原文作者:A1Research
原文编译:Tim,PANews
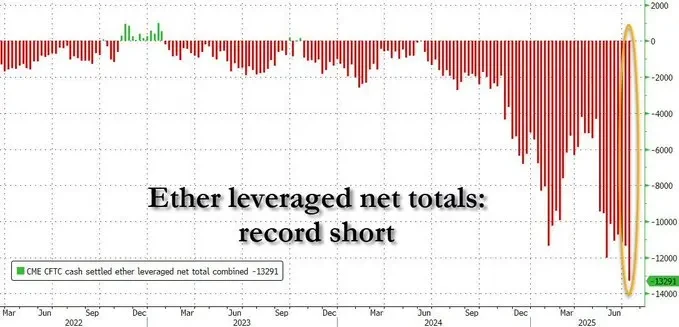
以太坊的价格波动看似简单:散户热情高涨,价格飙升,市场乐观情绪持续发酵。但表象之下,实则暗藏结构性复杂的市场机制。资金利率市场、中性策略机构的对冲操作与递归式杠杆需求相互交织,暴露出当前加密市场中深层的系统性脆弱。
我们正见证一个罕见现象:杠杆实质上已变成流动性本身。散户投入的巨量多头头寸正在根本上重塑中性资本配置风险的方式,由此催生出大多数市场参与者尚未充分认识的新型市场脆弱性。
散户跟风做多现象:当市场行为高度趋同时
散户需求集中在以太坊永续合约中,因为这类杠杆产品易于获取。交易者以远超现货真实需求的速度涌入杠杆多头头寸。想要押注ETH上涨的人数远超实际购买以太坊现货的人数。
这些仓位需要交易对手方承接。但由于买盘需求变得异常激进,做空盘正越来越多地被执行Delta中性策略的机构玩家所吸纳。这些并非方向性看跌者,而是资金费率收割机,他们介入并非看空ETH,而是要利用结构性失衡进行套利。
实际上,这种做法并非传统意义上的做空。这些交易者在持有等量现货或期货多头头寸的同时,永续合约做空。结果虽然不承受ETH价格风险,但他们通过散户多头为维持杠杆仓位支付的资金费率溢价获取收益。
随着以太坊ETF架构的进化,这种套利交易可能很快将通过叠加被动收益层(质押收益嵌入了ETF包装结构)得到增强,进一步强化Delta中性策略的吸引力。
这确实是笔绝妙的交易,前提是你能忍受其复杂性。
Delta中性对冲策略:合法“印钞”的响应机制
交易者通过做空ETH永续合约来承接散户做多需求,同时用现货多头头寸进行对冲,从而将因持续资金费率需求导致的结构性失衡转化为利润。
在牛市行情中,资金费率转为正值,此时多头需向空头支付费用。采用中性策略的机构在对冲风险的同时,通过提供流动性获得收益,从而形成盈利性套利操作,这种模式吸引着机构资金持续涌入。
然而,这催生了危险的幻觉:市场看似深度足够且稳定,但这种"流动性"取决于有利的资金环境。
激励机制消失的那一刻,其支撑的结构也将随之崩塌。表面的市场深度瞬间化为虚空,随着市场框架的轰然倒塌,价格或将剧烈震荡。
这种动态不仅限于加密原生平台。即便在以机构为主的芝加哥商品交易所,大部分空头流动也并非方向性押注。专业交易者做空CME期货,是因为其投资策略被禁止开设现货敞口。
期权做市商通过期货进行Delta对冲以提高保证金效率。机构则负责对冲机构客户订单流。这些都属于结构性必需交易,并非看跌预期的体现。未平仓合约量可能上升,但这很少能传递市场共识。
不对称风险结构:为什么它其实并不公平
散户多头在价格往不利方向波动时将直接面临被平仓的风险,相比之下,delta值中性空头通常资金更雄厚且由专业团队管理。
他们抵押持有的ETH作为担保物,能够在完全对冲、资金效率高的机制下做空永续合约。这种结构可以安全承受适度杠杆,而不会触发清算。
两者在结构上存在差异。机构空头拥有持久的抗压能力和完善的风险管理体系以抵御波动性;而加杠杆的散户多头则承受能力薄弱、风控工具匮乏,其操作容错率几乎为零。
当市场形势转变时,多头会迅速瓦解,而空头依然稳固。这种失衡会引发看似突然、实则结构上不可避免的清算瀑布。
递归反馈循环:当市场行为变成自我干涉
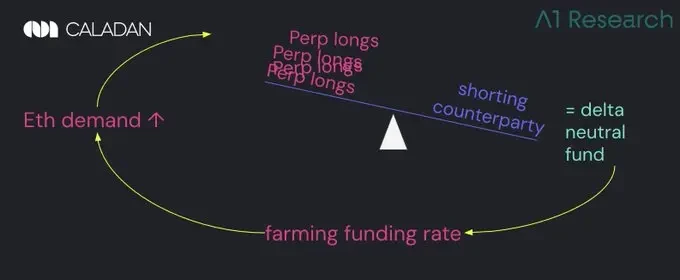
以太坊永续合约的多头需求持续存在,需要由Delta中性策略交易者充当对手方进行空头对冲,这种机制使资金费率溢价持续存在。各类协议和收益产品竞相追逐这些溢价,推动更多资本回流至这个循环体系中。
永不停转的赚钱机器,现实中根本不存在。
这会持续形成上行压力,但完全取决于一个前提条件:多头必须愿意承担杠杆的成本。
资金费率机制存在上限。在多数交易所(如币安),永续合约每8小时的资金费率上限为0.01%,折合年化收益率约10.5%。当达到该上限时,即使多头需求持续增长,追求收益的空头也不会再得到激励开单。
风险积累达到临界:套利收益固定,但结构性风险持续增长。当这个临界点来临时,市场很可能会迅速平仓。
为何ETH比BTC跌得更惨?双生态叙事之争
比特币正受益于企业财政策略带来的非杠杆买盘,而BTC衍生品市场已具备更强流动性。以太坊永续合约深度融入收益策略与DeFi协议生态,ETH抵押品持续流入Ethena和Pendle等结构化产品,为参与资金费率套利的用户提供收益回报。
比特币通常被认为是由ETF和企业的天然现货需求驱动的。但很大一部分ETF资金流其实是机械式对冲的结果:传统金融的基差交易者一边买入ETF份额,一边做空CME期货合约,以此锁定现货与期货之间的固定价差进行套利。
这与ETH的delta中性基差交易本质相同,只不过通过受监管的包装结构执行,且以4-5%的美元成本融资。这样看来,ETH的杠杆操作成为收益基础设施,而BTC的杠杆则形成结构化套利。二者皆非定向操作,均以获取收益为目标。
循环依赖问题:当音乐停止时
这里有个可能让你夜不能寐的问题:这种动态机制具有内在的周期循环性。Delta中性策略的盈利依赖于持续正向的资金费率,而这要求散户需求与牛市环境的长期延续。
资金费溢价并非永久存在,它十分脆弱。当溢价收缩时,平仓潮便会开始。如果散户热情消退,资金费率转为负值,意味着做空者将向做多者支付费用,而非收取溢价。
当大规模资本涌入时,这种动态机制会形成多重脆弱点。首先,随着更多资本涌入delta中性策略,基差将不断压缩。融资利率下降,套利交易的收益也随之降低。
若需求逆转或流动性枯竭,永续合约可能进入折价状态,即合约价格低于现货价格。这种现象会阻碍新的Delta中性头寸进场,并可能迫使现有机构平仓离场。与此同时,杠杆多头缺乏保证金缓冲空间,即便是温和的市场回调也可能引发连锁清算。
当中性交易者回撤流动性,多头强制平仓如瀑布般涌现时,流动性真空随之形成,价格下方不再存在真正的方向性买方,只剩结构性卖方。原本稳定的套利生态系统迅速翻转,演变为一场失序的平仓潮。
误读市场信号:平衡的幻觉
市场参与者常将对冲资金流向误认为看跌倾向。实际上,ETH的高空头头寸往往反映的是有利可图的基差交易,而非方向性预期。
许多情况下,表面上看似强劲的衍生品市场深度,其实是由中性交易台提供临时租赁的流动性所支撑,这些交易者通过收割资金溢价获取收益。
现货ETF的资金流入虽然能够产生一定程度的自然需求,但永续合约市场中的绝大部分交易本质上属于结构性人为操作。
以太坊的流动性并非根植于对其未来的信念;只要资金环境有利可图,它便存在。一旦盈利消散,流动性也将随之流失。
结语
市场能够在结构性的流动性支撑下长期活跃,营造出虚假的安全感。但当条件逆转,多头无法维持融资义务时,崩盘就在一瞬之间。一方被彻底碾碎,另一方则从容抽身。
对于市场参与者而言,识别这些模式既意味着机遇也预示风险。机构可以通过洞悉资金状况获利,而散户投资者应当辨别人为深度与真实深度。
以太坊衍生品市场的驱动因素并非对去中心化计算的共识,而是结构性收割资金费率溢价的行为。只要资金费率保持正收益,整个体系就能平稳运行。然而当形势逆转时,人们终将发现:看似平衡的表象不过是精心伪装的杠杆游戏。
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



