Original Title: Convergence and Divergence: US, China, CeDeFi
Original Author: @0xtony0x
Original Translation: zhouzhou, BlockBeats
Editor's Note: This article explores the changes in the global financial system, particularly the integration of cryptocurrency with traditional financial systems. As geopolitical tensions rise and the dominance of the dollar declines, blockchain technology has emerged as a neutral financial infrastructure, promoting the development of crypto assets, stablecoins, and tokenized RWA. Through the convergence of CeFi, DeFi, and TradFi, capital flows and interest rate markets are gradually converging, attracting more institutions into the blockchain world.
The following is the original content (reorganized for better readability):
US-China Divergence and De-dollarization
Recently, the dramatic fluctuations in the foreign exchange market have highlighted the intensifying global macroeconomic tensions and significant changes in the financial landscape. The USD/JPY has surged to the 145 mark, primarily driven by the Bank of Japan's continued dovish stance—maintaining interest rates unchanged without signaling any rate hikes—coupled with the rapid unwinding of long positions in the yen. The interest rate differential between the US and Japan remains substantial, making the dollar more attractive as the Federal Reserve maintains relatively high rates while Japan continues its loose monetary policy.
Meanwhile, the New Taiwan Dollar (TWD) surged over 8% against the dollar in just two days, a rare "19 sigma" event. This sudden movement stemmed from local Taiwanese institutions quickly adjusting their positions and reducing exposure to the dollar, highlighting the market's growing concerns over geopolitical risks and vividly reflecting the direct impact of escalating US-China tensions on the global foreign exchange market.
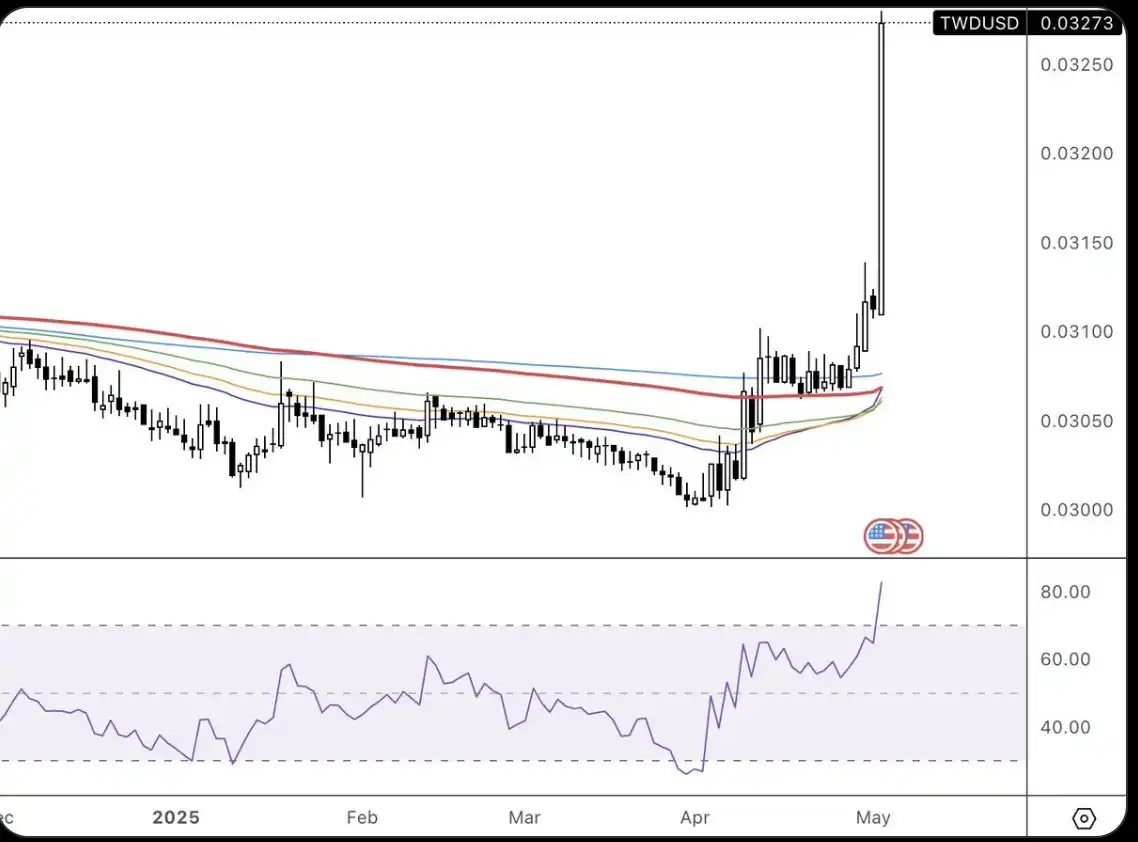
TSD/USD Price Chart
Earlier this month, geopolitical tensions between the US and China escalated sharply. President Trump raised tariffs on Chinese imports to an unprecedented 145%, prompting China to retaliate with a 125% tariff on US products, further deepening the economic rift between the two sides. This escalation echoes the classic "Thucydides Trap" theory, which posits that conflict is often unavoidable when a rising power challenges an existing hegemon.
However, this issue goes beyond trade barriers; it represents a systematic decoupling between the two major global economies, with the resulting "second-order effects" creating a chain reaction in global liquidity and the dollar's dominance.
For a long time, the dollar's dominance in global trade and finance has relied on deep trust in the US system—this trust is based on its political stability, predictability in foreign policy, and openness to capital flows. As Bipan Rai, Managing Director at BMO Global Asset Management, pointed out: "There are clear signs that this trust is eroding… the trend in global asset allocation is gradually shifting away from the dollar."
In fact, the foundation of dollar hegemony is quietly loosening due to geopolitical turmoil and the increasingly unpredictable foreign and economic policies of the US. Notably, despite President Trump's stern warnings to other countries against abandoning dollar-denominated trade, or face economic penalties, the dollar experienced significant volatility during his term—within the first 100 days of his presidency, the dollar saw its most severe depreciation since the Nixon era. This symbolic moment underscores a broader, accelerating trend: multiple countries around the world are actively exploring alternative paths to de-dollarization, marking a gradual shift in the global financial system away from reliance on the dollar.
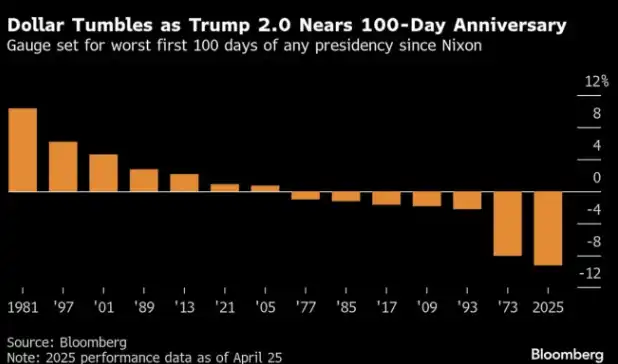
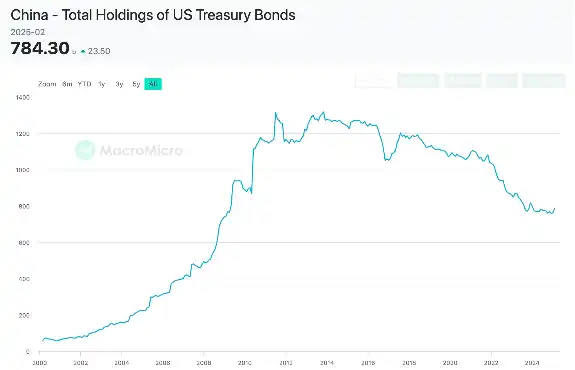
For decades, China's trade surplus in dollars has continuously flowed back into US Treasury bonds and financial markets, supporting dollar hegemony since the collapse of the Bretton Woods system. However, with the sharp deterioration of strategic mutual trust between the US and China in recent years, this long-standing capital cycle is facing unprecedented disruption. As one of the largest overseas holders of US assets, China has significantly reduced its exposure to US Treasuries, with its holdings dropping to approximately $760.8 billion by early 2025, nearly a 40% decline from the peak level in 2013.
This shift reflects China's broader strategic response to the increasing risks of US economic sanctions—after all, the US has previously frozen foreign assets multiple times, with the most notable example being the freezing of approximately $350 billion in Russian central bank reserves in 2022.
As a result, Chinese policymakers and influential economists are increasingly advocating for the diversification of China's foreign exchange reserves, gradually reducing reliance on dollar assets, fearing that these assets are evolving into potential geopolitical liabilities. This strategic adjustment includes adding approximately 144 tons of gold reserves in 2023, promoting the internationalization of the renminbi, and exploring digital currency alternatives.
This systemic "de-dollarization" is tightening global dollar liquidity, raising international financing costs, and posing a severe challenge to markets that have long relied on China to recycle its surplus dollars back into the Western financial system.
Additionally, China is actively advocating for the establishment of a multipolar financial order, encouraging developing countries to use their own currencies or the renminbi for trade settlements instead of relying on the dollar. The core of this strategy is the Cross-Border Interbank Payment System (CIPS), which is explicitly designed as a comprehensive alternative to the existing SWIFT and CHIPS systems globally, covering both information transmission (SWIFT functions) and settlement (CHIPS functions).
Since its launch in 2015, CIPS has aimed to simplify international transactions denominated in renminbi, thereby reducing global dependence on dollar-dominated financial infrastructure. Its increasingly widespread acceptance marks a systematic shift in the global financial system towards multipolarity: by the end of 2024, CIPS had 170 direct institutional members from 119 countries and regions, along with 1,497 indirect members.
This steady growth peaked on April 16, 2025—according to unverified reports, CIPS's daily transaction volume surpassed SWIFT for the first time, processing a record 12.8 trillion renminbi (approximately $1.76 trillion). Although this milestone has yet to receive official confirmation, it still highlights the transformative potential of China's financial infrastructure in reshaping the global monetary landscape—from a dollar-centric system to a decentralized, multipolar system centered around the renminbi.
As Keyu Jin, an economist at the London School of Economics, stated at a forum hosted by the Milken Institute: "In the past decade, trade denominated in renminbi has grown from 0% to 30%, and now half of China's capital flows are settled in renminbi, a proportion far higher than in the past."

Liquidity Must Flow: The Convergence of CeDeFi
However, as geopolitical boundaries become increasingly rigid and traditional financial channels narrow, a parallel phenomenon is quietly occurring: global liquidity is gradually converging into a borderless decentralized financial network. The liquidity integration between CeFi (Centralized Finance), DeFi (Decentralized Finance), and TradFi (Traditional Finance) marks a reconstruction of capital flow methods and is pushing blockchain-based networks towards a new core financial infrastructure position that reshapes the global economy.
Specifically, the trend of CeDeFi (the integration of centralized and decentralized finance) is being driven by multiple "gravitational" forces:
- Stablecoins as a payment method bring B2B and B2C liquidity on-chain
- CeFi institutions simultaneously offer crypto and traditional financial products
- DeFi protocols bridge on-chain and off-chain yields, creating new interest rate arbitrage paths
Stablecoins as Payment Infrastructure
Payments have always been the "holy grail" in the crypto space. Tether, as the de facto shadow bank of offshore dollars, has become the most profitable financial institution when calculated by average profit per employee. Recent geopolitical turmoil will only further drive demand for stablecoins, as global capital increasingly seeks to gain dollar exposure through an uncensored, borderless platform.
Whether it’s Argentine savers using USDC to combat inflation or Chinese merchants settling trades with Tether to bypass the banking system, the underlying motivation is the same: to obtain reliable value without relying on traditional financial systems.
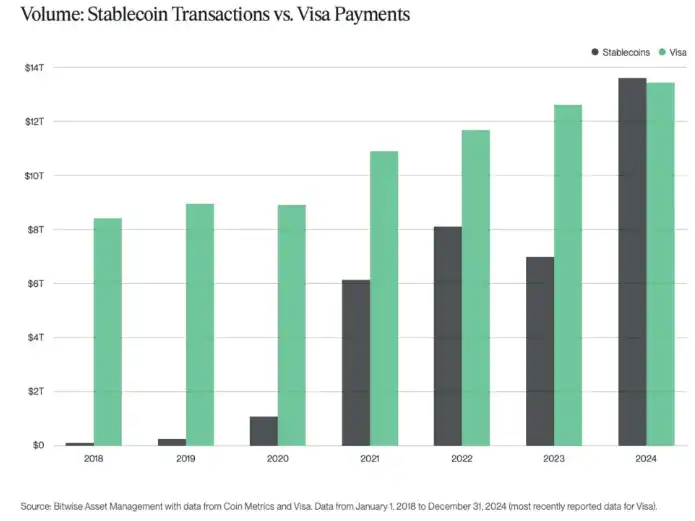
In an era of heightened geopolitical tensions and financial uncertainty, this demand for "transaction autonomy" is highly appealing. By 2024, the trading volume of stablecoins has already surpassed that of Visa. Ultimately, digital dollars (stablecoins) operating on crypto networks are reconstructing the offshore dollar system of the 20th century—providing dollar liquidity to markets concerned about US hegemony while bypassing the US banking system.
CeFi Institutions Offering Both Traditional Financial and Crypto Products
In addition to allowing global liquidity to continue settling in dollars, we also see CeFi platforms expanding vertically into the crypto space, and vice versa:
- Kraken acquired Ninja Trading to expand its traditional financial asset product line, ultimately achieving cross-asset margin trading between traditional finance and crypto trading.
- In China, major brokerages like Tiger Brokers and Futu (often referred to as the "Chinese version of Robinhood") have begun accepting cryptocurrencies like USDT, ETH, and BTC as deposit methods.
- Robinhood has positioned its crypto business as a core growth focus, planning to launch products such as tokenized stocks and stablecoins.
With the regulatory clarity brought about by new market structure legislation, the horizontal integration between traditional finance and crypto products will only become more important.
DeFi Protocols Bridging Crypto and Traditional Financial Yields
Meanwhile, we also see DeFi protocols leveraging the high yields native to crypto to attract traditional financial or off-chain capital, while also enabling TradFi institutions to access global on-chain liquidity for executing their off-chain strategies.
For example, the projects we invest in, BounceBit (@bouncebit) and Ethena (@ethenalabs), provide "basis trading yields" to traditional financial institutions. Due to the programmability of on-chain dollars, they can package these basis trading products into on-chain "synthetic dollars," directly targeting the $13 trillion fixed income market. Such products are particularly attractive to traditional financial institutions because basis yields are negatively correlated with government bond yields. Therefore, they effectively open new paths for interest rate arbitrage, further integrating capital flows and interest rate markets among CeFi, DeFi, and TradFi.
Additionally, Cap Lab (@capmoney_) allows TradFi institutions to borrow from on-chain liquidity pools to execute off-chain trading strategies, thereby providing retail investors with unprecedented high-frequency trading (HFT) yield channels. It also effectively extends the economic security scope of EigenLayer from on-chain activities to off-chain yield generation strategies.
These developments collectively drive liquidity convergence, compressing the gap between on-chain yields, off-chain yields, and traditional risk-free rates. Ultimately, these innovative solutions become powerful arbitrage tools, aligning capital flows and interest rate dynamics across the DeFi, CeFi, and TradFi sectors.
CeDeFi Liquidity Convergence -> CeDeFi Product Offering
The convergence of CeFi, DeFi, and TradFi liquidity towards blockchain networks marks a fundamental change in the role of on-chain asset allocators—from primarily crypto-native traders to an increasing number of complex institutions seeking diversified investments that go beyond crypto-native assets and yields.
The downstream effect of this trend is the expansion of the on-chain financial product suite, particularly with the introduction of more RWA products. As more RWA products enter the on-chain space, it will attract even more institutions from around the globe to join the on-chain market, creating a self-reinforcing cycle that ultimately brings all financial participants and financial assets together on a unified global ledger.
Historically, the trajectory of cryptocurrencies has gradually incorporated higher-quality real assets, evolving from stablecoins and tokenized treasury bills (such as Franklin Templeton's Benji and Blackstone's BUIDL) to increasingly complex financial instruments, such as Apollo's recent tokenized private credit fund, with the potential to further expand into tokenized stocks.
The declining interest of marginal buyers in speculative crypto-native assets highlights a significant market gap and provides opportunities for institutional-grade tokenized RWA. Against the backdrop of increasing global geopolitical uncertainty—such as the economic decoupling tensions between the US and China—blockchain technology is gradually becoming a credible neutral financial infrastructure.
Ultimately, all financial activities, from trading crypto-native altcoins to payments, tokenized treasury bills, and stocks, will converge on this verifiable and borderless global financial ledger, fundamentally reshaping the global economic landscape.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




