
BTC is currently the highest market value digital asset, but the vast majority is still idle. Based on this, the Babylon team proposed the concept of BTC staking, allowing BTC holders to stake their idle BTC to enhance the security of the PoS chain. The B² Network team proposes to build the execution layer of Bitcoin through modular design, allowing BTC holders to deposit BTC into the execution layer of Bitcoin (commonly known as Layer-2s) for various DApp operations, thereby increasing the liquidity of BTC. B² Network and Babylon will closely cooperate to establish infrastructure and services, using Rollup as the execution layer protected by the Bitcoin network.
The core component of B² Network, B² Hub, will enhance its security by integrating Babylon's BTC staking. Additionally, B² Network plans to integrate BTC staking functionality in B² Rollup, supporting BTC LSD and BTC re-staking scenarios in B² Rollup.
Modular design of B² Network
Due to the limitations of storage and transaction load of BTC itself, as well as the non-Turing completeness of Script, it cannot independently achieve the scalability of the network.
To support the scalability of Bitcoin, B² Network adopts a modular blockchain design architecture.
We believe that a scalable blockchain network consists of: the execution layer, the data availability layer, and the consensus layer. Among these three layers, the execution layer can achieve unlimited horizontal scalability through the Rollup solution; the data availability layer achieves DAS (Data Availability Sampling) through B² Hub, combined with decentralized storage, recording the final data index and proof on Bitcoin, ensuring the availability, security, and decentralization of transactions and states in the execution layer; the consensus layer verifies the state transition in the execution layer through commitment and challenge mechanisms, with sufficient security and decentralization.
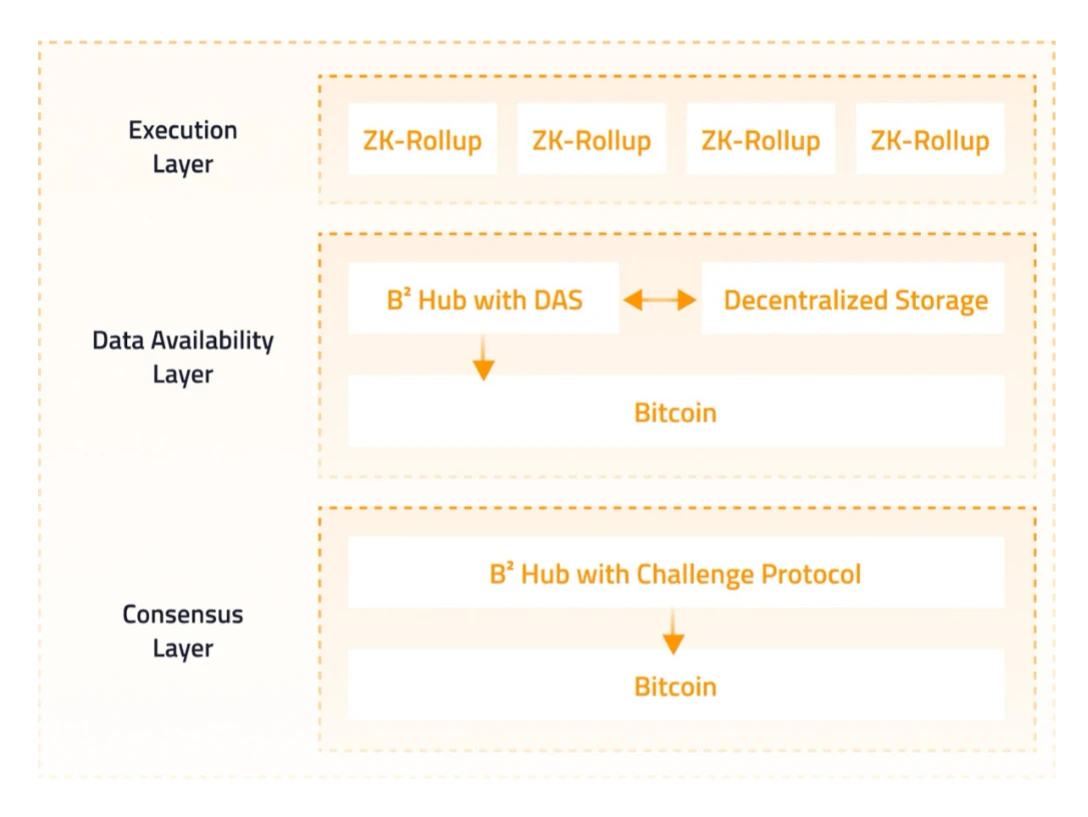
Development of B² Network is divided into two stages:
The first stage starts with B² Network running its own B² Rollup on B² Hub, running on Bitcoin through B² Hub, completing the first Bitcoin ZK-Rollup running on B² Hub.
The second stage supports launching any ZK-Rollup on B² Hub, completing the proof of data availability and state transition on Bitcoin through B² Hub.
First stage: B² Hub serving B² Rollup
The first stage of B² Network consists of the Rollup layer and the DA layer.
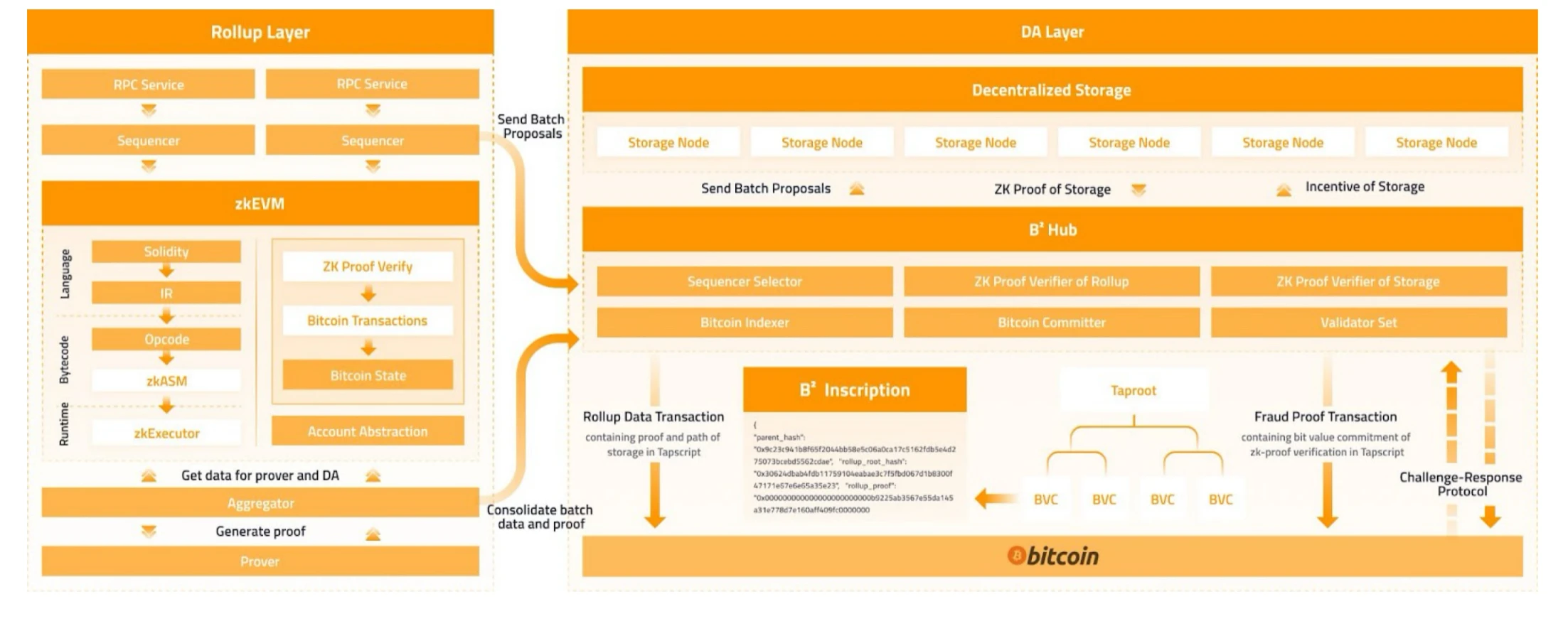
The Rollup layer adopts ZK-Rollup technology, and we are currently collaborating with Polygon to build ZK-Rollup through zkEVM. In the Rollup layer, data and proofs are sent to the DA layer and the consensus layer through Sequencer and Aggregator, respectively.
B² Hub acts as the core hub, receiving data and proofs from ZK-Rollup. On the one hand, it stores the transactions and detailed data of the Rollup layer in the DAS protocol and distributed storage protocol of B² Hub, and writes the data proof into Tapscript to submit to Bitcoin, ensuring data availability; on the other hand, it verifies the ZK proof of ZK-Rollup, generates the commitment of the verification process, and submits it to Bitcoin, allowing challengers to challenge based on these commitments, ultimately completing the verification of state transition.
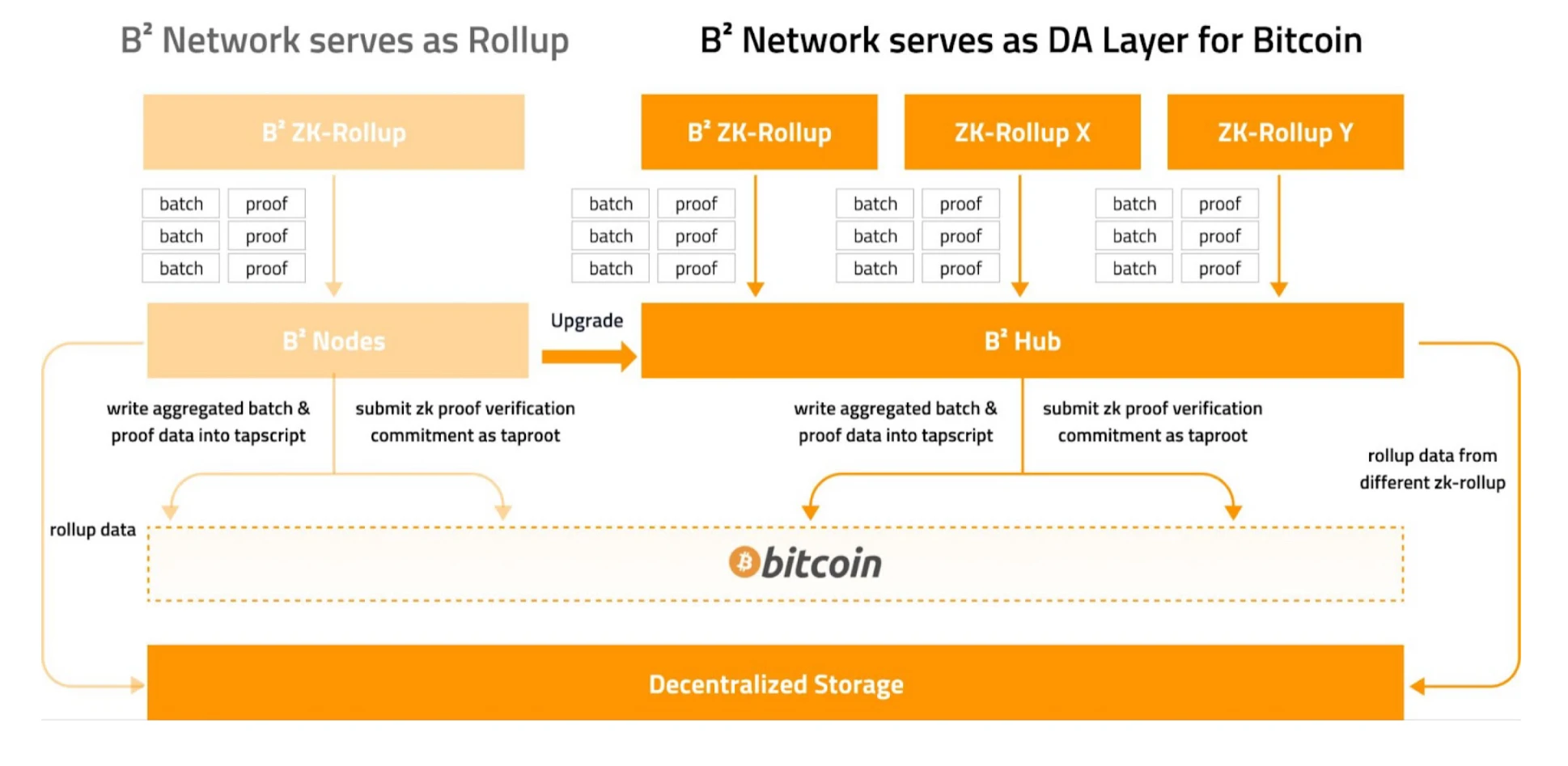
Second stage: B² Hub serving multiple Rollups
In the second stage of B² Network, B² Hub will provide services for more ZK-Rollups.
B² Hub will aggregate data submitted by different Rollups:
The transaction details and proofs of different Rollups will be stored in the DAS protocol and distributed storage protocol of B² Hub, then aggregated and finally submitted to Bitcoin.
The ZK proof data from different Rollups will be recursively aggregated into a single ZK proof data through STARK, verified, and then a commitment will be generated and submitted to Bitcoin to support challenges.
BTC staking in Babylon protocol
Babylon is a scalable Bitcoin security protocol designed to ensure the security of decentralized economies. One of the protocols is Babylon's Bitcoin staking protocol. This protocol allows users to stake their BTC on the Bitcoin network. These staked BTC can then be used to protect other external networks, such as PoS systems. The staking process is trustless and non-custodial, meaning users do not need to transfer their Bitcoin to a third-party Bitcoin address, as is typically required by Bitcoin bridge protocols. Instead, users can remotely self-custody their BTC and stake it in a Bitcoin script on the Bitcoin blockchain. If any malicious behavior is detected, these staked funds can be penalized remotely. Babylon's BTC staking is similar to ETH staking, but it can protect other external networks, such as PoS chains, making Babylon's BTC staking similar to Ethereum ETH staking 2.0, and has functionality similar to re-staking in Eigenlayer.
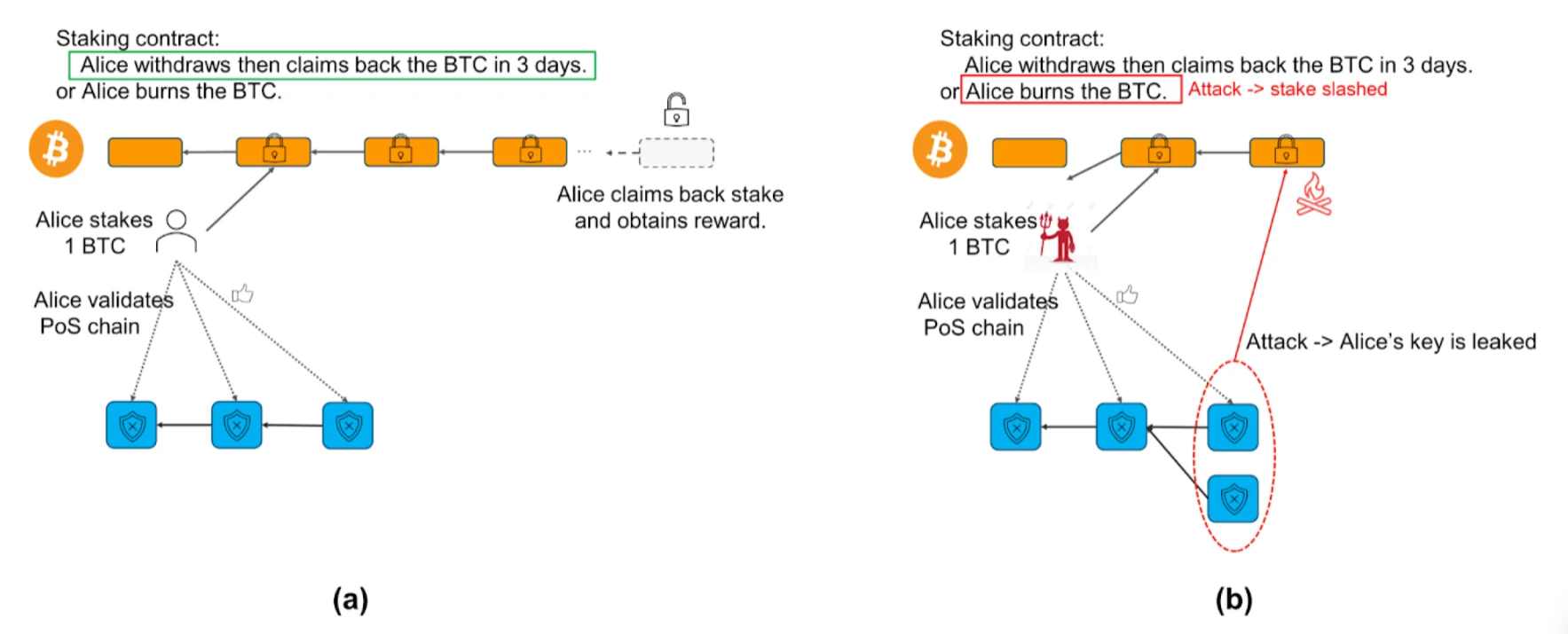
Excerpt from Babylon Bitcoin Staking Whitepaper
(https://docs.babylonchain.io/papers/btc_staking_litepaper(EN).pdf)
The process for Bitcoin stakers: (a) Optimistic scenario: Alice stakes, validates the PoS chain, requests unbinding, and withdraws the stake within 3 days; (b) Pessimistic scenario: Alice stakes, submits a security violation to the PoS chain, and then her Bitcoin is destroyed.
Due to the non-Turing complete design of Script on Bitcoin, no one can provide security violation evidence that can be directly verified on Bitcoin. The Babylon Bitcoin staking protocol introduces a mechanism to address security violations, prompting slashing behavior. This mechanism involves time-locking the staked Bitcoin and exposing the secret key that controls the locked Bitcoin whenever the staker or delegated validator double-signs (similar to double-spending) on the PoS chain. Babylon uses Extractable One-Time Signatures (EOTS) to achieve accountable assertions, where using the same secret key to sign different blocks at the same height leads to secret key exposure. Babylon introduces an additional signature round, called the final round, after the underlying consensus protocol. Only when a block receives EOTS signatures from over 2/3 of the staked Bitcoin, it is considered finally confirmed. In this round, all consensus security violations can be reduced to double-signing. If a security violation occurs in this modified protocol, some staked Bitcoin have been double-signed using EOTS at the same height, leading to the extraction of the secret keys associated with these stakers. The EOTS signature scheme can be implemented using Schnorr signatures, which are natively supported in Bitcoin. Therefore, these extracted secret keys can be used to slash the staked Bitcoin.
B² Hub Secured by Babylon
B² Hub is a PoS blockchain network that ensures the security of B² Hub through validators who have staked assets (BTC and B² tokens), and ensures the data availability and validity of state transitions through validators of B² Hub.
The consensus mechanism of B² Hub requires a valid validator set to perform BFT consensus on blocks during an Epoch, including proposing and voting. Then, each block is voted on by the final providers of staked Bitcoin through Babylon's Bitcoin staking protocol. Meanwhile, in B² Hub, the next Epoch checks the previous blocks to become a checkpoint through Babylon's Bitcoin timestamp protocol. The final confirmation of blocks in B² Hub requires passing through two checkpoints.
Accessing Rollup in B² Hub has two confirmations:
After validation by B² Hub, Rollup completes the first confirmation;
B² Hub submits DA proofs and state transition verification commitments to Bitcoin, completes the final confirmation after the challenge period.
B² Network enhances the consensus confirmation of B² Hub through Babylon's Bitcoin staking protocol. Additionally, B² Network avoids long-range attacks through Babylon's Bitcoin timestamp protocol.
Long-range attacks make PoS chains unable to slash and less secure. This attack is fundamental and cannot be solved by modifying the consensus protocol unless there are additional sources of trust. To mitigate this threat, some PoS chains adopt a social consensus approach, where stakeholders make offline decisions on the correct block at the latest height periodically and ignore other potential forks. However, this approach ties the security of the chain to the subjective opinions of participants. This approach is also known as weak subjectivity, violating the principle of decentralization. Additionally, since social consensus takes time, most PoS chains have very long unstaking periods, possibly lasting for weeks.
To prevent PoS chains from being vulnerable to long-range attacks, Babylon can use the blocks of the PoS chain as checkpoints for BTC and implement fork selection rules using earlier Bitcoin timestamps. This way, either the attacking fork will have a later timestamp on the Bitcoin canonical chain and will never be chosen by anyone, or to be chosen, the attacker would have to create a very long Bitcoin fork where the attacked PoS fork has an earlier timestamp, which is economically impractical. Therefore, long-range attacks are addressed through BTC timestamps.
In the PoS mechanism of B² Hub, a block needs to pass through two checkpoints before final confirmation. Therefore, in the consensus mechanism of B² Hub, after passing the second checkpoint, we submit the block information and corresponding validator signature information to the finality providers. The finality providers are nodes that need to stake BTC, and if they double-sign two blocks at the same height using EOTS, they may be slashed. The finality providers then submit this to the validators of B² Hub to collect finality votes. The validators store the collected finality vote signature information in a memory pool and broadcast it to the lightweight clients of B² Hub. Once 2/3 of the finality vote signatures are collected, the block on B² Hub is considered finally confirmed.
Through Babylon's Bitcoin staking and Bitcoin timestamp, B² Hub is able to effectively prevent long-range attacks and provide high security for different Rollups.
B² Rollup Supports Babylon Bitcoin Staking
The mainnet of B² Rollup will support BTC staking functionality.
The BTC staking functionality of B² Rollup will be divided into two stages:
Before the launch of the Babylon BTC staking mainnet, B² Rollup will support users to stake BTC as validators of B² Hub and receive B² token rewards.
After the launch of the Babylon BTC staking mainnet, B² Rollup will transfer the staked BTC on Bitcoin to a specific address to participate in Babylon's BTC staking.
B² Rollup will support projects related to LSD to use BTC staking for more DeFi activities, providing more liquidity for users participating in Babylon Bitcoin staking, and even conducting re-staking activities related to Bitcoin staking.
At the same time, Rollup will be able to use the infrastructure of Babylon and B² Network to ensure security through Bitcoin staking.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



