Recently, the full-chain application layer Skate introduced the basic infrastructure for implementing Stateless Apps in its latest official announcement, Skate 101. The aim is to build fully-chain deployed Stateless apps in the current multi-chain parallel environment, addressing the fragmentation and low interoperability issues of Web3 applications. This innovative technology, through unique design, achieves seamless connection of cross-chain applications, laying the foundation for a whole new realm of possibilities for future cross-chain applications.

Ethereum's Technological Evolution and Ecosystem Expansion
Since the introduction of smart contract functionality, Ethereum has given rise to a large number of innovative decentralized applications (DApps). As these applications are widely adopted, network congestion issues have become increasingly severe, leading to a sharp increase in transaction costs. In response to this challenge, new Layer 1 blockchain solutions have emerged. In order to address its scalability issues, Ethereum itself is transitioning towards a Rollup-centric approach, which has greatly promoted the development of Layer 2 blockchain technology. However, the challenge that follows is that each emerging blockchain needs to deploy a full set of basic Web3 applications, with DApps already deployed on as many as 30 chains in the market.
In the past year, the number of Ethereum Layer 2 solutions has surged, and it is expected that this growth trend will be even more rapid in the future. This rapid growth has driven the development of interoperability protocols, which support modular Rollup service models, reducing blockchain deployment time to as little as 5 minutes.
We are rapidly entering a future with thousands of active blockchains, which will fundamentally change the landscape of Web3 applications and their interactions.
Interoperability Challenges and Application Fragmentation Issues
Currently, as many as 90% of applications in the EVM ecosystem are forked versions deployed on new chains, leading to significant resource waste and application fragmentation issues. Despite numerous professional teams dedicated to application development, the "fork everywhere" model still prevails. Different blockchains have different block times, finality, and consensus mechanisms, further increasing the complexity of interoperability protocols.
Currently, applications are generally designed as monolithic applications on a single chain, and interoperability protocols are mainly used for message passing and asset bridging. Interoperability protocols are attempting to find a balance between decentralization and transaction speed to adapt to their specific use case requirements. However, most interoperability protocols still have significant delays in message finality time (ranging from 15 minutes to 7 days), which is the main reason why seamless interoperability at the Web3 application layer cannot be achieved. Therefore, the existing Web3 application space is characterized by fragmentation and inefficiency.
Reducing interoperability delays to a minimum and achieving seamless application layer interoperability is the industry's most urgent problem to solve.
How does Skate solve this problem?
Is Skate just another blockchain? Another interoperability protocol? Or chain abstraction technology?
Of course not. Skate is pioneering a new paradigm by addressing this issue at the application layer.
Skate's innovative cross-chain application solution: Moving towards the world of "Stateless Apps"
Skate proposes to create Stateless Apps that can interconnect across chains, allowing any DApp to run simultaneously on thousands of chains through a single state set, unlocking the cross-chain interoperability challenges of Web3 applications. Any non-EVM chain as well as EVM new chains can easily connect to Skate, and users and developers only need to interact with Skate to immediately access thousands of chains.
By breaking down the structure of Web3 applications into two basic components: the core contract (Kernel) that maintains its own logic and the peripheral contract (Periphery) responsible for user interaction, the core part handles the basic logic and state of the application, while the peripheral part handles user interaction. Skate's vision is to separate these two components, allowing applications to maintain a single state on all chains through a single core contract.
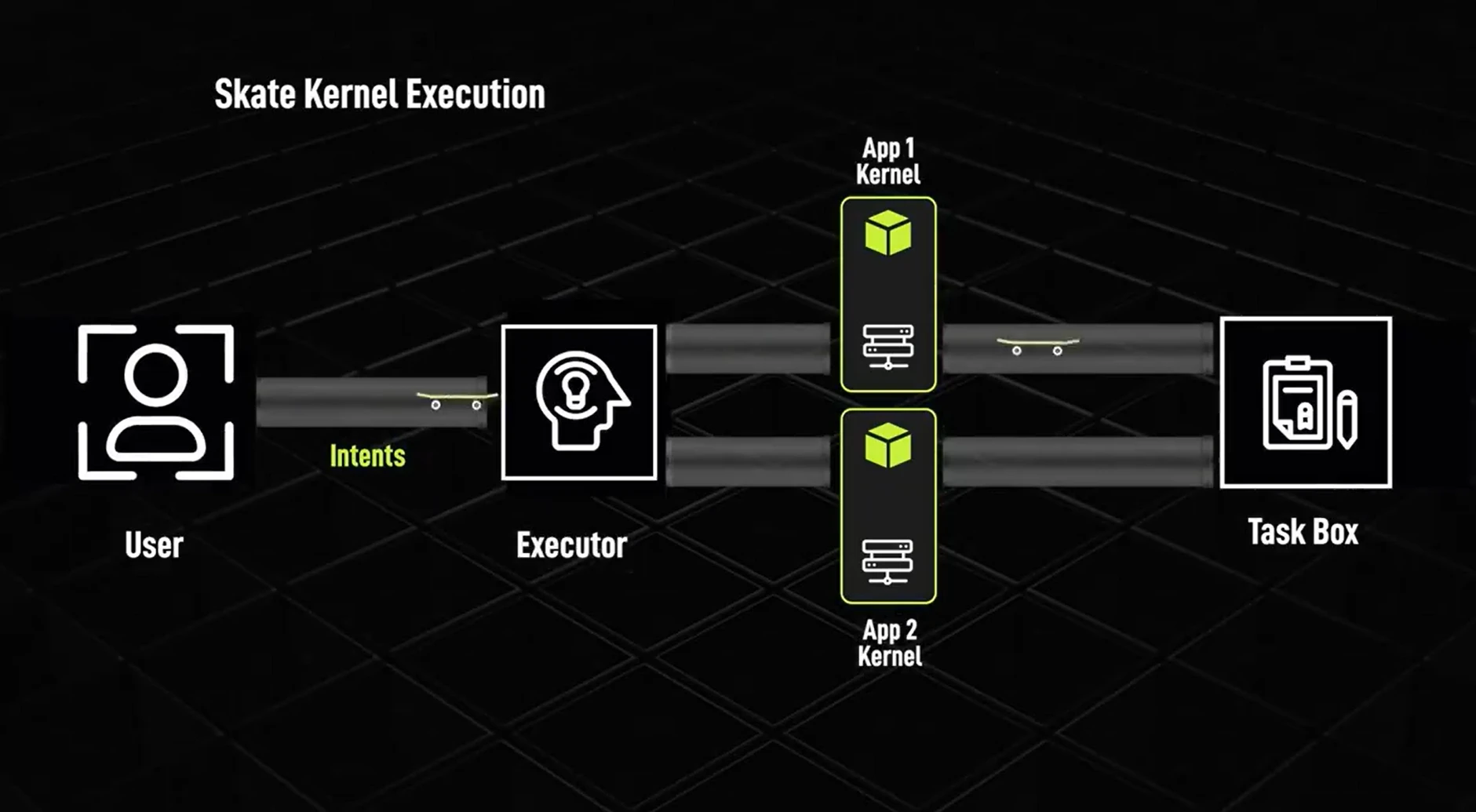
Each blockchain will have a Skate gateway contract, which is the only way for the application core to interact with the periphery. Users interact with applications on different chains through intents, which are quickly pre-confirmed by special executors (such as whitelisted entities), achieving interoperability at the application layer.
Whenever a user generates an output, the application's kernel creates a task and sends it to the task box on the Skate chain—the central chain, which stores the application's state. These tasks are assigned a task ID and call data, and are sent to the user's interaction chain through Skate's pre-confirmation layer AVS, provided with security by the Eigen Layer. The Eigen Layer provides a high level of economic trust, allowing Skate applications to share a single state across thousands of chains.
Skate's cross-chain interoperability extension
In addition, Stateless apps will adopt a plug-and-play model, using any interoperability protocol, such as Axelar or LayerZero, for actual finality confirmation, and ensuring risk control for pre-confirmed tasks. Tasks transition from a pending state in the task box to a pre-confirmed state, and the call data related to the task is then executed through the gateway contract to achieve the expected output in the application's peripheral components.
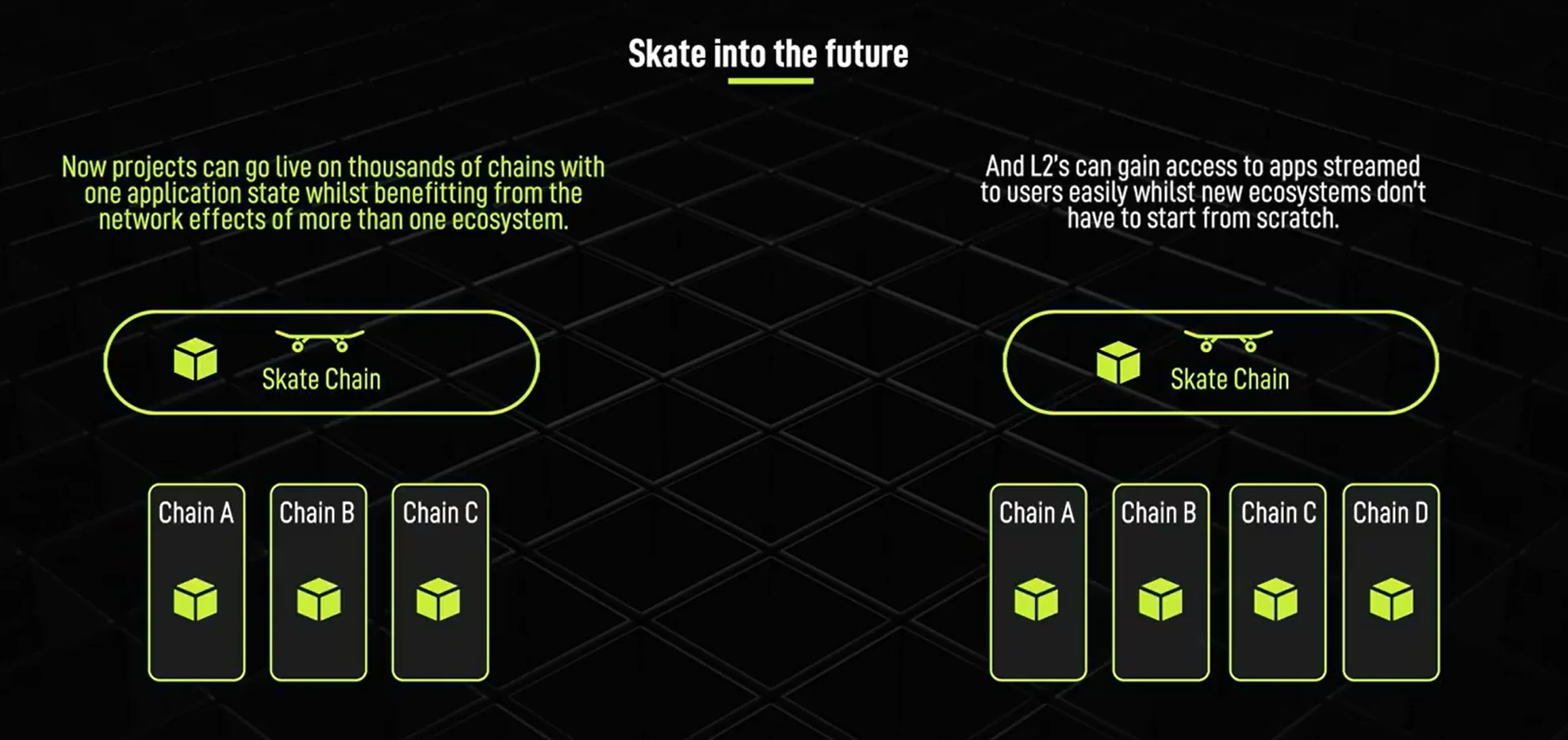
This revolutionary innovation enables applications to go live with a single application state on thousands of chains, leveraging network effects across all ecosystems. New and upcoming Layer 2 solutions no longer need to build all necessary applications from scratch. Skate is also developing gateway wrappers for non-EVM chains (such as Solana, SUI, Aptos, and Ton), allowing EVM applications to share application states on both EVM and non-EVM chains.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




