This article summarizes common phishing attacks on Solana, helping users effectively avoid related phishing incidents and reduce asset losses.
Author: Go+ Security
Recently, Solana's market value has soared, surpassing BNB to rank in the top three globally. The huge wealth effect has attracted a large number of active players and also drawn a large number of "Wallet Drainer" (phishing) groups from the EVM chain to Solana. Phishing websites and airdrop scams targeting Solana have been deployed on a large scale, resulting in significant user losses. Recently, the GoPlus security team analyzed multiple Solana phishing incidents and found that scam groups exploit the inadequate security infrastructure of some Solana wallets to quickly upgrade airdrop scams and implement social account theft. In response, GoPlus has summarized the common phishing attack methods on Solana to help users effectively avoid related phishing incidents and reduce asset losses.
Attack Types
In several recent phishing incidents, GoPlus found that phishing groups mostly use methods such as "enticing airdrop claims," "fake project websites," "free lotteries," and "guiding entry through NFT airdrops," which are almost identical to several common phishing methods on EVM. The main difference is that scammers use different "token or authorization transfers" to conduct phishing activities on Solana. Below are several different transfer attack methods observed.
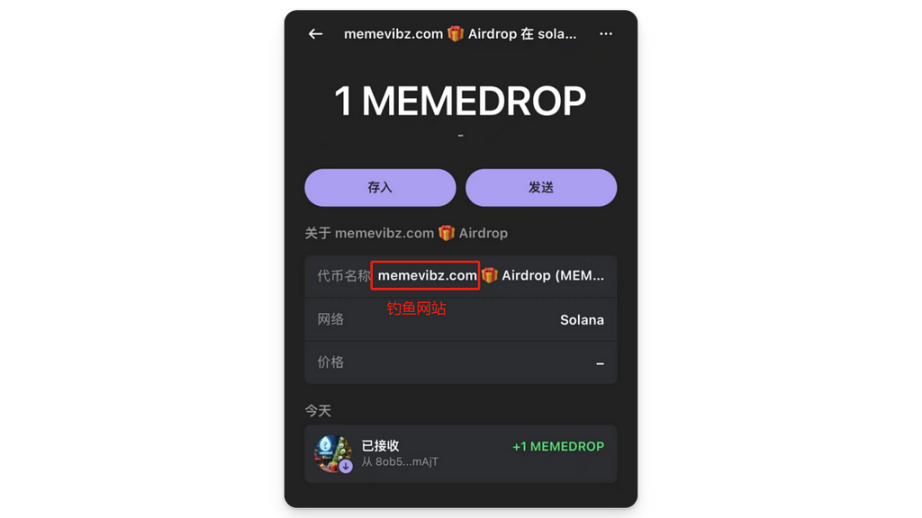
Inducing Transfer of Native Token SOL
This type of attack is the simplest. After the user links the wallet, the scam team calculates the current balance of all $SOL on the front end and directly completes the token transfer using the SystemProgram.transfer function. For example, a phishing website displays a UI for a swap interface, leading users to believe they can buy a certain token at a low price.
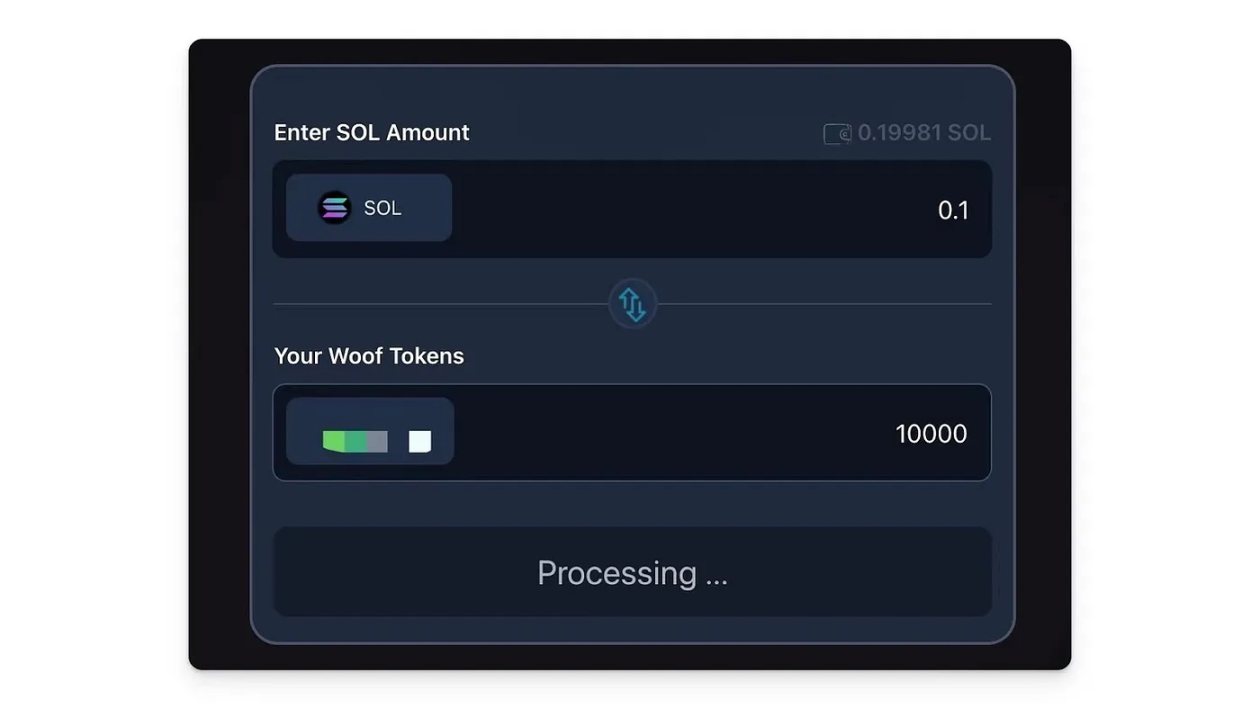
But in reality, only a simple transfer of $SOL is executed.
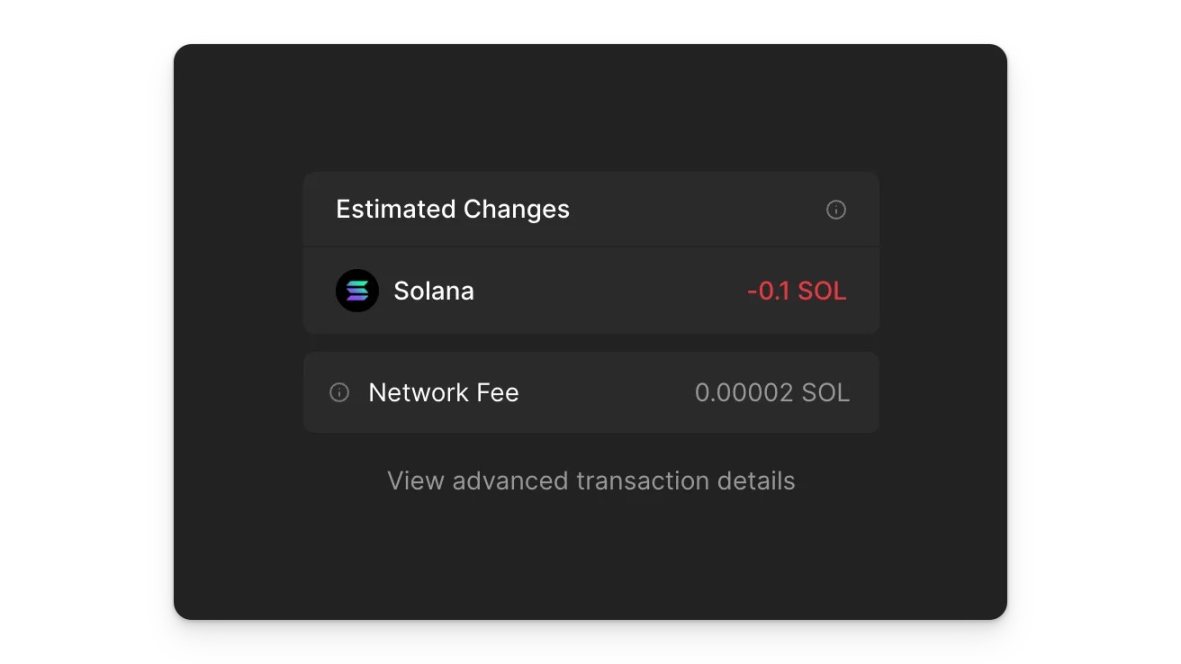
Inducing Transfer of Multiple Tokens
In addition to stealing the native token $SOL, scammers can simultaneously steal all the token assets held in the wallet in the same transaction signature. On Solana, each transaction can consist of multiple instructions, each completing a separate logic, such as transfers, program interactions, and account creation. This means that phishing groups have the ability to include multiple operation instructions in the same transaction. For example, if a user holds three different tokens, the phishing website only needs to include transfer instructions for the three tokens in the code of the same transaction. This means that scammers do not need to steal a specific asset individually but can use this feature to conduct a one-time wallet raid. Similar to the first inducement, hackers deceive users into clicking buttons to execute transactions through various means. This type of transaction will transfer all assets in one go, including not only the native $SOL token but also NFT-type assets and token-type assets. Here, the scam team mainly utilizes the createTransferCheckedInstruction of Solana SPL Token to complete the transfer instruction construction for non-native assets.
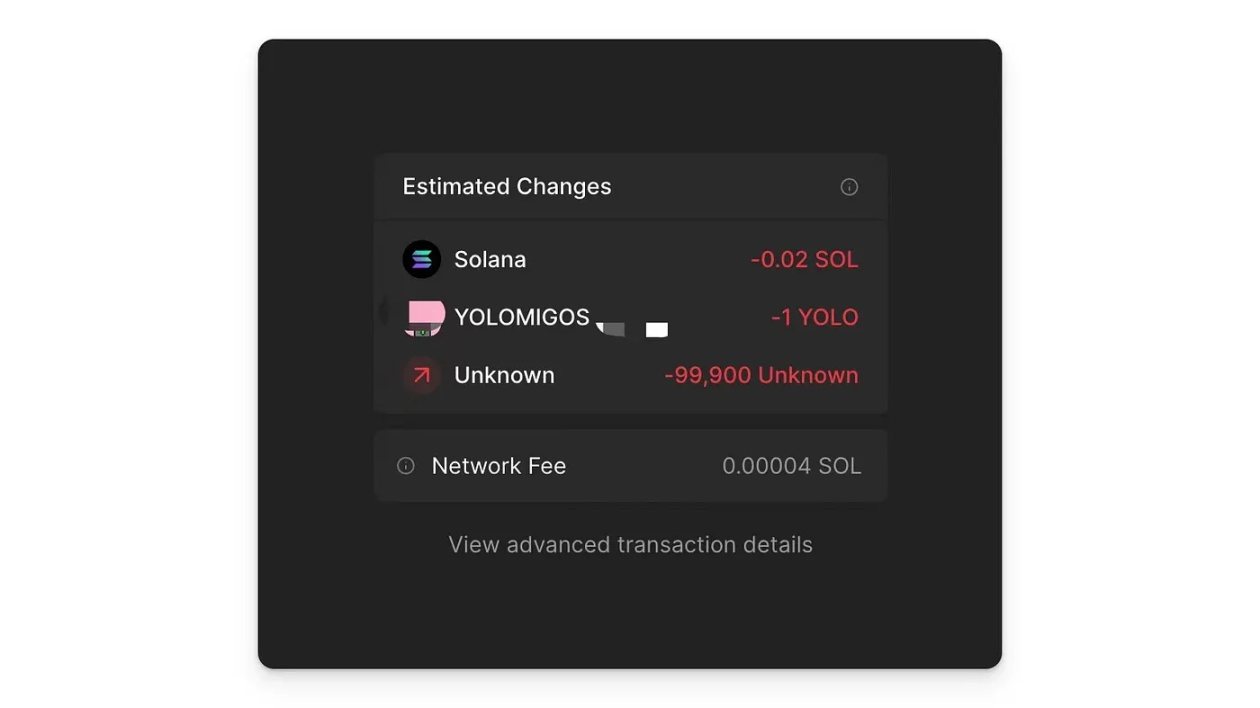
Phantom transaction simulation
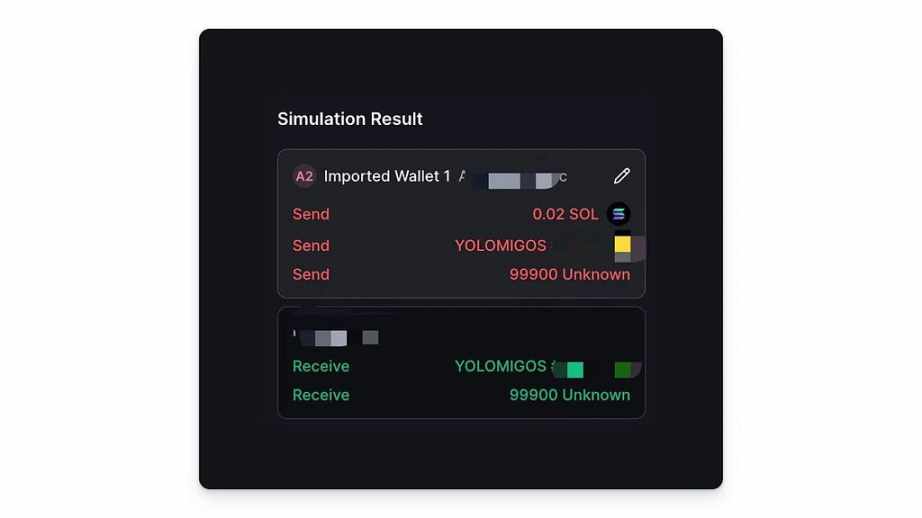
Backpack transaction simulation
Inducing Transfer of Token Account Ownership
In addition to direct tokens, GoPlus also found that some phishing websites use the createSetAuthorityInstruction operation to package instructions into transactions, which essentially transfers ownership of the tokens on the account. Solana's account model is different from EVM. Each account address has a dedicated Token Account corresponding to each token, with an owner that is the current account. The Token Account also records the balance and related information of the corresponding token. The createSetAuthorityInstruction operation can directly transfer ownership of the current token to another account, effectively transferring all the current tokens to that account. We conducted experiments with this operation on both Phantom and Backpack, and fortunately, both wallets provided special alerts and warnings.
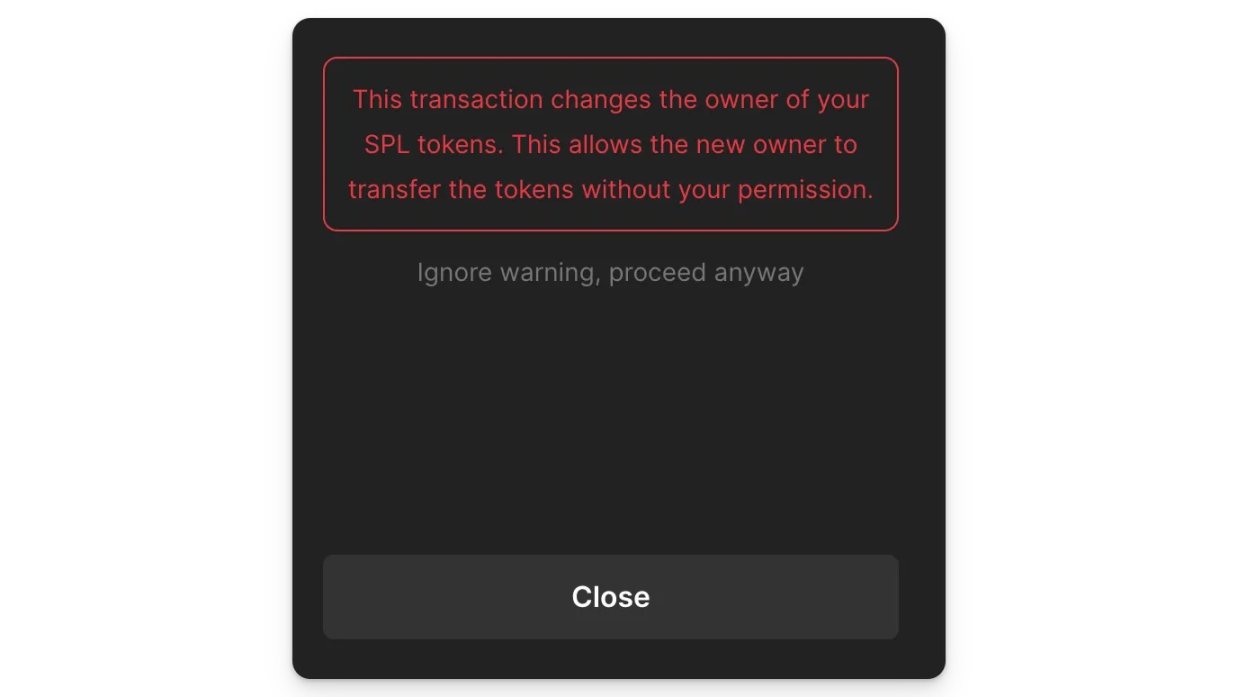
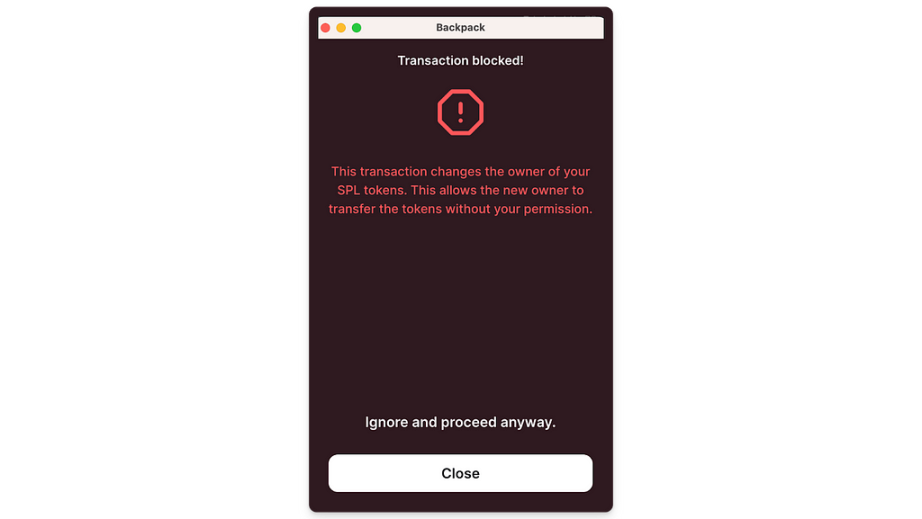
Even if the user clicks the Ignore and proceed anyway option, the change in balance can still be shown through transaction simulation.
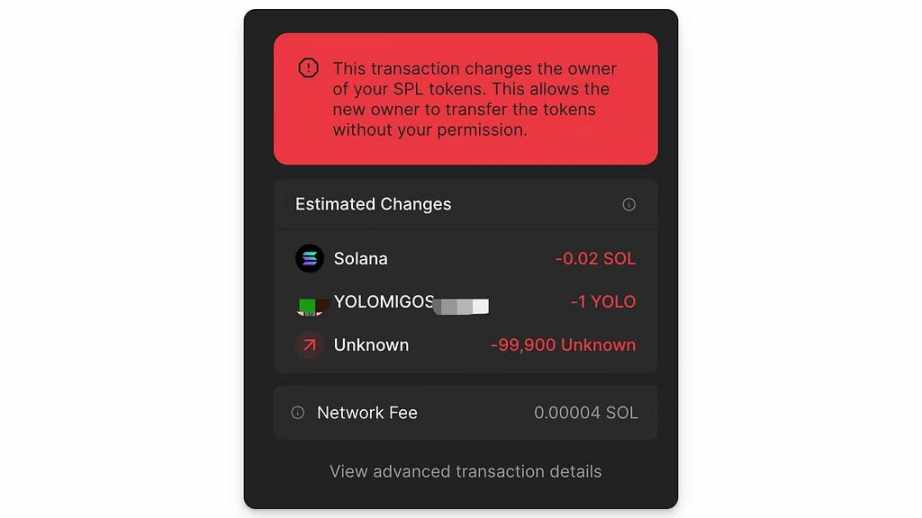
Note
Most mainstream Solana wallets currently provide the ability to predict results through transaction simulation, allowing users to clearly see the change in balance after clicking. Therefore, as long as users carefully and patiently review the results of each transaction, they can relatively avoid some phishing risks. This is because Solana's official JSON RPC interface provides the ability for "transaction simulation." However, as phishing and scam techniques continue to evolve, we have also discovered some very difficult-to-detect phishing methods.
Deceiving Token Authorization
For users familiar with EVM, token authorization is a common operation, but it differs on Solana. In the Solana network, scammers exploit users' misunderstanding of the EVM authorization mechanism to carry out scams. Phishing websites induce users to engage in seemingly normal interactive operations, but in reality, they execute authorization transactions Delegate in the background using createApproveCheckedInstruction. The key to this method is that it does not directly transfer assets but grants the attacker control over the user's assets. This type of attack is often hidden behind enticing interactive interfaces, such as pretending to vote or stake, while quietly changing the account's authorization settings.
Once attackers gain control over the user's assets, they can manipulate these assets at any time, including transferring or trading them. This type of attack is often not easily detected in a timely manner because it does not immediately result in asset transfers. These attacks also have a wide-reaching impact because attackers wait until enough users have fallen victim and the amounts are large enough before initiating token transfers. Users need to be especially cautious, and any requests to change authorization settings should raise alarm, especially on unfamiliar websites or applications. Through transaction simulation, users can see changes in authorization, so they need to not only pay attention to direct token balance changes but also be cautious of phishing risks caused by changes in authorization.
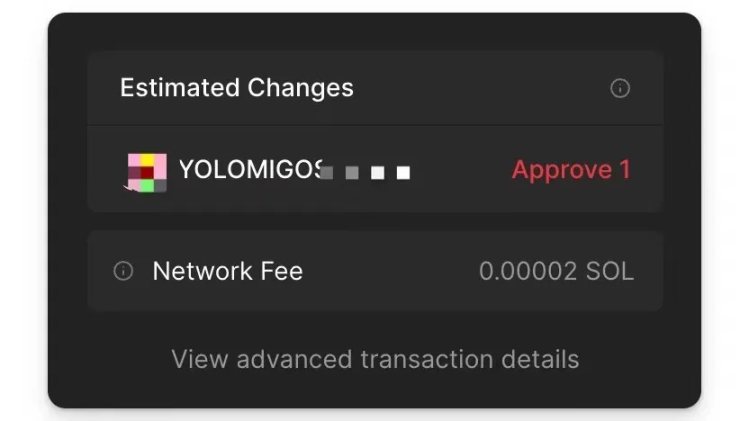
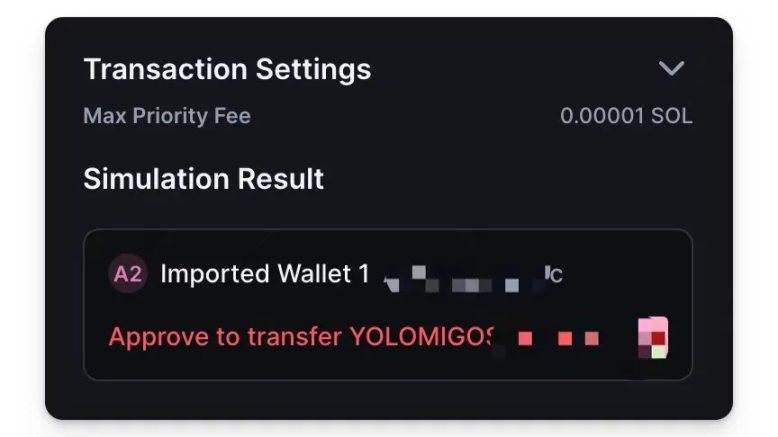
Durable Nonce Deceiving Transaction Signatures
Durable Nonce is a feature in the Solana blockchain that allows the creation of a special account to store a persistent, non-expiring nonce value. In Solana, every transaction requires a recent block hash as part of it, ensuring the timeliness and uniqueness of the transaction. Typically, this block hash expires after about 150 blocks, rendering the transaction invalid. The Durable Nonce mechanism provides a non-expiring nonce value, allowing transactions to remain valid for a longer period.
In phishing scams, scammers may abuse the Durable Nonce mechanism to induce users to sign transactions that appear normal but actually contain malicious operations. Because of the use of Durable Nonce, these transactions do not expire due to block hash expiration, giving scammers a longer time window to execute transactions. For example, scammers may design a transaction that appears to be a legitimate operation, such as participating in an airdrop or activity, but in reality, the transaction contains instructions to transfer the user's assets to the scammer. Users unknowingly sign such transactions, but they may find that the transaction did not occur on the blockchain because the attacker only obtained the signature of the transaction, and the transaction itself was not sent to the blockchain. They can broadcast the transaction to the blockchain at any time in the future. However, regardless of whether the transaction occurs, we found that this type of signature does not affect the judgment of transaction simulation results. Several mainstream wallets can still simulate and parse the transaction and inform the user of the results, so our previous judgment of transaction simulation results is still valid methodology.
However, we have still discovered an extremely covert and complex attack method that can "deceive the heavens and cross the sea."
Contract Upgrade to Evade Transaction Simulation Detection
This method combines the Durable Nonce and Solana's unique feature—upgradability. The potential danger of this attack method is further increased due to the upgradability of contracts. The Durable Nonce mechanism creates an account holding a long-term valid nonce value, allowing transactions to remain valid for a longer time window. This means that even if the user does not immediately send the transaction to the blockchain when signing it, the transaction can still be broadcast and executed at any time in the future. Attackers can take advantage of this by first having the user sign a seemingly normal contract transaction that appears harmless at the time of signing, making it difficult for even mainstream wallets and transaction simulation tools to warn the user in advance. However, after the user signs the transaction, the attacker successfully obtains the signature of the Durable Nonce. At this point, they do not rush to broadcast the transaction to the blockchain but instead use Solana's contract upgrade feature to change the originally normal contract to a malicious version. This malicious contract can execute operations such as asset transfers. After the upgrade, the attacker then broadcasts the signed transaction to the blockchain to execute the malicious operation and achieve their goal. This type of attack is particularly covert and poses a great risk to users because even experienced users may not be able to identify potential risks when signing transactions. To prevent this type of attack, users need to carefully review the reputation and history of contracts, maintain a skeptical attitude towards any unusual transaction behavior, and avoid interacting with contracts from unknown sources or newly established contracts. It is also hoped that all Solana wallets can pay attention to this attack method and provide effective alerts and protection for user assets in a timely manner.
Preventive Measures
When facing phishing attacks on the Solana network, the following comprehensive preventive measures can help minimize risks:
- Increase Security Awareness: Always maintain a high level of vigilance for any cryptocurrency-related transactions. Understand common methods of Solana phishing attacks, such as inducing token transfers, transferring token account ownership, and deceiving transaction signatures.
- Carefully Check Transaction Details: Before conducting any transactions, carefully review the specific content of the transactions. Exercise extra caution for transactions involving Durable Nonce or contract interactions.
- Use Transaction Simulation Function: Utilize the transaction simulation function provided by wallets to carefully review transaction simulation results. However, it should be noted that this is not a foolproof protective measure, as there are cases where transaction simulation fails.
- Monitor Authorization Changes: Stay vigilant for operations that result in changes to token balances after transactions. Be especially cautious on unfamiliar websites or applications regarding changes in authorization.
- Regularly Revoke Unused Authorizations: Use Solana's Revoke tool to regularly revoke unused authorizations to safeguard asset security.
- Regularly Update Knowledge: Regularly update knowledge about blockchain and cryptocurrency, especially regarding new phishing methods and prevention strategies.
- Keep Software Updated: Ensure that the wallet and related software are kept up to date to have the latest security features and fixes.
- Backup and Protect Private Keys: Safeguard private keys and important information, avoiding storing or sharing them in insecure locations.
At the same time, the GoPlus security team calls on the Solana public chain and its ecosystem to deeply prioritize user security, accelerate the construction of secure infrastructure for users, and provide a more secure trading environment for users, thereby achieving ecosystem stability and prosperity.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




