I. Introduction
2025 is seen as a "watershed" year for cryptocurrency regulation in the United States. Prior to this, U.S. regulatory agencies had a long history of fluctuating attitudes towards crypto assets, and the lack of a clear regulatory framework led to a prevalence of "enforcement-style regulation," making it difficult for the industry to progress. However, in 2025, the U.S. federal government and Congress achieved a series of groundbreaking advancements in crypto legislation and policy: Congress passed the first federal stablecoin bill (the GENIUS Stablecoin Act), the House pushed forward the Digital Asset Market Structure Act (the CLARITY Act), and successfully repealed inappropriate tax regulations targeting DeFi, among other measures. These initiatives not only clarified industry rules and boosted market confidence but also triggered significant price fluctuations and structural changes in the market.
The changing political environment in the U.S. paved the way for crypto-friendly policies: Trump returned to the White House, clearly stating his intention to make the U.S. the "global crypto capital," and issued an executive order elevating digital assets to a national financial strategy priority, while appointing several officials supportive of crypto innovation to key positions. With improvements in the legislative and regulatory environment, mainstream crypto assets like Bitcoin entered a new bull market in 2024, reaching historical highs in early 2025. Although the market experienced a pullback by the end of the year due to macroeconomic fluctuations, it can be said that regulatory benefits were a crucial pillar of this market recovery.
This article will delve into the crypto bills and policy measures that the U.S. has passed or is advancing in 2025, analyze market performance before and after these initiatives, and look ahead to regulatory trends and industry impacts in 2026. We will see that, bolstered by policy clarity, the short-term sentiment and long-term structure of the U.S. crypto market have undergone profound changes: in the short term, prices react swiftly to policy news, while in the long term, the compliance ecosystem is gradually improving, institutional funds are entering the market at an accelerated pace, and the industry is regaining development momentum. By sorting through this series of events, investors can gain a clearer understanding of the far-reaching impact of regulatory direction on the market.
II. The First Federal Stablecoin Bill: GENIUS Act
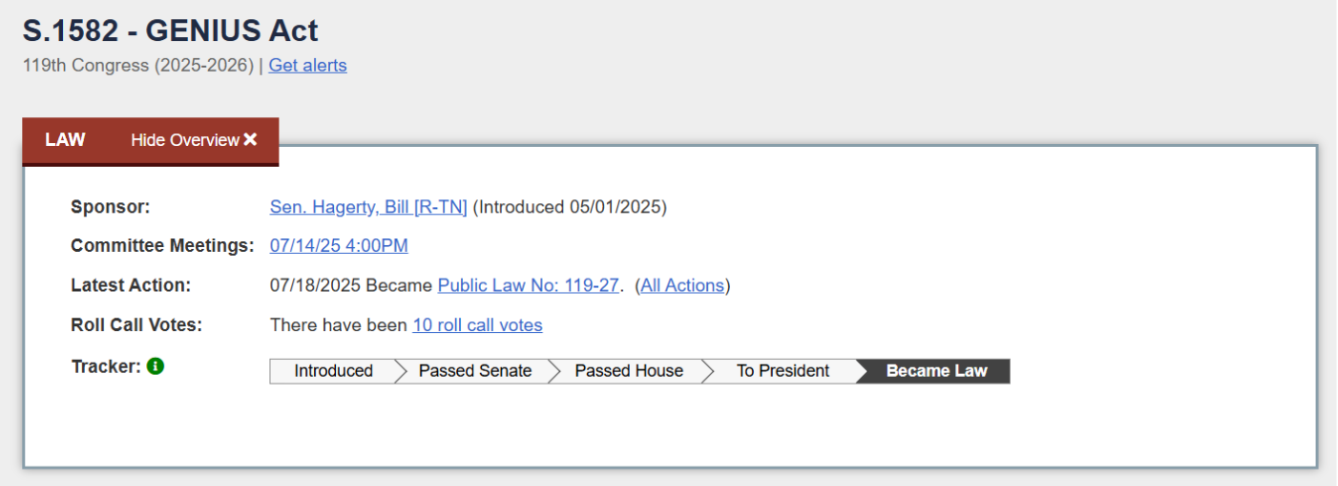
Source: https://www.congress.gov/bill/119th-congress/senate-bill/1582/text
In June 2025, the U.S. Senate passed the "Guiding and Establishing National Innovation for U.S. Stablecoins Act of 2025" (GENIUS Act) with a high vote. This is the first federal-level stablecoin regulatory bill in the U.S. and became the first significant crypto legislation passed by Congress. On July 17, the House passed the bill with an overwhelming result of 308 votes in favor and 122 against. The next day, President Trump signed the GENIUS Act, making it official law. This series of rapid legislative actions reflects a bipartisan consensus on stablecoin regulation, marking a shift in the U.S. attitude towards digital dollar stablecoins from a wait-and-see approach to active regulation.
1. Main Contents of the Bill
The GENIUS Act establishes a new federal regulatory framework for payment stablecoins. According to the bill, "payment stablecoins" are defined as digital assets pegged to the value of fiat currency, which can be used for payments and settlements, with issuers promising to redeem them at a fixed face value and claiming to maintain value stability.
Issuing Entity Requirements: Only qualified regulated entities can issue such stablecoins, including bank subsidiaries insured by the federal government, non-bank institutions approved by the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), and entities authorized by certified state regulatory agencies. The qualification review ensures that issuing entities have sufficient financial strength and compliance capabilities, meaning mainstream compliant companies like Circle will have clear pathways to obtain federal licenses, while non-compliant companies will be prohibited from issuing stablecoins, preventing risks from disorderly innovation at the source.
100% Reserve Requirement for Stablecoins: At least a 1:1 ratio of safe, highly liquid assets must be held as reserves. Qualifying reserve assets include: U.S. fiat currency (including Federal Reserve deposits), short-term U.S. Treasury bonds, high-credit-quality short-term repurchase agreements, and regulated deposits. The bill also allows for the "tokenized form" of these assets to count towards reserves, meaning that as long as these reserve assets comply with regulatory requirements, their blockchain token forms can also be accepted. This provision reserves space for the on-chain circulation of traditional financial assets in the future. Additionally, the bill explicitly prohibits stablecoin holders from earning interest to prevent "shadow banking" risks similar to deposits. Issuers must disclose the number of stablecoins in circulation and the corresponding reserve composition on their official website monthly, and the reports must be audited by independent accounting firms, with the issuer's CEO/CFO required to personally sign to guarantee the accuracy of the reports.
Regulatory Division and Balance: The GENIUS Act is implemented through cooperation between federal and state regulators. Non-bank issuers need to obtain OCC approval and accept federal oversight, while small issuers operating under state regulation must also meet requirements similar to federal ones. Meanwhile, the Federal Reserve is authorized to take enforcement actions against state-regulated stablecoin issuers in "special emergency situations" to prevent systemic risks. This "dual-layer regulation" model ensures that the potential impact of large stablecoin issuers on the financial system is directly controlled by central regulatory agencies, while small innovations can develop within state regulatory sandboxes, thus ensuring both financial stability and encouraging innovation.
Prohibition on Commercial Companies: The bill also specifically prohibits certain types of companies from issuing stablecoins. For example, non-financial commercial companies (especially large tech companies) are not allowed to issue payment stablecoins. This move aims to prevent platform tech companies with billions of users from bypassing financial regulation to issue currency directly, thus safeguarding financial sovereignty and competition from the impact of "digital monopoly currencies." This provision can be seen as a response to Facebook's previous Libra (later renamed Diem) initiative, clearly delineating the boundaries for tech giants in the digital currency space.
Clarification that Stablecoins Are Not Securities or Commodities: They are not subject to SEC or CFTC regulation but fall under the banking regulatory system. This provides an answer to the long-standing regulatory jurisdiction issue that has troubled the market: mainstream U.S. dollar stablecoins like USDC and USDT will be recognized as similar to prepaid payment instruments rather than securities, thus avoiding the inappropriate application of complex securities law requirements.
2. Market Impact of the GENIUS Act
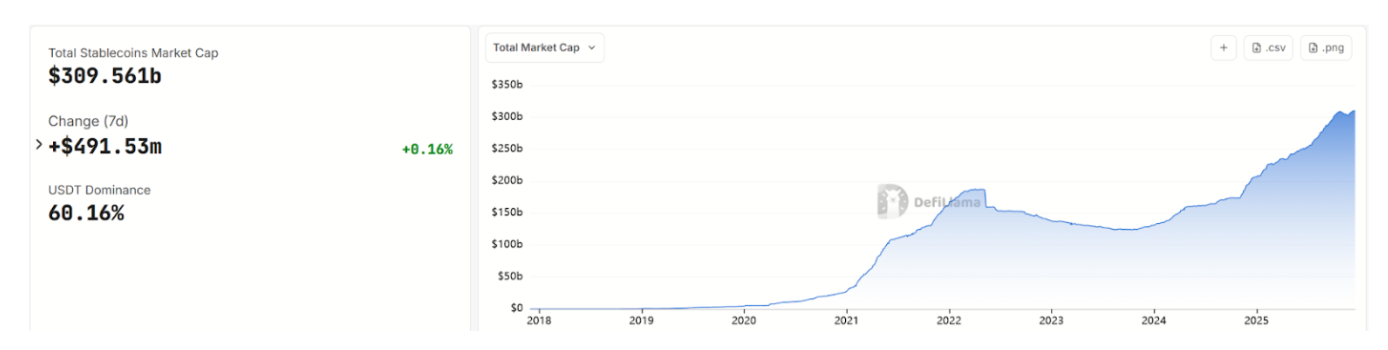
Source: https://defillama.com/stablecoins
The introduction of the GENIUS Act is believed to have significantly enhanced market trust in stablecoins. Following the announcement of the legislation, the stablecoin market reacted positively: by December 2025, the total market capitalization of global stablecoins had exceeded $300 billion. This growth is partly attributed to the overall recovery of the crypto market, but more directly, it stems from investors' expectations that the implementation of regulations will legitimize stablecoins, leading institutional investors to feel more comfortable using and holding stablecoins for transactions and payments, with some traditional financial institutions also considering entering the stablecoin business.
JP Morgan's research department predicts that the global stablecoin market capitalization could reach between $500 billion and $750 billion in the coming years. Some media outlets have stated that "2025 is the true year of stablecoins." With regulatory support, U.S. dollar stablecoins will accelerate their integration into mainstream finance. For example, payment giants like Visa and Mastercard have begun piloting the use of stablecoins for settling cross-border transactions; some banks are considering issuing their own branded stablecoins or collaborating with existing issuers to provide compliant digital dollar services to their customers.
III. Digital Asset Market Structure Act: CLARITY Act
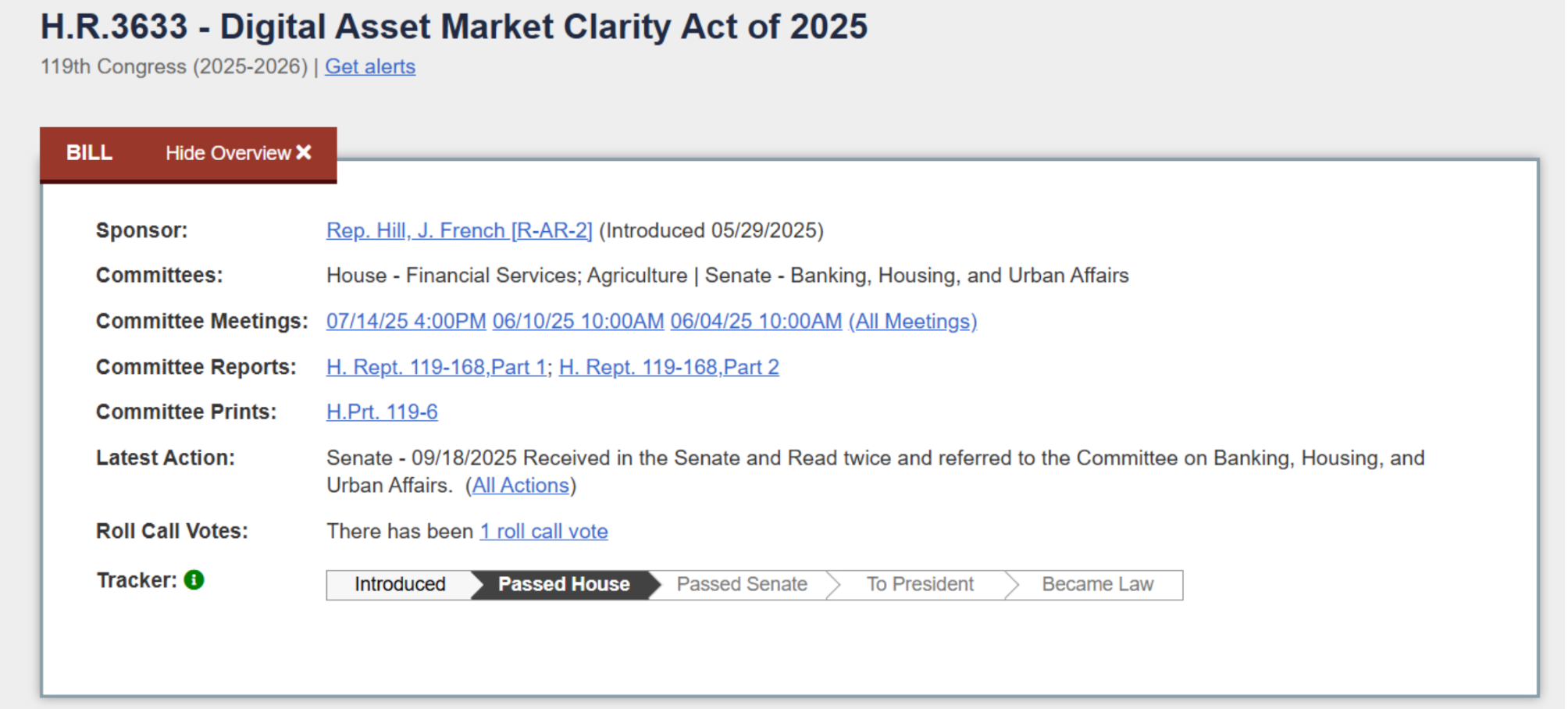
Source: https://www.congress.gov/bill/119th-congress/house-bill/3633/text
Following the stablecoin legislation, Congress is also rapidly advancing legislation regarding the broader crypto asset market structure. The focus is on the "Digital Asset Market Clarity Act of 2025" (CLARITY Act), proposed and passed by the House. This bill, drafted jointly by the House Agriculture Committee and the Financial Services Committee, is seen as a comprehensive solution to clarify the regulatory boundaries of digital assets.
On July 17, 2025, the CLARITY Act was passed in the House with 294 votes in favor and 134 against. The bill was then sent to the Senate for review. However, just a few days after the House passed it, the Senate Banking Committee also proposed a competing crypto market draft that runs parallel to the CLARITY Act. The Senate Agriculture Committee and Banking Committee held discussions and publicly solicited opinions on their respective jurisdictions' digital asset legislation, planning to merge the two proposals into a unified Senate bill for a vote in 2026.
1. Core of the Bill: Three-Class Regulatory System
The CLARITY Act attempts to fundamentally address a long-standing issue in the industry—who regulates crypto assets? To this end, the bill designs a "three-part" framework that categorizes digital assets into three classes and clearly defines the responsibilities of the SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission) and CFTC (Commodity Futures Trading Commission):
Digital Commodities: Refers to "digital assets that are intrinsically linked to the blockchain system itself, with value directly dependent on the functions or services of that chain." In simple terms, these are functional tokens that rely on the blockchain network itself for payment, governance, access to services, or as incentives, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. The bill explicitly excludes several categories that do not fall under digital commodities, including securities and their derivatives, stablecoins, bank deposits, fund shares, collectibles, etc. This classification corresponds to decentralized, non-profit-generating tokens, aiming to recognize their commodity attributes.
Investment Contract Assets: This is a new concept created by the bill, referring to "digital commodities issued or sold through investment contracts." In layman's terms, these are tokens sold in fundraising situations—such as tokens sold to investors through an Initial Coin Offering (ICO) by project teams. Additionally, the bill establishes a "chain maturity" recognition mechanism, allowing project teams or decentralized communities to apply to regulatory agencies for certification that a particular blockchain network has matured, thereby formally confirming that its tokens no longer fall under the category of securities. The standards for network maturity include: the blockchain has practical usable functions and services, core code is open source, rules are transparently predetermined and cannot be unilaterally altered, and no single entity controls more than 20% of the token supply. This design is similar to the lock-up period after a traditional IPO—early projects must accept securities regulation to protect investors, but once the network is sufficiently decentralized, the project team can exit strict regulation, and the tokens become freely tradable commodities.
Licensed Payment Stablecoins: Similar to the definition in the aforementioned GENIUS Act, the CLARITY Act categorizes stablecoins pegged to fiat currency and used for payments as a separate class. These assets must be linked to a specific fiat currency, with issuers regulated by state or federal agencies, and they promise to redeem at a fixed value. Under the CLARITY framework, stablecoins are not classified as securities or commodities but are treated as regulated payment instruments.
Through the above classifications, the CLARITY Act aims to clarify the regulatory boundaries between the SEC and CFTC. Specifically, the digital commodities sector is primarily under the jurisdiction of the CFTC, the issuance of investment contract assets is regulated by the SEC, and stablecoins are supervised by banking regulatory agencies. This arrangement ensures that each agency performs its role: the SEC no longer categorizes almost all tokens as securities but focuses on combating violations in the fundraising issuance phase; the CFTC fills the previous gap in direct jurisdiction over the crypto spot market and can actively govern market manipulation behaviors.
2. Compliance Pathways for Exchanges and Practitioners
In addition to defining asset attributes, the CLARITY Act also provides clear compliance guidance for market intermediaries and participants.
Crypto Exchanges: The bill requires digital commodity trading platforms to register with the CFTC as "digital commodity exchanges" and comply with a series of core principles, including: establishing listing standards (ensuring that the issuers of listed tokens have fulfilled necessary information disclosure, such as public source code, issuance volume, and economic models), implementing trading monitoring, preventing conflicts of interest, ensuring fund security and system security, etc. Exchanges must segregate customer assets from their own assets, ensure customer funds are held in qualified digital asset custodians, provide adequate risk disclosures, and join futures industry associations for self-regulation. The bill even imposes restrictions on innovative services offered by exchanges, such as allowing exchanges to provide staking services to enhance blockchain network security, but they must not force users to participate or mix these activities with their own trading to prevent conflicts of interest.
Brokers/Dealers: The bill breaks down the wall between digital asset and securities businesses under the current system, encouraging compliant brokers and exchanges to include digital assets in their business scope. The bill requires anyone engaged in digital commodity brokerage to register with the CFTC as a digital commodity broker and meet corresponding capital, reporting, and customer protection requirements. The SEC is required to allow its registered brokers, exchanges, or alternative trading systems (ATS) to handle transactions and custody of digital commodities and stablecoins, and cannot reject their registration or exemption applications solely because the platform simultaneously offers securities and digital asset trading. The SEC is also granted discretionary authority to use existing exemptions, allowing for special exemptions for certain decentralized financial activities to avoid inappropriate regulation stifling new developments.
Technical Developers: It is reported that the final text of the CLARITY Act explicitly states that individuals engaged in non-custodial activities such as blockchain development, node operation, and wallet development do not need to obtain state or federal licenses. This provision is crucial for the U.S. blockchain technology development ecosystem, meaning that pure technology providers will not bear heavy regulatory obligations due to financial activities occurring on-chain by users, thus clearing the legal uncertainty that previously loomed over miners, nodes, and smart contract developers.
3. Market Impact: Positive Expectations and Increased Volatility
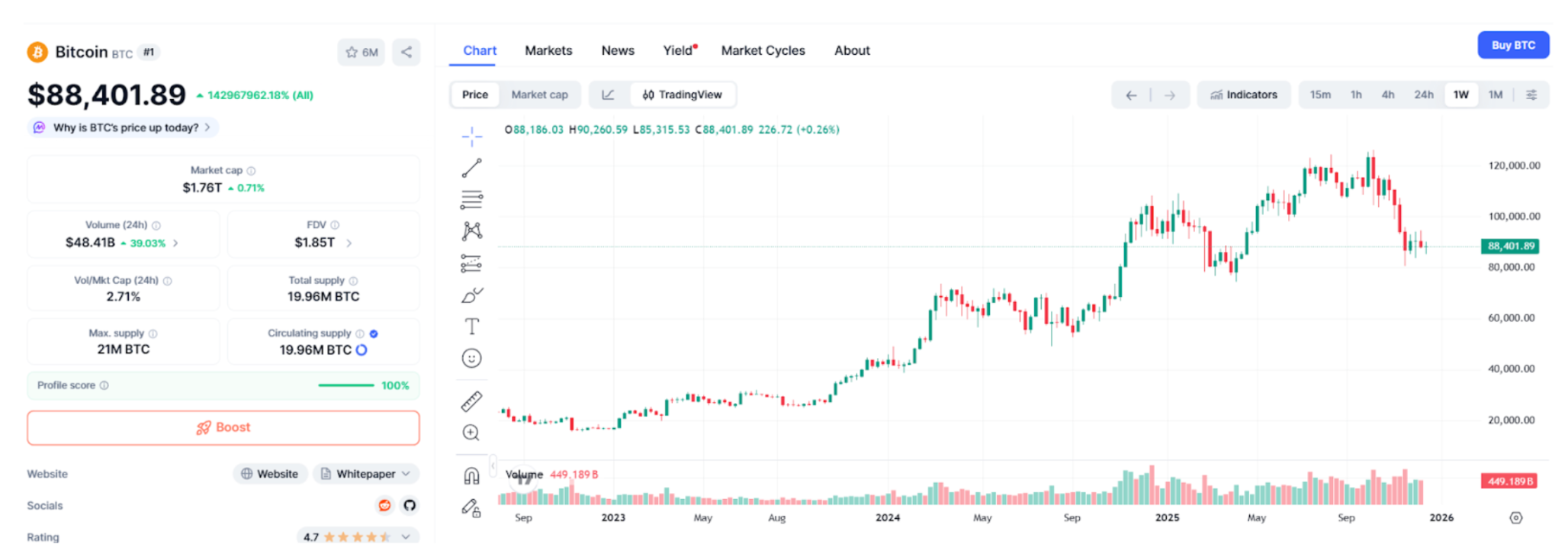
Source: https://coinmarketcap.com/currencies/bitcoin/
As the House announced mid-July 2025 as "Crypto Week," preparing to vote on the CLARITY Act, anti-CBDC provisions, and the stablecoin bill, market investor sentiment turned bullish. In fact, a significant catalyst for the strong performance of the crypto market in mid-year was this series of positive news: Bitcoin's price reached a rebound high in July, its market capitalization share increased, and many blockchain concept stocks listed in the U.S. recorded phase gains. After the legislation passed, there was a widespread belief that the long-standing unresolved issues in the U.S. crypto industry finally saw a glimmer of hope, enhancing traditional institutions' willingness to enter the market. Trading platforms like the New York Stock Exchange and Nasdaq, which had previously shelved digital asset trading or custody plans due to regulatory uncertainty, began reassessing the possibility of launching.
However, due to the slow and uncertain pace of policy advancement, the market also experienced news-driven fluctuations. For example, after the House passed the CLARITY Act and submitted it to the Senate, investors once envisioned that the Senate would quickly follow suit, allowing the bill to take effect by the end of the year, pushing Bitcoin's price to a historical high of about $126,000 in early October. But in mid-October, following the president's sudden announcement of a new round of tariffs on China, global market risk aversion rose, and Bitcoin plummeted alongside the stock market, with the day's leveraged positions liquidating at a record high of $19 billion in crypto history. Subsequently, the negative impact of macro factors made it difficult for the crypto market to remain insulated. Bitcoin's price recorded the largest monthly decline since 2021 in November, and as of now, it still hovers below $90,000. This indicates that crypto assets, as risk assets, are heavily influenced by macroeconomic conditions and overall market sentiment, with the correlation coefficient between Bitcoin and the S&P 500 index rising to 0.5 in 2025, significantly higher than the 0.29 in 2024.
IV. Other Representative Crypto Policies
In addition to heavyweight legislative projects, the U.S. government took significant actions on several crypto-related policies in 2025, further improving the compliance environment of the crypto ecosystem.
1. Anti-CBDC Bill: Protecting Financial Privacy
After the Trump administration took office, its attitude towards Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) underwent a 180-degree shift. In January 2025, President Trump signed an executive order directly prohibiting any federal agency from promoting, issuing, or advertising CBDCs. This tone was later reinforced by the legislative body: the House attached Title VI, the "Anti-CBDC Surveillance State Act," to the CLARITY Act. The core content legally prevents the Federal Reserve from launching CBDC accounts or products aimed at individual consumers, emphasizing the importance of privacy and freedom, and preventing the government from using CBDCs to obtain citizens' transaction data. In 2025, the House voted separately on this bill during "Crypto Week" and passed it; although the Senate has not yet completed its review of the bill, considering the new government's and House leadership's strong opposition, the door for the U.S. to launch a CBDC has effectively closed.
Supporters argue that banning CBDCs helps protect citizens' financial privacy and private sector innovation. Once CBDCs are issued, the government could monitor in real-time and even restrict individuals' use of funds, which contradicts the free market and privacy rights emphasized by the U.S. In this atmosphere, the Federal Reserve significantly slowed its research process on the digital dollar in 2025, focusing only on wholesale (interbank settlement) CBDCs. This means that private sector stablecoins will dominate the digital dollar process, aligning with the GENIUS Act's policy direction encouraging banks and compliant institutions to issue stablecoins.
2. Repeal of Strict Reporting Rules for DeFi
As early as 2021, the U.S. Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) included a controversial provision requiring broadly defined "digital asset brokers" to report user transaction information to the IRS. This definition was overly broad and could classify miners, nodes, and smart contract developers in the decentralized finance space as "brokers," forcing them to comply with burdensome customer identification (KYC) and tax reporting obligations. In 2025, both houses of Congress passed Joint Resolution No. 25 (H.J. Res. 25), which was signed into law by President Trump on April 10, 2025 (Public Law 119-5). This law formally repealed the Treasury Department's implementation rules for Section 80603 of the IIJA (Digital Asset Broker Information Reporting).
After the repeal of the rules, the IRS clarified that DeFi platforms that operate purely on the blockchain and do not provide fiat currency conversion do not need to submit 1099-DA transaction reports to tax authorities, nor are they required to collect user identity information. In contrast, centralized exchanges and service providers (holding customer assets and providing fiat currency exchange) still need to comply with information reporting obligations: they will record user digital asset transactions starting January 1, 2025, and submit new Form 1099-DA to users and the IRS in early 2026. This means that U.S.-licensed exchanges like Coinbase and Kraken still need to file on time, but decentralized protocols like Uniswap are exempt. Additionally, payment processors and institutions that frequently issue or redeem their own tokens continue to be regarded as "brokers" and must fulfill reporting obligations, primarily targeting stablecoin issuers with centralized entities.
3. Regulatory Personnel and Enforcement Shift
In addition to legislation and macro policies, the noticeable improvement in the U.S. crypto regulatory environment in 2025 is also reflected in personnel adjustments within regulatory agencies and a shift in enforcement style. After the new government took office, a number of officials with an open attitude towards crypto were appointed to key positions. Among them, the most significant was the appointment of former SEC Commissioner Paul S. Atkins as the chair of the Securities and Exchange Commission. Upon taking office, Atkins immediately launched an internal project code-named "Project Crypto," aimed at establishing formal token classification standards and guiding rules for digital assets, and formed a special task force called "Crypto 2.0." The new task force's mission is to assist the commission in developing a "comprehensive and clear regulatory framework" and to use enforcement resources more cautiously.
Accompanying the personnel adjustments is a rapid shift in the SEC's enforcement orientation. Since President Trump took office in early 2025, the SEC has suspended or withdrawn approximately 60% of its investigations and lawsuits related to cryptocurrencies. Some high-profile cases, such as the lawsuit against Ripple and enforcement actions against Binance, have shown significant signs of easing. For example, in July 2025, the SEC reached a settlement with Ripple, withdrawing charges against its executives; the investigation into Binance is reportedly no longer being actively pursued. The SEC even ended a four-year investigation into the decentralized lending platform Aave without taking any punitive measures. The SEC's changes have greatly alleviated industry pressure, and the new enforcement relaxation allows them to shift their focus from litigation back to operations. This has contributed to the market's recovery in 2025, and U.S. projects are no longer fleeing in large numbers.
At the same time, banking regulatory agencies, which had previously taken a hard stance against banks engaging in crypto business, have begun to moderately ease restrictions. The newly appointed Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent has expressed a welcoming attitude towards digital assets. Travis Hill, acting chairman of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), issued a public statement in January, promising to adopt a "more transparent approach to fintech collaboration and digital asset tokenization," and is considering issuing additional guidance to clarify the compliance pathways for banks participating in digital asset businesses. The Federal Reserve, OCC, and other agencies have gradually withdrawn some of their previous restrictive statements regarding banks engaging in crypto business, shifting to a case-by-case review of specific operations. As a result, some U.S. small and medium-sized banks are reconsidering providing account services to crypto companies, and cooperation between banks and crypto enterprises is beginning to warm up. After several "crypto-friendly banks," including Signature and Silvergate, went bankrupt, crypto companies had difficulty obtaining basic banking services, but this situation is expected to improve.
4. Executive Orders and Bitcoin Reserve Exploration
On January 23, President Trump signed an executive order titled "Strengthening American Leadership in Digital Financial Technology," announcing that "supporting the responsible growth and use of digital assets, blockchain technology, and related technologies across economic sectors" would be national policy. The order established a Presidential Digital Asset Market Working Group, which includes over a dozen high-ranking officials, such as the SEC chair, CFTC chair, Treasury Secretary, Commerce Secretary, and Attorney General, and can invite leaders from the private sector in digital assets to participate in consultations. The President has requested the working group to submit a report within 180 days, proposing a comprehensive federal regulatory framework for digital assets and assessing the feasibility of establishing a national "digital asset reserve."
Trump himself has shown a keen interest in establishing a national Bitcoin reserve, hoping to utilize the government's existing Bitcoin holdings (from law enforcement seizures) as a basis to explore diversifying part of the national reserves into digital assets. On March 6, he further issued Executive Order 14233, directing the establishment of a strategic Bitcoin reserve and a U.S. digital asset inventory.
It can be said that the U.S. government is officially embracing Bitcoin, which is not just an economic decision but also a geopolitical consideration: ensuring the dollar's dominant position in the future digital economy and preventing other countries' digital currencies or gold from gaining prominence. Although this idea is quite controversial in the eyes of traditional financial officials, at least in 2025, it has moved from science fiction to reality.
Overall, these policy measures in 2025 demonstrate the U.S. government's comprehensive embrace of crypto innovation: establishing rules through legislation, changing regulatory tone through personnel adjustments, and setting strategic direction through executive orders. This top-level design and strong execution send a clear signal to the global crypto industry: the U.S. aims to actively participate in and lead this financial revolution. While a more regulated market may reduce some speculative bubbles, in the long run, it will attract larger and more rational capital, and crypto assets are expected to gradually become a regular part of global asset allocation rather than an alternative asset wandering in the gray area.
Outlook for 2026: New Regulations and Industry Changes
Looking ahead to 2026, U.S. crypto regulation will continue to deepen and refine along the tone established in 2025. Here are several directions worth paying attention to:
1. Legislative Implementation and Rule Refinement
Legislation on the market structure of digital assets is expected to achieve final approval in 2026. Two Senate committees have planned to integrate their respective drafts by the end of the year and push for a full Senate vote in early 2026. Given that the House version has received significant support and the cooperation of the executive branch, industry insiders predict a high likelihood of the Senate bill passing.
Once both chambers of Congress reach an agreement on the final text, the CLARITY Act and related provisions (such as the anti-CBDC measures) may be formally signed into law in the first half of 2026. Subsequently, the SEC and CFTC will enter a busy rule-making period. During this process, industry associations and large enterprises will participate in negotiations to secure favorable terms.
The final details of the new regulations will determine the specific direction in which market participants adjust their business models. For example, if the registration process and requirements for exchanges are relatively relaxed and transparent, we may see platforms like Coinbase in the U.S. take the lead in applying for CFTC registration, and even overseas exchanges considering applying for U.S. licenses.
2. Formation of a Compliance Ecosystem and Accelerated Institutional Entry
As the regulatory framework becomes clearer and supporting rules gradually take effect, the U.S. crypto compliance ecosystem will begin to take shape. Legally operating exchanges, custodians, brokers, stablecoin issuers, and others will successively obtain formal registrations or licenses from regulatory authorities, and the participation of institutional investors will rapidly increase.
Currently, large asset management companies (such as BlackRock and Fidelity) have already brought some traditional funds into the market through products like ETFs. As regulations further clarify in 2026, these institutions may engage in more diversified businesses, such as establishing crypto hedge funds, providing custody, and trading derivatives. For example, Wall Street banks like Goldman Sachs may launch digital asset trading and custody services. In the stablecoin sector, qualified bank subsidiaries like JPMorgan may issue payment stablecoins, providing a pathway for non-bank institutions like PayPal to issue stablecoins through OCC approval.
The large-scale entry of traditional institutions will bring incremental capital and more mature risk management, which will help reduce the volatility of the crypto market in the long term and enhance market depth and pricing efficiency.
3. Industry Competition and Restructuring
The arrival of the compliance era also means a restructuring of the industry. Companies willing and able to meet regulatory requirements will prevail, while those resisting regulation or failing to meet standards will be eliminated. For example, compliant pioneers like Coinbase are expected to further expand their market share, while some trading platforms that have not obtained any licenses and operate in gray areas will find it difficult to continue serving U.S. customers.
Similarly, in terms of crypto projects, high-quality projects will be more willing to issue tokens compliantly in the U.S. If the SEC successfully establishes a token registration exemption system in 2026, we may see the first batch of token issuances registered with the SEC, sold to the public, and monitored by regulatory authorities. This would be a revolutionary change, meaning that crypto startups could raise funds compliantly like public companies through IPOs, and investors would enjoy corresponding transparency and legal protection.
At the same time, some emerging models in the decentralized space will further develop and thrive, as safe harbor provisions protect developers. For instance, decentralized exchanges, lending, and derivatives platforms may flourish even more after obtaining clear exemption boundaries and gradually connect with traditional finance.
4. Government Strategy and International Competition
From a governmental perspective, the Trump administration will continue to promote the strategic goal of "making the U.S. a global leader in crypto and blockchain innovation," ensuring that it holds a voice in the formulation of international standards, including designating FATF digital asset regulatory standards and cross-border payment frameworks. In 2026, the U.S. may seek to strengthen dialogue and cooperation with advanced regulatory economies such as Europe, the UK, and Japan, forming a certain degree of regulatory equivalence or mutual recognition. This will facilitate cross-border business operations, allowing legitimate and compliant crypto companies to operate smoothly in major markets.
At the same time, the U.S. may increasingly incorporate crypto into its financial diplomacy agenda, promoting the use of dollar stablecoins in developing countries to solidify the dollar's position. At the end of 2025, newly appointed Treasury Secretary Bessent praised the liquidity of the U.S. Treasury market and noted that the growth of stablecoins is expanding demand for U.S. debt. This indicates that the government is beginning to recognize the potential benefits of stablecoins and other crypto products for the U.S. financial market.
5. Risks and Challenges
Of course, even with a bright outlook, 2026 is not without risks. On the macro front, the U.S. economy may face new uncertainties, such as changes in interest rate cycles and geopolitical conflicts, which could still pose external shocks to the crypto market.
At the same time, regulatory goodwill does not mean a relaxation of vigilance. If a major crypto security incident occurs in 2026, regulators may quickly tighten policies and severely punish the parties involved as a warning. This raises higher demands for industry self-discipline: companies must strengthen security and risk control while enjoying policy benefits.
Additionally, the U.S. political cycle is also worth noting. 2026 is a midterm election year, and if the political landscape changes again, it is uncertain whether the current crypto-friendly stance will reverse. However, at least during the 2025-2026 cycle, both parties have reached a consensus on supporting reasonable regulation and encouraging innovation.
Conclusion
Looking back at 2025, the U.S. experienced a significant transformation in cryptocurrency regulation, moving from chaos to clarity and from passivity to proactivity. This year, Congress and the government jointly launched a series of milestone initiatives, including the stablecoin bill and market structure bill. In the short term, these policy announcements significantly influenced market sentiment and trends. While macro headwinds compounded, the market still experienced significant volatility. However, the more profound impact lies in the changes to the industry ecosystem and landscape: clear rules have removed barriers to compliant operations, traditional financial institutions can enter with confidence, and innovators are no longer deterred by regulatory uncertainty, allowing the U.S. to regain its status as a hotbed for crypto entrepreneurship and funding.
As regulatory clarity increases, the industry itself must also pay more attention to compliance and risk control to match the trust of regulators. Only through a positive interaction between regulation and the industry can crypto technology truly integrate into the socio-economic fabric and unleash its transformative potential. For investors, it is essential to closely monitor policy trends, as regulation is becoming an important variable driving the crypto market's movements. Positive policy developments can not only lead to price increases but, more importantly, reduce long-term risk premiums and enhance the intrinsic value and sustainability of assets.
Looking ahead, the U.S. regulatory exploration will provide valuable examples for the world: how to maximize the vitality of digital financial innovation while maintaining financial stability and security. It is foreseeable that in 2026, the crypto industry will continue to advance on a more solid legal foundation, and the U.S. is expected to solidify its position as a global center for crypto capital and technology. There may still be bumps along the way, but the direction is clear: crypto assets will emerge from the gray area and participate openly in shaping the future financial landscape.
About Us
Hotcoin Research, as the core research institution of Hotcoin Exchange, is dedicated to transforming professional analysis into your practical tools. Through our "Weekly Insights" and "In-Depth Reports," we analyze market trends for you; leveraging our exclusive column "Hotcoin Selection" (AI + expert dual screening), we identify potential assets and reduce trial-and-error costs. Each week, our researchers will also engage with you through live broadcasts to interpret hot topics and predict trends. We believe that warm companionship and professional guidance can help more investors navigate cycles and seize value opportunities in Web3.
Risk Warning
The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile, and investment carries risks. We strongly recommend that investors conduct investments based on a full understanding of these risks and within a strict risk management framework to ensure the safety of their funds.
Website: https://lite.hotcoingex.cc/r/Hotcoinresearch
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




