitget Wallet Research Institute may help you find the answer in this article.
2. The "Trust" Issue in Agent Collaboration: A Dilemma Unsolvable by x402 Alone
In the commercial collaboration of AI agents, payment (the issue solved by x402) is merely the last step of a closed loop. A more fundamental question precedes it: how can one AI agent be sure that another AI agent it employs is trustworthy? In other words, how can agents prove their ability to complete the tasks they are assigned?
To answer this question, we need to explore the foundational framework of agent commerce. According to the theory supported by Davide Crapis from the Ethereum Foundation, a decentralized AI agent commercial system must rely on three pillars to operate stably: Discovery, Communication, and Computation.
Three Pillars of the Agent Commercial Ecosystem
| Component | Core Function | Technical Implementation | Role and Description | |--------------------|----------------------------------------|--------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| | Discovery Layer | Agent Discovery | ERC-8004 | The first step in building trust and collaboration. ERC-8004 enables AI agents to locate and identify each other through its Ethereum-based identity registry. | | Communication Layer | Agent Communication | x402, A2A, AP2 | Facilitates interaction between agents. x402 is an open standard for on-chain payments, operating alongside protocols like Google’s A2A and AP2 to handle payments and data exchange between agents. | | Computation Layer | Verifiable Computation | EigenCompute, EigenAI | Ensures that all agents' reasoning and actions can be cryptographically verified, with the verification results recorded on the data availability layer to achieve trustworthy computation. |
Source: X tweet forwarded by Davide Crapis
From the table above, it can be seen that the x402 protocol primarily addresses the payment standard issue within the communication layer, but it cannot answer the critical questions of identity verification and reputation assessment. Before making payments, AI agents first need to be securely "discovered" to establish trust and collaboration—ERC-8004 is precisely the solution to this problem, building a decentralized trust layer.
ERC-8004 was jointly launched by the Ethereum Foundation's dAI team and Consensys, in collaboration with institutions like MetaMask, Google, and Coinbase, aiming to become the on-chain "trust layer" for AI agents. It is a decentralized business registration and recording system—providing each AI agent with a verifiable identity, complete historical performance, and capability proof. All information will be immutably recorded on-chain and made publicly accessible to all participants.
Source: ERC-8004 official website
3. ERC-8004: The Decentralized Trust Layer for Agents
ERC-8004 is positioned as the underlying infrastructure of the agent economy, with its core value being: through blockchain technology, it addresses the fundamental issue of the lack of trustworthy identities among AI agents, freeing them from the constraints of traditional centralized platforms and establishing verifiable, cross-platform collaborative relationships.
The operation of this mechanism begins with ecosystem contributors inputting trust data: AI developers are responsible for registering the unique identities of agents; application developers continuously provide behavioral feedback to accumulate reputation data; and verification services act as independent auditors, providing trustworthy on-chain verification of agents' operational results.
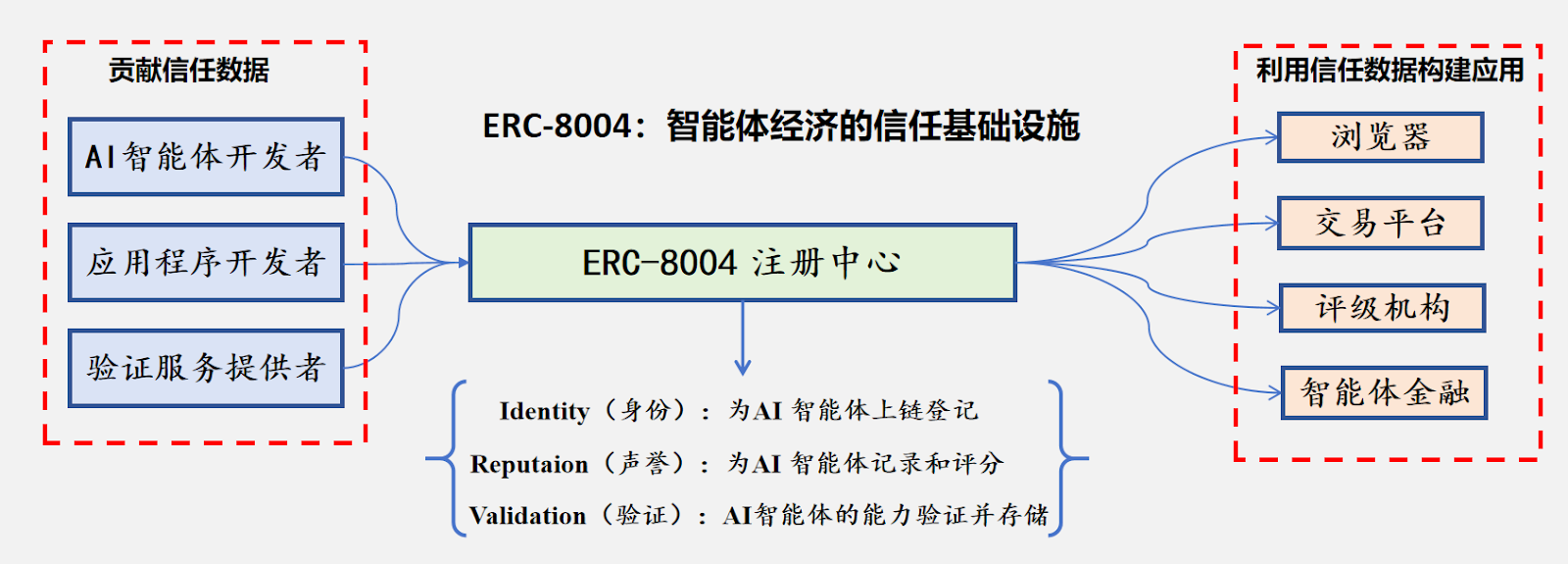
Source: Compiled by Bitget Wallet
This information collectively feeds into the ERC-8004 registration center, which consolidates the three core functions of the protocol:
- Identity Registry: It assigns a unique digital identity to each AI agent through the ERC-721 NFT protocol. This design not only makes identities transferable but also allows them to link to standardized "Agent Cards," which detail the agent's name, capabilities, and metadata, ultimately enabling permissionless discovery across platforms.
- Reputation Registry: This mechanism acts as a decentralized review system based on identity registration. Clients or other agents can submit structured feedback. The key design is that these evaluations can be linked to x402 payment proofs, ensuring that only genuine transaction participants can provide assessments, effectively reducing fraud and ensuring the transparency of all reputation data.
- Validation Registry: It provides final assurance for high-risk or high-value transactions. Agents can request trusted verification from third parties, such as TEE oracles, staked inference, or zero-knowledge machine learning proofs. These verification methods can provide cryptographic proof for specific model executions and outputs, thereby establishing a verifiable accountability mechanism similar to traditional market professional certifications.
Relying on the trustworthy data foundation provided by ERC-8004, a new downstream application ecosystem can thrive, including explorers for agent discovery and queries, marketplaces allowing agents to trade freely based on reputation, and professional rating agencies, even giving rise to innovative services like InfoFi and AgentFi. These advanced applications are all built on the trustworthy identities and verification records of agents, marking the formal establishment of a permissionless, efficiently collaborative agent service ecosystem.
4. Collaborative Operation: The Complete Process of an Agent Transaction
So, how do these components work together in practice? The complete lifecycle of a decentralized AI agent transaction can clearly illustrate this process.
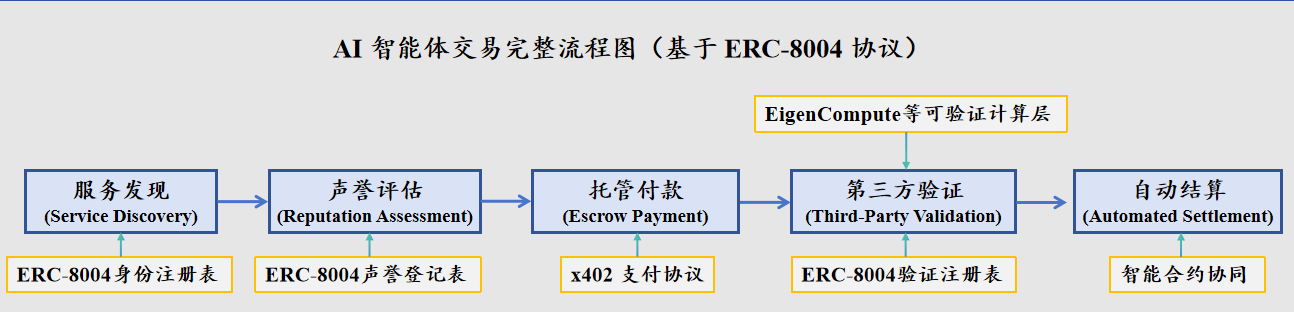
Source: Compiled by Bitget Wallet
- First, the demand-side Agent uses the ERC-8004 identity and reputation registry to discover and evaluate services, querying and filtering for service agents with specific capabilities and good credit.
- After both parties reach an agreement, the demand-side locks the required payment in a smart contract (i.e., financial assurance) through the x402 payment protocol.
- Subsequently, the service agent begins executing the task and accepts third-party verification, with the work results running on a verifiable computation layer like EigenCompute to generate cryptographic proof, which is then recorded by an independent third-party verification agent in the ERC-8004 validation registry.
- Finally, the automatic settlement phase begins, where the x402 smart contract automatically detects the trusted signature in the ERC-8004 validation registry, and once the task is confirmed to be qualified, the funds are automatically released to the service agent.
In this closed-loop process, ERC-8004 is responsible for access and acceptance, x402 handles payments, and verifiable computation ensures the process, with none of the three being dispensable. This also indicates that, unlike the early focus on payment tokens in x402, the ecosystem of ERC-8004 (as shown in the figure below) will be distributed across multiple levels, including infrastructure, middleware, and applications.

Source: BlockFlow
5. Conclusion: The Order and Future of the Machine Economy
It must be acknowledged that ERC-8004 is still in the early stages of promotion and implementation—the cold start of related products and whether its grand vision of "machine economy identity verification" can be realized remains to be observed in the market. Additionally, the costs and specific implementation paths of third-party verification, as well as its interoperability with protocols like x402, are significant variables that need to be addressed in the future.
However, what can be confirmed is that the emergence of protocols like ERC-8004 marks a transition of the machine economy from "barbaric growth" to "establishing order." It provides a cross-platform identity and credit system for autonomously operating AI agents for the first time.
If x402 is the "currency" of the machine economy, then ERC-8004 provides the "passport" and "credit report," marking the beginning of a permissionless, efficiently collaborative, and trustworthy agent service ecosystem.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



