Introduction to Modular Blockchain
The design concept of modular blockchain provides more possibilities for the development and innovation of blockchain. By decomposing the functions of blockchain into composable modules, developers can customize and optimize their blockchain solutions according to different needs and scenarios. Modular blockchain also provides a better foundation for the interoperability and compatibility of blockchain, as different modules can more easily communicate and collaborate with each other or with chains. Modular blockchain is the future trend of blockchain technology, bringing more opportunities and challenges for the adoption and prosperity of Web3.
I. Introduction to Modular Blockchain
Modular blockchain is a technical solution focused on modularizing the functions of a monolithic blockchain. Traditional monolithic blockchains usually integrate functions such as execution, settlement, consensus, and data availability, while modular blockchain modularizes these functions, allowing them to operate independently and interact with each other through interfaces, thereby achieving higher scalability, flexibility, and performance. This allows developers to flexibly combine, replace, or integrate different blockchain modules to meet diverse needs in different application scenarios.
Features of Modular Blockchain
Modular blockchain has several significant features:
Scalability: By decomposing the functions of blockchain into independent modules, modular blockchain can more flexibly expand and adjust system performance to meet the needs of different scales and scenarios.
Flexibility: Modular design makes the blockchain system more flexible, allowing different functional modules to be combined according to requirements to build customized blockchain solutions suitable for specific scenarios.
Reduced complexity: Modular blockchain decomposes complex systems into multiple independent modules, reducing system complexity and facilitating development, deployment, and maintenance.
Improved availability: Independent functional modules can be optimized and upgraded separately, thereby improving system availability and stability and reducing the risk of single point of failure.
As of now, the Web3 asset data platform RootData has included 35 modular blockchain projects. According to coinmarketca data, as of January 30, 2024, the market value of modular blockchain tokens has exceeded 17.5 billion US dollars.

II. Mechanism and Principles of Modular Blockchain
From the initial design of blockchain, both Bitcoin and Ethereum belong to monolithic blockchains, where each transaction serves as a carrier, storing valid transaction records in blocks and achieving decentralized, trustless, and tamper-resistant distributed ledger networks through specific consensus mechanisms.
A monolithic blockchain can be divided into the following four functional layers:
Execution module: Responsible for processing transaction execution and deployment of smart contracts to ensure the correct execution of various transactions and smart contracts in the blockchain system.
Settlement module: Used to complete transactions and resolve disputes, verify the validity of transactions, and ensure the smooth completion of transactions and secure asset transfers.
Consensus module: Responsible for ensuring consensus among all nodes on the state transition of the blockchain system, ensuring decentralization and security of the system.
Data availability module: Ensures the verifiability and availability of transaction data, ensuring that transaction data can be correctly obtained and verified by all participants.
For a monolithic blockchain, all four functional layers are on a single chain, and the network has to bear all tasks alone. This creates the "impossible triangle" of monolithic blockchains, where scalability, decentralization, and security can only satisfy two characteristics on the chain at most. With the increase in blockchain transaction volume and decentralized applications, monolithic blockchains face a series of problems such as transaction congestion and rising transaction costs. To solve the "impossible triangle" problem, developers have proposed the "modular blockchain" solution, which independently separates these functional modules and achieves decoupling and independent operation of each functional module through a unified interface. This modular blockchain solution safely improves performance without compromising decentralization and expands the network to meet diverse application scenarios.

III. Modular Practice in Ethereum
Initially, Ethereum and other early blockchains adopted monolithic blockchain designs. However, to address issues such as performance, scalability, and sustainability, Ethereum is undergoing a transition from a single structure to a modular framework.
Introduction of Ethereum 2.0 Shard Technology
Ethereum 2.0 introduces shard technology, dividing the system into multiple independent sub-chains, each responsible for different parts of network activities. In the shard design of Ethereum 2.0, 64 shard chains will run simultaneously, used for processing transactions (execution shards) or storing blockchain data (data shards). This shard design significantly increases data throughput, reduces processing time, and allows nodes to only store data on their shard chains. By segmenting multiple components, Ethereum 2.0 can more effectively utilize network resources and lay the foundation for future expansion and upgrades.
Application of Rollup Technology
Rollup technology is a significant breakthrough in modular blockchain, bringing higher execution efficiency to Ethereum. By bundling a large number of transactions into a single transaction, executing them off-chain, and then submitting the results to the main chain, Rollup technology improves transaction speed and efficiency. Rollup technology utilizes the consensus and settlement functions of the main chain, outsourcing the execution function to off-chain sequencers, achieving modular division of labor and bringing new possibilities for the expansion and optimization of Ethereum.
Optimistic Rollup and ZK-Rollup are two common Rollup practices. Optimistic Rollup uses optimistic execution, requiring challenge periods to verify transaction validity. Settlement, consensus, and data availability still occur on the Ethereum mainnet. ZK-Rollup uses zero-knowledge proof technology, providing real-time finality. The execution process occurs off-chain, but data verification and settlement are still completed by the Ethereum mainnet.
Evolution of Modular Rollup
The latest modular Rollup further optimizes the cost of the data availability layer. Projects like Mantle utilize the data availability layer for sorting and providing data proofs, while outsourcing the execution process to the Rollup execution layer. This modular structure reduces data submission costs and provides a more flexible solution for Rollup to handle large-scale user groups.
IV. Top 10 Representative Projects of Modular Blockchain
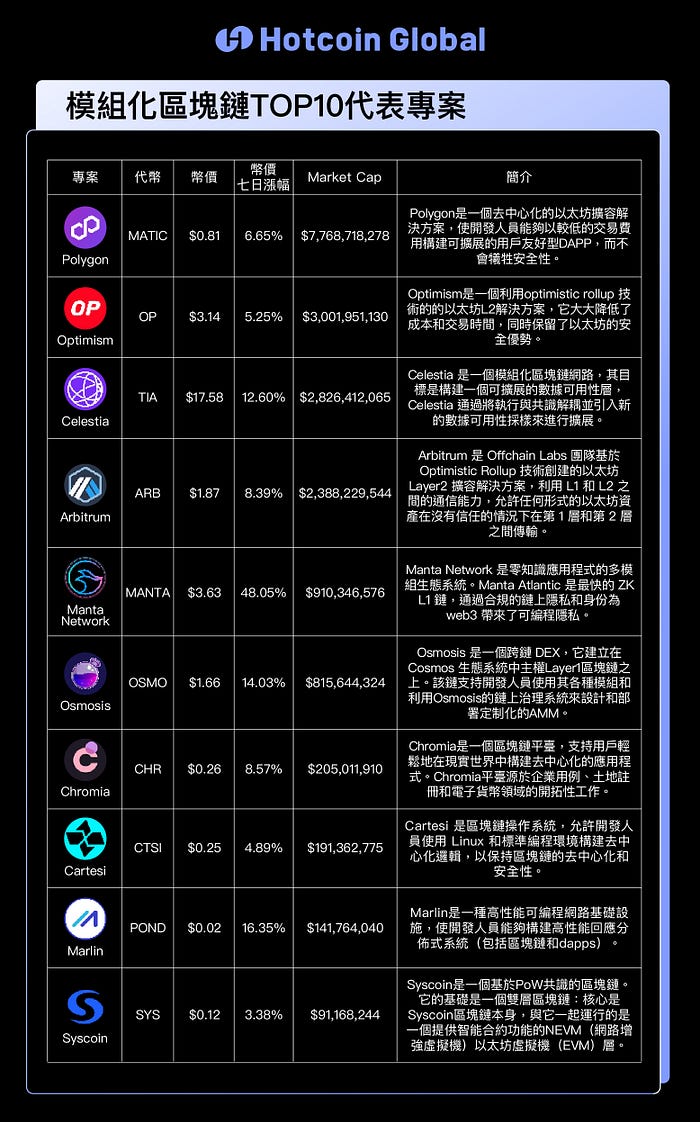
V. Risk Analysis of the Modular Blockchain Track
Although the development of the modular blockchain track has attracted much attention, it also faces some risks and challenges. The following are some key factors that may affect the development of this field:
Technical Complexity: Modular blockchain involves coordination and integration between multiple layers or networks, requiring solutions to various technical challenges such as the selection and design of consensus protocols, assurance and verification of data availability, compatibility and interoperability of execution layers, and standards and protocols for cross-chain communication. These technical issues require a high level of expertise and experience, and the current blockchain talent supply is insufficient, with incomplete technical standards and regulations, posing significant difficulties and costs for the development and deployment of modular blockchain.
Standardization and Interoperability: The lack of interoperability and standardization between different modular blockchain projects may affect the development of the entire ecosystem. The absence of common standards and protocols may lead to isolation between projects, limiting the scalability and flexibility of modular blockchain.
Security and Trustworthiness: Due to its decentralized and open nature, modular blockchain is also susceptible to various internal and external attacks and disruptions. The complexity of modular blockchain also increases the risk of security vulnerabilities, potentially leading to data loss, tampering, or leakage, transaction failures or delays, and even network collapse or fragmentation. As modular blockchain typically involves multiple components and vendors, ensuring the security and trustworthiness of the entire system is a challenge.
Network Effects and Ecosystem Construction: Modular blockchain projects need to establish a strong ecosystem to support their development. The lack of sufficient developers, users, and partners may limit the growth of projects and affect their long-term sustainable development.
Technical Maturity and Availability: The modular blockchain technology is still in a relatively early stage, and its technical maturity and availability are still to be improved. Projects need to continuously optimize and improve their technical architecture to meet the needs of users and developers and ensure the continuous stable operation of the projects.
VI. Prospects of the Modular Blockchain Track
The modular blockchain track has shown tremendous potential in the current cryptocurrency and blockchain industry, and its prospects are highly anticipated.
Higher Scalability: Modular blockchain technology is expected to address the scalability issues of traditional monolithic blockchains. By splitting the blockchain into multiple modules and customizing them with professional providers, modular blockchain can more effectively expand, increase transaction throughput, and network throughput, thereby providing support for a wider range of application scenarios.
Enhanced Security and Flexibility: The layered structure and modular design of modular blockchain help improve system security and flexibility. By deploying and maintaining different functional modules separately, modular blockchain can reduce the risk of single points of failure in the system and more flexibly adapt to different business requirements.
Continued Growth of the Ecosystem: With the continuous emergence and development of modular blockchain projects, the entire ecosystem is also growing. More and more developers, users, and partners will join the modular blockchain ecosystem, collectively driving the industry's development and innovation.
Improved Cross-Chain Interoperability: Modular blockchain technology is expected to provide better solutions for cross-chain interoperability. Through modular design and standardized protocols, different blockchain networks can more easily interoperate, achieve cross-chain asset and data flow, and promote the development and popularization of the entire blockchain industry.
Diverse Application Scenarios: Modular blockchain technology will support a wider range of application scenarios. From financial services to supply chain management, from digital assets to identity verification, modular blockchain can provide efficient, secure, and scalable solutions for various industries and fields, driving the development and popularization of the digital economy.
In conclusion, as an innovative blockchain design paradigm, modular blockchain provides new ideas and solutions for the scalability, interoperability, security, and decentralization of blockchain, opening up new space and possibilities for the development and application of blockchain. The development prospects of the modular blockchain track are broad, injecting new vitality and momentum into the development of the blockchain industry and making positive contributions to the construction of the digital economy. With the continuous advancement of technology and the continuous growth of the ecosystem, modular blockchain is expected to become one of the important infrastructures of the future digital world.
Hotcoin Community
Official Chinese Group: https://t.me/hotcoinglobalcn
Official English Group: https://t.me/HotcoinEX
Official Korean Group: https://t.me/hotcoinkorea
Discord: https://discord.gg/NwYqKWkcZn
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/HotcoinExchange
Twitter: https://twitter.com/HotcoinGlobal
Hotcoin Official Website: https://www.hotcoin.com
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




