作者:Biteye 核心贡献者Wilson Lee
编辑:Biteye 核心贡献者 Crush
背景介绍
4 月 10 日,A16z Crypto 发布了零知识解决方案 Jolt,以加速和简化区块链扩展操作。
Jolt 集成了 SNARK(非交互式简洁零知识证明),可以让开发人员快速创建基于 SNARK 的 L2 解决方案。团队还表示,Jolt 比目前的 zkVMs 快达 2 倍。
ZK 技术是加密行业贯穿周期的主线之一,ZK-Rollup 更是被 Vitalik 称作以太坊扩容长期的解决方案。A16z 从去年 8 月推出 Jolt 到今年正式发布,表明了ZK-Rollup 仍是长坡厚雪的赛道。
ZK-Rollup 已经有众多玩家入局,已经形成了更加细分的技术类别来区分项目之间的差异性,对 EVM 的兼容性是最具代表性的分类标准。
EVM 由于历史性的原因,存在大量的 ZK 不友好设计,然而大量现有项目在早期又是基于 EVM 构建的,且 ZK-Rollup 还被视作未来的扩容方案,因此绝大部分 ZK-Rollup 项目都天然面对着更兼容 EVM 还是更兼容 ZK 的权衡。
由 Metis DAO 孵化的 ZKM 则是从更底层的角度出发,提出了通用性的 zkMIPS 方案。
zkMIPS 通过使用更底层的 MIPS 指令集来实现程序执行过程到 ZKP 的转换,除了兼容 EVM 外,可以兼容其他的 VM,例如 MoveVM 和 RustVM,让 ZK-Rollup 能够面向更多元的开发者敞开大门。
本文将为读者深度解读 Metis 在 ZK 和去中心化 Sequencer 上的努力与进展。
ZKM 与 Hybrid Rollups:OP 与 ZK 的调和
Metis 能够在市场中取得亮眼表现,离不开其创新的 Hybrid Rollups 机制,即将欺诈证明和有效性证明相结合,从而兼具两者的优点。
ZKM 的 zkMIPS 技术又为 Metis 的 Hybrid Rollups 提供坚实的兼容性支持,让 Metis 实现 ZK 和 EVM 的有机融合。
Hybrid Rollups 的机制与优点
在 Hybrid Rollups 中,关键角色包括:
Sequencer:负责接收和处理用户交易,确定交易的最佳顺序,并将其打包发布到共识和数据可用性层。
Proposers:评估Sequencer提交的交易和状态根,记录到状态承诺链(State Commitment Chain, SCC)中。
Verifiers:验证Rollup链上的状态根,确保交易的正确性并防止欺诈行为。
在标准的L2解决方案中,Sequencer 收集并处理交易,然后将交易数据发布到以太坊主网(L1)。这个过程需要L1进行最终的数据验证和确认,从而确保安全性和一致性。
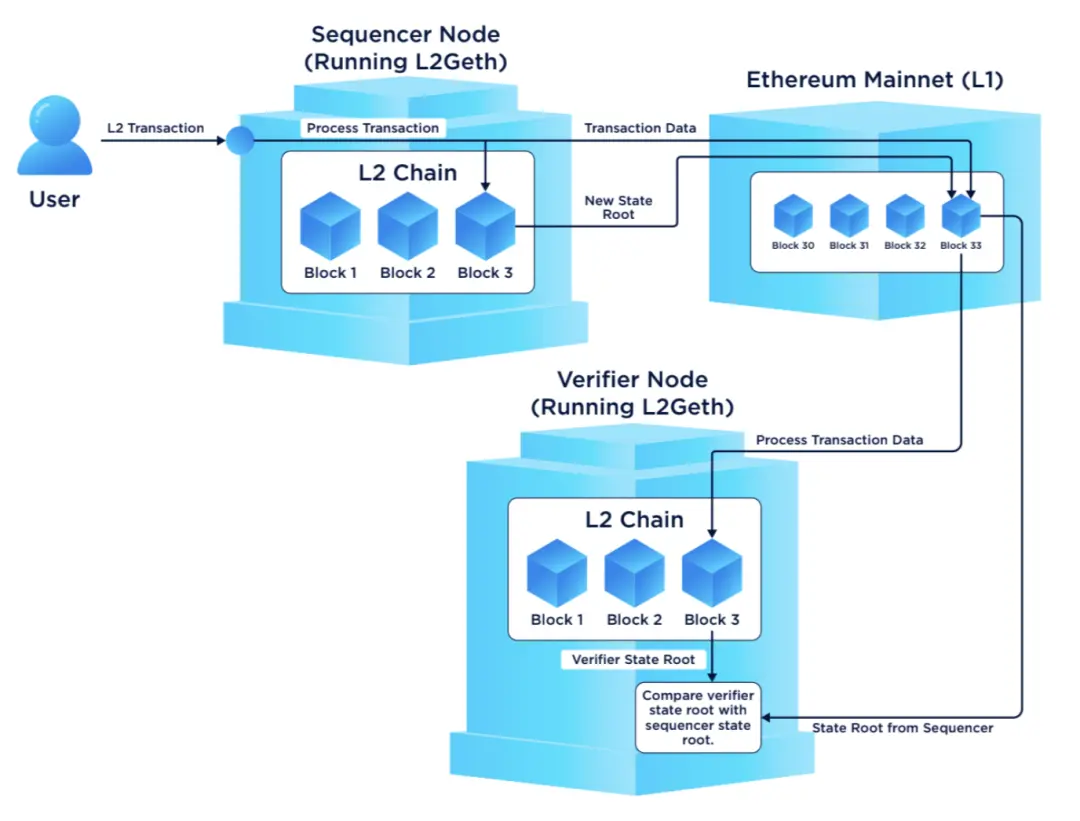
Hybrid Rollups在处理和优化L2交易时采取了一种混合方法,具体步骤如下:
1. 交易的发起和处理:
用户在 L2 发起交易。
Sequencer 接收并处理这些交易,决定它们在规范交易链(Canonical Transaction Chain, CTC)中的顺序。
2. 状态提交和验证:
Proposers 评估交易后提交状态根到SCC。
Verifiers 对SCC中的状态根进行审核,确保其准确无误。
3. 零知识证明的生成和验证:
Prover从L1读取数据,生成ZK证明,这一点是Hybrid Rollups的关键特性,允许系统在不泄露具体交易内容的情况下验证交易的有效性。
一旦ZK证明生成,如果未按时提交,Verifier会启动欺诈证明流程,可能会对Sequencer进行惩罚。
4. 数据和状态的最终确认:
通过智能合约,一旦ZK证明被验证通过,交易最终确定。
L1和L2之间通过智能合约桥接,确保资金和状态的安全转移。
Hybrid Rollups的设计提供了多个显著优势:
效率和成本效益:通过使用ZK证明,Hybrid Rollups能够在消耗更少的gas的同时,处理更多的交易。
增强的安全性:结合了传统的欺诈证明和ZK证明,即使在遇到潜在的恶意行为时也能保障交易的安全和正确性。
可扩展性:利用递归证明,Hybrid Rollups能够处理大规模的交易而不牺牲性能,支持更广泛的区块链应用。
兼容性和灵活性:支持多种智能合约和编程语言,使得开发者能够轻松地将现有应用迁移到Hybrid Rollups上。
zkMIPS 如何实现良好的 ZK 兼容性
ZK 的核心思想是将程序执行过程转换成可以简单验证的数学证明,让所有人都能够轻易验证程序执行的正确性,且不需要重复执行程序,其中的难点在于如何将任意的程序逻辑转变成相对稳定的数学证明。
开发者通常使用高级语言来进行程序的开发,而不同的高级语言则使用不同的逻辑与硬件“对话”。
因此,现有的 ZK 项目的实现路径通常互不兼容。Scroll 直接为 EVM 的每个操作码编写电路,实现了操作码级别的等效,其准确地反映了 EVM,但带来了巨大的工程量;
Polygon zkEVM 则创建了具有优化性能的自定义 VM,将 EVM 字节码直接转换为 VM 的字节码,更高效地实现了操作码级别的等效性,但大量自定义代码的引入可能在长期偏离 EVM;
zkSync 则创建了自己的 VM (SyncVM),并基于寄存器定义了自己的代数中间表示 (AIR),然后构建了一个专门的编译器来将 Yul(一种中间语言,可以编译为不同 EVM 版本的字节码,认为是较低级别的 Solidity)编译成 LLVM-IR,然后将其编译成自定义 VM 的指令,从而实现了 Solidity 级别的兼容,但其无法直接使用现有的以太坊工具,语言之间的转换也可能需要重新审计程序;
StarkNet 则放弃 EVM 兼容,直接使用自己的低级语言 (Cairo) 运行自定义智能合约 VM (Cairo VM),来获得极致的 ZK 效率。
相比于上述项目的解决方案,ZKM 选择了一条更具包容性的道路:zkMIPS。
MIPS,全称为"Microprocessor without Interlocked Pipeline Stages",是一种设计简洁的微处理器指令集,始于 1985年 。
MIPS 的基本原则是将复杂的微处理器指令简化至最基本形式,这样做不仅提高了处理速度,还降低了执行程序时的复杂性。
在 zkMIPS 系统中,这种指令集被用来实现程序到ZK证明的转换。
zkMIPS的实现过程如下:
程序到 MIPS 的转换:首先,高级编程语言(如 Solidity 或 Rust)编写的智能合约或程序被编译成 MIPS 指令集。这一步是将较高级别的抽象转换成可以在硬件级别执行的具体操作。
生成 ZK 证明:随后,这些 MIPS 指令被用来生成对应的零知识证明。由于 MIPS 的简化特性,这一步在计算上更为高效,可以更快地产生证明而不牺牲安全性。
zkMIPS的优势
兼容性:zkMIPS 不仅支持 EVM 兼容的 Solidity,还能支持如 Rust 和 Move 等其他主流开发语言。这使得 zkMIPS 能够服务于更广泛的区块链开发生态系统,从而带来更多的应用可能性。
成本效益:由于 MIPS 指令集的高效性,zkMIPS 在生成零知识证明时能显著降低运算成本,增加了系统的整体可持续性。
递归证明:zkMIPS 支持递归证明,可以将多个证明聚合成一个更易管理的单元,这在提高系统可扩展性方面至关重要。
实际上,MIPS 的优势已经被 Optimism 等项目集成。Optimism 的 Cannon 机制就是将执行过的程序转换成 MIPS,从而方便执行过程被挑战时更加简单高效地查找错误和重新执行。
Metis 也跟进了这一趋势,将 Cannon 集成到其生态系统中,这也进一步验证了 zkMIPS 技术的实用性和效率。
去中心化 Sequencer:去中心化与可持续性
除了使用 Hybrid Rollups 来综合 OP 和 ZK 的优点之外,Metis 还积极推进去中心化 Sequencer 的落地,为 Rollup 树立去中心化的表率。
在传统的Rollup模型中,单一的 Sequencer 虽然能有效处理交易和数据,但也集中了极大的权力,可能导致多种风险:
操作风险:如果sequencer发生故障或者遭受攻击,整个系统的交易处理将会被阻断。
审查风险:sequencer有能力选择性地处理或拒绝交易,这可能限制用户访问特定的去中心化金融(DeFi)协议或服务。
操纵风险:在交易排序中,sequencer可能优先处理自身的交易,通过提高交易费用来获取不正当利益,即最大可提取价值(MEV)。
为了解决上述问题,Metis 设计了一个去中心化的 Sequencer 池,该池由多个 Sequencer 节点组成,共同完成交易的聚合、排序和执行。这一设计确保了系统的公正性和透明度:
共识机制:超过三分之二的 Sequencer 节点必须就每个新区块的状态达成共识,之后才能将交易批次提交到以太坊主网(L1)。
多方计算(MPC)签名:在交易批次提交到L1之前,通过MPC签名验证批次的真实性,确保数据的正确无误。
去中心化 Sequencer 的优势:
增强安全性:通过多个节点共同决策,降低了单点失败的风险,增加了网络的鲁棒性和安全性。
降低审查和操纵的可能性:多个 Sequencer 的存在使得单一节点难以操纵或审查交易,保护了用户的交易自由。
稳定性和冗余:系统支持 Sequencer 的平滑轮换,最小化了故障或中断的影响,提高了整个网络的稳定性。
在 Metis 的去中心化 Sequencer 模型中,每个节点都由几个关键组件组成:
L2 Geth(包括OP-Node):负责交易排序和区块组装。
适配器模块:作为与其他外部模块(主要是PoS节点)交互的中介。
批次提交者(Proposer):负责构建交易批次并在获得多个 Sequencer 的认可后提交到 L1。
PoS节点:在以太坊、共识和 Metis 层之间进行协调,确保资产的安全锁定并奖励验证者。
共识层:包含一组与以太坊主网并行运行的 Tendermint PoS 节点,保证操作效率而不妨碍主网的进程。
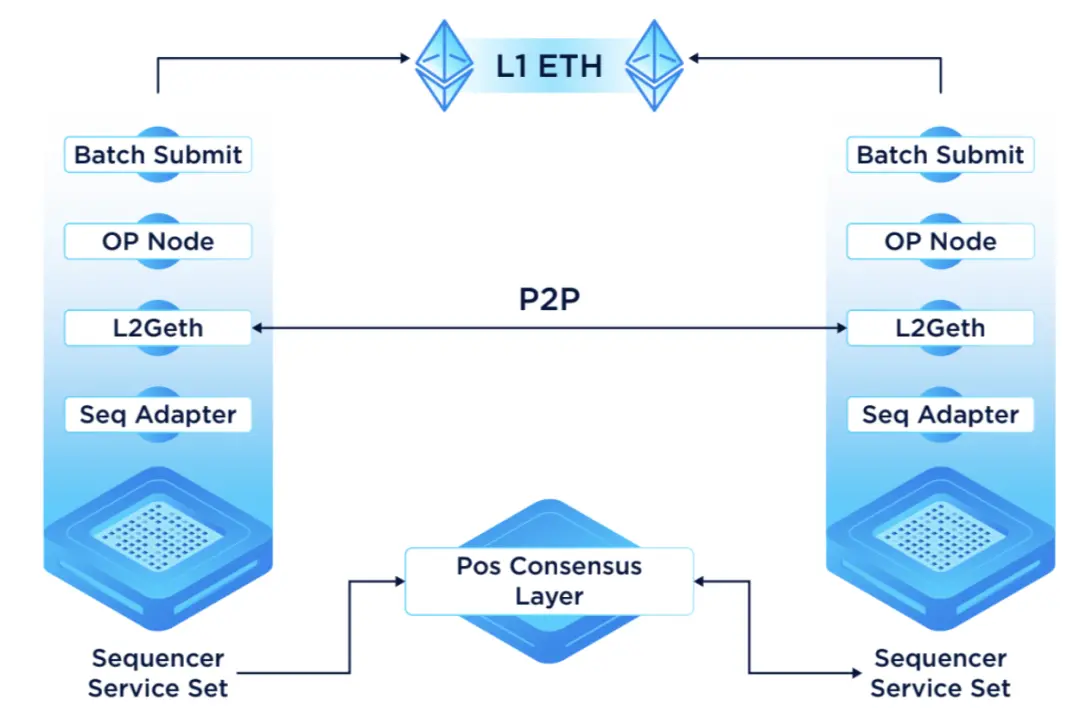
通过这种设计,Metis 的去中心化 Sequencer 池不仅提高了交易处理的公正性和透明度,还通过分散权力来增强了网络的安全性和稳定性,这些都是构建可信和可持续区块链生态系统的关键要素。
总结与展望
Metis 在技术和理念上的优势为未来的进一步发展打造了坚实的基础。其基于 zkMIPS 的 Hybrid Rollups 有望能够为 ZK-Rollup 解决兼容性的问题,从来带来更多元的开发者生态;
对于去中心化 Sequencer 的推进则展现了团队追求去中心化的愿景。随着 Metis 的生态不断成熟,我们有理由相信 Metis 会在未来的 L2 竞争中成为持续奔跑的黑马,为用户和开发者创造源源不断的价值。
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




