On April 17th, IOSG Ventures' 12th Old Friends Reunion was held as scheduled, with the theme "Singularity: AI x Crypto Convergence". Therefore, we also invited outstanding representatives from the industry who are emerging. The purpose of this gathering is to explore the convergence of artificial intelligence and cryptocurrency, and the impact of this convergence on the future. At such an event, participants have the opportunity to share their insights, experiences, and ideas, thereby promoting cooperation and innovation within the industry.
Next is one of the keynote speeches of this event, brought to you by Illia Polosukhin, co-founder of NEAR Protocol, a portfolio of IOSG Ventures, titled "Why AI Needs to be Open - 为何AI需要Web3".

Why AI Needs to be Open
Let's explore "Why AI needs to be open". My background is in Machine Learning, and for about ten years of my career, I have been involved in various machine learning work. But before getting involved in Crypto, natural language understanding, and founding NEAR, I worked at Google. We developed a framework that drives most modern artificial intelligence, called Transformer. After leaving Google, I started a Machine Learning company so that we could teach machines to program, thereby changing how we interact with computers. However, we did not do this in 2017 or 2018, as it was too early and there was not enough computing power and data to do so.

What we did at the time was to attract people from all over the world to annotate data for us, most of whom were students. They were in China, Asia, and Eastern Europe. Many of them did not have bank accounts in these countries. The United States is not willing to remit money easily, so we started to use blockchain as a solution to our problem. We wanted to pay people around the world in a programmatic way, making it easier for them no matter where they are. By the way, the current challenge of Crypto is that, although NEAR has solved many problems, in general, you need to purchase some Crypto first in order to trade on the blockchain to earn, which is going the opposite way.
Just like companies, they would say, "Hey, first, you need to buy some shares of the company to use it." This is one of the many problems that NEAR is solving. Now let's delve a little deeper into artificial intelligence. Language models are not something new; they have been around since the 1950s. It is a statistical tool widely used in natural language processing. For a long time, starting from 2013, with the resurgence of deep learning, a new innovation began. This innovation is that you can match words, add them to multi-dimensional vectors, and transform them into mathematical forms. This works well with deep learning models, which are just a lot of matrix multiplication and activation functions.
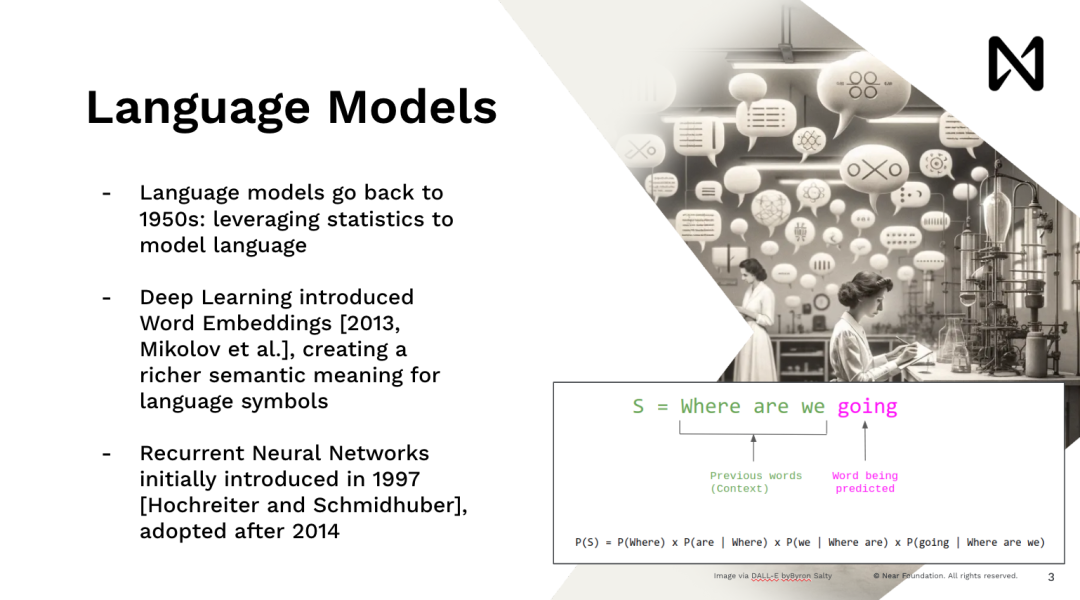
This allows us to start advanced deep learning and train models to do many interesting things. Looking back now, what we were doing at the time was neural networks, which largely mimic human models, where we can read one word at a time. So, it was very slow, right? If you try to show some content to users on Google.com, no one will wait to read Wikipedia, for example, five minutes later to get an answer, but you want to get the answer immediately. Therefore, the Transformer model, which drives ChatGPT, Midjourney, and all the recent advancements, all come from this idea, all hoping to have a model that can process data in parallel, reason, and provide answers immediately.
So, a major innovation here is that every word, every token, every image block is processed in parallel, leveraging our highly parallel computing capabilities of GPUs and other accelerators. By doing this, we can infer it at scale. This scalability can scale up the training scale, thereby handling automatic training data. Therefore, after this, we saw Dopamine, which did amazing work in a short time, achieving explosive training. It had a lot of text and began to achieve amazing results in reasoning and understanding world languages.
The current direction is to accelerate the innovation of artificial intelligence, which was previously a tool used by data scientists and machine learning engineers, and then somehow explained the content of their products or discussed data with decision-makers. Now we have this mode of AI directly communicating with people. You might not even know that you are interacting with a model because it is actually hidden behind the product. So, we have undergone this transformation from understanding how AI works to understanding and being able to use it.

So, I'm giving you some background here. When we say we are using GPUs to train models, it's not the kind of gaming GPU we use on our desktops.

Each machine typically comes with eight GPUs, all interconnected through a motherboard and stacked into a rack, with about 16 machines per rack. Now, all these racks are also interconnected through dedicated network cables to ensure information can be transmitted directly and rapidly between GPUs. So, the information is not suitable for the CPU. In fact, you wouldn't process it on the CPU at all. All the computation happens on the GPU. So, this is a supercomputer setup. Again, emphasizing, this is not the traditional "hey, this is a GPU thing". So, a model like GPU4 used 10,000 H100s for training in about three months, with a cost of $64 million. You can understand the scale of the current costs and the expenditure for training some modern models.
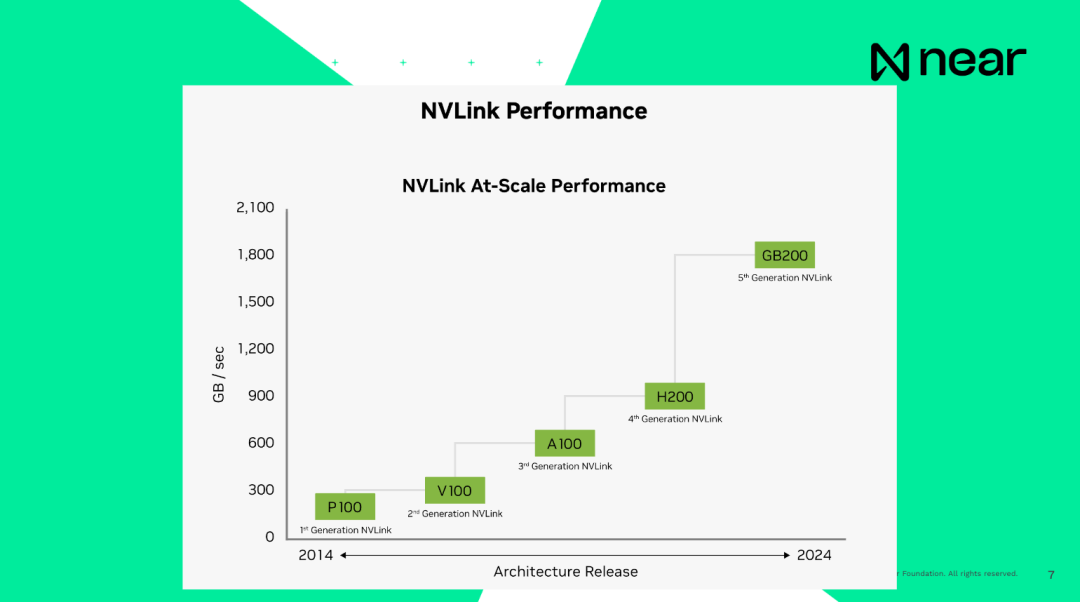
Important is when I say the systems are interconnected, the current connection speed of H100, the previous generation product, is 900GB per second, and the connection speed between the CPU and RAM inside the computer is 200GB per second, all local to the computer. Therefore, the speed of sending data from one GPU to another within the same data center is faster than your computer. Your computer can basically communicate within the box. And the connection speed of the next generation product is basically 1.8TB per second. From a developer's perspective, these are not individual computing units. These are supercomputers with huge memory and computing power, providing you with massive-scale computing.
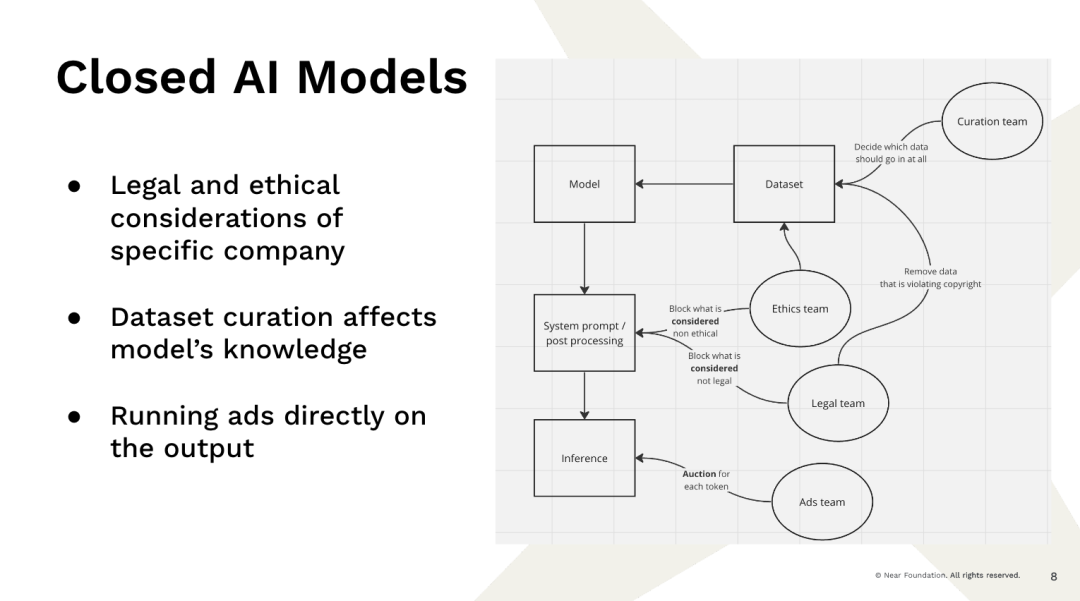
Now, this leads to the problem we are facing, that these big companies have the resources and capabilities to build these models, which now almost provide this service for us, I don't know how much work is actually involved, right? So, this is an example, right? You go to a completely centralized provider and input a query. The result is, there are several teams that are not software engineering teams, but teams that decide how the results are displayed, right? You have a team deciding which data goes into the dataset.
For example, if you are just scraping data from the internet, the number of times Barack Obama was born in Kenya and the number of times Barack Obama was born in Hawaii are exactly the same because people like to speculate controversies. So, you have to decide what to train on. You have to decide to filter out some information because you don't believe it's true. So, if individuals have already decided which data will be adopted and there is this data, these decisions are largely influenced by the people making them. You have a legal team deciding what content we cannot view due to copyright, what is illegal. We have an "ethical team" deciding what is unethical and what content we should not display.
So, to some extent, there is a lot of filtering and manipulation. These models are statistical models. They pick from the data. If certain content is not in the data, they won't know the answer. If certain content is in the data, they are likely to take it as a fact. Now, when you get an answer from AI, it can be worrisome. Right? You are supposed to get an answer from the model, but there is no guarantee. You don't know how the result was generated. A company might sell your specific conversation to the highest bidder to actually change the result. Imagine you ask which car to buy, and Toyota decides it should lean towards Toyota, and Toyota pays the company 10 cents to do that.

So even if you use these models as a neutral knowledge base representing the data, a lot happens before you get the result, and these things bias the result in a very specific way. This has raised a lot of issues, right? This is basically a week of different legal battles between big companies and the media. The SEC, now almost everyone is trying to sue each other because these models bring so much uncertainty and power. And looking forward, the problem is that big tech companies will always have the incentive to continue increasing revenue, right? For example, if you are a public company, you need to report revenue, you need to keep growing.
To achieve this, if you already have the target market, for example, you already have 2 billion users. There are not that many new users on the internet anymore. You don't have much choice but to maximize average revenue, which means you need to extract more value from the users, and they may not have much value at all, or you need to change their behavior. Generative AI is very good at manipulating and changing user behavior, especially if people think it is appearing in the form of all-knowing intelligence. So, we are facing a very dangerous situation where there is a lot of regulatory pressure, and regulatory agencies do not fully understand how this technology works. We have almost no protection for users from manipulation.

Manipulative content, misleading content, even without ads, you can just take a screenshot of something, change the title, and post it on Twitter, and people will go crazy. You have economic incentives that cause you to constantly maximize revenue. And this is actually not like doing something evil within Google, right? When you decide which model to launch, you do A/B testing to see which one brings in more revenue. So, you constantly maximize revenue by extracting more value from the users. And the users and the community have no input into the content of the model, the data used, and the actual goals attempted to be achieved. This is the situation of application users. This is a regulation.
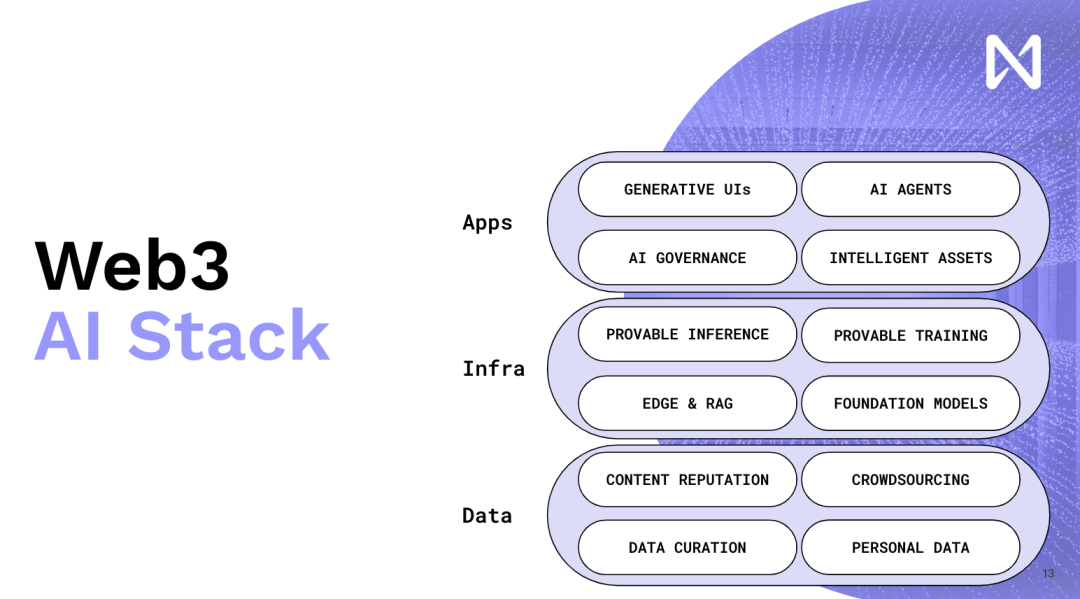
This is why we need to continuously push for the integration of WEB 3 and AI, web 3 can be an important tool that allows us to have new incentive mechanisms and incentivize us to produce better software and products in a decentralized form. This is the general direction of the entire web 3 AI development. Now, to help understand the details, I will briefly talk about specific parts. First, the first part is Content Reputation.

Again, this is not purely an artificial intelligence problem, although language models have had a huge impact on people's manipulation and exploitation of information and have expanded the scale. What you want is an encrypted reputation that can be tracked and traced, which will manifest when you look at different content. So imagine you have some community nodes that are actually encrypted and can be found on every page of every website. Now, if you go beyond this point, all these distribution platforms will be disrupted because these models now almost read all this content and provide you with personalized summaries and personalized outputs.
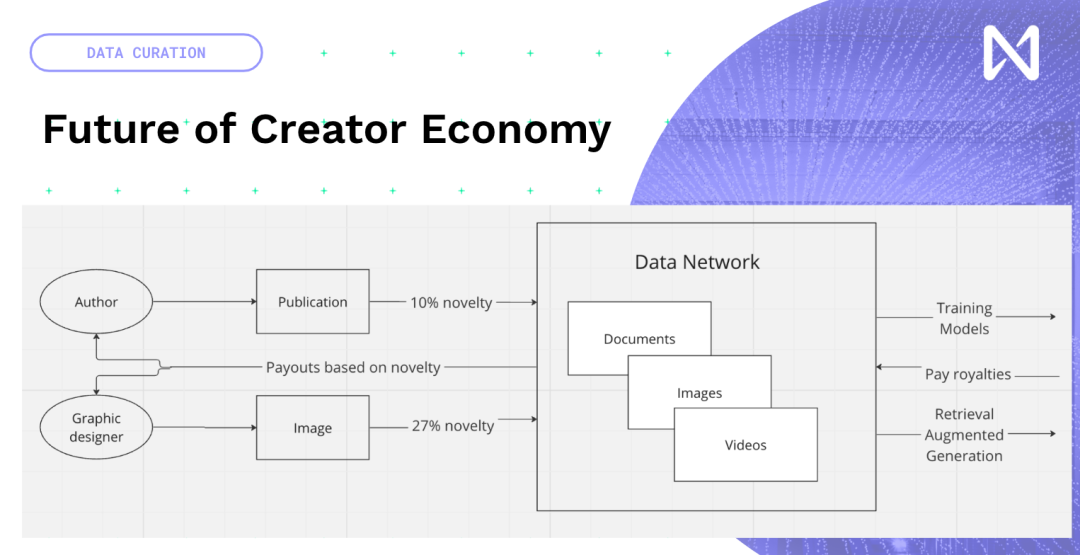
So, we actually have the opportunity to create new creative content instead of trying to reinvent, let's put blockchain and NFTs on existing content. The new creator economy around model training and inference time, the data created by people, whether it's new publications, photos, YouTube, or music you create, will enter a network based on its contribution to model training. So, based on this, content can receive some rewards globally. So, we are transitioning from the attention economy driven by advertising networks to an economy that truly brings innovation and interesting information.
I want to mention one important thing, which is that a lot of uncertainty comes from floating-point operations. All these models involve a lot of floating-point operations and multiplication. These are operations of uncertainty.
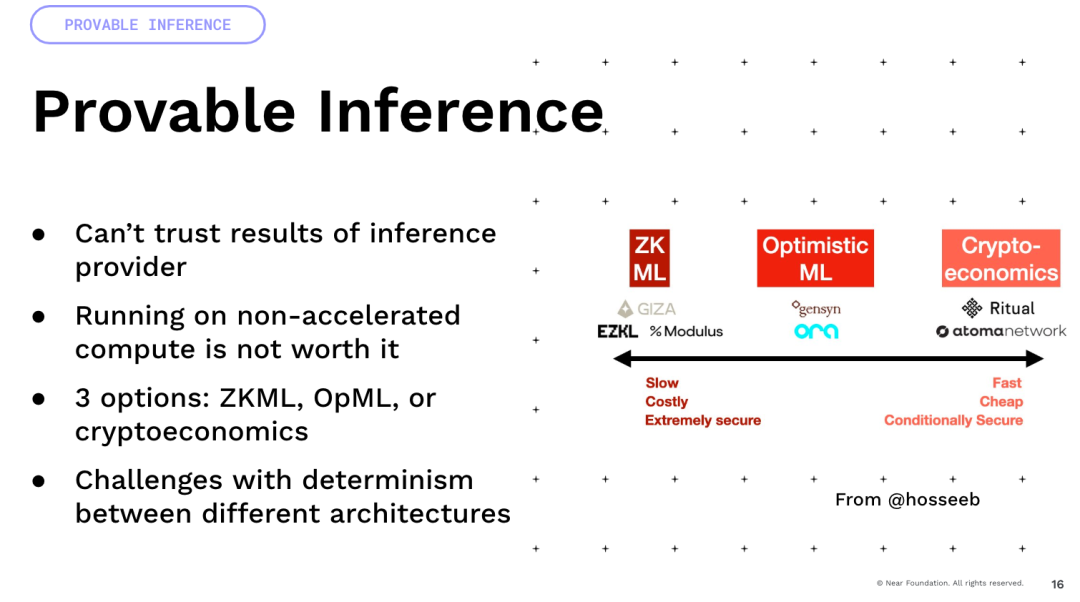
Now, if you perform multiplication operations on them on GPUs of different architectures. So if you take an A100 and an H100, the results will be different. Therefore, many deterministic methods, such as the encrypted economy and optimism, will actually encounter many difficulties and require a lot of innovation to achieve this. Finally, there is an interesting idea. We have been building programmable currencies and programmable assets, but if you can imagine, if you add this kind of intelligence to them, you can have intelligent assets, which are not defined by code, but by the ability to interact with natural language and the world, right? This is how we can have a lot of interesting profit optimization, DeFi, and we can trade strategies within the world.
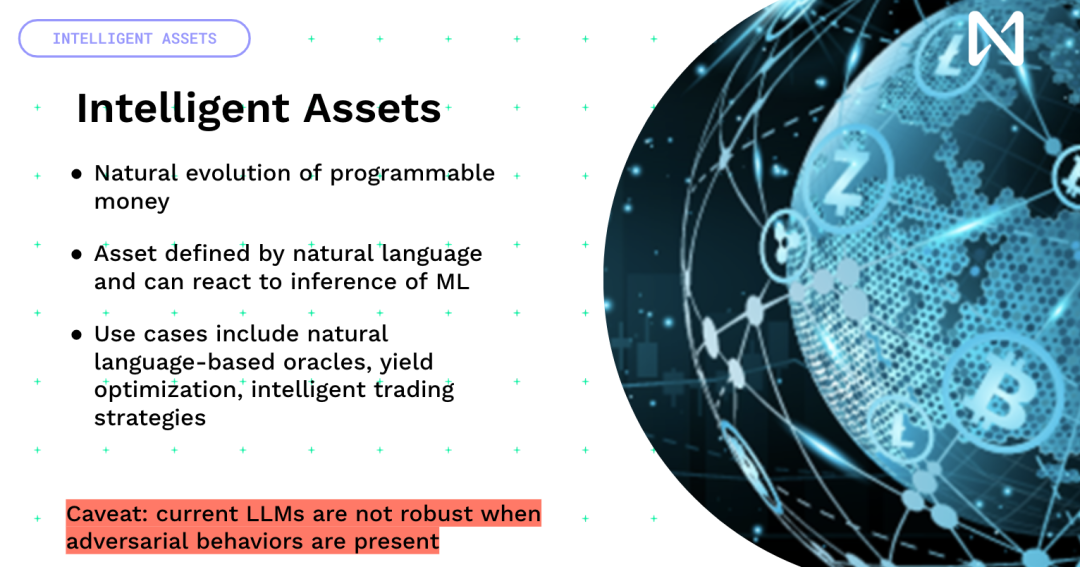
The current challenge is that all current events do not have strong Robust behavior. They have not been trained to have adversarial strength, because the purpose of training is to predict the next token. Therefore, convincing a model to give you all your money will be easier. It is actually very important to solve this problem before continuing. So I leave you with this idea, we are at a crossroads, right? There is a closed artificial intelligence ecosystem with extreme incentives and flywheels, because when they launch a product, they generate a lot of revenue and then reinvest that revenue into building the product. However, the product is inherently designed to maximize the company's revenue, thereby maximizing the value extracted from the users. Or we have this open, user-owned approach, where users control the situation.

These models actually work in your favor, trying to maximize your interests. They provide you with a way to truly protect yourself from many dangers on the internet. So this is why we need more development and application of AI x Crypto. Thank you, everyone.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




