Core Points
– Merged upgrade to enhance operational efficiency: Pectra synchronously updates the execution layer (Prague) and the consensus layer (Electra), making the upgrade process smoother and reducing synchronization issues for developers and validators.
– Key feature updates: Account abstraction (EIP-7702) allows for more flexible transactions, increased staking limits (EIP-7251) optimizes the staking mechanism, and enhanced data availability (EIP-7742) provides better support for Layer-2 scaling.
– Potential challenges: This may lead to validator centralization, security risks associated with account abstraction, and issues in testnets (such as chain splits and empty block phenomena).
– Ecological impact: Institutional staking may significantly increase, DeFi and NFT platforms can utilize fee sponsorship mechanisms, and Layer-2 networks can reduce costs and improve transaction speeds through more efficient data processing, further promoting the development of Ethereum.

Ethereum will welcome the Pectra upgrade in mid-March 2025, marking a significant milestone in its development history. Unlike previous upgrades, Pectra adopts a dual-layer upgrade model, synchronously updating the execution layer (Prague) and the consensus layer (Electra), and further enhancing scalability, security, and user experience through multiple Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs).
Previously, Ethereum typically upgraded the execution layer and consensus layer separately to reduce technical complexity and upgrade risks. This time, Pectra chooses a merged upgrade, allowing developers, validators, institutions, and regular users to adapt to new features more smoothly while minimizing synchronization issues and disruptions caused by the upgrade.
However, despite Pectra's successful deployment on multiple testnets, it has also exposed some technical challenges, leading the community to remain cautious about potential risks while being hopeful.
This article will take you through the history of Ethereum's upgrades, analyze the core features of Pectra, and explore its potential impacts and challenges for the entire ecosystem.
Table of Contents
Review of Ethereum's Upgrade History
- – Important milestones: From Frontier to The Merge
Why Conduct a Dual-Layer Upgrade?
– Execution Layer (Prague)
– Consensus Layer (Electra)
– Advantages of Merged Upgrades
Core Features of the Pectra Upgrade
– Account Abstraction (EIP-7702)
– Increased Validator Staking Limits (EIP-7251)
– Enhanced Data Availability (EIP-7742)
– On-chain Processing of Validator Deposits (EIP-6110)
– Smart Contract Controlled Staking Withdrawals (EIP-7002)
Recent Progress and Testing Status
– Holesky Testnet Issues
– Findings from Sepolia Testnet
Impact on the Ethereum Ecosystem
– Institutional Adoption and Staking Growth
– Impact on DeFi and NFT Markets
– Changes in Layer-2 Scaling Solutions
Potential Risks and Challenges
– Concerns about Validator Centralization
– Security and Technical Complexity of Account Abstraction
– Potential Delays in Upgrade Deployment
– Challenges for Developers Adapting to New Changes
Review of Ethereum's Upgrade History
Since the official launch of Ethereum in 2015, it has undergone several major upgrades, each aimed at addressing system bottlenecks or introducing new features:
– Frontier (2015) – Laid the foundation for Ethereum's infrastructure, supporting smart contract execution.
– Homestead (2016) – Improved network stability and optimized development tools.
– Byzantium (2017) & Constantinople (2019) – Enhanced scalability and security, optimized the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
– Istanbul (2019) – Reduced gas fees and improved network operational efficiency.
– Beacon Chain (2020) – Introduced Proof of Stake (PoS), allowing validators to deposit staking funds.
– The Merge (2022) – Ethereum officially transitioned to a PoS consensus mechanism, replacing PoW.
– Shapella Upgrade (2023) – Opened up the ability for validators to withdraw staked ETH.
– Dencun Upgrade (2024) – Introduced Proto-Danksharding (EIP-4844), reducing Layer-2 operational costs.
Each upgrade builds upon the previous one to further enhance scalability, security, and operational efficiency. The upcoming Pectra upgrade (March 2025) will continue this trend by merging the execution layer (Prague) and the consensus layer (Electra), simplifying network operations and further strengthening Ethereum's infrastructure.
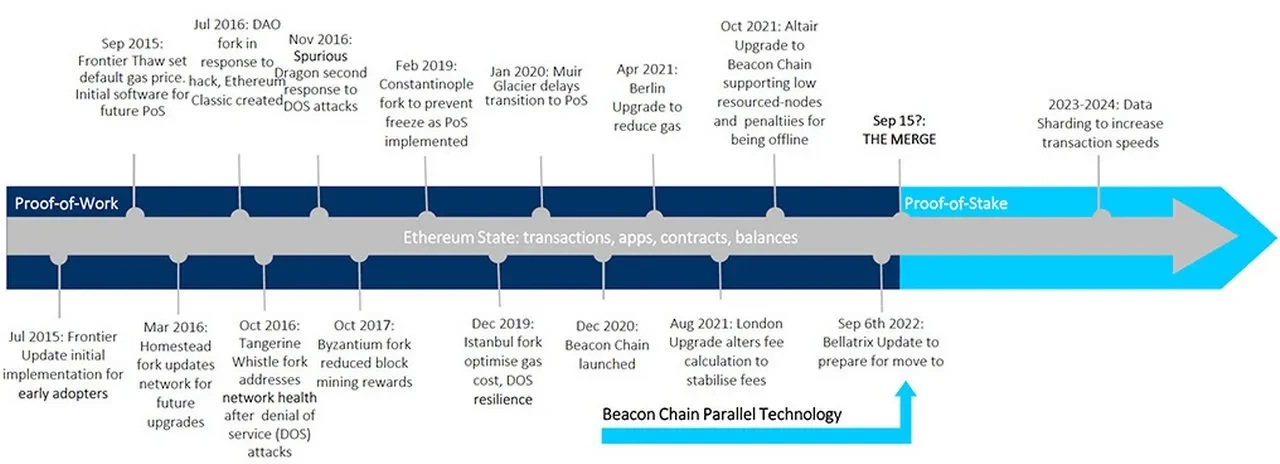
Image Credit: Deutsche Bank
Why Conduct a Dual-Layer Upgrade?
The architecture of Ethereum consists of two key layers:
– Execution Layer (Prague) – Responsible for processing transactions, running smart contracts, and executing state changes.
– Consensus Layer (Electra) – Manages validators and block production through the PoS (Proof of Stake) mechanism, ensuring the security of the blockchain.
In the past, these two layers were typically upgraded separately to reduce technical complexity and mitigate potential risks. However, Pectra adopts a merged upgrade approach, bringing the following benefits:
– Simplified upgrade process – A single hard fork allows node operators and validators to adapt more easily to new changes.
– Reduced risk – Unified adjustments to both layers avoid synchronization issues and version compatibility problems.
– Overall optimization – Many EIPs (Ethereum Improvement Proposals) affect both the execution layer and the consensus layer, and a merged upgrade allows for more efficient implementation of these improvements.
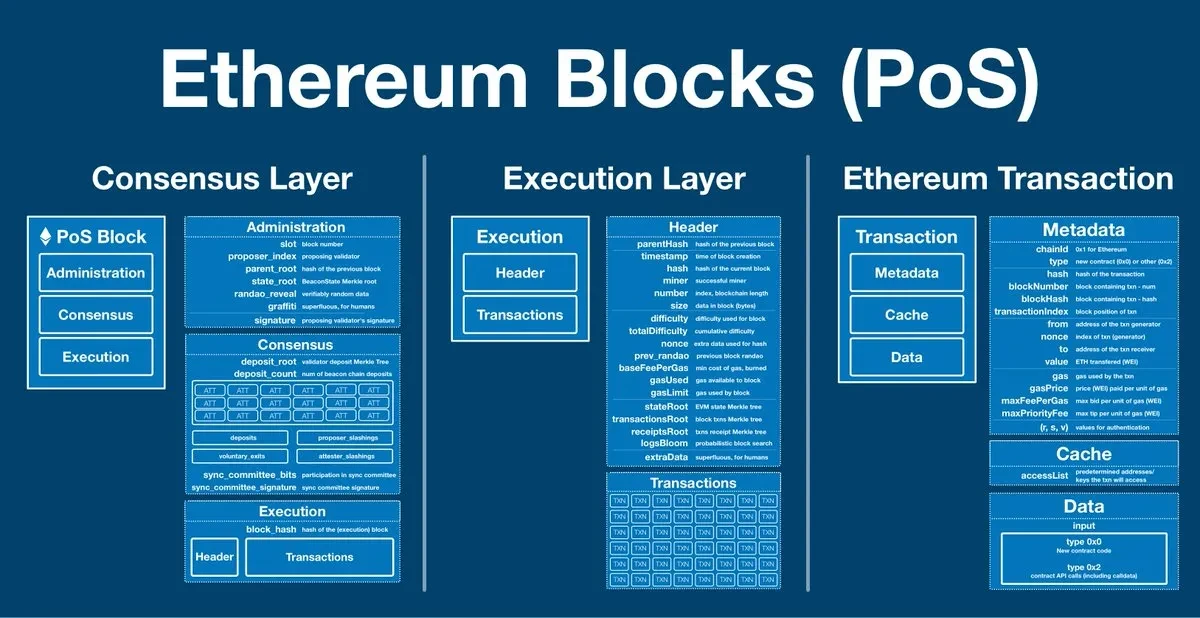
Image Credit: Rex Kirshner
Core Features of the Pectra Upgrade

Image Credit: Benjamin Thalman
The Pectra upgrade introduces several Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) aimed at enhancing user experience, optimizing development tools, improving staking efficiency, and enhancing data availability. Here are the most critical proposals:
1. Account Abstraction (EIP-7702)
EIP-7702 narrows the gap between External Owned Accounts (EOA) and smart contracts, allowing accounts to have more flexible functionalities:
– Fee sponsorship – Allows third parties to pay transaction fees on behalf of users.
– Transaction batching – Users can execute multiple transactions at once, reducing gas costs.
– Multi-factor authentication – Supports multi-signature, biometric, hardware keys, and other methods.
– Fund management and recovery mechanisms – Allows for daily spending limits, time-locked transactions, social recovery, and other features.
Use cases:
– Game dApps can pay gas fees for users, lowering the barrier to entry.
– Enterprises can adopt customized authentication methods to enhance account security.
– DeFi platforms can batch execute transactions to reduce gas fees.
Potential risks:
– Increases technical implementation complexity, requiring developers more adaptation time.
– The expanded account logic may introduce new security risks.

Image Credit: Emmanuel Abedide
2. Increased Validator Staking Limits (EIP-7251)
EIP-7251 raises the maximum effective staking amount for a single validator from 32 ETH to 2,048 ETH, with the main goals being:
– Reduce the number of validators – Allow larger-scale stakers to lower hardware and operational costs.
– Improve operational efficiency – Optimize block proposals and network operations by reducing the number of small nodes.
– Adapt to institutional staking needs – Allow institutional investors to manage fewer validator nodes while maintaining large stakes.
Impact on decentralization: – May lead to the concentration of validation power among large stakers, weakening decentralization.
- – However, supporters argue that reducing the number of validators can lower operational costs and improve network efficiency.
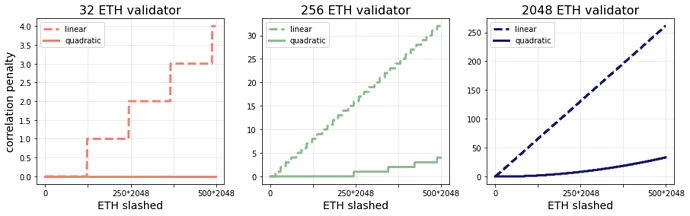
Image Credit: Mike Neuder
3. Enhanced Data Availability (EIP-7742)
EIP-7742 aims to improve data availability, particularly for Layer-2 solutions (such as Rollups). This proposal allows for dynamic adjustments to blob storage capacity, optimizing data storage based on network demand:
– Optimize Rollup scalability
– Ensure Layer-2 solutions have sufficient data storage space without excessively bloating the blockchain.
– Improve resource utilization
– Reduce unnecessary data storage during low traffic periods, lowering operational costs.
This proposal is crucial for Layer-2 solutions like Arbitrum, Optimism, and zkSync, helping them improve efficiency and reduce transaction costs.
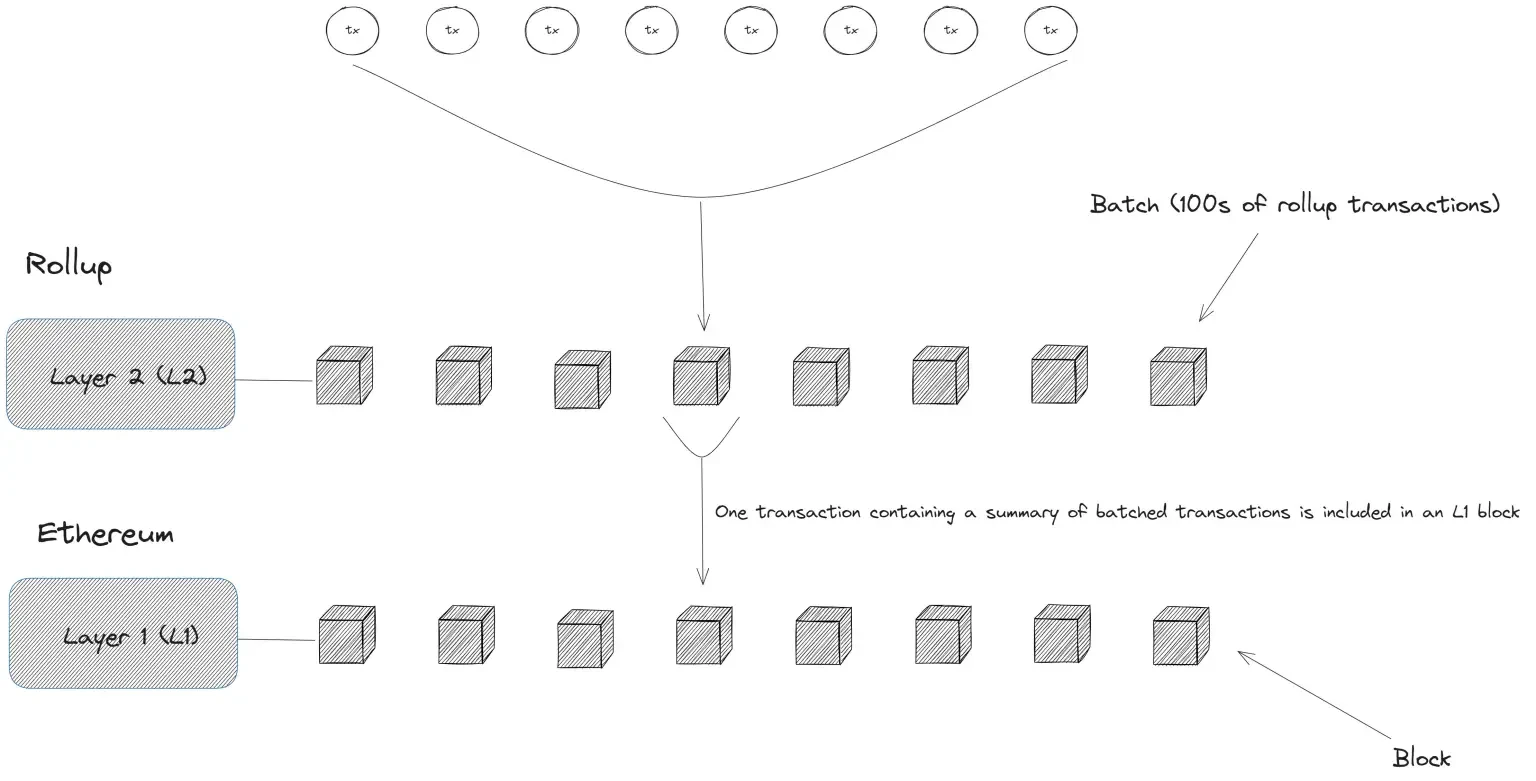
Image Credit: Ethereum 2077
4. On-chain Processing of Validator Deposits (EIP-6110)
EIP-6110 allows validator deposit transactions to be processed directly on the consensus layer, eliminating reliance on the execution layer:
– Reduce security risks
– Eliminate deposit queue delays, reducing potential attack risks.
– Accelerate the speed of validator onboarding
– Simplify the deposit process, improving the overall efficiency of the PoS mechanism.
This improvement reduces the complexity of the PoS mechanism, allowing Ethereum validators to participate in the network more quickly.
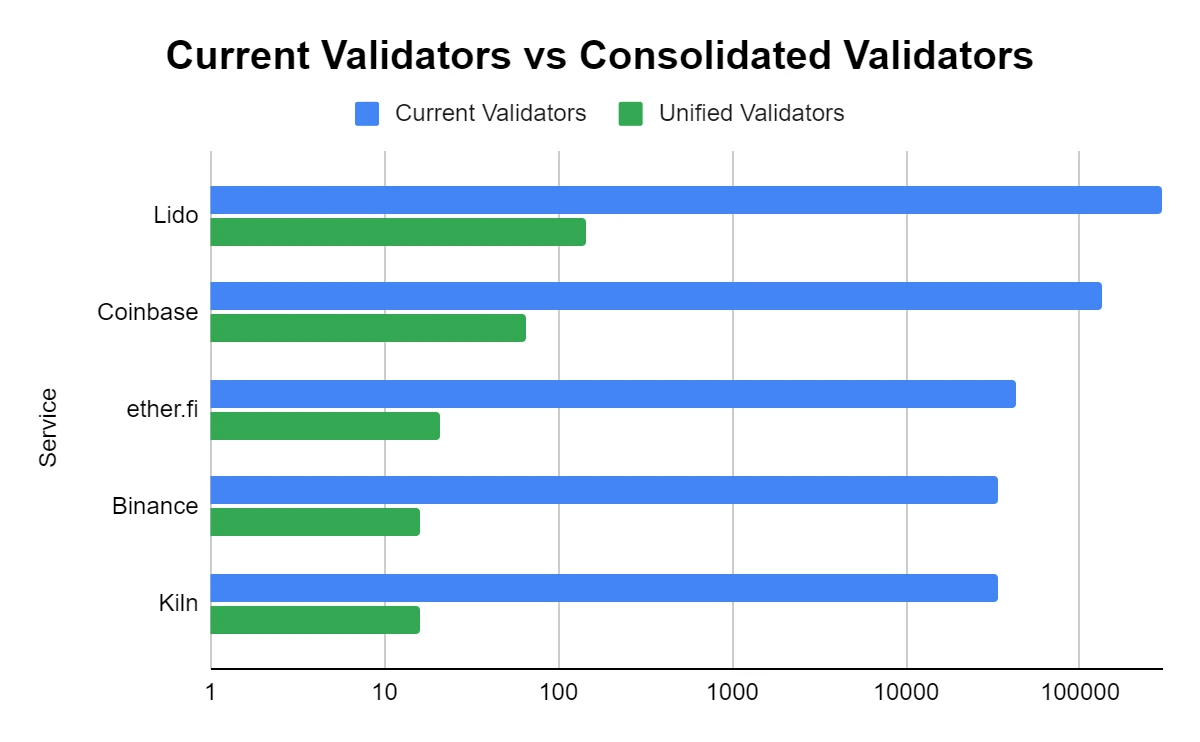
Image Credit: SafeStake
5. Smart Contract Controlled Staking Withdrawals (EIP-7002)
EIP-7002 allows smart contracts to proactively initiate validator withdrawals, bringing the following advantages to staking management:
– Staking automation – Contracts can automatically reinvest or allocate staking rewards.
– More flexible fund management – Institutional investors and staking pools can use smart contracts to adjust fund flows more efficiently, optimizing yield strategies.
Security considerations:
- – If there are vulnerabilities in the smart contract, it could lead to large-scale fund losses, posing risks to the entire Ethereum ecosystem.
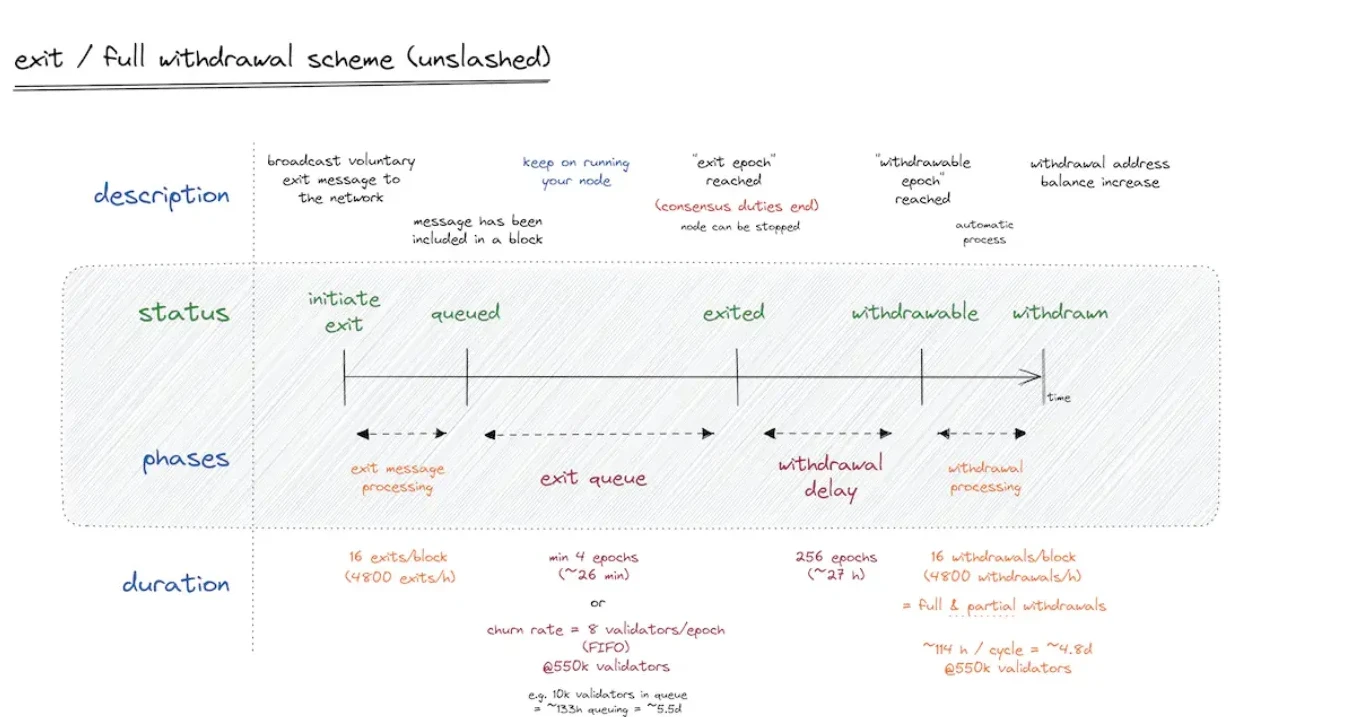
Image Credit: ladislaus.eth
Recent Progress and Testing Status
Holesky Testnet (February 24, 2025)
Holesky is one of the first testnets to implement the Pectra upgrade. However, due to validator configuration errors, a chain split occurred, affecting network performance. Although developers quickly fixed the issue, this incident exposed the technical challenges that a dual-layer upgrade may bring.
In discussions on the Ethereum Magicians forum, some community members expressed concerns that the issues in the testnet might indicate similar problems for the mainnet upgrade. If these issues are not adequately resolved, they could impact Ethereum's stability and security.
Sepolia Testnet (March 5, 2025)
In the Sepolia testnet, the Pectra upgrade initially ran smoothly, but then some blocks suddenly appeared as empty blocks, meaning there were no transactions in those blocks.
Several core developers analyzed the situation and believed this could be a bug caused by the new consensus layer logic of EIP-6110 (on-chain processing of validator deposits), which might affect transaction processing. Therefore, some developers suggested postponing the Pectra mainnet upgrade to ensure all issues are thoroughly resolved before the official deployment.
This situation is reminiscent of the Constantinople upgrade, where developers discovered a critical vulnerability before the mainnet upgrade and ultimately chose to delay the release to ensure network security and stability.
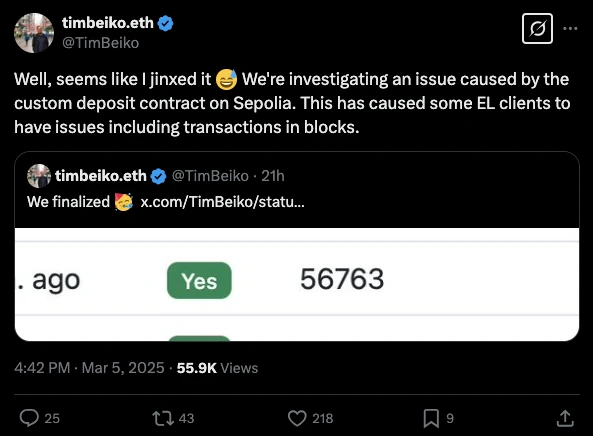
Image Credit: Ethereum Core Dev Tim Beiko X (Twitter)
Impact on the Ethereum Ecosystem
Institutional Adoption
Large financial institutions and enterprises have been closely monitoring Ethereum's transition to Proof of Stake (PoS), primarily because the PoS mechanism consumes less energy and can provide stable, predictable returns through staking.
EIP-7251 increases the maximum staking limit for a single validator to 2,048 ETH, allowing institutional investors to invest larger amounts while simplifying operational management, thereby enhancing Ethereum's appeal as an institutional-grade investment asset.
Some market analysts predict that as the Pectra upgrade goes live, institutional capital may flow significantly into the Ethereum staking market, impacting ETH's liquidity and price trends.

Image Credit: Julien Riedel
DeFi and NFT Sectors
DeFi platforms are expected to significantly enhance user experience with the help of account abstraction (EIP-7702), which is crucial for attracting mainstream users into the Web3 ecosystem. For example:
– DeFi applications can use transaction batching features to simplify user operations and reduce gas fees.
– NFT markets can implement gas fee sponsorship mechanisms, allowing new users to purchase NFTs without paying gas fees, thereby improving user conversion rates.
– Enhanced data availability makes Layer-2 solutions more suitable for large-scale NFT issuance or blockchain game dApps, reducing the previous issues of gas fee spikes due to transaction congestion.
These improvements will help Ethereum attract more Web2 users into the Web3 ecosystem, increasing the adoption rate of blockchain applications.
Image Credit: Pixelplex
Layer-2 Scaling Solutions
Layer-2 solutions like Arbitrum, Optimism, and zkSync heavily rely on Ethereum's data availability, and the dynamic blob storage adjustment mechanism of EIP-7742 brings the following advantages:
– Improved Rollup computational efficiency
– Rollups can dynamically acquire storage data based on actual needs, avoiding excessive data burden on Layer-1 chains.
– Reduced Layer-2 transaction fees
– With improved data storage efficiency, transaction costs are expected to decrease further.
– Increased transaction throughput – Applications relying on Layer-2, such as DeFi, NFT trading markets, and blockchain games, can support larger user bases and transaction volumes.
The collaborative optimization between Layer-1 (Ethereum mainnet) and Layer-2 is at the core of Ethereum scaling plans, and the Pectra upgrade is a key milestone on this development path.

Image Credit: Thirdweb
Potential Risks and Controversies
Concerns about Validator Centralization
– Increasing the staking limit may lead to individuals or institutions with strong capital further dominating the staking market, creating a trend of concentration in large staking pools, weakening the diverse validator ecosystem that Ethereum should have.
– Currently, the Ethereum PoS mechanism relies on a widely distributed set of validators to maintain network security and fairness, but if a few large stakers control too many validation nodes, it may affect the degree of decentralization.
Technical Complexity of Account Abstraction
– EIP-7702 introduces more flexible account management features, but this also raises the security threshold for smart contracts.
– If the technical implementation of account abstraction is not rigorous enough, it may introduce new attack vectors, leading to contract vulnerabilities being exploited and affecting user asset security.
– Stricter security audits and best practice guidelines are needed to ensure developers correctly implement these features and reduce potential risks.
Upgrade Delays and Deployment Risks
– Current testnets have exposed some technical issues, such as chain splits in the Holesky testnet and empty blocks in the Sepolia testnet.
– Past upgrades (such as the Constantinople upgrade) have been delayed multiple times due to security issues, so Pectra may also face delays, and developers need to ensure all problems are fully resolved before the mainnet launch.
– If the upgrade is rushed, it may lead to chain splits on the mainnet or other instability factors, affecting user confidence in Ethereum.
Developer Adaptation Challenges
– Many development tools, libraries, and best practice guidelines need to be updated to support the new features of the Pectra upgrade, which may increase technical adaptation costs for small development teams.
– Small teams may require more time to adjust to the new changes, especially those related to account abstraction and staking management, which may impact the development speed of the DeFi and DApp ecosystem.
Future Outlook
The Pectra upgrade will be an important turning point in the development of Ethereum, expected to enhance network performance and provide a more efficient and user-friendly experience. However, many unresolved issues remain, such as whether the technical failures in the testnets will delay the mainnet upgrade and how the community will balance efficiency with maintaining decentralization.
Further development of account abstraction: Future EIP proposals may deepen the concept of account abstraction, allowing transaction validation logic to be fully customized at the protocol level, further enhancing flexibility and security.
In-depth integration of Layer-2: As Rollup technology matures, the synergy between on-chain data availability (EIP-7742) and off-chain computation execution will continue to be at the core of Ethereum's scaling plans.
Innovation in staking models: After the implementation of EIP-7251, new staking financial products may emerge in the market, such as derivative staking tokens (LST) or algorithmic yield strategies, further optimizing yield management through automated withdrawals via EIP-7002.
Community forums (such as Ethereum Magicians, EthStaker Community) and the official channels of the Ethereum Foundation will remain important platforms for community discussion and collaboration. The future development direction remains highly flexible and will be driven and decided by the Ethereum community in an open-source and iterative development model.
Conclusion
The Ethereum Pectra upgrade has made significant strides in scalability, security, and usability. By integrating improvements in Prague (execution layer) and Electra (consensus layer), this upgrade makes the evolution of Ethereum more efficient, laying the foundation for future scaling and optimization.
Key EIP Proposals
– Account abstraction (EIP-7702) allows External Owned Accounts (EOA) to simulate smart contracts, enhancing transaction flexibility.
– Increased staking limits (EIP-7251) help enhance the returns of large validators but also raise concerns about centralization.
– Enhanced data availability (EIP-7742) and on-chain deposits (EIP-6110) support network scaling and security improvements.
– Smart contract-controlled withdrawals (EIP-7002) could fundamentally change the way staking is managed.
For validators, developers, and regular users, Pectra brings both opportunities and challenges. Testing, strategy adjustments, and familiarization with new features will be key. Before the official launch of Pectra in mid-March 2025, the Ethereum community needs to remain flexible and delay the upgrade if necessary to ensure long-term stability and security.
Pectra embodies Ethereum's commitment to continuous improvement and bold upgrades, marking an important step in its future development.
Quick Links
– March Global Economic Trends: A Must-Read for Crypto Investors
– Monad vs. Ethereum: Can This Emerging L1 Disrupt the Market?
– Hong Kong Web3 Revolution: Key Trends and Regulatory Policies Released at Consensus 2025
– Nine Major Trends in Cryptocurrency for 2025: AI, DeFi, Tokenization, and More Innovations
About XT.COM
Founded in 2018, XT.COM currently has over 7.8 million registered users, with over 1 million monthly active users and user traffic exceeding 40 million within the ecosystem. We are a comprehensive trading platform supporting over 800 quality cryptocurrencies and more than 1,000 trading pairs. XT.COM cryptocurrency trading platform supports a rich variety of trading options, including spot trading, margin trading, and futures trading. XT.COM also has a secure and reliable NFT trading platform. We are committed to providing users with the safest, most efficient, and most professional digital asset investment services.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




