The significance of ERC-7786 lies not only in making cross-chain interactions more convenient but also in its attempt to establish a unified standard for "multi-chain collaboration" to combat "entropy increase." This can further promote the "unification" process of on-chain liquidity and drive the multi-chain ecosystem towards maturity.
Written by: imToken
The Ethereum ecosystem may soon transition from the chaotic "Warring States" phase of L2 to a unified era.
The key to this transition is the ongoing ERC-7786, which aims to set a universal "interface specification" for cross-chain communication on Ethereum, integrating various messaging standards under a unified API to enable communication between smart contracts across different blockchain networks within the Ethereum ecosystem.
As early as April 15, Ethereum Foundation member joshrudolf.eth publicly emphasized that "cross-chain messaging is one of the key elements in solving the cross-chain user experience issues on Ethereum."
So, what exactly is ERC-7786, what problems does it aim to solve, and why is it important? This article will help you understand this new standard that deserves the attention of all Ethereum users.
01 Ethereum Needs a Unified Cross-Chain Communication Protocol
As we know, from the initial multi-chain concepts of Cosmos and Polkadot to the flourishing Rollup era of Ethereum L2, especially with the significant development of application chains like OP Stack, Arbitrum Nova, and Starknet, liquidity has become increasingly fragmented across Ethereum and L2.
According to incomplete statistics from L2BEAT, there are broadly over a hundred Ethereum L2s, leading to a long-discussed issue—extreme fragmentation of liquidity.
It is important to note that even though they are all based on the Ethereum ecosystem, different L2s do not communicate with each other. If users want to transfer assets from Arbitrum to Starknet or interact with contracts across different L2s, they can only rely on cross-chain bridges or cross-chain messaging protocols to achieve secure interactions between contracts, users, and assets across multiple networks.
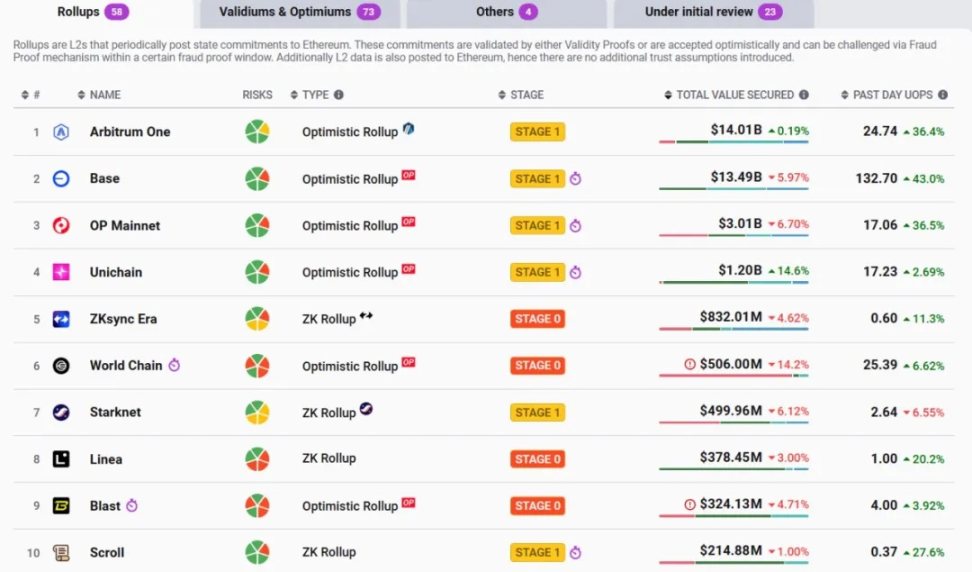
Source: L2BEAT
This not only causes users to incur friction costs due to cross-chain barriers but also severely weakens the synergistic effects within the Ethereum ecosystem, especially among various L2s. Although many protocols have already implemented inter-chain communication functions, each protocol has its own interfaces, calling methods, and security models, making it nearly impossible for developers to reuse code or interface logic across different protocols. This directly leads to repeated "wheel reinvention" and high operational costs, resulting in an extremely fragmented user experience.
Thus, the introduction of ERC-7786 aims to break this fragmented ecosystem by providing a unified standard interface for all inter-chain communication protocols, allowing DApps to communicate securely with any chain through the same "gateway" without being tied to a specific protocol:
This standard is led by OpenZeppelin and supported by multiple cross-chain and modular projects, including the Ethereum Foundation and Axelar. As a unified cross-chain messaging interface standard for DApps, it aims to standardize a universal interface for decentralized applications (DApps) to securely send and receive messages across multiple blockchains.

Source: erc7786.org
02 ERC-7786: A "Unified Interface" for Cross-Chain Communication
In a nutshell, ERC-7786 is like the "ERC-20" of the cross-chain communication field.
Just as ERC-20 provides a standard interface for tokens and ERC-721 defines a universal standard for NFTs, ERC-7786 also attempts to establish a unified, general "communication interface" for cross-chain messaging—you can think of it as the "USB standard" in the Web3 world; as long as you connect to the standardized interface, any protocol can be plug-and-play.
The following diagram presents the core components and processes of ERC-7786, demonstrating how to send and receive messages between different blockchains through standardized interfaces. An ERC-7786 message includes four basic elements:
Sender: Identified using CAIP-10 format (e.g., eip155:1:0xabc…)
Receiver: Also identified by CAIP-10 format for the target address
Payload: Any execution data (bytes)
Attributes: Additional parameters, such as gas limits and processing priorities, expressed in function signature form (e.g., minGasLimit(uint256))
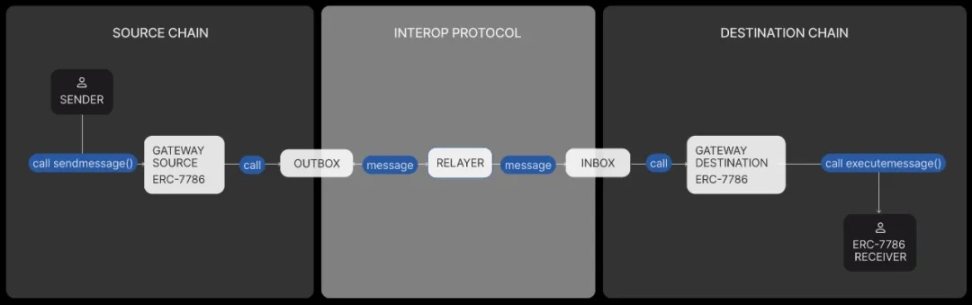
Source: erc7786.org
Here, sendMessage() is used to initiate a message from Chain A, while executeMessage() is used for Chain B to receive and execute it. This "send-receive closed loop" forms the basic logic of cross-chain communication, allowing DApps to encapsulate the standard interface once and be compatible with multiple cross-chain protocol modules, achieving true "protocol decoupling + communication freedom."
Currently, ERC-7786 has announced that its interface functionality is complete and is awaiting the final merge of the binary interoperability address specification (i.e., unified address encoding). In the future, it also plans to add a "Gas sponsorship" extension, allowing users to have Gas prepaid by a third party when executing transactions on the target chain, thereby optimizing the user experience of inter-chain interactions.
More importantly, ERC-7786 is designed to support modular adaptation, allowing developers to build adapters for existing mainstream cross-chain protocols (such as Axelar, LayerZero, Wormhole, etc.) without needing to reconstruct logic, enabling quick compatibility with the ERC-7786 standard interface.
This means that even if users, liquidity, and applications are distributed across multiple L2s or heterogeneous chains, DApps can leverage ERC-7786 to build native cross-chain calling capabilities without being tied to specific bridge protocols or relying on cumbersome UI switches, significantly enhancing the overall experience and reducing integration complexity.
It is worth mentioning that the attribute mechanism (Attributes) of ERC-7786 also allows for the integration of extended functionalities from different cross-chain protocols, such as verification logic, state proofs, and limit controls, without affecting the standard main process, leaving ample flexible interface space for the evolution of middleware and verification mechanisms.
From this perspective, the significance of ERC-7786 goes beyond merely "being compatible with multiple cross-chain protocols"; it represents a new era of "native interoperability" in the Web3 multi-chain architecture, moving away from "cross-chain deployment."
03 What Can ERC-7786 Bring?
For this reason, ERC-7786 is widely regarded as an important infrastructure for promoting higher interoperability in the Ethereum and multi-chain ecosystems. It not only breaks down long-standing protocol barriers but also lays the groundwork for future cross-chain functionality expansion, verification mechanism upgrades, and multi-chain collaboration with a unified standard infrastructure.
From a practical implementation perspective, the value brought by ERC-7786 can be summarized into two core beneficiaries—developers and end-users:
For developers, they only need to develop once for multi-chain deployment, without having to repeatedly adapt to different protocols, and can switch cross-chain backends at any time, enhancing security and maintainability, while also supporting more customizable attributes and functional expansions (such as Gas, state verification, etc.);
For users, there is no longer a need to switch bridges and UIs back and forth between Arbitrum and zkSync; they can complete cross-chain operations with a simple confirmation click. Perceptually, the boundaries between chains are becoming blurred, making it feel as natural as using a single chain;
Currently, ERC-7786 is continuously advancing its ecosystem implementation. According to publicly disclosed information, in the next 3 to 6 months, ERC-7786 will successively release standard adapters for mainstream protocols, promoting more DApps, bridges, and verification middleware to integrate this standard, forming a truly meaningful Web3 cross-chain infrastructure.
It is noteworthy that on June 13, Axelar developer Interop Labs and OpenZeppelin jointly launched the open-source framework OpenBridge based on ERC-7786. This tool will allow developers to access multiple bridge protocols at once, further enhancing construction efficiency and protocol redundancy, making it easier for developers to connect to multiple interoperability protocols at once.

Source: Axelar
From a broader perspective, the significance of ERC-7786 goes far beyond the specification of technical interfaces; it opens up an "ordered interconnection path" for the current chaotic multi-chain ecosystem:
It blurs the boundaries of "chains" within the broader Ethereum ecosystem, laying a crucial foundation for the evolution of a truly meaningful Web3 user experience.
04 Conclusion
Looking back at the development trajectory of Ethereum, from the composability of smart contracts to the rapid formation of modular infrastructure, and the trends of L2 generalization and dedicated chains, "cross-chain interoperability" has become a necessary condition for the next stage of explosion.
The significance of ERC-7786 lies not only in making cross-chain interactions more convenient but also in its attempt to establish a unified standard for "multi-chain collaboration" to combat "entropy increase." This can further promote the "unification" process of on-chain liquidity and drive the multi-chain ecosystem towards maturity.
As for whether ERC-7786 can indeed lead Ethereum to touch the critical point of transformation, it remains to be seen.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



