Author: MiX
Editor: Faust, Geek web3
On March 2, 2024, the founder of the Runes ecosystem infrastructure project Rune alpha, engaged in a discussion with Casey, the founder of the Runes protocol, in a public issue on Github, exploring the expansion of the "public engraving" mechanism of the Runes protocol. The topics discussed include:
Whether to relax the requirement of non-reservable "public engraving"?
Pointing out the view that Runes runes issued using the "public engraving" method do not have management rights
Proposing a mechanism for issuing NFT inscriptions and rune FTs to work together
Due to a strong interest in Bitcoin derivative asset protocols, the author of this article combined some of the latest topics related to Runes to explore the development of Runes and Ordinals protocols and similar asset issuance methods, believing that it can help everyone understand the Bitcoin ecosystem.
What is the Runes Protocol
The so-called Runes protocol is a protocol for issuing homogeneous tokens on the Bitcoin network, which was redeveloped by Casey, the founder of Ordinals, after releasing the Ordinals scheme, based on the characteristics of Bitcoin UTXO, and the overall design concept is very simple.
It is worth mentioning that the Runes protocol plans to go live on the mainnet in late April this year, when Bitcoin halves in 2024 (block height 840000). The Runes protocol is still in the process of optimization and version iteration.
Before briefly explaining the principles of Runes, let's first quickly understand the background and what exactly "public engraving" represents.
Casey, the proposer of Runes, did not initially intend to create a homogeneous token protocol. As early as December 2022, Casey released the Ordinals protocol, intending to permanently record NFT data on the Bitcoin blockchain, simply put, to engrave NFT metadata like inscriptions in the witness data of Bitcoin transactions (witness mainly contains digital signature information), so that any form of content (such as text, images, etc.) can be engraved on specified satoshis.

(Image source: https://yishi.io/a-beginner-guide-to-the-ordinals-protocol/)
Subsequently, the gears of history began to turn. On March 8, 2023, an anonymous developer @domodata, based on the typical NFT issuance protocol Ordinals, ingeniously created a set of BRC-20 standard for issuing homogeneous tokens, which specifies a unified format and attributes (token name, total supply, maximum minting amount per transaction, etc.) for derivative asset data that needs to be uploaded to the Bitcoin blockchain in an inscription manner, and then uses an indexer to parse and track this information, displaying wallet accounts and asset amounts related to BRC-20 tokens.

The key point is that the issuance of BRC-20 depends on the Ordinals Bitcoin inscription NFT protocol, so the initial issuance mechanism becomes similar to the NFT minting process, naturally possessing the characteristic of "first come, first served," whoever mints first owns it, completely different from the asset issuance on Ethereum ERC-20, where "the project party deploys the asset contract first, defines the asset allocation mechanism, and the official can control the distribution as they wish."
This Fair Launch feature gives most people the opportunity to fairly participate in the initial issuance of homogeneous tokens, with no reservations or lock-ups by the project party, and everyone can participate at the initial issuance of the asset. Soon, BRC20 brought about a craze for issuing derivative assets on the Bitcoin blockchain, and even directly sparked this bull market. It can be seen that the "public engraving" issuance method we are focusing on today is very important for the Runes protocol.
However, BRC-20 also brought about many problems: every operation of BRC-20 assets requires a specific transaction to be initiated on the Bitcoin blockchain. As BRC-20 assets became popular, the Bitcoin UTXO dataset quickly expanded, which caused Bitcoin core developers to publicly question BRC-20.
Casey, the founder of Ordinals, not only opposed BRC-20, but also did not recognize the FT assets issued based on Ordinals. However, the popularity of BRC-20 made him feel that although 99% of the tokens are scams and gimmicks, these things will still be unable to disappear like a casino.
At the same time, BRC-20 left "too many traces" on the Bitcoin blockchain, bringing data burden to Bitcoin nodes. However, if someone proposes a set of asset protocols that can "reduce the burden" on on-chain data, it may alleviate the problems caused by BRC-20.
So Casey decided to build a "better homogeneous token protocol" for Bitcoin, and then on September 25, 2023, he released the initial concept of the Runes protocol.
From a technical perspective, the Runes protocol is built on Bitcoin UTXO and additional information. Each triggered transaction must put the off-chain generated digital signature information on chain, and we can carry specific format messages in the signature information. The Runes protocol marks out "specific messages" through the OP_RETURN opcode, which are the information related to the change of Runes assets.
Compared to the BRC-20 protocol, Runes has many advantages, the most important of which are:
Simplified transaction steps, and will not generate redundant and useless UTXO, which can better "reduce the burden" on Bitcoin nodes. In addition, a single transfer transaction of BRC-20 only supports one recipient and one type of token, while Runes supports simultaneous transfers to multiple recipients and multiple types of Runes tokens.
Simpler storage and indexing of asset data: BRC-20 data is stored in the witness data of specific transactions in JSON format, and BRC-20 is based on an account model, where asset balances are associated with specified accounts. The data of the Runes protocol is stored in the OP_RETURN field of specific transactions, and the asset is recorded using the UTXO model, which can be directly "isomorphically bound" to the UTXO on the Bitcoin blockchain.
When confirming a person's Runes asset status, it is only necessary to verify the special UTXO bound to the person's Runes assets, although some information still needs to be traced to complete the calculation, it does not require scanning the complete UTXO set on the Bitcoin blockchain like BRC-20, this lightweight approach is more friendly to data indexing.
- Compatible with UTXO extension layers: Runes, based on the UTXO design, enables better compatibility with UTXO-based extension layers such as CKB, Cardano, Fuel, etc. Through "UTXO isomorphic binding" similar to RGB++, the above-mentioned extension layers can provide smart contract scenarios for Runes.

After briefly discussing the technical aspects, let's return to the issue of the issuance mechanism that was discussed at the beginning of this article. Casey designed two issuance methods for Runes runes, namely "fixed total supply" and "public engraving":
Fixed total supply means that the issuer directly engraves all Runes runes and then distributes them, which is relatively more centralized.
Public engraving is a way of issuing Runes runes by setting parameters, such as specifying a block height or timestamp. Within the specified time period, users can mint assets, and the total supply of the rune is determined by the amount minted during the specified period.
The scenarios and mechanisms corresponding to these two issuance methods are completely different. In the following discussion, we will only talk about "public engraving."
In fact, Sondotpin began discussing this topic from the Runes Issues#124 topic and received approval from Casey.
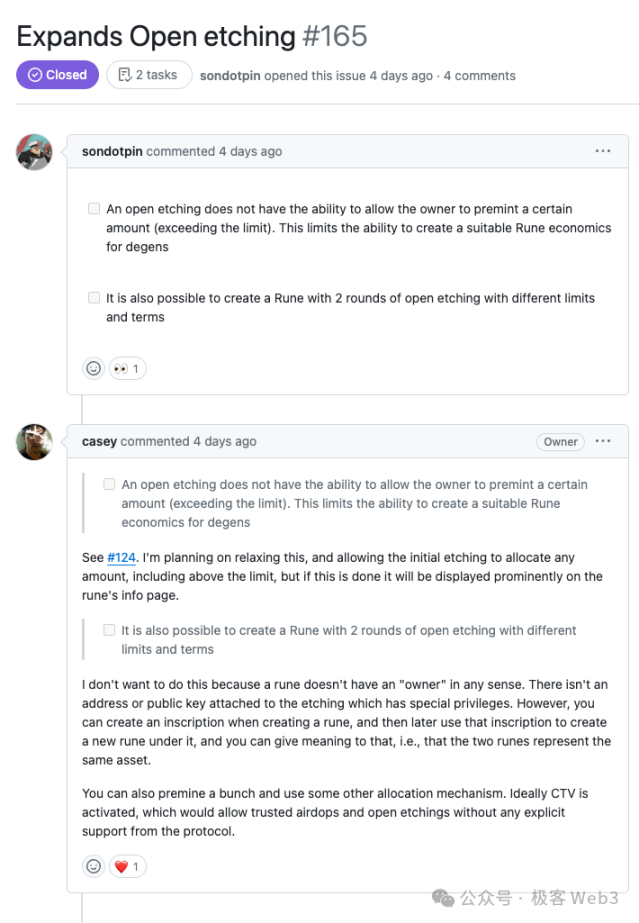
The specific content of Issues#165 is as follows:
Sondotpin: Currently, in the public issuance, the project issuer cannot reserve Runes runes in advance, which limits the opportunity for the project issuer to design a good token economic model.
Casey: Please refer to the previous Issues#124. I am considering relaxing this requirement, allowing the issuer to arrange the runes in a reasonable way at the time of issuance, even beyond the set parameters. If designed in this way, the relevant information will be prominently displayed on the details page of the Runes runes.
Sondotpin: Can we design a mechanism for multiple issuances, such as having two rounds of "public engraving" for Runes runes, and then setting different parameters for each round of issuance?
Casey: I am not inclined to do this because Runes runes fundamentally do not have a "manager." The issuance authority should not be held by a single entity with special privileges. However, you can add an inscription when issuing the runes, and then issue new runes based on this inscription, so that two rounds of issuance of the runes are the same asset. Of course, you can also use pre-mining and then use other allocation methods for issuance.
If the CTV function can be successfully launched in the future, there will be no need for protocol support. CTV can directly set conditional templates in advance, and once the conditions are met, it can carry out airdrops and public issuances that meet the conditions.
Regarding the discussion between Casey and SonPin, here are some personal opinions:
1. It is necessary to reserve some tokens in the early stages of the project
In the early stages, project issuers need to have a certain token reserve to incentivize the core team and unite the community for the self-bootstrapping of the business. If the protocol can be implemented according to the discussion this time, it is a supplement to the fairness and value of mass participation in the "public engraving," allowing more valuable foundational project issuers to participate in the Runes ecosystem through the "public engraving" method.
2. Whether to reserve and how to reserve gives the means of self-certification to the issuer
In fact, Casey has repeatedly stated in YouTube videos that 99.9% of homogeneous tokens are scams, and everyone should not grandiosely claim to change the world. It is an industry full of gambling and speculation, so let's be honest and treat everyone with sincerity. IT’S JUST FOR FUN!
From issue#124 to #165, it can be seen that Casey has become more accepting of the use cases of homogeneous tokens. There is no need to question the "public engraving" method, and expanding on this basis, such as adding a reservation mechanism, gives the issuer the right to choose and the means of self-certification, and is also a good way to prevent bad money from driving out good money.
3. There will be more innovative space for NFT inscriptions and FT runes
Casey's idea of NFT inscriptions and FT runes working together for multi-round issuance mechanisms is quite interesting. As mentioned in the background, Ordinals and Runes are both protocols designed by Casey and should be considered as two parallel relationship protocols. However, on Github, they are both part of the Ord project, and there is a lot of cross-cooperation and coordination in terms of technology, such as sharing underlying logic like synchronous blocks.
Current hot projects like Runestone and Runecoin are also innovative combinations of inscriptions and runes. The way Runecoin is played is the most mainstream inscription pre-mining. Holding the RSIC inscription issued by Runecoin will continuously mine the project's runes, and then distribute FT when the Runes protocol goes live at the end of April. Looking forward to more projects bringing new and innovative ways of playing.
4. Runes runes issued using the "public engraving" method do not have ownership
In the original text, Casey only expressed that "Rune does not have ownership," but the author believes that this should specifically refer to the fact that Runes runes issued using the "public engraving" method do not have ownership. SonPin's proposal for two rounds of "public engraving" will definitely involve an address with very high privileges to operate, which is not what the crypto community hopes to see.
Just like the project Runecoin, after issuing 21,000 RSIC inscriptions, quickly sent the parent inscription to the Satoshi address, which means that no one can use it again, that is, it promises not to issue more through technical means. This operation itself has brought a wave of praise and gained a lot of popularity.
PS: What is a parent inscription? Because the interaction speed and gas cost are high on BTC, to improve efficiency when there are a large number of operations, a parent inscription is usually set first. In the transaction of the parent inscription, multiple child inscriptions are processed in batches, which can save blockchain storage space and processing time during interaction.
Finally, let's talk about Casey's mention of CTV, which stands for "Check Template Verify."
CTV is a proposed protocol upgrade for Bitcoin, aimed at enhancing the smart contract and locking capabilities of the Bitcoin network by allowing users to specify future transaction templates when creating transactions. The activation of CTV will allow users to create more complex transaction types, such as trusted airdrops and open engravings, without the explicit support of the protocol.
This CTV proposal increases the programmability and flexibility of the Bitcoin network, and in this discussion, it is mentioned that, simply put, it can create a UTXO-based unlocking condition template, which may create more ways to play with Runes. For example, through the "Runes protocol + CTV," 10 users can jointly use CTV technology to mint runes, and then preset some future Bitcoin payment transactions' commitments, and so on.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



