Author: FinTax
News Overview
According to reports, on July 14, 2025, the Federal Reserve, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), and the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) issued a joint statement (hereinafter referred to as "the Statement") guiding banks on how to provide custody services for crypto assets to their customers. This is the latest initiative by regulatory agencies from the Trump era as they weigh how traditional lending institutions should engage in the digital asset business. The Statement states that banks considering providing custody services for crypto assets should take into account the ever-changing characteristics of the crypto market, including the technology behind crypto assets, and they must implement a risk management framework that can appropriately adapt to the associated risks.
Previously, regulators withdrew guidance on the risks of the crypto industry in April, allowing lending institutions to more freely offer products and services to customers engaged in digital asset trading. At that time, the Federal Reserve also rescinded a 2022 directive requiring banks to notify in advance about crypto asset activities.
FinTax Commentary
1. Statement Content: Six Key Risk Points for Bank Crypto Custody
The joint statement outlines a series of existing laws, regulations, guidance, and risk management principles related to providing custody services for crypto assets, focusing on various risk management, legal, and compliance risks, and elaborating on relevant mitigation measures. The Statement is divided into six parts:
(1) General Risk Management Considerations: Banking institutions should consider potential risks before providing custody services for crypto assets. Effective risk assessments should involve the bank's core financial risks, the ability to understand asset classes, the capacity to ensure a robust control environment, emergency plans, and necessary employee knowledge of crypto asset custody, thereby providing services in a safe and sound manner. Additionally, banks providing custody services for crypto assets should consider the continuously changing characteristics of the crypto asset market and build a risk governance framework that can appropriately adapt to these changes.
(2) Crypto Key Management: The loss or leakage of crypto keys or other sensitive information is one of the main risks of crypto asset custody. Banking institutions should have control over crypto assets, meaning they must reasonably demonstrate that no other party can obtain sufficient information to transfer the crypto assets out of the bank's control. Such control standards should also apply to the bank's sub-custodians. Furthermore, banks should consider how to securely generate crypto keys, develop emergency plans for key loss or leakage, and prioritize their cybersecurity environment as a key aspect of risk management.
(3) Other Risk Management Considerations: Different types of crypto assets require different key management solutions, or there may be a lack of experience or capability in handling software or hardware requirements. The potential risks associated with different account models may also vary. Therefore, while banking institutions follow standard custody risk management principles, they also need to adjust based on the specific custody services provided.
(4) Legal and Compliance Risks: First, like other banking activities, crypto asset custody activities must comply with the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA), Anti-Money Laundering (AML), Counter-Terrorism Financing (CFT), and the Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) requirements. Second, changes in the regulatory environment for crypto assets can also bring higher compliance risks, and banking institutions should ensure that relevant activities comply with all applicable laws and regulations. Finally, customers may misunderstand the role of banks in custody arrangements, leading to risks, which requires banks to provide clear, accurate, and timely information about their custody activities to mitigate such risks. Additionally, banks should adhere to applicable record-keeping and reporting requirements.
(5) Third-Party Risk Management: "Third-party risk" refers to the risks posed by sub-custodians or other service providers (such as technology providers, cash management institutions) that banks collaborate with. Banks are responsible for the activities conducted by their sub-custodians under the terms and conditions, so they should conduct thorough due diligence, including assessing the sub-custodian's key management solutions, compliance with custody risk management principles, handling of customer assets in the event of bankruptcy or operational failure, and the appropriateness of their risk management and record-keeping. For other service providers, banks should weigh the risks of purchasing third-party software or hardware, as well as the risks of maintaining such software or hardware as a service.
(6) Audit Requirements: Audit procedures are crucial for effective risk management and internal controls. Therefore, the audit procedures of banking institutions should adequately cover crypto asset custody services (including third-party risk management), focusing on risks unique to crypto asset custody, such as key generation, storage, and deletion, the transfer and settlement of crypto assets, the adequacy of related information technology systems, and assessing employees' capabilities in identifying and controlling crypto asset risks. If a banking institution lacks auditing expertise, it should hire an appropriate independent third party to conduct the audit.
2. Policy Background: Trump Drives Crypto Regulatory Reform
Since Trump's second term began, the U.S. government's attitude towards crypto assets has undergone a significant shift, and this joint statement was issued in this context. In recent months, several banking regulatory agencies in the U.S. have taken a series of actions, withdrawing various interpretive letters and regulatory statements related to crypto assets from the Biden era. One major initiative was the removal of the "reputational risk" assessment from the regulatory process, replacing the vague reputational risk with more specific categories of financial risk. This effectively avoided the phenomenon of regulatory agencies pressuring banks to refrain from providing services to crypto asset companies, helping to alleviate banks' real concerns about providing services to controversial industries like crypto assets.
Another significant measure was the elimination of the prior notification requirement for engaging in crypto asset-related activities. Under previous policy, banks were required to obtain a written "no objection letter" from regulatory agencies before participating in crypto asset-related activities. Now, banks' crypto activities do not need to follow this procedure and are monitored through regular regulatory processes.
Additionally, banking regulatory agencies have restored previous regulatory policies that conflicted with the Biden administration's regulatory philosophy, such as the OCC again allowing its regulated entities to buy and sell custody crypto assets based on customer instructions, and permitting them to outsource custody and execution services to third parties, provided that those third parties can manage risks appropriately.
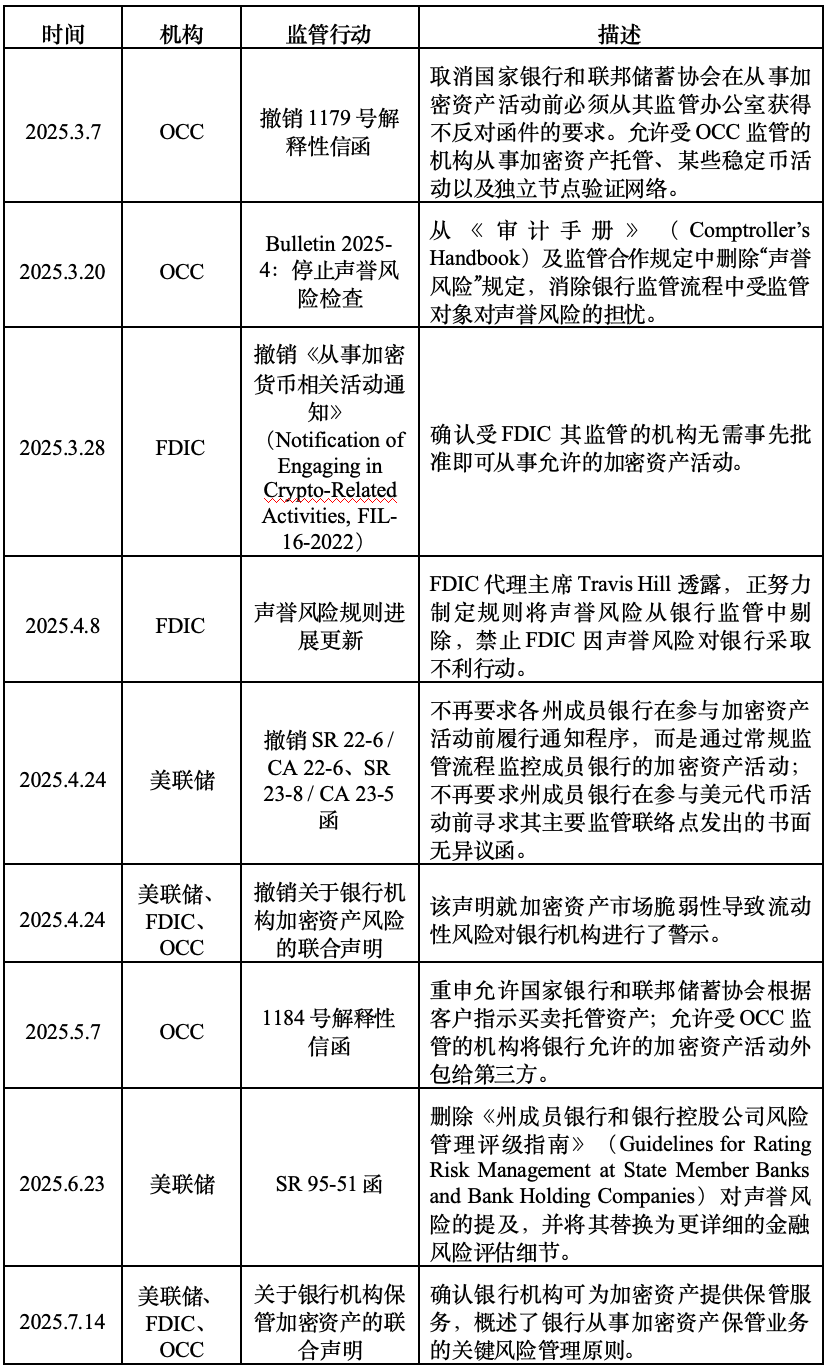
After Trump took office, he reversed the previous U.S. government's guidance urging banks to exercise caution in the crypto space and implemented comprehensive regulatory reforms for crypto assets. This is a fulfillment of his political commitment and an important measure to position the U.S. as the "crypto capital" of the world and stimulate innovation and development in the U.S. economy. The joint statement released constitutes a part of the U.S. crypto asset regulatory reform, marking the government's shift from enforcement-focused regulatory policies to releasing market vitality by refining regulatory rules and enhancing business guidance, guiding banks and other entities to participate in crypto asset activities in a compliant, safe, and sound manner, supporting the innovative development of the crypto industry, and potentially leading to more crypto-friendly statements being issued in the future.
3. Significance and Outlook: The Regulatory Future of Bank Crypto Custody
Overall, the statement discusses how existing laws, regulations, and risk management principles apply to crypto asset custody, aiming to provide guidance for banks that offer or consider offering custody services for crypto assets, reflecting a more relaxed regulatory environment while still emphasizing that banking institutions should strictly control risks in crypto asset custody activities and adhere to core principles of safety, soundness, and consumer protection, reflecting the regulatory baseline of U.S. banking regulators in the crypto industry.
For banking institutions engaged in or considering engaging in crypto asset custody business, on one hand, the statement provides an entry opportunity in the crypto asset custody field for banks with appropriate risk control capabilities and sound governance structures, bringing new opportunities. On the other hand, the statement also offers specific references for risk control matters for banks already engaged in crypto asset custody business, with regulatory scrutiny still focusing on the compliance and safety of all aspects, including operations, legal, and financial. According to the statement, banking institutions may need to make certain adjustments to product rules and internal policies and procedures to reflect the unique risks and compliance obligations of crypto asset custody, such as improving cybersecurity protocols and key management systems, and conducting regular security testing.
It is important to note that although the statement provides some clarity, under the backdrop of government crypto regulatory reform, there remains uncertainty in the regulatory and legal environment at both federal and state levels, and merely meeting the elements of the statement may not fully comply with regulatory requirements. Banks and regulatory agencies at all levels still need to maintain ongoing communication and keep compliance records in preparation for rigorous regulatory scrutiny.
From a longer-term perspective, the refinement of U.S. crypto custody regulatory rules may attract more crypto asset companies to return or enter the U.S. market and promote innovation and development in the U.S. blockchain industry. As traditional financial institutions deepen their participation in the crypto asset space, services such as crypto asset custody will be integrated into existing regulatory frameworks, and financial activities surrounding crypto assets will thrive in a safer and more regulated environment.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



