Author: IOSG Ventures
Background
Two years ago, at the beginning of the rise of modular blockchain narratives, we wrote about our views and predictions on the data availability (DA) track. As we expected, the narrative of modular blockchain has prevailed and driven infrastructure innovation, enhanced network interoperability, and promoted more cooperation and integration within the ecosystem. Various Rollup-as-a-Service (RaaS) solutions (Altlayer, Caldera, Conduit, Gelato) have begun to emerge. The following image shows the interface of the Rollup development tool Conduit, demonstrating that deploying Rollup and selecting DA solutions has become exceptionally simple and convenient.
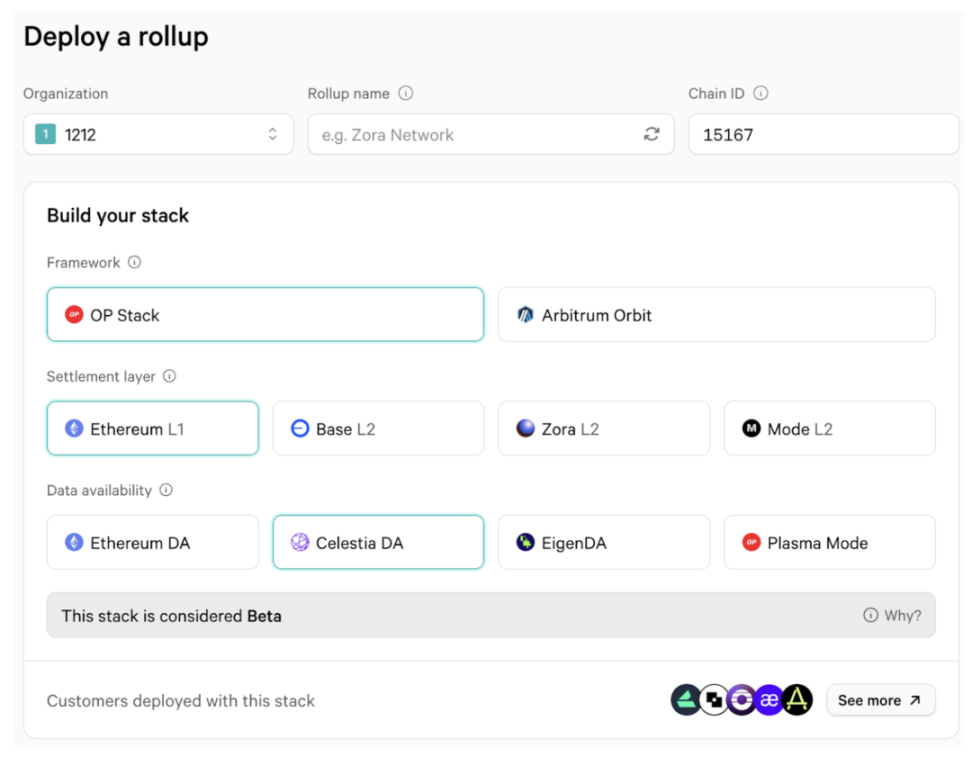
Source: Conduit
Over the past two years, alternative DA solutions (Alt-DA) such as Celestia, EigenDA, Avail, and NearDA have made significant progress, each demonstrating unique technical advantages and market share. Meanwhile, with the launch of Ethereum EIP-4844, which introduces blobs to replace calldata, the cost of using Rollup on the Ethereum native DA layer has been greatly reduced. Today, developers and projects face more trade-offs when choosing a data availability layer. This article will track and analyze existing DA solutions, delve into their performance costs, technical features, and market performance, and present our views and thoughts on the future development of the DA track.
1. Adoption of Existing DA Solutions
The use of Ethereum's native DA on-chain solutions for Rollup is mainly concentrated in mainstream Layer 2 solutions that have transitioned from calldata storage to Blob compatibility, including Arbitrum, Optimism, Base, Starknet, zkSync, and Scroll. Rollup uses Ethereum as the DA layer, with data being verified and stored by Ethereum's full nodes, benefiting from Ethereum's security, decentralization, continuity of protocol upgrades, and economic incentives. Comprehensive L2 solutions play a crucial role in Ethereum's ecosystem and require the above-mentioned legitimacy brought by native DA as a core differentiator. (Vitalik believes that the core of rollup is an unconditional security guarantee: even if everyone is against you, you can still withdraw your assets. If data availability depends on external systems, this equivalent security cannot be achieved.)
However, publishing data to the Ethereum mainnet comes with high costs, especially before EIP-4844 (calldata cost 16 gas per byte, and just in December 2023, L2 spent over 15,000 ETH on DA costs). Therefore, various Alt-DA off-chain solutions have emerged, such as the launched Celestia, EigenDA, and the upcoming Avail, which reduce the cost of data storage and transmission through different technical means, such as DAS, erasure coding, KZG commitments, etc.
Among them, Celestia, as a modular blockchain specifically designed for DA, has become the leading project in the DA track since its mainnet launch in October 2023. Its main target customers include projects requiring modular architecture: cross-chain bridges, settlement layer solutions, DeFi projects, games, sorters, and not limited to Layer 2 solutions in the Ethereum ecosystem. Its existing clients include Omnichain DEX protocol Orderly, modular L2 Manta Pacific customized for EVM-native ZK applications, L3 Hokum based on Base, and DEX Lyra and Aevo focusing on derivative trading. Celestia's advantage as a modular design DA layer pioneer not limited to a specific ecosystem has made it the preferred choice for many emerging Layer 2 projects.
EigenDA, developed by EigenLabs, utilizes EigenLayer's restaking mechanism to provide efficient, secure, and scalable DA service solutions, to some extent inheriting the security and massive validator network of the Ethereum mainnet. EigenDA focuses on providing high-performance DA solutions for the Ethereum ecosystem. As the first active validation service (AVS) on Eigenlayer, EigenDA went live in April along with the Eigenlayer mainnet. Its existing client base is also diverse, including Ethereum L2 Swell, Celo, Mantle Network, and several other AVSs built on Eigenlayer, such as decentralized computing stack Versatus, Polymer, DEX protocol DODO, and CyberConnect as a Social L2.

Source: EigenDA
2. Balancing Native DA (EIP-4844) and Existing Alt-DA
2.1 Ethereum Native DA
A brief review of the development changes of Ethereum's native DA solutions: before the Cancun upgrade, Rollup mainly used calldata as the means of data storage and transmission. Due to permanent storage and high network congestion, high costs became the main obstacle to expansion and adoption. EIP-4844, as a mainnet upgrade, introduced Blob as a new data structure. Blobs can accommodate large amounts of data, but correspondingly increase the storage burden on nodes. Over time, storage requirements will continue to increase, potentially leading to high hardware requirements for running nodes, thereby compromising decentralization. Therefore, Blobs only need to be stored for about 18 days (4096 epochs) before being deleted.
Since Blobs only need temporary storage and use a separate fee market, after the implementation of EIP-4844, the average daily DA cost before and after the adoption of blobs by major L2 solutions has decreased by around 99% (Scroll & Starknet take the average of the 30 days before and after). The cost reduction is more significant for OP rollup Layer 2 compared to Zk Rollup due to the different types of data uploaded (transaction data or state differences).
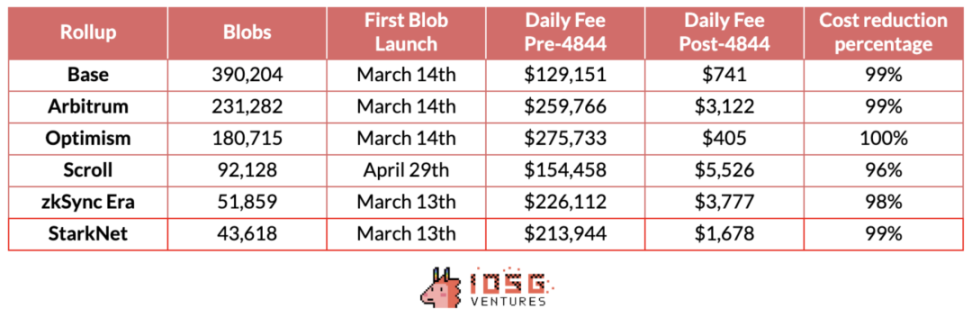
Source: Dune & Growthepie
Blob Capacity, Storage Characteristics, and Pricing Mechanism
Blob's capacity and storage characteristics:
Each block can accommodate up to 6 Blobs
Each Blob can store up to 128KB of data (even if the 128KB space is not fully utilized, the sender still needs to pay the full Blob fee)
The new blob gas market operates similarly to EIP-1559, adjusting the base fee based on supply and demand changes.
- If the number of blobs in a block exceeds the target (currently 3), the base fee for blobs will increase.
- If the number of blobs in a block is less than the target, the base fee for blobs will decrease.
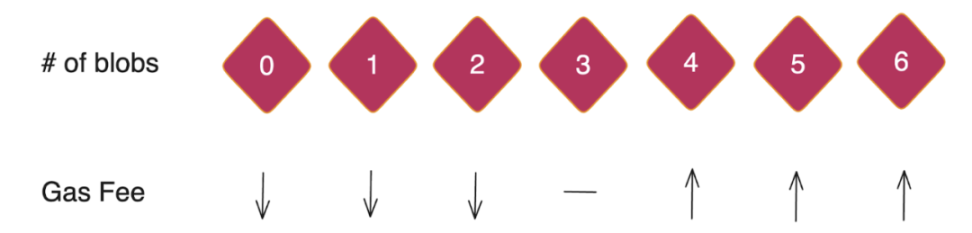
Source: IOSG Ventures
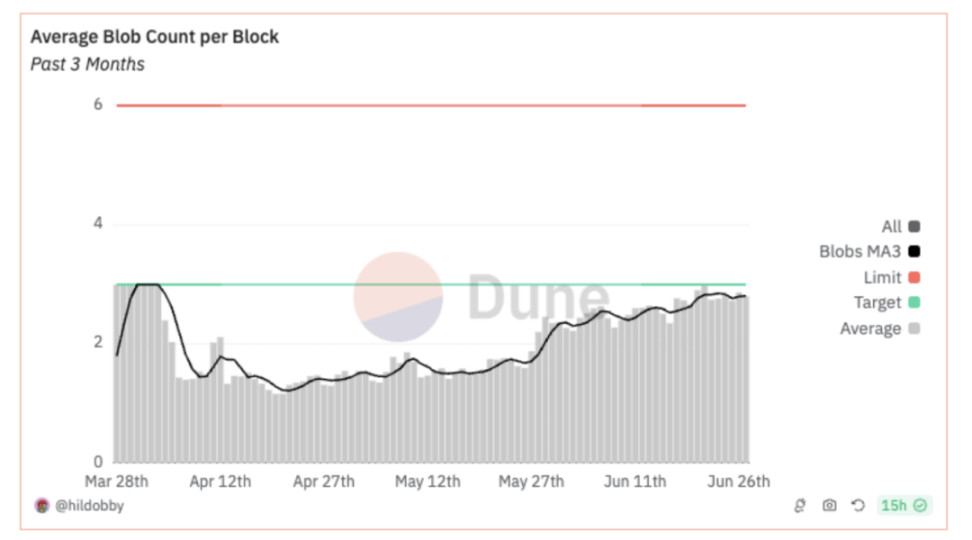
Source: Dune / Ethereum block blobs 3-day moving average
L2 primarily uses the newly introduced type 3 transactions, adding the maxfeeperblobgas and blobversionedhashes fields to previous transactions, representing the maximum fee per blob gas that users are willing to pay and the hash output list of kzgtoversioned_hash.
This new pricing mechanism means that type 3 transactions still require the maxfeepergas and maxpriorityfeeper_gas fields and are constrained by the existing EIP-1559 market. In addition to blob space, type 3 transactions still need to pay for the EVM space they use.
Therefore, there is still contention for block space with blobs, leading to cost uncertainty, as the blob gas fee market dynamically adjusts based on demand in each block.
As a general-purpose chain, Ethereum's weakness lies in the uncertainty of block space—sudden on-chain activities such as NFT minting and airdrop claims can cause congestion, leading to increased blob pricing, making it difficult for Rollup to estimate cost basis. This uncertainty in Rollup expenditure budgets leads to unstable profit margins, raising barriers to entry for new projects in the early stages, making it difficult for project teams to determine whether Ethereum DA can be a long-term solution. In the majority of the time shown in the graph, using blobs for data transmission is approximately 98% cheaper than using calldata, but in a specific period, using blobs is only about 59% cheaper than using calldata.
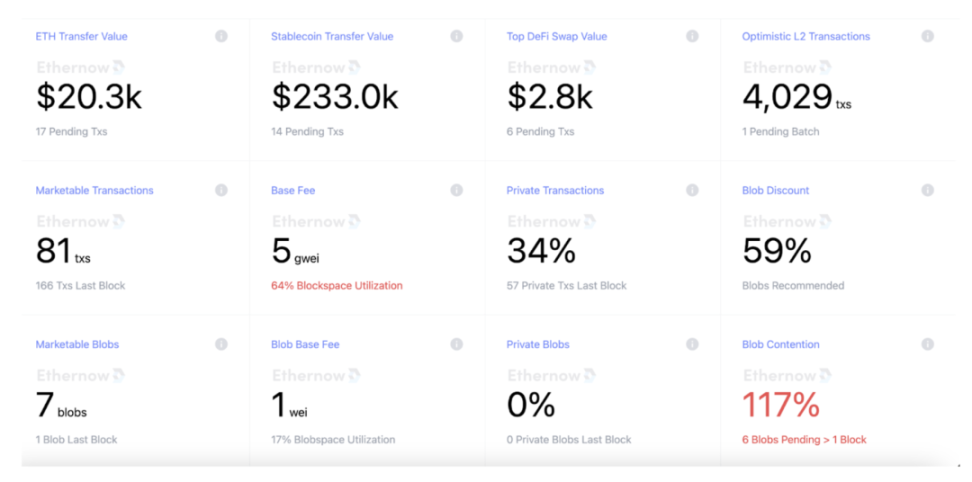
Source: Ethernow
Let's calculate the cost of two blob transfers as an example:
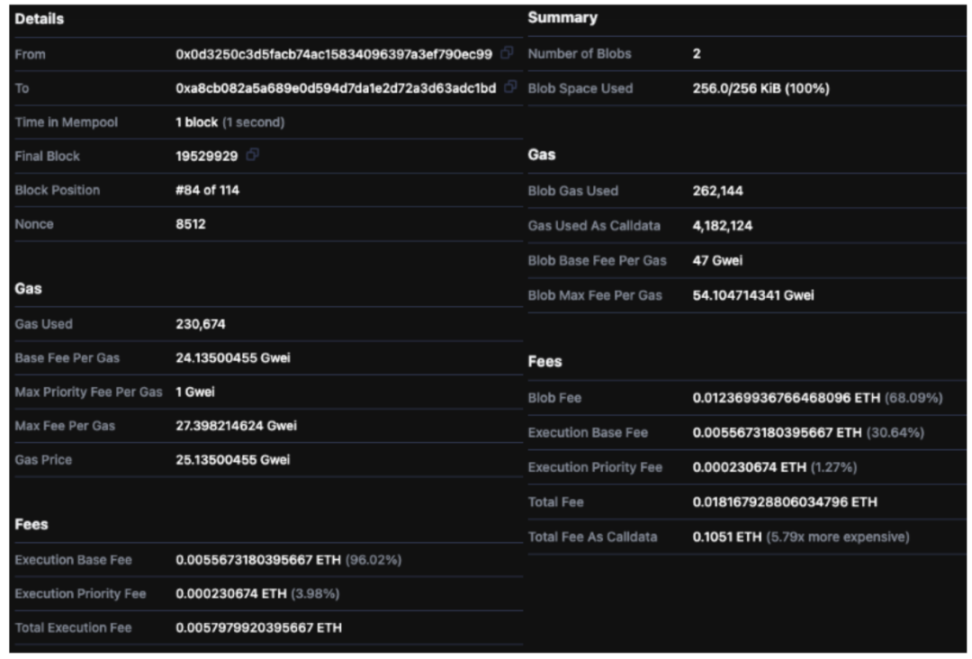
Source: Ethernow
The image shows a type 3 transaction of Zksync's Validator Timelock in a block on March 28, 2024. Based on the blob cost, let's break down the base fee and priority fee to calculate its data cost:
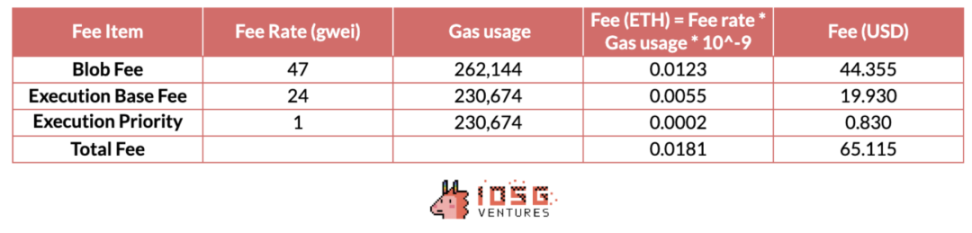
Assuming the price of Ethereum is $3600, the data cost of using a 1Mib blob at that time is approximately:
4×0.018ETH×3600USD/ETH = 259.2USD
Now let's look at a type 3 transaction of zksync era on June 24:
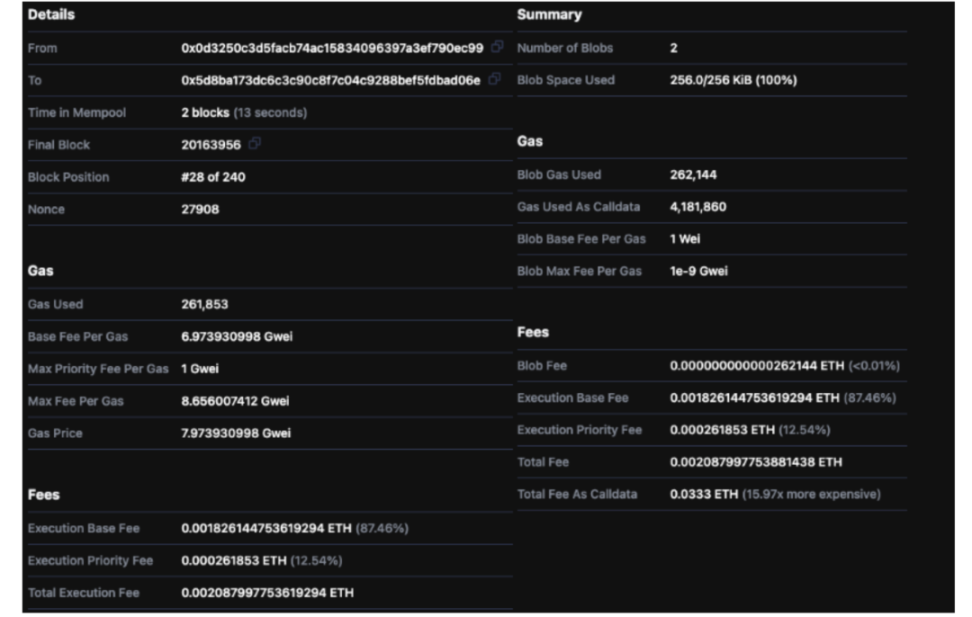
Source: Ethernow
At that time, there was a slight decrease in mainnet activity. Let's break down the data cost:
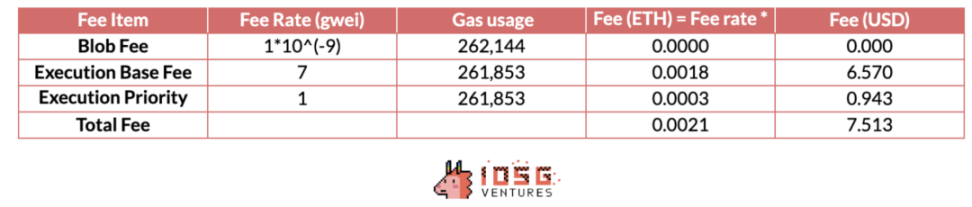
The data cost of using a 1Mib blob at that time is approximately:
4×0.0021ETH×3600USD/ETH = 30.24USD
This shows the uncertainty and relatively high cost of using blobs for data transmission. However, for a rollup, the stability of cost structure is a key consideration when choosing a DA solution.
2.2 Celestia
As the pioneer of modular blockchain, Celestia focuses on providing the DA layer and consensus layer, separating the execution layer to specifically optimize DA functionality, improving efficiency and scalability. As an off-chain solution L1, Celestia has many different technical features compared to using Ethereum's on-chain methods, reducing the cost of data availability and providing higher flexibility and scalability. The modular design of Celestia allows developers to freely choose the execution environment, not limited to a specific virtual machine (VM), enabling Celestia to support various application scenarios and meet diverse needs.
For Rollup to integrate Celestia as the DA layer, it needs to submit transaction data (Data Blob) generated by the execution layer to the Celestia network, rather than the original Layer 1 (Ethereum), to ensure data availability for verification and transactions. Celestia's data availability sampling (DAS) technology re-encodes block data using a two-dimensional RS erasure coding scheme, allowing light nodes to verify data availability through multi-round random sampling with only a small portion of the block data downloaded, and allowing multiple nodes to process different data parts in parallel, improving overall efficiency.
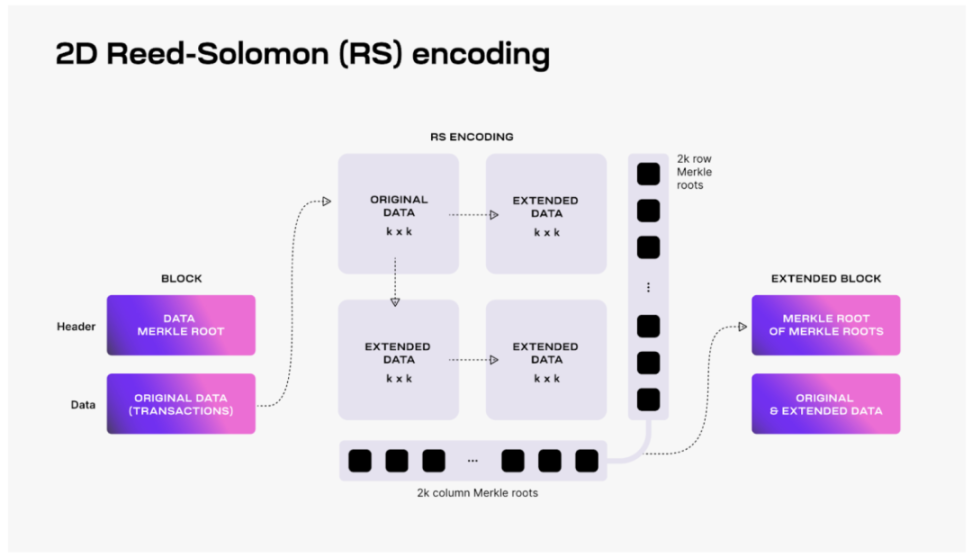
Source: Celestia.org
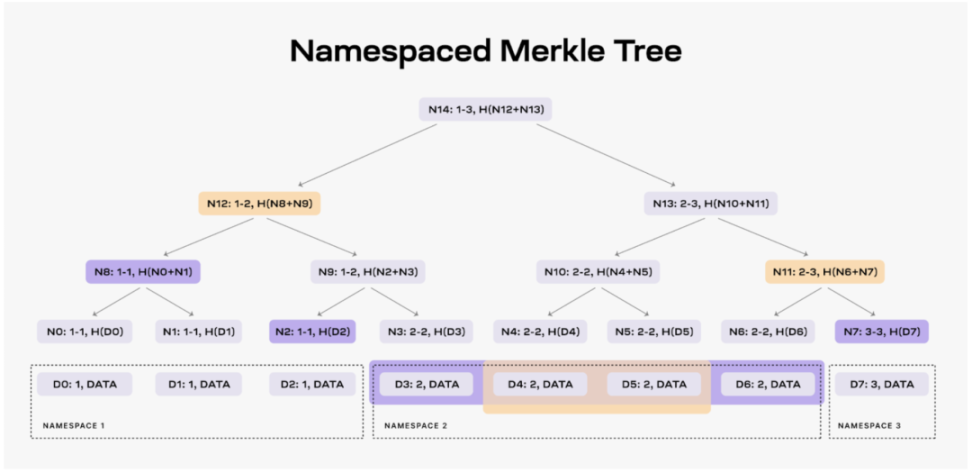
Another key technology introduced by Celestia is the Namespace Merkle Trees (NMTs), allowing different rollups to download only the transaction data relevant to them, thereby improving data processing efficiency. NMTs not only reduce data redundancy and improve system performance but also provide developers with a more efficient way of data processing.
In terms of security, Celestia is based on the Tendermint consensus mechanism, where validators reach consensus on Data Blob to ensure data availability and consistency in the network. It can tolerate up to one-third of validator nodes failing or engaging in malicious behavior. By staking TIA tokens, Celestia's validators are economically incentivized to ensure honest behavior and penalize malicious or improper operations, thereby ensuring network security. Currently, Celestia's Total Value Locked (TVL) is approximately $64.4 billion, with 100 full nodes.
Regarding scalability, Celestia's block size can be dynamically adjusted based on the number of active light nodes in the network. As more nodes join, Celestia can safely increase block size, theoretically increasing throughput and scalability infinitely. Current data shows that its data throughput is approximately 6.67 MB/s.
Celestia's Blob capacity, storage characteristics, and pricing mechanism:
For cost comparison, let's discuss Celestia's performance and pricing mechanism. When users submit data on Celestia, it is done through Blob transactions (BlobTx), with fees consisting of blob space costs and gas fees.
Specifically, the maximum size limit for each Blob is slightly less than 2 MiB (1,973,786 bytes), and each block can contain multiple Blobs, depending on the total block size limit. The current maximum block size is 64x64 shares (approximately 2 MiB), with a total of 4096 shares, where one share is reserved for PayForBlobs (PFB) transactions, and the remaining 4095 shares are used for data storage. Celestia's fee market is similar to Ethereum's EIP-1559 mechanism, using a priority memory pool based on gas prices. Transactions with higher fees are prioritized by validators, with fees consisting of a fixed fee per transaction and a variable fee based on the size of each Blob.
According to comprehensive statistics on rollup data on celenium (as of June 17), for various clients integrating Celestia, the cost of using Celestia's DA ranges from 0.02-0.25 Tia/Mib, equivalent to a price of $TIA on June 17 ($7.26). The DA costs for several major clients range from $0.15 - $1.82/MiB. Therefore, compared to native DA on the Ethereum chain, Celestia provides a competitive and stable cost structure.
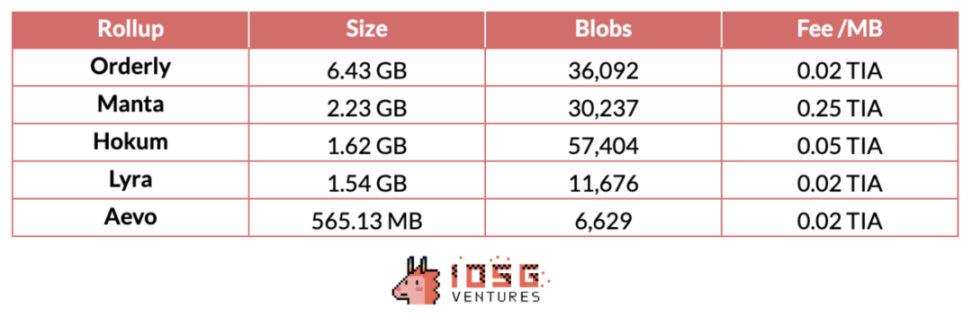
Source: Celenium
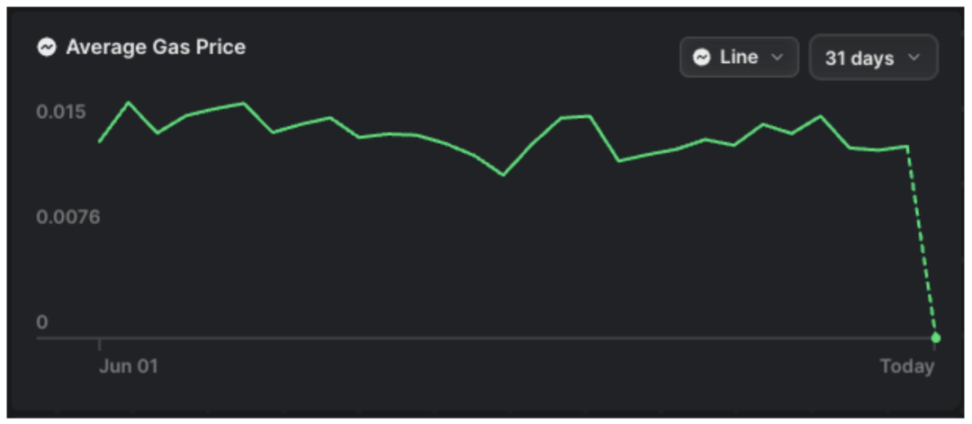
Source: Celenium, gas price stabilizes at around 0.015UTIA (1 uTIA = TIA × 10 − 6)
However, Celestia itself is a Layer1 blockchain network that requires P2P network broadcasting and consensus for Data Blob. Although light nodes can use DAS to ensure data availability, the network still places high demands on its full nodes (128 MB/s download and 12.5 MB/s upload), posing obstacles to decentralization and future throughput improvements. In contrast, EigenDA uses a different architecture—no need for consensus or P2P network.
2.3 EigenDA
As an Active Verification Service (AVS) built on EigenLayer, EigenDA utilizes re-staking mechanisms to leverage Ethereum's security (without introducing a new set of validators, Ethereum validators can freely choose to join, and EigenDA's re-staked nodes are a subset of Ethereum nodes) to ensure data availability, directly leveraging existing infrastructure. Its main workflow involves the Rollup sequencer generating Blob Data and sending it to the Disperser (operated by the rollup itself or a third party, such as EigenLabs). The Disperser shards the Blob Data, generates erasure codes and KZG commitments, then publishes them to EigenDA nodes, which verify Attestations and ensure data availability. After verification, nodes store the data and send the digital signature back to the Disperser. Finally, the Disperser collects the signatures and uploads them to the EigenDA smart contract on the Ethereum mainnet for final aggregate signature correctness verification.
The core idea is still to reduce the data storage and verification computational requirements on nodes using technology. However, EigenDA chooses to use KZG commitment verification technology consistent with Ethereum upgrades. Additionally, EigenDA does not rely on consensus protocols and P2P propagation, using unicast to further improve consensus speed.
To ensure that EigenDA nodes have indeed stored data for availability, EigenDA uses the Proof of Custody method. If any lazy validators appear, anyone can submit proof to the EigenDA smart contract, which will be verified by the smart contract. If successful, the lazy validators will be slashed.
Therefore, EigenDA's solution processes are all conducted on Ethereum, with Ethereum providing consensus assurance, thus not being limited by the low throughput of consensus protocols and P2P networks. Nodes do not need to wait for sequential ordering and can directly process data availability proofs in parallel, greatly improving network efficiency.
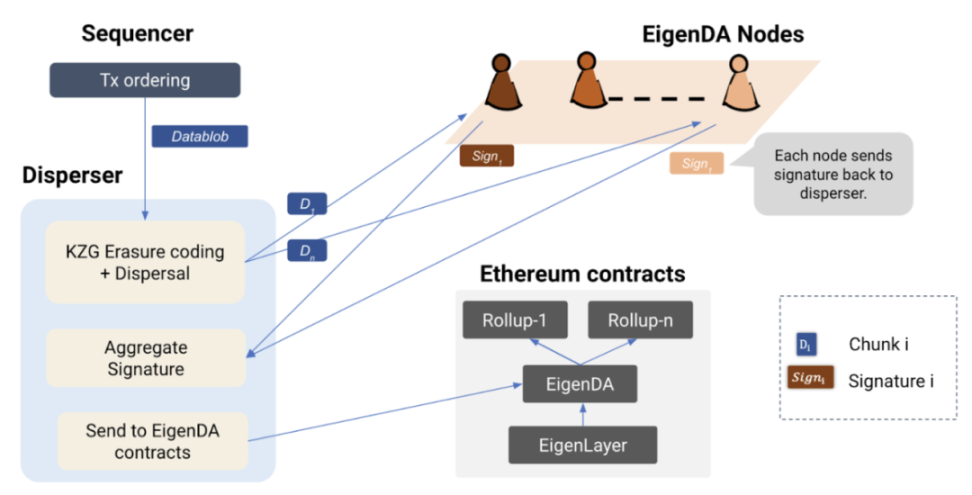
Source: Eigenlayer
EigenDA's capacity performance and costs:
EigenDA currently has 266 node operators. Its maximum throughput target is 10Mbps. Based on a 7-day average, EigenDA's data throughput is 0.685Mib/s, with data storage and transmission costs of approximately 0.001Gas/Byte. Assuming a gas cost of 10gwei and an Ethereum price of $3600, the cost of 1MB of data is approximately $0.038. The total staked TVL is 3.33M ETH, close to $12 billion.
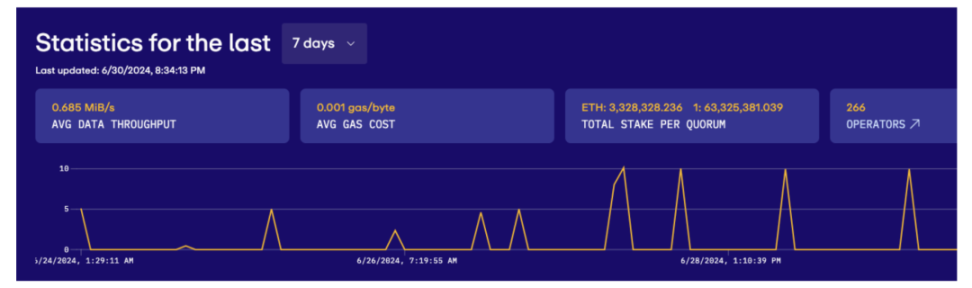
Source: EigenDA.xyz
Comparative analysis of Celestia vs. EigenDA
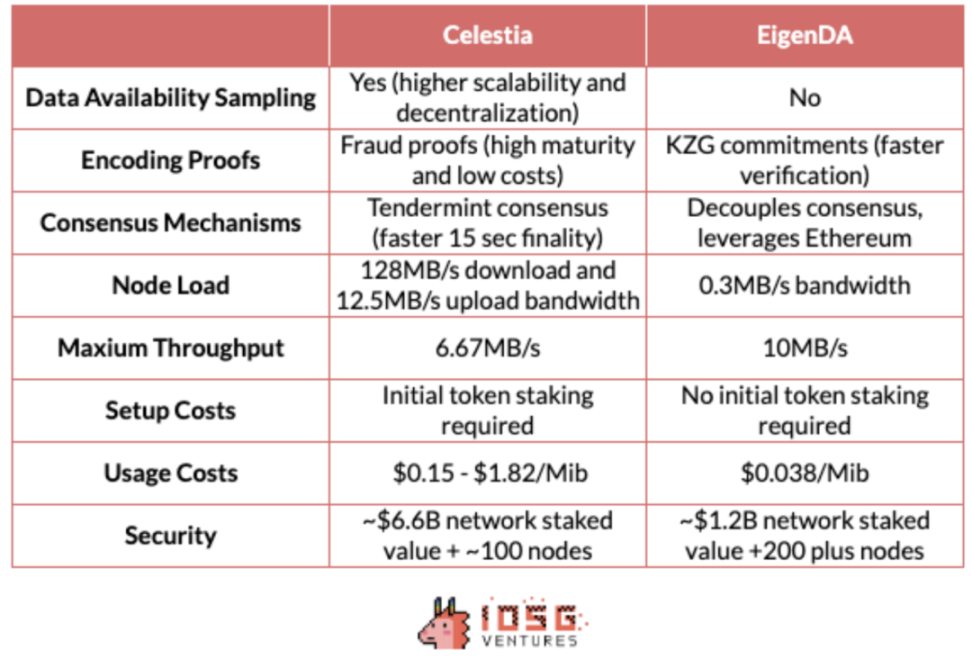
From a technical perspective, Celestia and EigenDA differ in several aspects. Firstly, in terms of node load, Celestia's full nodes need to handle broadcasting, consensus, and validation, with a download bandwidth requirement of 128MB/s and an upload bandwidth requirement of 12.5MB/s, while EigenDA's nodes do not handle broadcasting and consensus, with a bandwidth requirement of only 0.3MB/s, and it can use a subset of Ethereum nodes. Secondly, in terms of throughput, Celestia's maximum throughput is approximately 6.67MB/s, while EigenDA aims to achieve a maximum of 10MB/s. In terms of security, Celestia's security comes from its network value, with a staked value of approximately $66.5 billion and an attack cost exceeding $40 billion. EigenDA inherits a portion of Ethereum's security based on the re-staked asset value and the share of mainnet operators, with the current TVL close to $12 billion, approximately inheriting 2% of Ethereum's security.
Overall, Celestia's competitive advantage lies in its flexible modular design and higher data throughput, making it more favored by small and medium-sized L2 and application chains. EigenDA's advantage lies in using Ethereum infrastructure and the orthodoxy brought about by decoupling data availability from consensus. In the future, with the development of modularization and application chain trends, Celestia may benefit from incremental markets, while EigenDA may occupy a larger share in the Ethereum-centric market that requires higher security.
3.Avail and NearDA
Although Celestia and EigenDA currently dominate the data availability market, the competitive landscape is expected to further intensify with the potential launch of Avail and NearDA.
Avail is a blockchain network focused on data availability, aiming to provide efficient transaction ordering and data storage services for EVM-compatible blockchains and Rollups. It adopts the BABE and GRANDPA consensus mechanisms inherited from the Polkadot SDK. Avail uses KZG polynomial commitments as proof of validity, supports up to 1,000 validators through NPoS, and provides reliable backup through a unique light client P2P network sampling mechanism.
On the other hand, NearDA is a data availability solution launched by the NEAR Foundation, primarily providing DA services for ETH Rollups and Ethereum developers. Its goal is to provide a cost-effective DA solution with a level of decentralization comparable to the Near Protocol. It has already established strategic partnerships with major participants in the Ethereum ecosystem such as Polygon CDK, Arbitrum, and Optimism.
In the short term, for Rollups, adjusting revenue and cost models based on market conditions is a better solution to effectively reduce marginal costs.
4.DA for Specific Scenarios
In addition to general-purpose DAs for Rollups, there have been some early and specific-scenario DA projects emerging in the DA track, such as the high-throughput DA solution Zerogravity (0G) tailored for AI and the Bitcoin DA solution Nubit.
4.1Zerogravity (0G)
The data availability requirements for AI applications differ from traditional blockchain applications. AI model training and operation require processing a large amount of data, including model parameters, training datasets, real-time data requests, etc. This data needs to be stored and transmitted quickly and reliably to ensure the efficiency and performance of AI models. However, existing general DA solutions, such as Celestia and EigenDA, are primarily designed to meet the data availability needs of regular blockchain applications, and have certain limitations when it comes to handling high-throughput, low-latency, large-scale data transmission.
ZeroGravity (0G) aims to specifically meet the needs of AI applications through modular design and high-performance data transmission. Its modular design divides the data availability workflow into data publishing and data storage channels, allowing the system to scale linearly with an increase in the number of nodes. The data storage channel focuses on large data transmission, ensuring that large data can be stored and accessed almost instantaneously. The data publishing channel is used to ensure data availability through an arbitration system based on the assumption of majority honesty. 0G Storage is an on-chain database network composed of storage nodes. Storage nodes participate in the mining process through Random Access Proofs (PoRA) to ensure data availability and integrity. It supports the storage of various types of AI-related data, including models, training data, user requests, and real-time retrieval augmented generation (RAG) data.
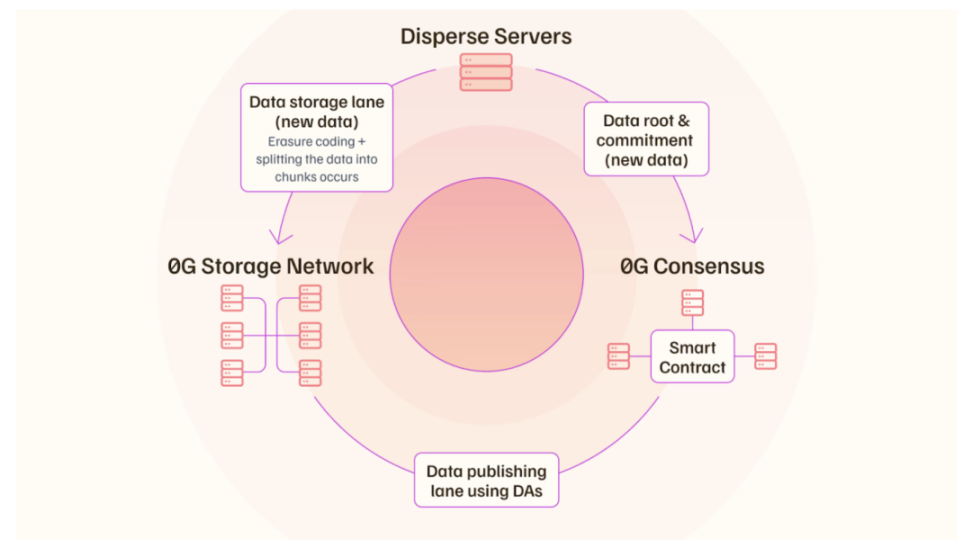
0G claims to achieve on-chain data transmission of gigabytes per second, far exceeding other DA solutions on the market (such as Celestia and EigenDA, which achieve megabytes per second data transmission). Specifically, 0G claims a data throughput of 50 to 100 GB per second, supporting scenarios such as AI model training that require large data transmission.
4.2Nubit
As the Bitcoin ecosystem gradually gains momentum and attention, various technical routes in the Bitcoin ecosystem are flourishing. With the development of these technical routes, applications such as Ordinals, Layer 2, and oracle programs have an increasingly urgent need for efficient and secure data availability solutions. These applications require fast and reliable data storage and transmission to ensure their normal operation and improve user experience. For example, Ordinals requires efficient data storage and transmission to support the creation and trading of digital artworks, Layer 2 solutions require high throughput and low latency to achieve better scalability, and oracles require reliable data transmission to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of data.
Nubit is the first native data availability (DA) layer project in the Bitcoin ecosystem, aiming to address the limited throughput of the Bitcoin mainnet and provide infrastructure support for the long-term development of the Bitcoin ecosystem. Nubit's workflow includes data submission, validation, broadcasting, storage, sampling, and consensus, ensuring efficient processing and high availability of data. The data submitted by users is processed through RS encoding and then validated by validator nodes using the NuBFT consensus algorithm, generating KZG commitments. The validated data blocks are broadcast to the entire network, and storage nodes are responsible for storing complete data blocks, while light clients verify data availability through the Data Availability Sampling (DAS) protocol. Even in the event of network failures, nodes can recover data through full storage nodes and KZG commitments on the Bitcoin network.
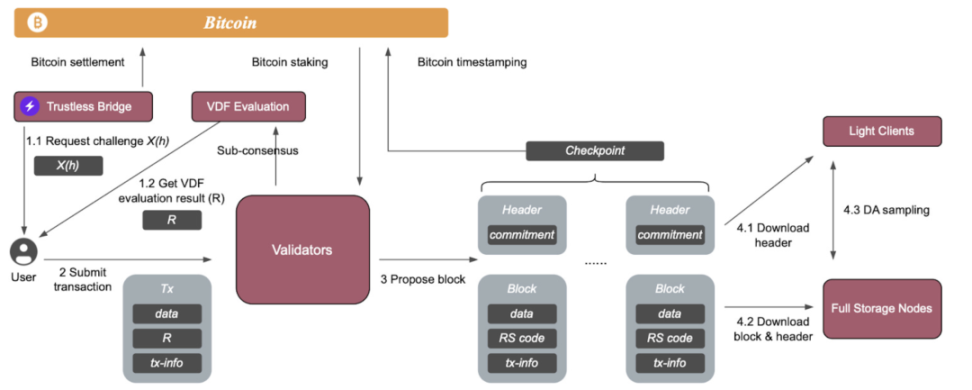
Nubit aims to provide infrastructure for Bitcoin ecosystem projects and has established partnerships with multiple projects such as Babylon, Merlin Chain, and Polyhedra. Nubit will reduce data storage costs, for example, in the case of a surge in demand for encrypted market data, Nubit can significantly reduce data publishing costs for Bitcoin Layer 2, making it more cost-effective to store and process data on Bitcoin.
5. Closing Thoughts
Analyzing the differences among projects in the DA track, we have seen a series of unique technical and market positions in terms of security (including data integrity, network consensus, etc.), customizability and interoperability, performance, and cost as these DA solutions are widely adopted and different projects choose different DA layers.
In the future, we believe that more App-Rollups will enter the market. However, while the potential market is expanding, there is a clear winner-takes-all effect in the DA track, with Celestia, EigenDA, etc. occupying the majority of the market share, leaving little opportunity for others and intensifying competition. Currently, the capacity for Rollups is greater than the demand. For example, after the mainnet launch, the utilization of Celestia's network bandwidth has been consistently below 0.1%, far below its maximum supported capacity of 46,080 MB per day. However, compared to Ethereum's current 15 Rollups and daily data volume of 700 MB, there is still a lot of available space for activity in Celestia.
Of course, it is not ruled out that there may be future demand for high-performance networks for high DA bandwidth, such as for AI projects. In addition, there are some early and specific-scenario DAs, such as Bitcoin DA, which may gain a decent market share in niche areas. However, DA is fundamentally a B2B business, and the income of DA projects is closely related to the quantity and quality of ecological projects. At present, we believe that there is no need for an excessive number of off-chain DA solutions in the market, unless there is a leap in cost and efficiency by several orders of magnitude.
Overall, at present, the DA business model appears to have sufficient supply, but the track's development is still evolving, with various solutions demonstrating different competitiveness in terms of technology and market positioning. The future development will depend on continuous technological innovation and dynamic changes in market demand.
References:
https://www.theblockbeats.info/news/51171
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



