Original Authors: MatthewSigel, PatrickBush
Original Translation: Mars Financial, MK
Introduction
It is expected that by 2050, Bitcoin (BTC) will consolidate its position as a major global medium of exchange and eventually become one of the world's reserve currencies. This prediction is based on the view that people's trust in existing reserve assets may be eroded. The key is that Bitcoin's scalability issues have long hindered its widespread use, and emerging second-layer (L2) technology solutions are expected to completely solve this problem. Combined with Bitcoin's immutable property rights and sound monetary principles, the enhanced functionality provided by second-layer technology will build a global financial system that better meets the needs of developing countries.
Summary
We predict that by 2050, the price of Bitcoin will reach $2.9 million. By then, Bitcoin will be used for 10% of global international trade and 5% of domestic trade settlements. This will result in central banks holding Bitcoin assets accounting for 2.5% of their reserves. Based on assumptions about global economic growth, investor demand for BTC, and its trading volume, we calculate the potential price of Bitcoin to be approximately $2.9 million through the currency circulation velocity equation, with a corresponding total market value of $61 trillion. Using our valuation framework for Ethereum L2, the total value of Bitcoin L2 could reach $7.6 trillion, accounting for approximately 12% of BTC's total market value.
Trends in the International Monetary System
To accurately grasp Bitcoin's potential role in the future financial architecture, it is necessary to analyze the current status and trends of the International Monetary System (IMS). As various economies gradually phase out the current reserve currencies, this ongoing trend in the international monetary system favors the rise of Bitcoin. We speculate that the main driving force behind this shift is the relative decline in the global GDP share of current economic leaders (such as the United States, the European Union, the United Kingdom, and Japan). Unrestrained deficit spending and short-sighted geopolitical decisions by issuing countries will further weaken people's confidence in the current reserve currency as a long-term store of value, accelerating this transformation. In addition, concerns about the property rights guaranteed by Western currencies and financial systems (especially the United States) are increasing.
The content of this article includes:
- Transformation of the international monetary system
- Future trends in the monetary system
- IMS issues and Bitcoin solutions
- Expanding Bitcoin using second-layer technology
- Predicting the price of Bitcoin in 2050
- Trust is the cornerstone of the international monetary system
- Trust is the pillar of the international monetary system
The status of a currency in the international monetary system is most directly reflected in its share in cross-border payments and central bank reserves. Currently, the international monetary system is mainly dominated by a few currencies such as the US dollar, euro, pound sterling, and yen. The application of a currency depends on its utility, perceived value stability, and trust in the fiscal discipline of its issuing country. The larger a country's share in global GDP, the more widely its currency is used in international trade, forming a self-reinforcing feedback loop that consolidates its dominant position in international trade. Historically, changes in the international monetary system have been slow, but we are at a critical turning point.
After the gradual exit of the dollar-dominated gold standard
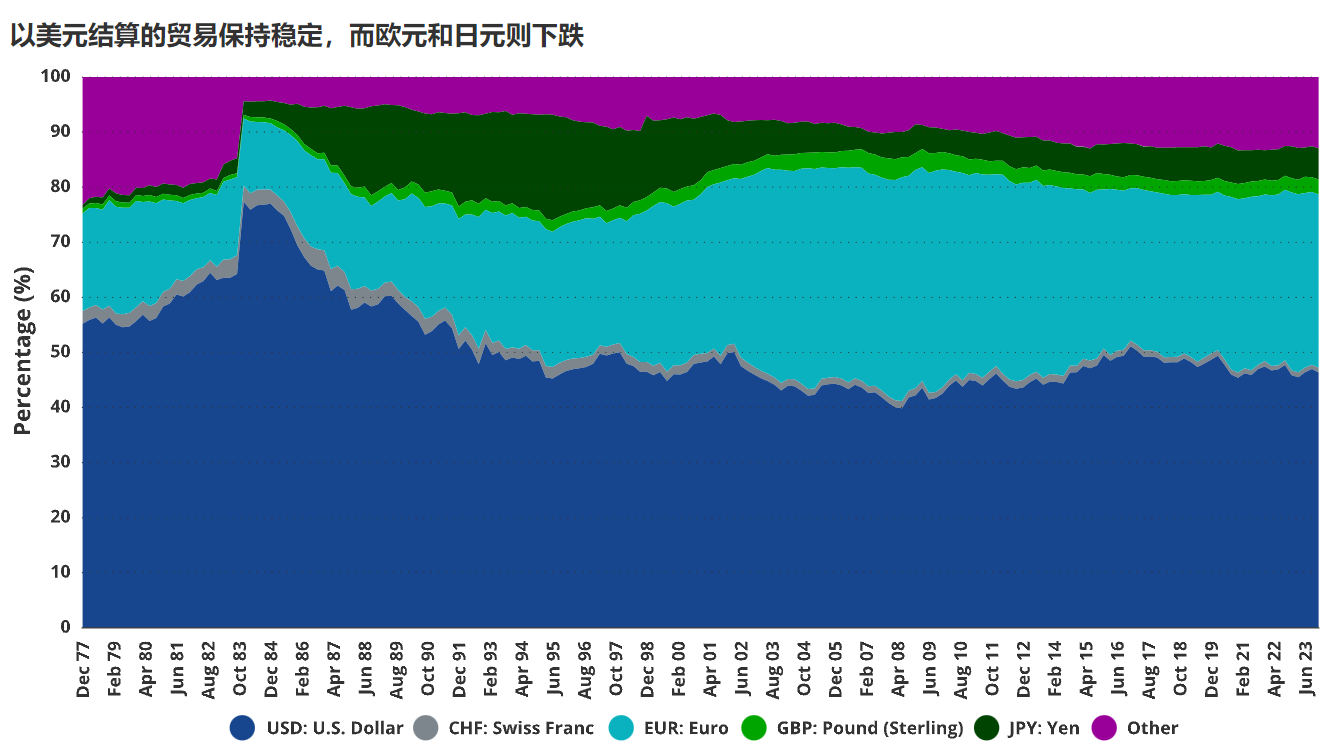
At the beginning of the 20th century, the pound-dominated gold standard gradually transitioned to a system supported by the US dollar in the 1970s. Over the past 45 years, the share of the dollar in cross-border payments has been extremely stable. Except for a brief surge in the early 1980s during the dollar's rebound, the dollar's share has remained at around 61%. This dollar-centric system is attributed to reliable fiscal policies, a consistently strong global GDP share (25%), a dominant share of world defense spending (48%), and a sound domestic legal system. The cumulative effects of these deliberate policies have solidified the trust of dollar holders in its role as a globally recognized store of value for goods and services. The dollar can be used to purchase high-quality capital/consumer goods, invest in top global companies, and even earn risk-free interest by lending to the US government. Most importantly, dollar holders believe that the legal system ensures their currency's status and can seek legal redress in the fair US court system. However, this system is facing change.
The relationship between GDP share and currency usage
During the period from 1980 to 2023, the EU's share of global defense spending significantly decreased from 25% to 14% (a 45% decrease). In the same time frame, the EU's share of global GDP also decreased from 29% to 16% (a 43% decrease). Meanwhile, from 1995, the EU's sovereign debt-to-GDP ratio increased from 66% to 89% in 2023, an increase of approximately 34%. Although Japan has maintained a low share of global military spending at 2-3% due to its security agreement with the United States, its share of global GDP has also been declining. At the same time, its government debt-to-GDP ratio has increased. Specifically, from 1995 to 2023, Japan's share of global GDP decreased from about 17% to just over 4%—a decrease of 77%. From 1980 to 2023, Japan's government debt-to-GDP ratio surged by 426%, from 47.8% to 251.8%. These events are synchronous with the declining use of the yen and euro in global trade.
After conducting a regression analysis of the major reserve currencies, we evaluated the relationship between changes in GDP share and changes in cross-border payment (CBP) share. CBP refers to international transactions involving cross-border fund transfers. These analyses show a highly significant correlation between GDP and CBP, with t-values greater than 4 and R2 values ranging from 0.3 to 0.5. This finding provides a basis for predicting the dominant currency of the future international monetary system. Our model predicts that by 2050, the share of Japan, the United Kingdom, and the EU in global productivity will decrease from 27% in 2020 to less than 15%. We believe this will lead to a corresponding decrease in their currency usage, as changes in population structure are bound to affect the dominant status of currencies.
The correlation between GDP decline and cross-border payments (CBP): Japan, the UK, and the EU will lose their foreign exchange share
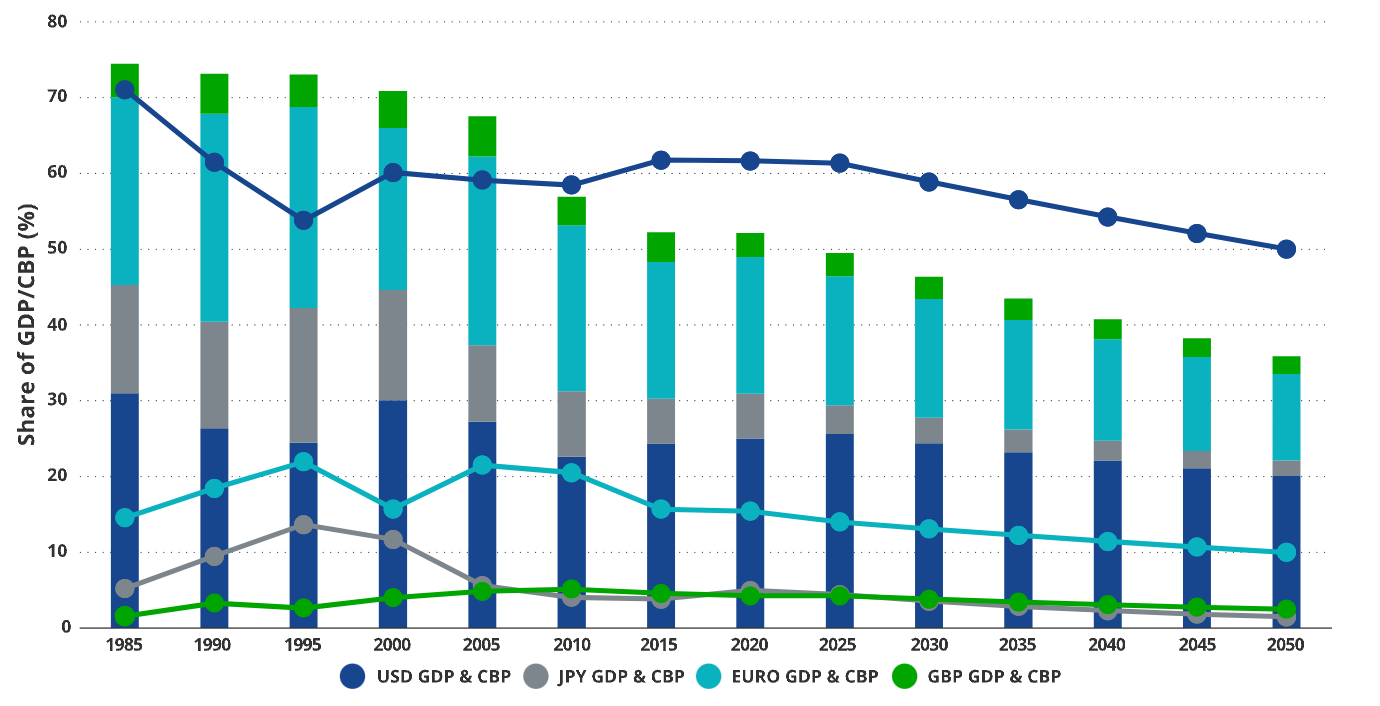
Data sources include VanEck Research, IMF, and BIS, as of June 21, 2024. The presented forecasts are for reference only and are valid as of the date of publication. Any changes will not be notified separately.
Future Trends of the "Big Four" Currencies
Our data analysis strongly indicates that the existing reserve currency status is gradually declining as the economic importance of issuing countries decreases and fiscal responsibility is lacking. This trend is expected to continue and may accelerate. In particular, we have ample reason to believe that the share of the US dollar, yen, euro, and pound sterling (the "big four major currencies") in cross-border payments will continue to decrease. Based on our forecasts of the proportion of these currencies in GDP, we expect that by 2050, the share of these currencies in cross-border payments will decrease from 86% in 2023 to 64%. During this period of declining value for these currencies, Bitcoin has ample opportunity to become an important alternative currency for international trade settlements.
Our analysis is based on a well-known fact: the population of developed economies is gradually aging. By 2050, the proportion of the elderly population in the four major economies will increase by 20-40%. Taking Japan as an example, the proportion of the population aged 65 and above will reach 39%, with the population over 75 years old accounting for 25% of the total population. These demographic trends will force the productivity of these countries to decrease over time. Additionally, compared to developing economies, developed economies have difficulty significantly enhancing their economic growth rates through simple investments in infrastructure, education, and technology. The interaction of these demographic and economic realities leads the International Monetary Fund to predict that the economic growth rates of developed countries will be far lower than those of developing countries. As mentioned above, we predict that the share of the four major economies in global GDP will decrease from 71% in 1984 to 36% in 2050.
The decrease in the share of the four major countries in global GDP will be accompanied by a deterioration in the fiscal situation of each country. The combination of population decline and low growth rates will lead to a sharp increase in the debt-to-GDP ratio of these countries. To assess the fiscal situation of the four major countries in 2050, we referred to the IMF's estimates of GDP growth and population forecasts for these countries, and then calculated based on the average debt maturity, inflation, deficit spending, and expected GDP growth. Our long-term forecasts are based on long-term debt forecasts for each governing body, with appropriate adjustments made based on population trends.
Debt and Interest Rate Scenarios in 2050
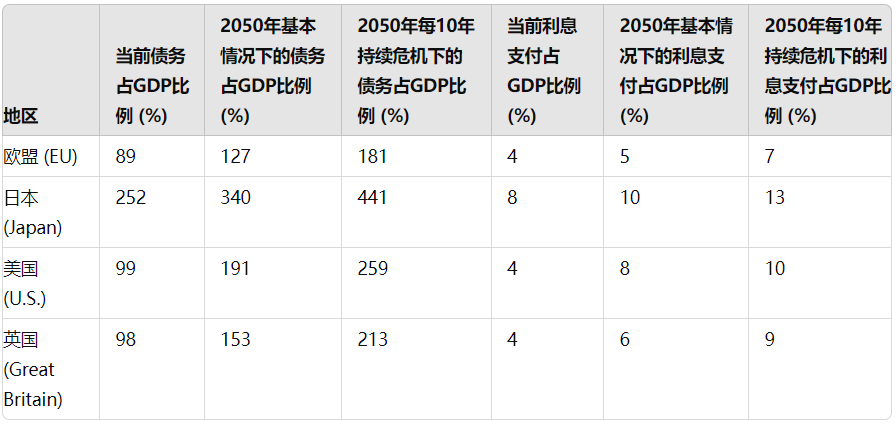
Debt Forecast in the Baseline Scenario
In our "baseline" scenario, we expect that the federal government debt payments of the four major reserve currency countries will account for an average of over 5% of GDP annually. Specifically, for Japan and the United States, this proportion could reach 10% and 8%, respectively. It is worth noting that these forecasts do not include major crisis situations such as the 2001 terrorist attacks, the 2008 financial crisis, or the 2020 pandemic, during which the fiscal deficits of reserve currency countries significantly increased. Over the past 25 years, the United States has accumulated debt equivalent to 19%, 40%, and 26% of GDP due to these major disasters. Given the frequent occurrence of these catastrophic events, we can almost certainly expect them to continue in the future. This continuous cycle of crises will lead to an upward revision of our forecasted debt-to-GDP ratio and interest payments. It is expected that within the next 26 years, these three deficit spending shock scenarios will increase the proportion of interest payments to GDP by approximately 25%.
Further Analysis of the Baseline Forecast
There are more factors that may lead us to be overly optimistic about our "baseline" debt situation forecast. In developed countries, especially the United States, fiscal profligacy continues to grow due to structural factors. We have not included the analysis of cost disease and the inefficiency of some institutions in the United States, which has led to billions of dollars being invested in failed cases such as electric vehicle charging stations, subway lines costing $40 billion per mile, high-speed rail costing $360 billion per mile, and coastal combat ships worth billions of dollars but unable to operate in coastal areas. Therefore, we have ample reason to believe that the debt-to-GDP ratio of the government will exceed our initial forecasts. Most puzzlingly, even during periods of strong economic growth, the fourth largest government deficit still exists. Clearly, governments in developed economies have realized that cutting spending is political suicide. In this logic, large deficits will continue to exist until a dramatic reckoning forces people to make changes. Our forecasts should be viewed as conservative estimates, as we also assume a relatively optimistic interest rate environment, with average rates between 3-4%. As the cost of debt repayment increases, global bond investors are likely to demand higher interest rates.
Management Issues in the United States and Its Western Allies
It is also worth noting that the United States and its Western allies are increasingly inclined to address expensive bureaucratic management issues rather than seek cost-effective solutions. The continuous intervention of management and bureaucratic institutions has led to the continuous inflation of costs in society, government, and the private sector, significantly increasing the cost of solutions. In the fields of healthcare, higher education, and defense, this interest group-driven management cost will continue to exist. Although politicians can provide symbolic positions for their preferred districts, employees within the institutions see hiring more staff as a means to increase their salaries and positions. This practice has created an incentive structure for vested interests to continuously expand bureaucratic institutions rather than streamline them. The result is not the resolution of problems, but the continuation of problem-ridden management. The anti-drug, homelessness, and counter-terrorism wars have spawned billion-dollar industries that rely on the continuous and long-term management of these issues, rather than seeking cost-effective reductions and solutions. This is an incurable fiscal cancer that will continue to erode the long-term productivity and financial health of the four major institutions. There are numerous beneficiaries of administrative generosity, and there is no effective political force to counterbalance them.
Interest payments for the four major banks are expected to surge
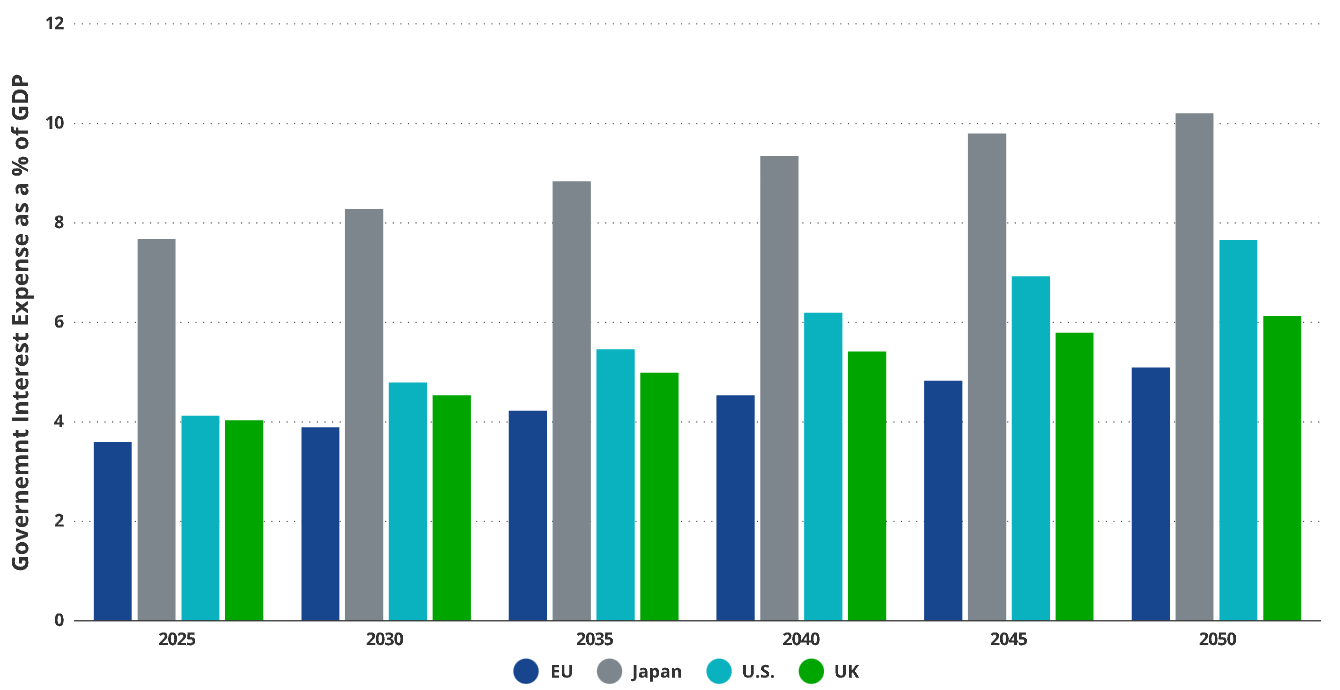
Data source: CNAS data as of June 21, 2024.
In the past 25 years, the United States has increasingly used sanctions to advance its geopolitical strategy. Specifically, by 2022, the number of entities sanctioned by the United States reached 2,796, an increase of 529% compared to 2009. Although part of this increase in 2022 was due to sanctions against Russia, this trend of increased use of sanctions indicates that the United States has clearly chosen this policy direction since the September 11, 2001 terrorist attacks. In 2002, just a year after the September 11 attacks, the official report on sanctions in the United States was as long as 17 pages. By 2021, 2022, and 2023, the same OFAC list had expanded to 247 pages, 825 pages, and 479 pages, respectively. Even before the Russian invasion, sanctions had become an increasingly important tool in US foreign policy.
In addition to the five countries that have been comprehensively sanctioned by the U.S. Office of Foreign Assets Control, 17 other countries have suffered varying degrees of sanctions. Furthermore, 13 countries have been prohibited from using the U.S. dollar to purchase military equipment. These 35 countries collectively account for 31.6% of the global population and 22% of global GDP. Recently, the sanctions imposed by the U.S. and Europe on Russia, including the freezing of its $300 billion in foreign exchange reserves and other offshore assets, have further escalated the situation. Therefore, many countries naturally have concerns about the security of their assets in the current international monetary system. However, actions that undermine confidence in reserve currencies are not limited to the international stage; our analysis suggests that the reputation of the U.S. dollar as an inviolable property tool is also being eroded.
In the United States, some actions by government departments have raised widespread questions about the rule of law and property rights protection. Recently, a U.S. judge canceled contractual obligations related to company performance targets, citing these rewards as excessive. In another notable case, a company was fined a huge amount for business fraud charges, despite there being no victims. Additionally, factors such as national security, eminent domain, and civil asset forfeiture have also infringed on the rights of property owners. It is worth recalling historical precedents of property rights violations during the New Deal era, including the confiscation of private gold holdings and the fourth devaluation of the free loan. Logically, the precedent of seizing gold could also be used for other assets to offset fiscal shortfalls. Looking ahead, we see the rise of populism imposing new restrictions on the U.S. property rights system through investment restrictions or unfair asset seizures.
Overall, the momentum to abolish property rights within the U.S. is strengthening. At the same time, property seizures for fiscal reasons are becoming a reality. How will holders of the U.S. dollar and other reserve currencies cope with this legally supported arbitrary seizure environment? More and more countries are not only strongly protesting current and potential injustices, but are also beginning to move away from the pillars of the existing international monetary system.
A New International Monetary System is Emerging
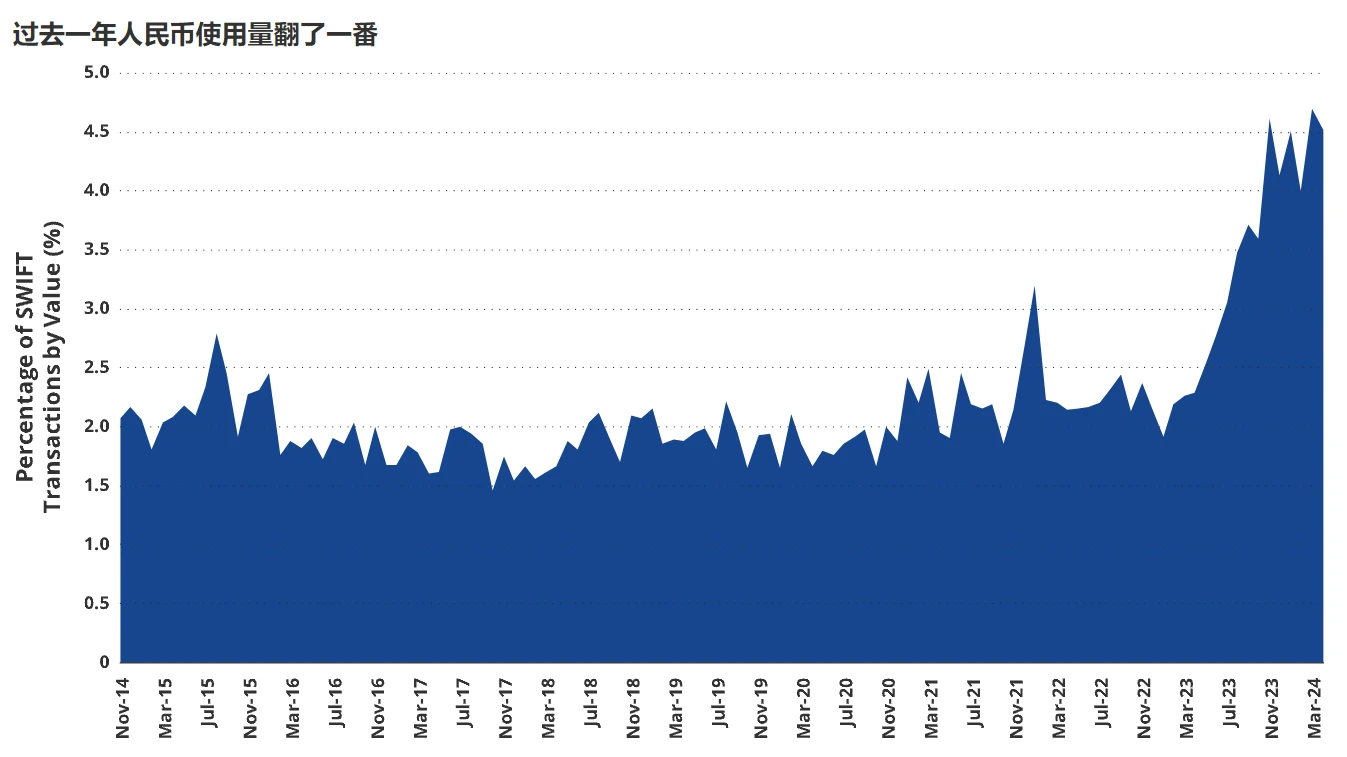
Data source: SWIFT data as of June 18, 2024.
The renminbi is becoming one of the beneficiaries of the changing global currency landscape. Recently, China has reached agreements with several countries, including Saudi Arabia, Gulf countries, Bolivia, Ecuador, and Brazil, to settle bilateral trade in renminbi. Currently, the use of the renminbi in China's international trade settlements has surpassed the U.S. dollar. As the international pariah of currencies, Russia recently halted trading in U.S. dollars and euros on its Moscow Stock Exchange. Meanwhile, its major commodity producer, the Russian oil company, issued two bonds denominated in renminbi, with amounts reaching 10 billion and 15 billion yuan, respectively. Some Indian oil refiners have started using the renminbi to pay for their oil purchases. As a result, as of April 2024, the renminbi's share in all transactions conducted through the SWIFT system reached 4.52%, nearly double that of April 2023.
In addition to the renminbi, an increasing number of countries are starting to use their own currencies for international trade, rather than relying on the four major currencies. For example, India has reached agreements with countries such as Malaysia to purchase oil in rupees and settle trades, and has established local currency settlement systems with nine other central banks. Of particular note, Saudi Arabia announced in 2023 its willingness to accept currencies other than the U.S. dollar for pricing oil, and recently joined a Chinese-led central bank digital currency project.
A Multipolar Currency System
By 2050, it is expected that the market share of BTC, the renminbi, and other currencies will increase from 4.77% to 23%.
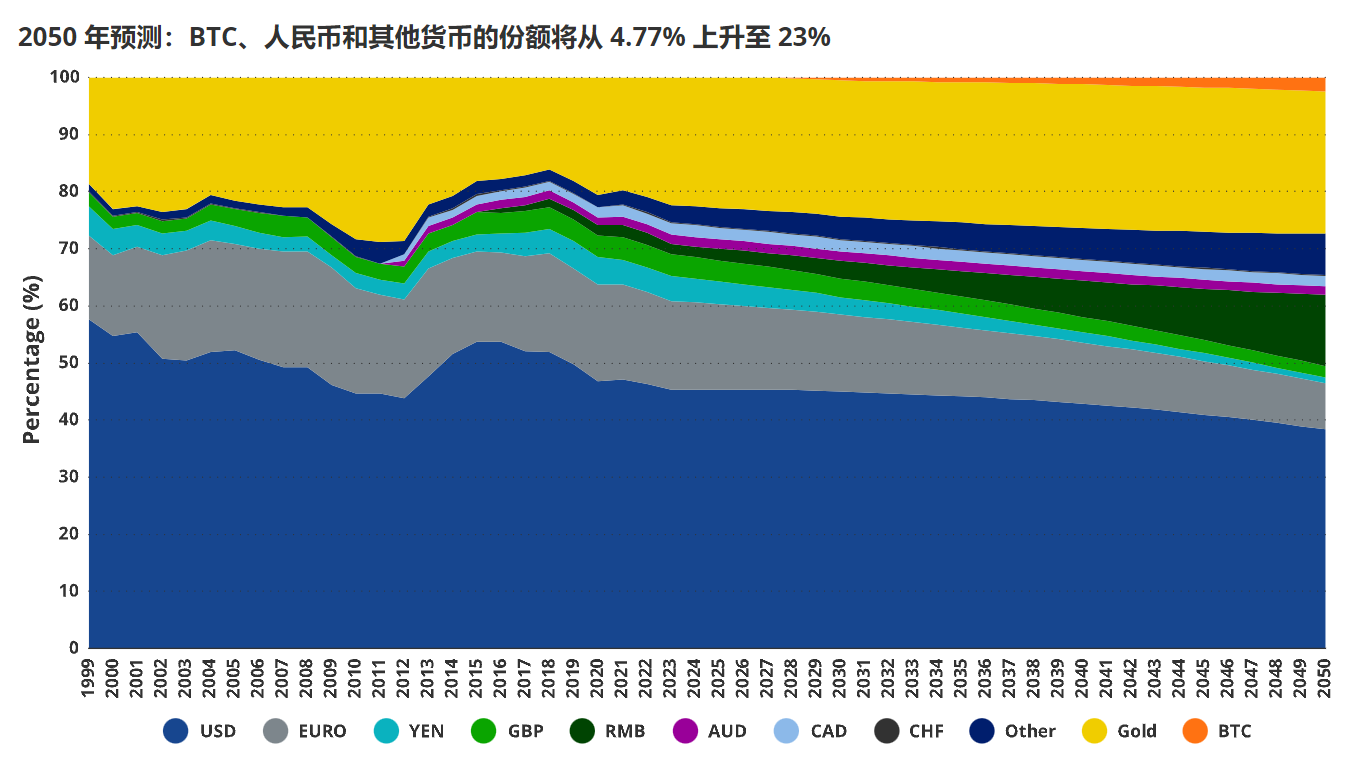
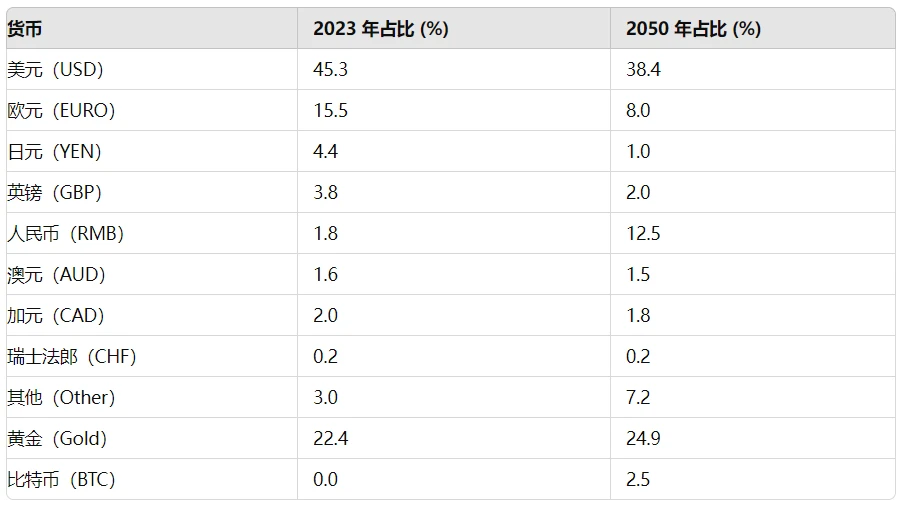
Changes in the Structure of International Currency Reserves
It is expected that by 2050, several countries exploring alternatives to the existing international monetary system will face limited attractive choices. It is anticipated that the number of bilateral trade agreements will increase, and the frequency of renminbi usage will also rise. Therefore, it is expected that the application of emerging market currencies in transactions will drive the "other" category of central bank reserves from 3% to 7.5%. At the same time, the proportion of the renminbi in global reserves may also increase to about 12.5%. These changes may come at the expense of the four major reserve currencies, with less market share loss for developed commodity-producing countries such as Canada and Australia. It is worth noting that in the scenario we anticipate, the proportion of BTC in global reserves is expected to reach 2.5%, with its share in domestic and international trade potentially rising to 5% and 10%, respectively.
This dynamic may unfold due to the challenges posed by other potential alternative solutions that could replace the current system of the four major currencies. While bilateral trade agreements and the rise of emerging market economies may promote the widespread adoption of emerging market currencies, trust issues may hinder their full acceptance. For example, the Latin American debt crisis of the 1980s and the Asian currency crisis of the 1990s highlighted the risks and motivations of developing countries in fulfilling international obligations or curbing money printing.
Although the renminbi is appreciating relative to China's GDP, widespread skepticism about China and the level of acceptance of the renminbi as a reserve currency may limit its usage and make it difficult to compete with the U.S. dollar. Additionally, using more domestic currency in international trade implies a high degree of economic alignment. However, the value of the main export products of most developing countries, such as commodities, is usually unable to compete with the high-value manufactured goods of developed economies. This difference in trade value may compel debtor countries to weaken their fiscal obligations through currency expansion.
Bitcoin as a Reserve Currency
In summary, the most challenging issue in adopting a new currency system is trust and issuance policy regarding potential alternative currencies. Frankly, only a few emerging market countries can inspire enough confidence to give people ample reason to include them in reserve currency status. Some countries may turn to China and other developing economies to hold reserve balances. However, many are dissatisfied with poor reserve choices and may increasingly turn to Bitcoin, as it addresses many of the problems faced by current reserve currency users.
The characteristics of Bitcoin make it a useful reserve currency, providing its holders with:
- Trustlessness
- Neutrality
- Immutable monetary policy
- Secure property rights
Bitcoin is designed to replace fiat currencies, and its system replaces corrupt human authority with immutable logic. Holders need not worry about physical dilution of BTC value, using Bitcoin for political purposes, or abusing its users. Through its innovative approach, Bitcoin eliminates government bias behaviors that could hinder the property rights of BTC holders. As a politically and economically neutral system, Bitcoin replaces biased actors with a simple software algorithm.
Bitcoin's framework allows anyone, from national governments to local citizens, to hold and trade BTC without the need for intermediaries. From a national sovereignty perspective, this is crucial for controlling foreign policy. Considering costs, Bitcoin also eliminates many financial expenses incurred through the current international monetary system. Unlike fiat currencies, which are often affected by currency inflation and have an average lifespan of only 35 years, Bitcoin has a fixed monetary policy focused on maintaining the value of BTC. Once the total supply of BTC reaches 21 million, the inflation strategy will peak, and BTC holders can rest assured that the value of Bitcoin will not be arbitrarily diluted by central banks due to conflicts of interest. Bitcoin's robust hard money design is supported by a loyal group of users and core contributors dedicated to upholding its economic principles. Therefore, Bitcoin can be seen as the "religion of sound money."
Bitcoin provides value propositions that no fiat currency can offer to central banks, investors, and international trade participants. Each fiat currency is subject to control by the political class, whose ultimate goal is often money printing. The purpose of the constitution is to delineate the limits of government power and prevent the abuse of power that has been common throughout history. Bitcoin applies constitutional constraints to the monetary field, embodying a system created by the people, for the people. In the international monetary system, Bitcoin's uniqueness lies in providing holders with unlimited property rights. The issuer of BTC is the Bitcoin software itself, and its protocol does not allow for the seizure of BTC, ensuring that only those with access to their Bitcoin private keys can use them. Unless subjected to hacking and theft, Bitcoin holders need not worry about their assets being arbitrarily seized due to interactions with improper individuals or participation in protests. Given people's concerns about asset seizures by the U.S. or other major countries, we believe that the inviolable property rights system provided by Bitcoin is extremely valuable.
International Payment System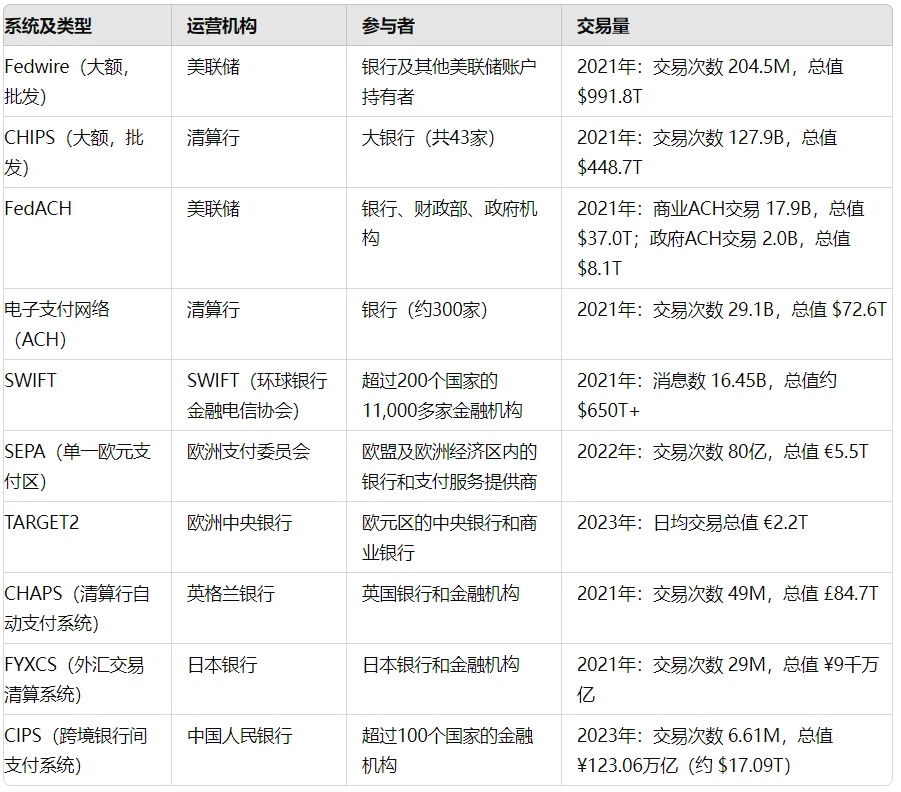
Challenges Faced by Bitcoin as an International Trade Medium
For Bitcoin to become an effective medium for international trade, fundamental reforms are necessary. Bitcoin has the potential to bring significant value to users of the International Monetary System (IMS) by addressing many of the existing system's issues. However, Bitcoin has not yet become a mainstream cross-border payment tool. This is mainly due to Bitcoin's processing capacity being insufficient to meet the demands of the global financial system.
Currently, Bitcoin's transaction processing speed is approximately 7 to 15 transactions per second, depending on specific metadata. A Bitcoin block is processed every 10 minutes, and a transaction typically requires confirmation through 5 to 6 blocks. Therefore, Bitcoin can process approximately 576,000 transactions per day, or about 4,000 transactions every 10 minutes. In comparison, the SWIFT system can process about 45 million messages per day, and the CHIP system handles approximately 350 million transactions per day.
Additionally, the software managing the Bitcoin network does not support complex smart contract languages. This means that users cannot create complex financial applications on the Bitcoin network, as is feasible on more advanced blockchain platforms like Ethereum or Solana. Therefore, for banking operations, transaction execution, and complex custody services, Bitcoin users typically need to rely on centralized institutions. While this approach can expand the use of Bitcoin, it also weakens some of its core features in international trade.
The limited functionality of Bitcoin is a deliberate choice in its design. The main developers of Bitcoin believe that adding more features could introduce new security risks, increase centralization tendencies, and potentially undermine the fundamental purpose of Bitcoin. Historically, those who support versions of Bitcoin with more complex, higher processing capacity, and smart contract functionality often choose to create new cryptocurrency projects.
However, the attitude of the Bitcoin community is rapidly changing as new solutions are developed and adopted to meet the needs of both hard money advocates and users who expect more functionality from Bitcoin. These solutions are the result of deep consideration by many people about the long-term sustainability of Bitcoin.
Why Countries Do Not Use Gold for Trade
By exploring why countries currently do not use gold for trade, we can better understand the challenges faced by Bitcoin as an international trade medium. Historically, gold has been widely used as a reserve currency and international trade medium. However, several key issues have led to its decline in this role.
Physical Inconvenience and Logistics: In theory, gold can be traded by transferring gold bars from one vault to another, but this method is not practical on a large scale. The physical properties of gold make its transportation and secure storage cumbersome and costly. While electronic systems can be used to record gold transactions, the physical transfer of gold remains a major challenge, especially in cases involving large transactions.
Lack of Flexibility: Gold cannot meet the flexibility required by modern financial systems. Due to the limitations of its physical properties, gold is difficult to divide into smaller units for daily transactions and is not suitable for supporting complex financial instruments. Although digital forms of gold exist, their practical application is still limited by the fundamental attributes of gold as a physical asset.
Security Risks: The holding and transportation of gold involve significant security risks, including theft and loss. Extensive security measures are required, increasing the cost and complexity of using gold as a trade medium. These risks are more pronounced in international transactions involving multiple parties and jurisdictions.
Integration of Technology and Finance: Modern economies rely heavily on advanced financial systems that require fast, secure, and flexible means of transactions. Even if gold is digitized, it is difficult to seamlessly integrate with these systems. In contrast, the transaction speed and efficiency of electronic fiat currencies far exceed that of gold, making them more suitable for modern financial infrastructure.
While Bitcoin also faces certain challenges, such as potential security risks, it has overcome many of the limitations of gold. Unlike gold, Bitcoin inherently has digital properties, making it easier to transfer and divide. Despite some limitations at present, the programmability of Bitcoin provides greater flexibility and potential for future improvements. Additionally, through cryptographic protection, Bitcoin transactions can reduce certain security risks associated with physical gold. While it seems unlikely to use neutral currencies like Bitcoin (or gold) for trade payments in the current environment, it is conceivable that the demand for a stable, secure, and flexible medium of exchange may drive significant changes in the future amid the evolving geopolitical landscape.
By 2024, Bitcoin's circulation speed is expected to be only 25% of that in 2018
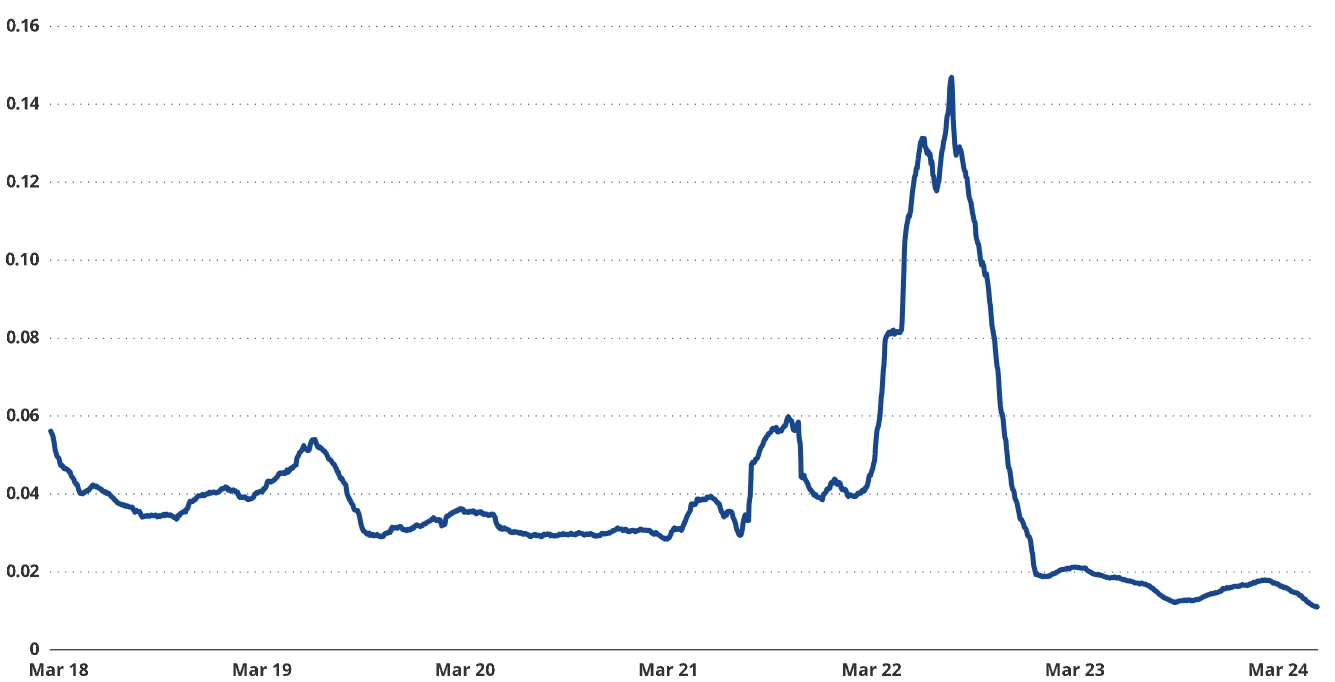
Source: Glassnode, as of June 30, 2024.
Scaling Bitcoin Using Second-Layer Solutions
Given that Bitcoin's transaction throughput is limited by the economic principles upheld by its community, many industry professionals have explored various technological means to expand its network scale. It is widely believed that the development and even survival of Bitcoin require scalability. This is because the high fixed and variable costs are borne by miners, who are the guardians of the Bitcoin network. Since the establishment of the Bitcoin network, miners' main income (up to 94%) has come from block rewards in the form of inflation. As Bitcoin's inflation is limited, to offset the decrease in the inflation rate, transaction fees on the network will become the main source of miner income. In the year leading up to the halving of Bitcoin's inflation on April 19, 2024, Bitcoin miners earned nearly $13 billion through inflation, while income from transactions amounted to $1.1 billion. To ensure that miners can sustain operations in the long term, the price of Bitcoin must rise sufficiently, or transaction volume must increase to offset most of the costs.
Therefore, the Bitcoin community is actively pushing for an increase in transaction volume to expand Bitcoin's scale and provide basic income security for miners. Additionally, subtle but crucial changes to core software are also part of this transformation. However, the role of Bitcoin as a store of value asset and the demand for it as a medium of exchange are somewhat contradictory—ideally, a store of value should not be frequently traded. This is reflected in Bitcoin's currency circulation speed, which has decreased from 0.042 in 2018 to 0.014 in 2024. Nevertheless, the demand to expand Bitcoin's scale has given rise to various solutions that can transfer the value of Bitcoin without directly using the Bitcoin chain, often referred to as "second-layer solutions." Off-chain scaling mainly takes two forms: one is the creation of encrypted tokens supporting Bitcoin on other blockchains by centralized entities, and the other is achieving the same purpose in a decentralized manner.
In a centralized model, entities such as cryptocurrency exchanges, trading companies, or miners hold Bitcoin and issue certificates representing ownership of these Bitcoins. These certificates can be exchanged for Bitcoin on various blockchains and exchanges, usually created through the "minting" of cryptographic tokens. The most famous example is wBTC, also known as "wrapped Bitcoin." In this model, a centralized exchange called BitGo holds and locks Bitcoin, issuing cryptographic assets called wBTC to users providing Bitcoin. Subsequently, wBTC circulates in ecosystems like Ethereum, with its value closely tied to the price of Bitcoin. wBTC is widely used in DeFi applications on Ethereum and Tron, with approximately $10 billion worth of Bitcoin converted into wBTC.
The key point about these wrapped BTC products is that users must trust the issuing entity not to engage in fraud or rehypothecate the underlying Bitcoin. The challenge this system faces is the potential counterparty risk regardless of who is safeguarding and wrapping the Bitcoin. A drawback of centralized solutions like wBTC is that they do not add additional income to the Bitcoin network, as the locked Bitcoin does not generate transaction revenue, which is the lifeblood of the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Bitcoin Total Value Locked (TVL) is mainly dominated by wBTC, with other currencies gradually increasing
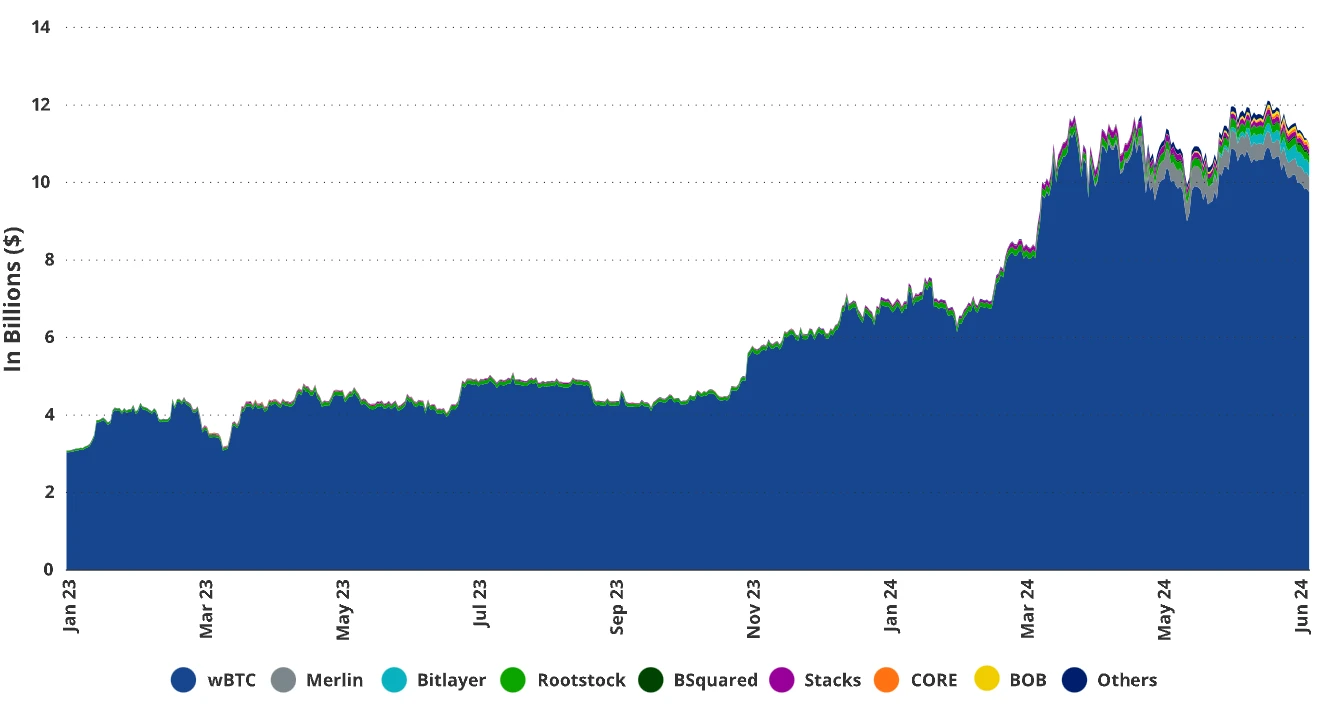
Source: Defillama, as of June 24, 2024.
Decentralized Bitcoin Tokens
Another type of "off-chain" scaling solution is considered "trustless" because it does not rely on centralized entities but is based on decentralized solutions. These solutions involve various software that combines Bitcoin components with off-chain networks (such as other blockchains or similar trustless networks). The core of these solutions is typically Bitcoin's multi-signature scheme, which locks BTC in a Bitcoin account while minting tokens representing Bitcoin on another blockchain. This series of off-chain scaling solutions allows users to transfer these representations, essentially ownership certificates corresponding to BTC locked on the Bitcoin chain. This is often referred to as "bridging," and these Bitcoin off-chain solutions are collectively known as Bitcoin Layer 2 (L2). However, unlike the more specific definition of Ethereum L2, the concept of Bitcoin L2 encompasses various different solutions (see our article on Ethereum L2 for more details). First, Bitcoin L2 is not always a blockchain like most Ethereum L2 solutions; second, Ethereum L2 relies on Ethereum to securely operate its blockchain, while some Bitcoin L2 solutions intend to use Bitcoin for security in the future, but many blockchains simply bridge BTC to their chains to allow transactions. Most importantly, only some Bitcoin L2 solutions aim to increase the network's value by creating value for miners.
Lightning Network and "State Channels"
A popular but limited-function Bitcoin Layer 2 is the Lightning Network, which allows users to create Bitcoin certificates off-chain and send Bitcoin through the created network (called "payment channels"). In this setup, users can conduct any number of transactions off-chain, and when they decide to settle these transactions, they can close this payment channel. Subsequently, the changes in BTC balances between different parties will be ultimately settled as a single transaction on the Bitcoin chain. Payment channels are a subset of a broader set of scaling solutions (called "state channels") that allow off-chain representations of Bitcoin to interact with off-chain dApps and settle transaction results sporadically or at scheduled intervals.
The term "state" in state channels refers to the current state of balances and other relevant variables for all participants in a series of transactions. The main feature of state channels is that most transaction data is stored off-chain, meaning transactions occur privately between parties and are not immediately recorded on the blockchain. Only the final state or the results of multiple off-chain transactions are submitted to the blockchain. This approach can speed up transaction times and reduce costs because only the final settlement is recorded on-chain. When participants wish to withdraw balances, the final state of off-chain data is reconciled and broadcast to the Bitcoin blockchain. Due to the Lightning Network's numerous drawbacks and potential security vulnerabilities, its usage is extremely low (TVL is $323 million, accounting for 0.026% of the Bitcoin supply).
Sidechains and Merge Mining
Another widely used form of Bitcoin L2 is "sidechains." They apply the concept of state channels to extend Bitcoin by minting representations of Bitcoin off-chain and completing off-chain transactions on a blockchain different from Bitcoin. Sidechains have consensus mechanisms and may (but not always) rely on Bitcoin's consensus. They can be seen as microeconomic zones pegged to Bitcoin through bridges. These bridges are protocols that use various combinations of complex mathematics, software, and economics to lock BTC on the Bitcoin blockchain, allowing tokens representing locked BTC to be created on the sidechain. When users trade BTC representations on the sidechain, they can settle the transactions back to Bitcoin by "settling" the transaction results.
These sidechains allow trading of Bitcoin against BTC, achieving a larger transaction throughput (in terms of BTC) than the Bitcoin blockchain allows. This is because many transactions can occur off-chain on the bridged Bitcoin chain and then settle back to Bitcoin in bulk when necessary. This is similar to the ACH batch processing system in the United States, where banks maintain databases of interbank transfers and settle at the end of the day. A significant difference between sidechains is whether BTC is the "native currency" of the blockchain. If BTC is the primary currency, all transactions must be paid in BTC fees; if not, transactions fees can be paid in other currencies. Regarding the issue of adding value to the Bitcoin network, most sidechains do not increase the value of the Bitcoin network because almost all transactions involving the value of BTC occur off-chain. However, in cases where BTC is the native currency of the sidechain, they increase the value of Bitcoin by creating more demand for BTC.
Bitcoin L2 "Rollups" operate in vastly different ways. Some may be proof-of-stake networks like Ethereum, where there are validators running the chain and various cryptocurrencies are staked. Others, like Stacks, use BTC locked on Bitcoin to support validators running and securing the chain. Another interesting consensus mechanism is "merge mining." The merge mining used by Bitcoin L2 Rootstock and BOB refers to Bitcoin miners embedding compressed data of blocks from the "merge-mined" chain into a specific location in the Bitcoin block. Almost at no extra cost, any Bitcoin miner choosing to merge mine another blockchain will add a checkpoint of events on that chain to Bitcoin. In return, miners are compensated with transaction fees (in BTC) from these chains for providing this service.
Advantages of Bitcoin Layer-2 Rollups
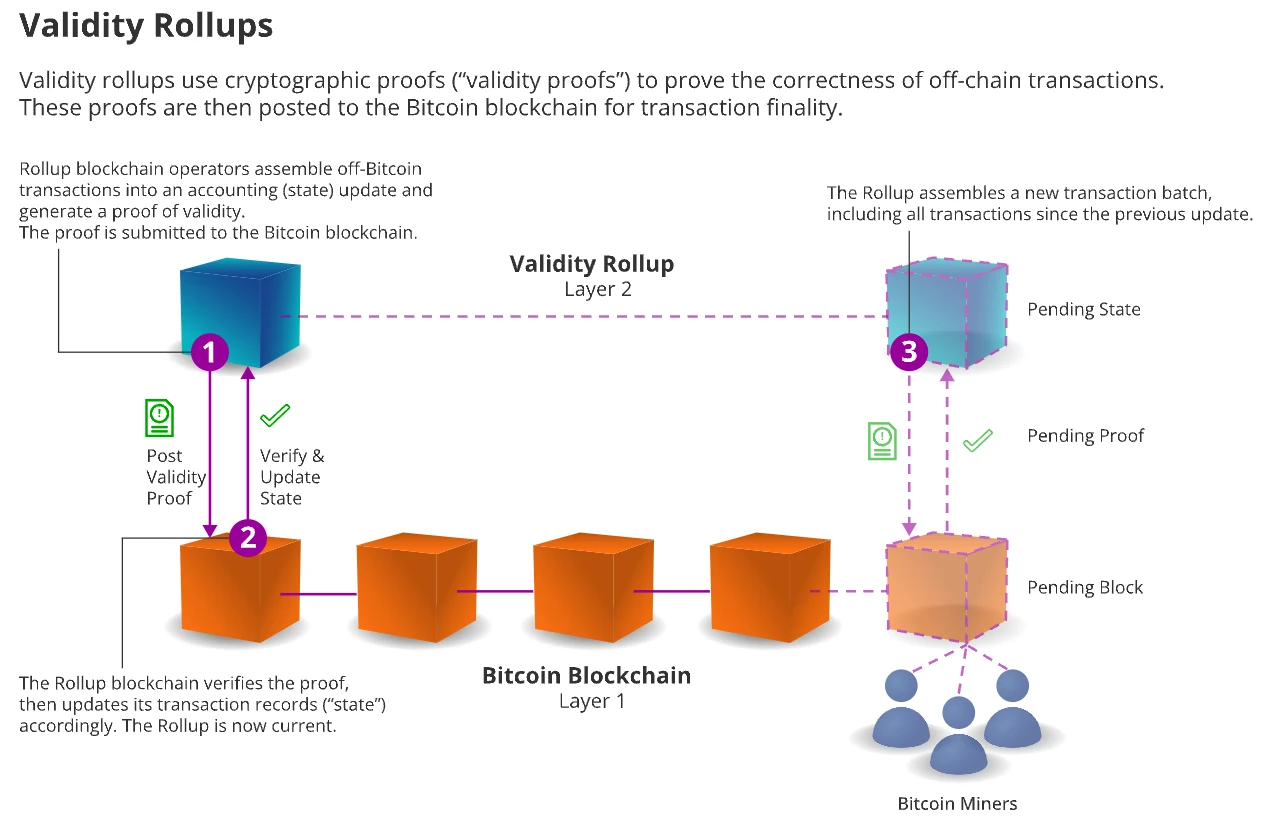
Source: VanEck Research, as of June 25, 2024.
Hailed as the next generation of Bitcoin Layer 2 technology, "Rollup" aims to expand the Bitcoin network and spread its blockchain security attributes to other blockchain platforms. Rollup technology achieves its function by publishing transaction data or verification information on a parent blockchain like Bitcoin or Ethereum. Leveraging publicly verifiable data on the parent blockchain, the security of the Rollup system relies on its parent blockchain. In "Optimistic Rollup," the published data allows external parties to verify the authenticity of transactions, while "Validium Rollup" involves sending transaction proofs of Bitcoin L2 Rollup to Bitcoin and executing them.
The main difference between these two Rollup types lies in the amount of data published and the software requirements. Optimistic Rollup publishes more data to Bitcoin's limited capacity without the need to modify the Bitcoin core software. In contrast, Validity Rollup requires less data to be published but it necessitates an update to the Bitcoin software, typically achieved through a "soft fork." Rollups are seen as the ideal solution for Bitcoin scalability as they enhance off-chain scaling capabilities without compromising Bitcoin's core principles of trustlessness and decentralization. Additionally, they bring more transaction revenue to Bitcoin miners as settlement proofs and data publishing involve multiple transactions. Despite the bright prospects for Rollups, their implementation on Bitcoin still faces significant challenges in terms of the need to modify core software.
Challenges of Aggregation and Software Changes
Updates to Bitcoin software brought the first wave of scalability improvements, although significant, they are still limited. For example, the introduction of Segregated Witness (SegWit) and the Taproot upgrade. SegWit greatly improved the efficiency of Bitcoin transactions by separating transaction signatures from transaction data, allowing each 1MB Bitcoin block to accommodate up to four times the transaction volume. The Taproot upgrade optimized Bitcoin's cryptographic infrastructure, making transactions more compact and faster. These two upgrades enabled the Bitcoin core software to store more transactions and various types of data, with the rise of NFTs and memecoins serving as evidence.
However, achieving sovereign aggregation does not require modification of the Bitcoin software. Despite the massive amount of data published by these aggregations (even after compression), they still limit the scalability potential of Bitcoin. Even with similar compression levels as Ethereum aggregations like Base and Arbitrum, the transaction throughput of Bitcoin is only about 55 transactions per second at full load. To achieve large-scale scalability, significant increases in data compression or the simultaneous creation of multiple aggregations for data publishing are necessary.
Validity Rollup addresses the issue of Bitcoin's data capacity limitation but requires modifications to the Bitcoin core software for execution of verification. Some developers are working on an upgrade solution called BitVM, aimed at enabling Validity Rollup on Bitcoin. BitVM introduces a challenge and response mechanism sent through Bitcoin transactions to verify fraud and validity proofs. This not only expands Bitcoin's capabilities but also enables trustless bridging, replacing centralized BTC representations like wBTC. The development of BitVM is expected to be completed in approximately 18 months, and its implementation will require a soft fork by the Bitcoin community.
Future Outlook: OP_CAT and Contracts
OPCAT is a promising software update that may enable Bitcoin to scale to meet the needs of the global financial system. The introduction of OPCAT increases the complexity of Bitcoin programming, allowing the use of primitive smart contracts called contracts on Bitcoin. Through contracts, software engineers can create the logic required for sovereign and validity aggregations on Bitcoin. Starknet, a second-layer blockchain on Ethereum, has pledged a $1 million grant to researchers studying OPCAT. Starknet also plans to use OPCAT to address the implementation of validity proofs on Bitcoin.
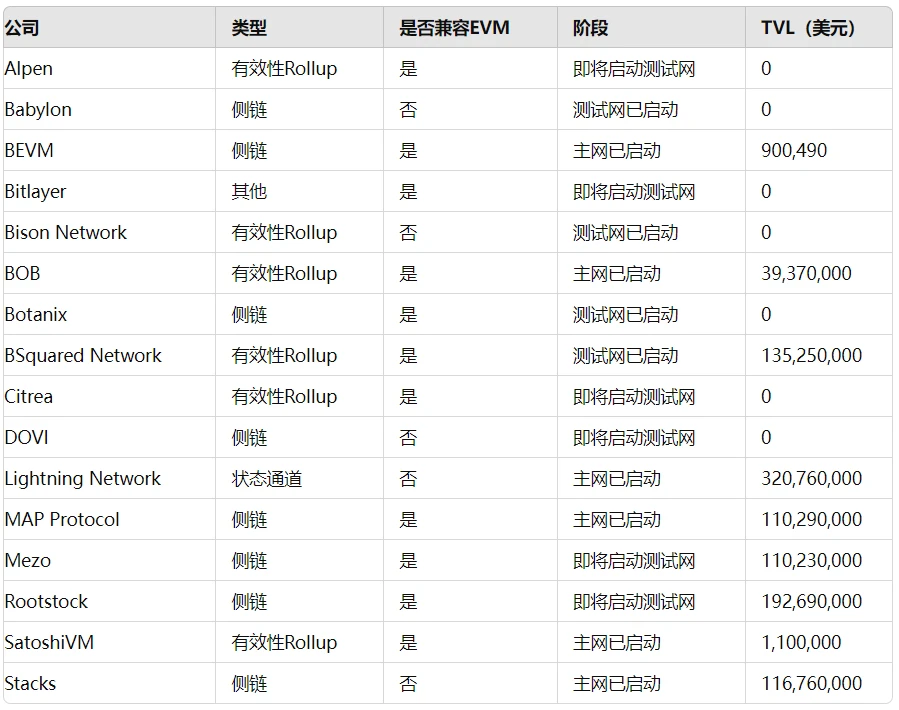
Current Status of Bitcoin L2s
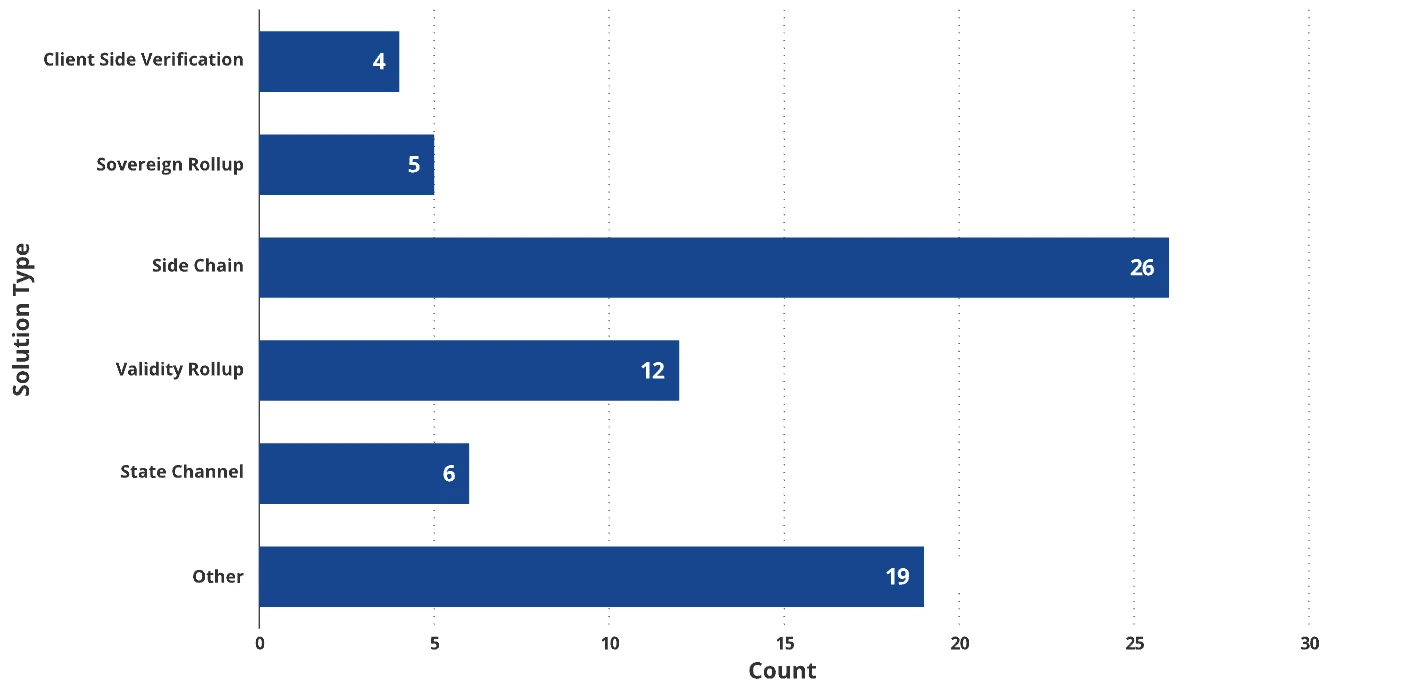
Source: BTCL2.INFO, as of June 24, 2024
Currently, over 73 active projects are developing Bitcoin L2 solutions, with a total locked value (TVL) exceeding $3.61 billion. Although these projects are still in the early stages, only 26 of them have real-time mainnets in operation. Due to the early stage, most projects have not yet shown significant traction. As one of the early leaders, Merlin Chain has the largest Bitcoin L2 TVL, calculated by bridging BTC to the on-chain, with a TVL of $1.33 billion, but its daily transaction volume is only between 50,000 and 80,000 transactions. In terms of activity, it is on par with Cosmos Hub, Cardano, and Gnosis Chain. The lack of early traction for Merlin Chain is due to its most popular application, MerlinSwap, having a TVL of only $2.85 million.
The competition in the current Bitcoin L2 space is mainly focused on attracting TVL and developers. TVL mainly comes from large holders such as independent whales, miners, and investment funds. Private investment rounds offer incentives for investors to introduce BTC to L2. Business development operations mainly target large BTC and other cryptocurrency holders, ensuring the realization of promised TVL. Attracting developers is also another important strategic goal, with about 40 projects supporting EVM aiming to recruit Ethereum developers. Currently, there are approximately 312 developers working on BTC L2, while Ethereum L2 has 960 developers, and Ethereum has 966 developers.
Although there are no clear winners in the Bitcoin L2 space yet, as many projects have not yet launched or conducted official marketing, we are focusing on the 16 projects that we believe have high potential for Bitcoin scalability. We evaluate these projects based on the reputation of their builders, supporters, and promised TVL (if any).
The Huge Potential of Bitcoin Layer 2
Regarding the 2050 Bitcoin valuation analysis
To accurately assess the value of Bitcoin in 2050, this analysis adopts a simple equation based on the velocity of money circulation, covering three core factors:
The total volume of domestic and international trade settled in Bitcoin (GDP);
The active circulation supply of Bitcoin (BTC);
The velocity of BTC transactions.
Basic Assumptions for Valuation
For the 2050 forecast, a key assumption is that Bitcoin will become a significant force challenging the four major currencies and will be integrated into the international monetary system. It is expected that BTC will be widely used in international trade as a primary medium of exchange and a valuable store of wealth. This trend forms a positive feedback loop similar to Gresham's Law: as the utility and value of BTC increase, central banks and long-term investors will tend to increase their holdings of BTC, thereby reducing the floating supply in the market.
First, we calculated based on the 2023 global trade and world GDP benchmark data and their growth forecasts. We assume that due to the resurgence of populist movements and desires for trade protectionism, trade growth will be lower than the average growth rate of global GDP—2% to 3%. Furthermore, we predict that Bitcoin will account for a certain percentage in cross-border payments, based on our outlook for the use of other currencies in international trade. Given the expected decrease in market share of the four major currencies due to deteriorating economic and fiscal fundamentals and property rights erosion, we anticipate a 20% reduction in market share, with the renminbi, BTC, emerging market currencies, and gold taking their place. From the perspective of a medium of exchange, we believe that BTC will account for 10% of cross-border payments and 5% of domestic trade.
In this scenario, we expect that 2.5% of central bank assets will be held in the form of BTC. Considering its importance as a store of value, we also anticipate that 85% of BTC will effectively be removed from the circulating supply due to investor demand for its store of value properties. Assuming a circulation velocity of BTC of approximately 1.5, which is the average circulation velocity of the US currency since the global financial crisis, we calculate the value of Bitcoin to be $2.9 million. Based on the overall global asset base, this valuation will account for 1.66% of all financial assets, whereas we estimate today's share to be only 0.1%.
Bitcoin Price Scenarios in 2050: Base Scenario, Bear Market Scenario, Bull Market Scenario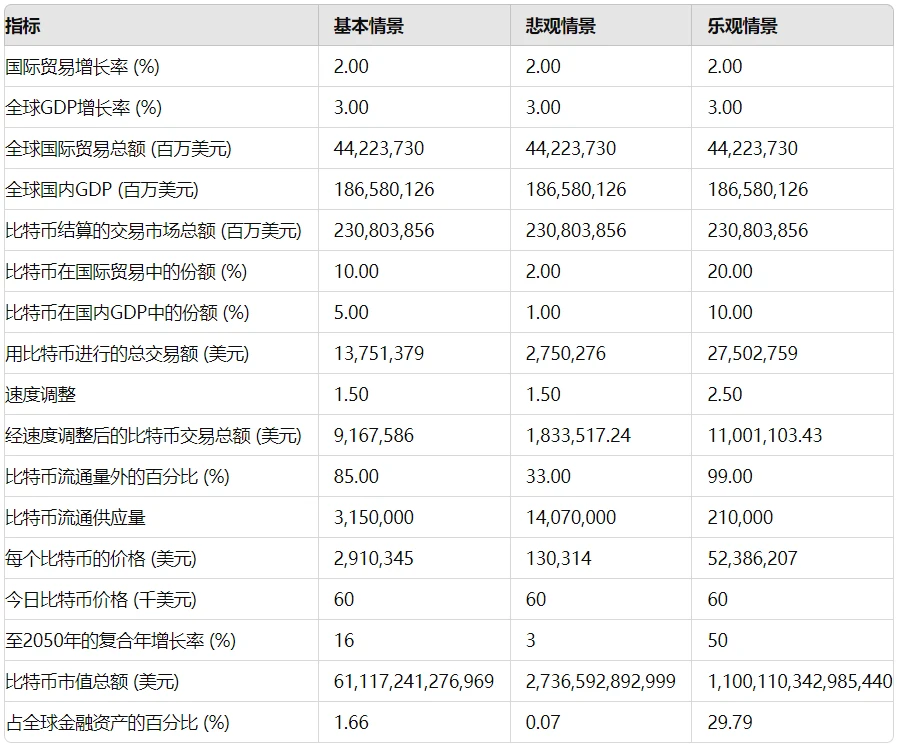
Valuation Scenarios for Bitcoin L2
We have comprehensively evaluated the Bitcoin Layer 2 space based on the market share forecast, applied to the valuation system of the Smart Contract Platform (SCP) in 2050, and drawing on our analysis methods for Solana, Ethereum, and its second-layer blockchains. Our predictions take into account the total addressable market (TAM) revenue of enterprises that will adopt public SCPs such as Ethereum and Bitcoin L2 in the future. Based on this data, we estimate the activity fees that SCPs will charge from enterprises deploying their services, similar to the platform fee model used by Apple's App Store or Amazon's online marketplace.
Bitcoin is not only a driving force behind the development of blockchain technology but also the most critical blockchain platform. As a store of value, Bitcoin has demonstrated strong product-market fit. Currently, key members of the Bitcoin community are working to position Bitcoin as a settlement system for smart contract platforms, a strategy similar to Ethereum. Given Bitcoin's strong brand influence and its more significant success compared to Ethereum, we anticipate that Bitcoin L2 will capture a 50% market share in the smart contract platform market.
Assuming Bitcoin becomes a reserve asset, we expect its share in the smart contract platform market to reach approximately 50%. We anticipate that the Bitcoin L2 space will encompass thousands of L2 projects, including state channels, aggregation technologies, and potential new types of technologies in the future. Assuming BTC becomes a significant part of the international monetary system, financial institutions worldwide will rush to establish their own L2 networks to support their BTC-related activities such as trading, exchange, and lending. Some of these solutions may rely on centralized trust-based strategies. Nevertheless, we believe that the value proposition of Bitcoin L2 will be diluted unless it maintains its decentralized characteristics.
We can even predict the emergence of a partial reserve system similar to the early banking business before fiat currency appeared. In this scenario, most blockchain technologies may transform into Bitcoin L2, leveraging BTC as a valuable asset. In any case, we have sufficient reason to believe that BTC has become one of the most important assets in the world, and Bitcoin L2 has tremendous potential for value appreciation by enhancing the utility of Bitcoin. We predict that the valuation of the entire L2 ecosystem will reach $76 trillion, accounting for approximately 12.5% of the value of Bitcoin itself.
The valuation scenarios for Bitcoin L2s unfold as follows: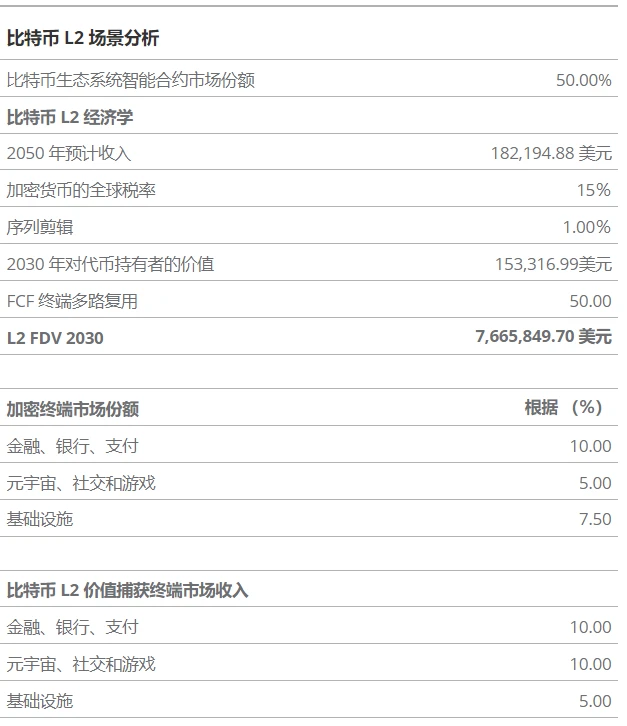
Bitcoin Investment Risks
Bitcoin has demonstrated extraordinary resilience over multiple economic cycles since its inception over 15 years ago. Despite becoming a critical store of value asset, the price predictions for Bitcoin over the next 25 years are based on the assumption that an increasing number of people worldwide will view Bitcoin as a medium of exchange. In fact, the future value of Bitcoin lies in its widely perceived ideal form of currency, and its potential for success lies in its unique position in the form of currency. The fragility of Bitcoin's value stems from subjective perceptions, which form the cornerstone of its existence. However, we believe that the memetic value of Bitcoin as a robust currency is the most solid foundation for its survival.
The main risks to our Bitcoin thesis include:
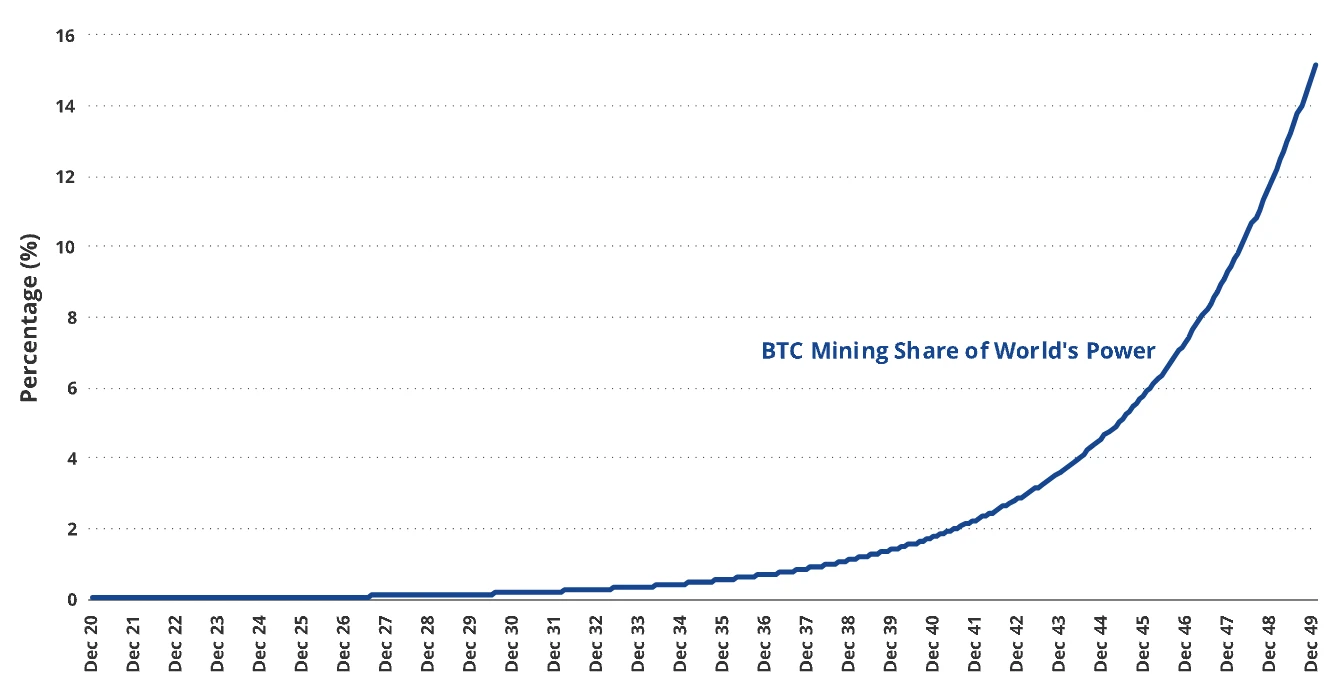
Sustainability of Bitcoin mining: While we reserve judgment on most of the premises and conclusions regarding "ESG," it must be recognized that there is implicit electricity demand for future Bitcoin mining. This is particularly concerning from the perspective of the cost of maintaining network security. Since 2018, the hash rate of the Bitcoin network has achieved a compound annual growth rate of 71.7%, while the price has achieved a compound annual growth rate of 24%. According to our $2.9 million BTC scenario forecast, the compound annual growth rate of the hash rate is 48%, and the hash rate is expected to increase from 600M TH/s to 13.1B TH/s. Assuming a 12% annual decrease in energy consumption per TH/s of mining efficiency, the total energy consumption of the Bitcoin network will reach 9.181M GW/h, approximately 2.16 times the capacity of the US grid in 2022, equivalent to 15% of the projected global electricity generation in 2050. We predict that our Bitcoin thesis may be difficult to achieve without new innovations in chip design and further breakthroughs in energy production costs.
Expected BTC consumption to reach 15% of the world's electricity supply in 2050
Failure of Miner Economics: Bitcoin, like a financial shark, requires a continuous buying pressure to balance the selling pressure of miners, as miners face the dual pressures of fixed and variable costs. With the decrease in Bitcoin's inflation rate, on-chain transactions must increase to support the demand for BTC and cover the expenses of miners.
Inability to Scale: If Bitcoin fails to achieve sufficient scalability, it cannot become a significant medium of exchange, and our core argument about its rapid rise will collapse.
Competition from Other Cryptocurrencies: Currently, we are in the early stages where competition is creating more robust, permissionless currencies. While BTC is trusted due to its potential massive market cap exceeding $1 trillion, ecosystems competing to carve out market share from Bitcoin are emerging. These competing blockchains offer higher processing capabilities and can onboard more users into networks similar to the current financial system. While many blockchains may not promote their native currency as money and may even contribute to the promotion of BTC, many of them are likely to attempt to position their tokens as perfect money. Ethereum, for example, views ETH as the currency in its ecosystem and inevitably competes with Bitcoin.
Community Split: We discuss the challenges BTC faces and the costs it needs to pay to miners for long-term stability. The BTC community consists of individuals who firmly believe in its long-term potential. However, there are significant differences among them regarding how to create a sustainable environment for Bitcoin. This controversy could lead to another community split, triggering one or multiple Bitcoin hard forks, resulting in the differentiation of BTC's value in the new networks.
Catastrophic Changes in Bitcoin's Monetary Policy: To maintain the long-term stability of BTC, it may be necessary to impose taxes on BTC holders. This is because the circulation speed of BTC is extremely low, only 1/30th of the US dollar, which cannot meet the economic needs of Bitcoin miners. The possible consequence is the "taxation" of fixed BTC through methods such as inflation. While this new form of "taxation" may not destroy BTC, it will undermine the inherent concept of permanent monetary policy. Changes in Bitcoin's policy, like Caesar crossing the Rubicon, may lead many BTC holders to question whether sound monetary policy will continue to deviate from its established course.
Government Bans and Attacks: Many national governments firmly believe that the currency system should remain under federal control. If BTC achieves massive success, countries worldwide are likely to coordinate actions to prohibit its circulation. Banning Bitcoin is not difficult due to its public ledger and the traceability of many wallets to IP addresses. Considering the US's authority in currency control, they can easily provide reasons to shut down domestic mining operations. Due to the dependence of Bitcoin miners on high prices, an organized attack, even just a verbal announcement, is enough to severely disrupt Bitcoin's stability. While Bitcoin may survive, organized government actions will undoubtedly reduce its long-term development potential.
Control by Oligarchic Financial Entities: In January 2024, the cryptocurrency and Bitcoin community celebrated the approval of Bitcoin spot ETFs. As of the writing of this article, BTC spot ETFs hold over 865,000 BTC, approximately 4.1% of the total BTC supply. Over time, we believe that the BTC held by large financial institutions will significantly increase. If large financial institutions hold most of the BTC supply, it may lead to many negative impacts. One of them could be Bitcoin increasingly coming under the control of large financial institutions and governments. A more far-fetched possibility is governments seizing BTC from these centralized entities and dumping it in the market to destroy Bitcoin's economic system. Another potential risk is a financial crisis triggered by the re-collateralization of BTC through certain lending networks, exposing everyone to the "naked swim." Meanwhile, the financial control of large investment firms over BTC may change Bitcoin's culture and lead to new policies favoring large holders at the expense of small holders.
Theft and Hacking Attacks: As permissionless, pseudonymous assets, assets like BTC belong to anyone who can control the private keys to move them. Hacking attacks targeting Bitcoin are frequent, primarily aimed at centralized institutions holding large amounts of BTC. With the upgrade of Bitcoin software and the emergence of second-layer solutions, the surface area for hacking attacks is expected to increase significantly. If theft by actors from sanctioned countries continues, this may provide more reasons for governments worldwide to ban Bitcoin.
Financial Attacks: Financial overreach leads to high rewards for financial professionals who have the ability to disrupt poorly designed economic systems. This dynamic has already triggered financial attacks in the G7 country's currency system. The disruption of the Bitcoin economic system could bring profits far exceeding the disruption of the Bank of England. The economic security of Bitcoin is directly related to the amount spent on "protecting" its network. As the miner equity value hovers around 1.2 EV/S, meaning the value of enterprises to miners is approximately $21 billion (assuming 1.5 times EV/S is generous). Meanwhile, the market value of BTC is $1.2 trillion. A direct financial attack (a simple trick hated by BTC holders!) would be to buy all BTC miners, short BTC worth hundreds of billions of dollars, and then shut down the mining machines. The resulting chaos could bring returns far exceeding the cost of purchasing mining machines. Currently, there have been no liquidity or secure counterparties to complete this trade, but this situation may change.
Core Software Failures: The simplicity of Bitcoin software enhances its ability to resist hacking attacks. The simpler the system code, the less likely there is a vulnerability that could destroy Bitcoin. Bitcoin may need at least two significant software upgrades to remain viable. As mentioned earlier, Bitcoin must change its economic system to achieve long-term sustainability for miners. Additionally, Bitcoin must upgrade its encryption scheme to counter the rise of quantum computing. While the breakthrough in quantum computing may still be years away, Bitcoin will eventually have to change critical components of its system by introducing quantum encryption technology. This is because quantum computing will render current encryption techniques insecure and easily crackable. Regardless of how these major upgrades are carried out, the introduction of new vulnerabilities during Bitcoin's core software upgrades could threaten its long-term success.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



