原文标题:《BTC 生态竞逐下半场:谁是价值承载的最优解?》
原文作者:Evan Lu, Waterdrip Capital
从 2023 年 Ordinals 协议大火,带起了 BTC 生态轰轰烈烈的建设至今,BTC 生态在短短一年半时间内走完了 ETH 过去多年的演进路径。到今年 Q1 结束,BTC 生态的 1.0 周期也逐渐地告一段落。BTC 的价格也一改以往暑期的低迷,连续突破了 11 万,12 万美元/枚,触达了新的 ATH 时刻;但 BTC 生态相关代币在交易所的市场表现却差强人意;但一项技术从提出到发展,再到落地和广泛采用,只有短短一年必然是不够的。更不用说在最大的价值存储网络 BTC 上进行新技术的实践了。
观察 BTC 生态的不同技术路径可以发现,我们仍然处于一个 BTC 生态的发展期。BTC 生态真正的繁荣还远没有来临。因此,BTC L2 的路线之争才刚刚开始。
BTC 生态的 1.0 和 2.0
既然 BTC 已被广泛认可为「数字黄金」,为什么仍需要推动 BTC 生态的发展?这是因为 BTC 网络本身的脚本语言极为简化,再加上 PoW 共识机制,保证了极高的安全性和去中心化程度;但也限制了比特币的可扩展性与可编程性。而作为整个加密行业的底层锚定资产,BTC 实际上还有大量的价值尚未被充分释放。想象一下,若仅有 10% 的 BTC(即约 210 万枚)被用于 DeFi,按每枚 10 万美元计算,将有高达 2100 亿美元的资产流动性被释放!
从生态组成看,BTC 生态可分为基础设施层(L2)和上层金融协议(BTCFi);下文将主要聚焦于 BTC 基础设施技术路径的诠释与比较。
在 BTC 生态的 1.0 时代,其典型特征是「TVL 优先」——先通过资产桥或托管将 BTC 转移至 L2 网络,再在 L2 上部署 DeFi 协议,激活 BTC 的流动性。这也是早期 ETH 侧链的玩法,知名代表就是 Polygon;这也对 ETH 时代过来的加密用户非常友好,其实逻辑就是 EVM 的 L2——只不过底层是 BTC 网络,所以此技术路径能快速累积资金与用户基础;但短板也特别明显:BTC 资产的安全性得不到保证。
BTC 生态的 2.0 时代则回归到技术本质的革新:如何在安全性、效率和原生兼容性方面实现突破。从雷电网络的主网上线,到 ZK Rollup、RGB、BitVM 等技术路线的活跃推进,我们看到越来越多项目开始探索链上原生资产如何在 L2 上实现更安全、更高效、更原生的生息与流转。对于开发者而言,这意味着更具可能性的创新空间;对于 VC 而言,这代表着 BTC 生态从「估值驱动」走向「PMF 驱动」的重要转折点。
BTC L2 技术路径全景对比
根据现有的技术栈,可以分为下表的若干种技术路径。但如果对每种技术路径和所代表的项目进行深度探讨,就会出现即使不同的技术路径也会有共同使用同样解决方案的情况,不同技术和堆栈之间也会存在子母集关系。
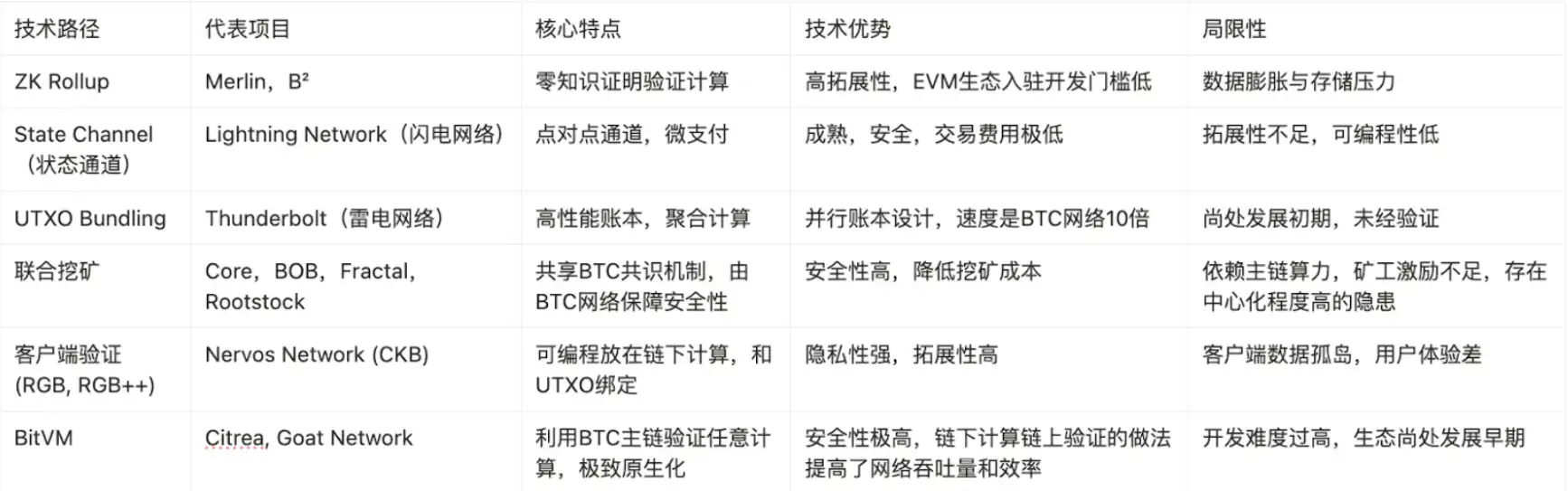
BTC L2 的不同技术路径对比,数据来源:https://worried-eagle-e5b.notion.site/BTC-21b34b2a8d7a80cb83c1d0021e3a5696
根据较为知名的 6 种技术路径,该表格选取了 15 家 BTC L2 将其 TVL 数据和所采用过的技术方案进行了数据可视化进行对比:
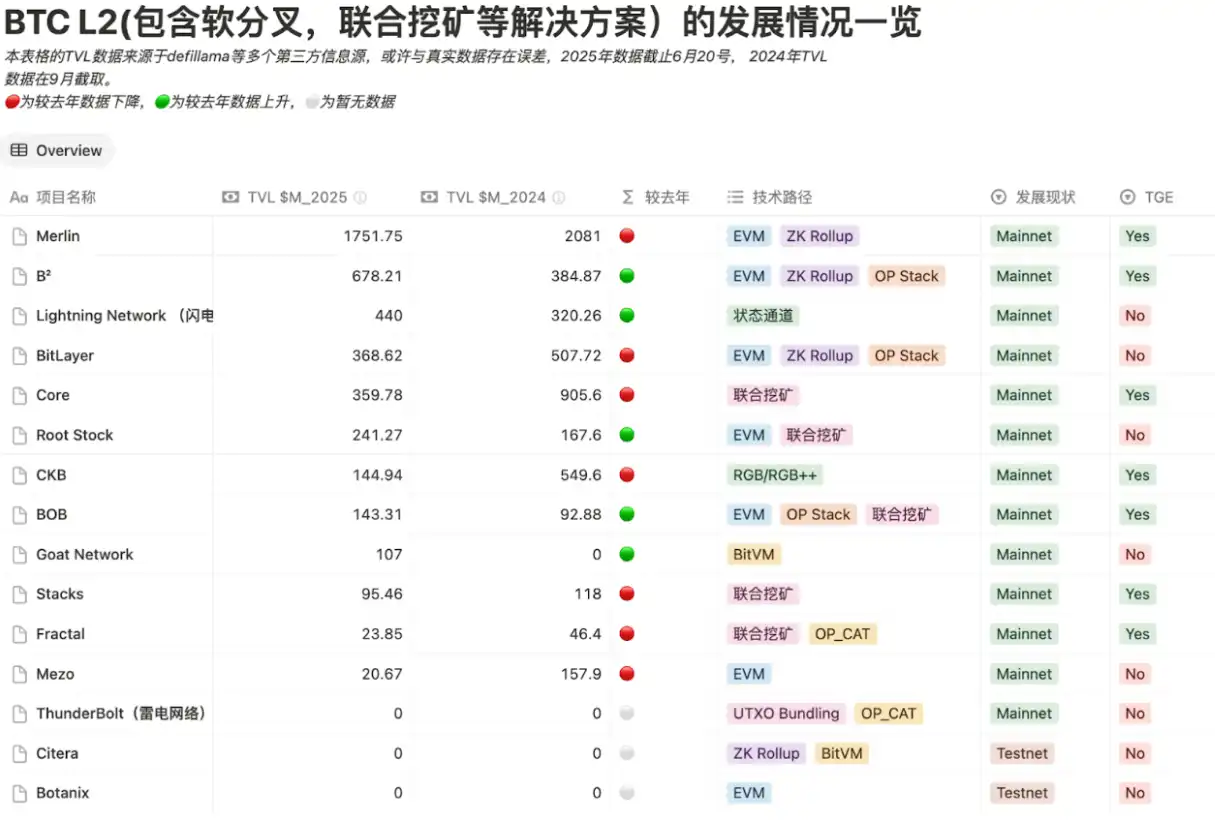
BTC L2 发展情况一览,数据来源:https://worried-eagle-e5b.notion.site/BTC-21b34b2a8d7a80cb83c1d0021e3a5696
可以看出,大部分 L2 的 TVL 受到市场影响均出现了大幅度的下降。此外,闪电网络的 TVL 数据虽然较去年是上升的,但对比去年的 BTC 数量,今年的闪电网络锁仓量无疑是下降的。
BTC L2 的不同技术路径概况
BTC 最正统的 L2 方案:闪电网络(Lightning Network)
可以说是 BTC 上最早的 L2 之一。其基本机制是,用户之间在链上创建一个 2-of-2 多签地址,构建一个双向支付通道,并通过哈希时间锁合约(HTLC)确保交易双方在链下多次交互后,仍能以最新状态安全结算到主链。整个过程中,只有开启和关闭通道的两笔交易需写入主链,大量中间交易则在链下完成,从而大幅节省区块空间并提升效率。
不过早期的闪电网络仅支持 BTC 作为支付货币,大大限制了应用场景的落地。为此,Lightning Labs 专门推出了 Taproot Assets 协议(以下简称 TA 协议),支持在 BTC 网络发行原生资产发行的同时还能和闪电网络无缝兼容。TA 协议基于 BTC 的 UTXO 模型和 21 年的 Taproot 升级,资产状态以稀疏默克尔树(MS-SMT)结构记录,仅将交易数据的根哈希写入链上,确保比特币主链的数据整洁。同时,TA 资产也能被嵌入至闪电网络通道中进行快速转移,实现「在比特币网络上流通稳定币」的设想。
此外,不仅仅是稳定币,RWA 资产和项目代币也得以在 BTC 上发行,BTC 多资产交易网络会因为 TA 协议的引入真正地构建起来。
开发进度
截至 2025 年 6 月,闪电网络已上线了 10 年,运行稳定,拥有超过 1.6 万个节点和 4.1 万个活跃通道;而在去年 BTC 破 10 万美元/枚的总锁仓容量就已经超过了 5,000 BTC。现今也保持接近 4,000 BTC 左右。
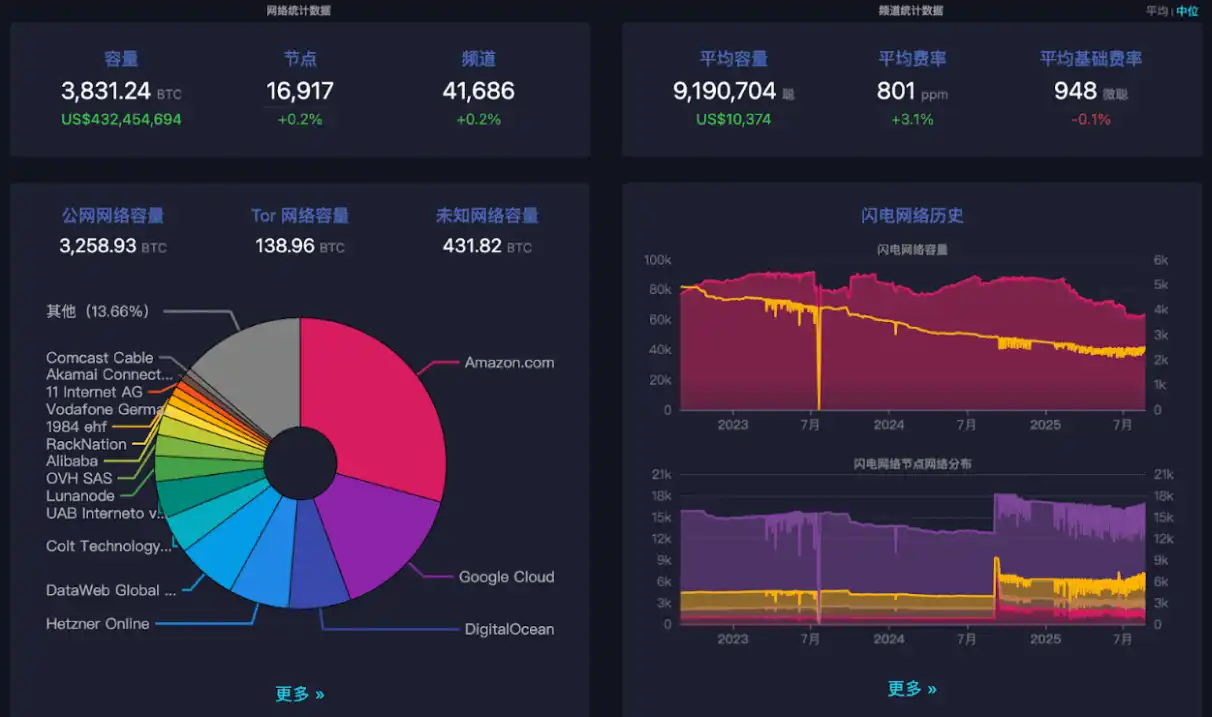
闪电网络各项数据一览,数据来源:https://mempool.space/zh/lightning
今年 Q1,USDT 背后的 Tether 公司宣布将通过 TA 协议发行 USDT 进入闪电网络生态,意味着 Tether 对闪电网络的认可。
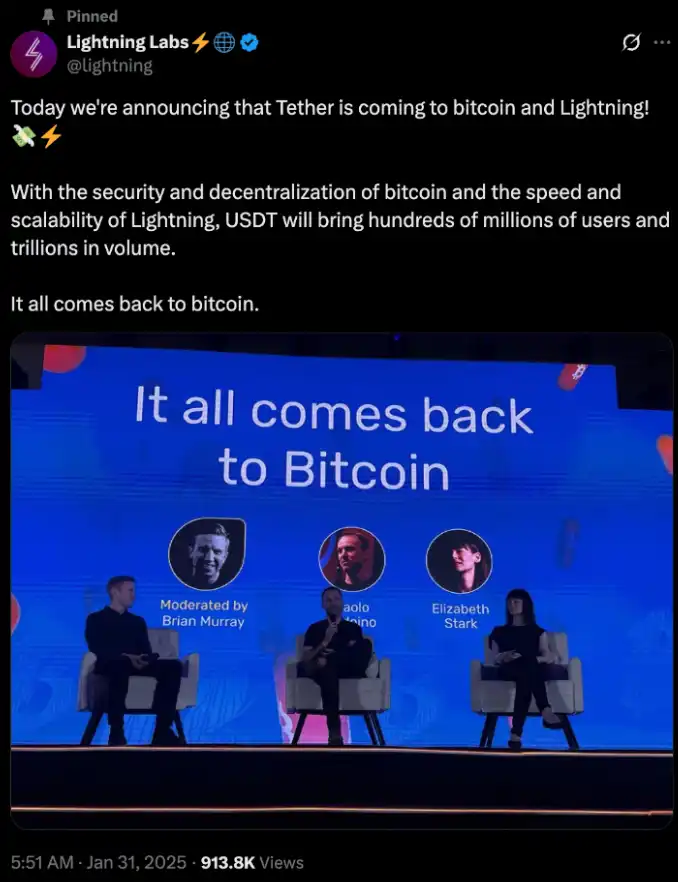
Lightning Lab(闪电网络母公司)宣布 Tether 接入闪电网络,数据来源:https://x.com/lightning/status/1885083485678805424
此外基于闪电网络的生态也慢慢成型了,例如金融基础设施协议 Lnfi,旨在成为 BTC 及 Taproot 资产的首选平台,覆盖资产发行、募资、收益及交易全流程。核心产品 LN Exchange 日交易额达 3,000 万美元,LN Node 提供超 5% 的无需信任 BTC 收益。近期,Lnfi 就联合了泰达与 Lightning Labs 在 X Space 讨论闪电网络上发行稳定币的机遇和挑战。

X Space of USDT ON LIGHTNING,数据来源:https://x.com/i/spaces/1vOxwXmjVbRKB
此外,「AI Agent + 微支付」正依靠 BTC 网络的安全性逐渐构建起新型支付体系,其中典型代表是 AIsa。其原理利用了闪电网络毫秒级相应的特性,和 BTC 网络强大的安全性解决了传统系统难以支持的海量微交易问题。为 AI 服务商和企业提供实时、高效、低价的支付能力。AIsa 支持如每次 API 调用仅 $0.0001 的自动微支付、DePIN 节点实时结算、跨链路径智能优化等操作,几乎无需人工干预。
局限与挑战
尽管闪电网络在近些年发展的已经足够成熟,但其拓展性仍然受限于网络效应和通道路径设计,网络承载性有限。TA 协议虽弥补了资产层的不足,但需要用户自建节点以保障安全性的设计拉高了用户参与的门槛,产品的完善程度仍需解决。
而例如像 BitTap 就为 TA 协议上的用户提供了自托管钱包的权利。BitTap 专注于解决闪电网络和 TA 生态的去中心化和易用性问题,他们已上线了去中心化浏览器插件钱包,并且即将上线稳定币支付钱包 APP,用户可以在闪电网络层和 TA 层进行稳定币的支付、转账,同时还支持稳定币在闪电网络层和 TA 层之间进行安全、自由的跨层转移(Bridge)。
原生账本扩容:雷电网络(Bitcoin Thunderbolt)
就在上个月,雷电网络正式上线主网。并且被汇丰银行发布的官方新闻稿中披露。这是第一次传统金融的业界权威对 BTC 为代表的区块链基础设施表示出正面回应并加以关注。
严格来说,雷电网络并不是传统意义上的 BTC L2,而是基于 BTC 主网的软分叉兼容的原生账本扩容方案。其核心技术在于扩展 BTC 脚本语言的 OP_CAT 指令,加以结合 UTXO Bundling 技术,从而实现高性能合约的执行。
与闪电网络的异同:
不同于闪电网络需要保持链下交互的支付通道时刻开启;雷电网络采用一种去交互式的异步设计,支持用户之间无需直接信任或持续连接即可完成链下 UTXO 所有权转移。其关键在于引入拜占庭容错委员会(BFT Committee)管理 Schnorr 签名,实现对资产所有权的链下委托与链上最终确认。在 3f+1 模型下,这种机制可以容忍最多 f 个恶意节点,确保交易在异步网络的条件下依然保持安全性与一致性。
此外,通过 UTXO Bundling 技术,雷电网络可以将多个 UTXO 聚合处理,其交易速度和效率是 BTC 网络的 10 倍以上。在资产协议方面,雷电网络提出了 Goldinal 的 BTC 一层资产统一标准,再配合其开发的 BitMM((Bitcoin Message Market)系统,实现了 BTC 网络上原生的链上 AMM。
在设计上,雷电网络使用可验证、可调整的签名组件实现了递归式的链下 UTXO 转移结构,并通过 Bitcoin Core 原生逻辑运行。这种从主链架构层出发的加速机制,不仅保持了 BTC 的安全性与抗审查特性,还支持包括 BRC-20,Runes 等 BTC 原生资产的转移。
开发进度
雷电网络由部分 OG 矿工、汇丰银行及 BTC 核心开发者,Nubit 社区贡献者共同推动,是当前 BTC 技术栈中少数具有正式学术背书的协议之一。
目前,雷电网络仅对获得加速码(Boosting Code)的用户开放访问。该码由 Nubit 等核心贡献方通过社区限量发放,并附带稀有 BTC 原生空投奖励。
截止 6 月中旬,雷电网络的主网已经有接近 5 万名用户,总交易笔数接近 400 万笔:
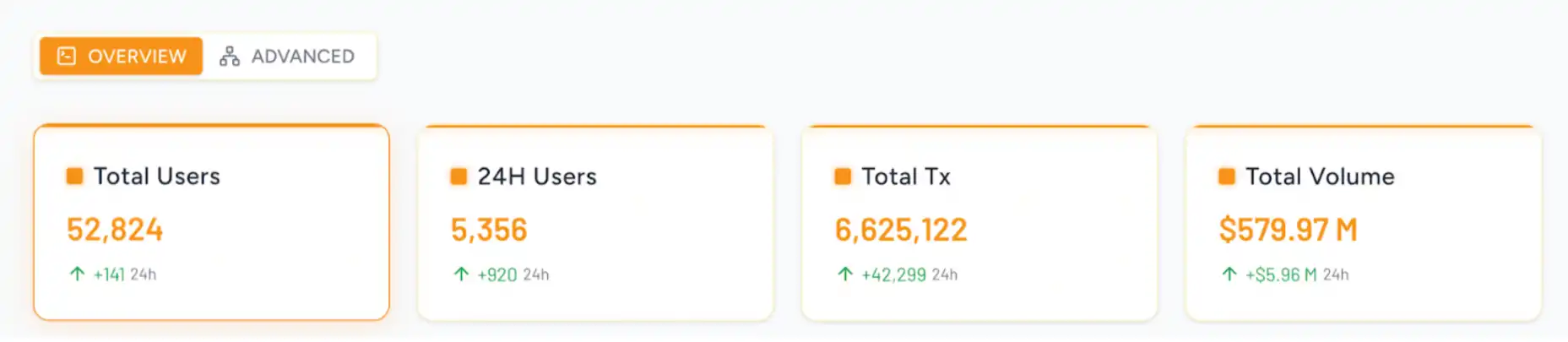
雷电网络链上数据一览,数据来源:https://data.thunderbolt.lt/?new
局限与挑战
雷电网络的技术栈让我们看到了 BTC L2 另一种实现的可能性。由于目前主网还暂未上线,其产品 PMF 还需要市场检验;另一方面,虽然 BFT 委员会模型在安全性上虽优于传统桥接方案,但是否能获得比特币极端去中心化社区的广泛接受,仍然需要打一个问号。
联合挖矿
联合挖矿(Merged Mining)是一种允许矿工在不增加额外计算资源的情况下,同时为多个区块链进行挖矿的技术。其中,Stacks 和 Fractal 是采用联合挖矿机制的两个代表性项目,但两者在共识机制和区块验证机制上采用了不同的解决方案,Stacks 通过采用独特的「转移证明」(Proof of Transfer,PoX)共识机制。在该机制中,Stacks 矿工在 BTC 主网上发送 BTC 来竞标生成 Stacks 区块的权利,成功的矿工就能拿到区块打包权和对应的挖矿奖励。
而 Bitflow 是基于 Stacks 主网上的 DEX,支持交易 BTC、Stacks 代币以及 BRC20,Runes 等多种 BTC 原生资产。此外,Bitflow 在 2024 年 12 月推出了基于 Stacks 的比特币 Rune 自动做市商(AMM),这是 BTC L2 上的首个 Rune AMM。
而 Core 在联合挖矿的基础上,对共识机制稍作了改进:Core 的共识机制叫做 Satoshi Plus 共识机制,结合了委托工作量证明 (DPoW) 和委托权益证明 (DPoS) ;具体实现原理是 BTC 矿工将其算力委托给 Core 链上的验证者,从而利用 BTC 强大的挖矿基础设施为 Core 链提供安全性。这部分算力被称为「委托工作量证明(DPoW)」,由比特币矿工和矿池执行;同时,CORE 代币持有者可以将自己的代币质押或委托给验证者,参与网络的安全维护和治理。这部分权益被称为「委托权益证明(DPoS)」。通过这种组合,Core Chain 将 BTC 矿工纳入图灵完备的智能合约的安全性中,解锁这些矿工超越简单维护 BTC 账本的功能和效用,并以 CORE 代币的形式为他们提供纯粹的附加补充收入奖励。
Fractal 则采取扩容的解决方案,其技术原理是采用递归扩展结构,在 BTC 主网上上创建多个独立运行的扩展层,形成树状结构,以提高交易处理能力和速度。同时,Fractal 在保留 PoW 机制的同时引入了名为「Cadence Mining」的混合挖矿机制,每生产三个区块,其中两个通过无需许可的挖矿方式生成,剩下的一个则采用 BTC 的联合挖矿。
此外 Fractal Bitcoin 重新启用了 OP_CAT 操作码,这是 BTC 早期版本中曾存在但被长期禁用的一条指令。OP_CAT 的功能是将 2 个字符串拼接成 1 个。理论上,一个脚本利用 OP_CAT 可以将 1 字节的数据扩展成超过 1 TB 的内容。如果没有严格限制,这种无限扩展的特性可能被恶意利用进行 DoS 攻击,从而拖垮节点或造成网络拥塞。正因如此,OP_CAT 在早期就已经被社区禁用。如今,Fractal 所采用的「净化版」OP_CAT 为开发者提供了更灵活的脚本处理方式,尤其在链上大整数计算与智能合约功能上展现出潜力。尽管技术机制已得到改善,OP_CAT 的重启仍可能在极端场景存在安全隐患。
发展现状:
Fractal Bitcoin 当前已初具规模,市值约 2012 万美元,日交易量达 1.43M FB,活跃地址超过 176 万。其合并挖矿算力达 648.13 EH/s。挖矿难度 0.01t,尚在早期。
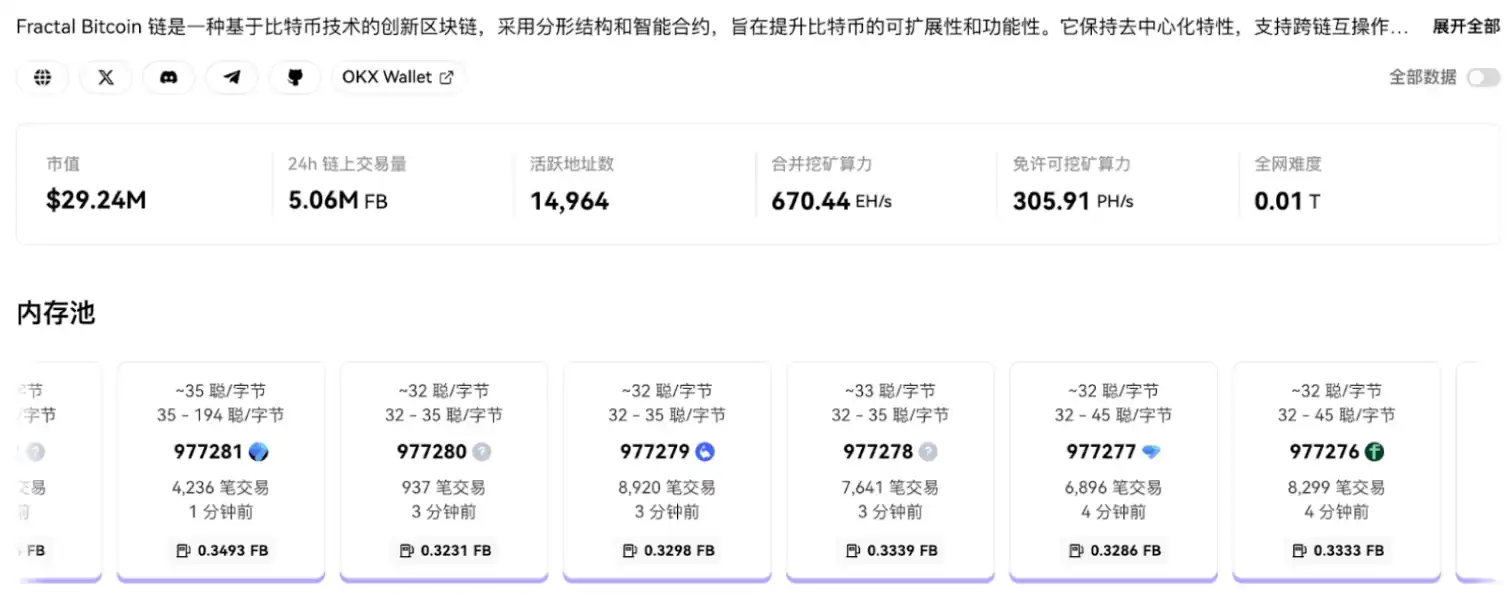
Fractal 链上数据一览,数据来源:https://www.oklink.com/fractal-bitcoin
RGB & RGB++
在 2025 年 8 月 7 日凌晨,预热 2 年之久的 BTC 扩展方案 RGB 协议终于上线 BTC 主网。
RGB 源于 LP/BNP 协会提出的一种技术架构,是基于 BTC 网络的 UTXO 模型的链下资产发行和智能合约协议。RGB 最被人们推崇的一个技术点在于:RGB 上运行的数据会被压缩封装到 BTC 网络上的每一个 UTXO 中。通过「一次性密封条」(Single-use Seals)和「客户端验证」(Client-side Validation)机制,实现了资产状态的私密变更和验证。每个资产状态绑定于一个特定的 BTC UTXO,当该 UTXO 被花费时,资产状态随之更新。这种设计使得资产的所有权和状态变更无需在链上公开,增强了隐私性。RGB 协议还可兼容闪电网络,具备 DeFi 逻辑构建能力。
RGB 0.12 版本上线,数据来源:https://x.com/lnp_bp/status/1943318227854950809
Bitlight Labs:首个支持 RGB 资产的钱包,RGB 协会官方成员
Bitlight Labs 致力于通过为 BTC 和闪电网络开发本地智能合约基础设施来引领原 BTC Fi。此外,不仅是 RGB 协议标准制定协会 INP/BP 的董事会成员,也是 RGB 协议开发的核心贡献者,可以称得上是 RGB 生态不可缺少的核心产品。
Labs 旗下的产品——Bitlight Wallet 则是一种专门为闪电网络和 RGB 协议设计的钱包。最近一同与 RGB 主网的正式上线推出了首个基于 RGB 主网的资产代币「RGB」的铸造活动。
BitMask Wallet:
Bitmask 则是第一个支持 RGB 协议上 NFT 资产的钱包。Bitmask 背后的团队也是早期对 RGB 协议贡献最大的安全钱包之一,其产品开发更注重隐私和用户的资产控制权。最近日,BitMask 仍在推进 RGB 与 RGB++ 的完全互通,当前也正全力准备主网版本上线,以在 BTC 网络上真正实现隐私、可编程性和易用性的结合。
从 RGB 到 RGB++:
Nervos(CKB)是使用 RGB 逻辑实现了 BTC L2 的热门项目,并在 RGB 的基础上提出了 RGB++的概念。RGB++ 引入了「同构绑定」技术,将 BTC 的 UTXO 映射到 Nervos CKB 的 Cell 上,利用 CKB 的图灵完备智能合约能力和链上验证机制,提升了资产状态管理的效率和安全性。在 RGB++ 中,资产的状态变更不仅在 BTC 链上有记录,CKB 链上也有对应的交易和状态验证,实现了链上和链下的协同验证。
尽管 RGB++ 实现了 BTC 与 CKB 的资产映射;但跨链交互基于 RGB 协议的特性在处理一些特定交易时仍然不够简洁,存在安全隐患。
沿袭 ETH L2 思路:ZK-Rollup
Rollup 核心在于将大量链下交易打包后生成加密证明(Proof),并将其提交至主链进使用 ZK 技术进行验证。
热度最大的 BTC L2 之一
Merlin 就是延续这个思路的 BTC L2 网络,也是一条 EVM 兼容的 BTC L2,Merlin 采用了多方计算(MPC)钱包解决方案,由 Cobo(HK 的加密货币托管机构)共同管理用户资产。此外,在验证技术方面,Merlin 仍然采用的是 ZK-Rollup 技术,将大量交易数据压缩后提交到 BTC 主网,确保数据的完整性和安全性。
自主网上线以来,Merlin 成为了 BTC 生态中备受关注的 Layer 2 项目之一。据报道,其总锁仓量(TVL)在上线 30 天内达到了 35 亿美元,吸引了超过 200 个项目在其平台上部署和运行。Merlin Chain 支持多种 BTC 一层原生资产,如 BRC-20、BRC-420 等,并通过与 ETH 兼容,拓展了其生态系统的广度。
加强 BTC 桥接的安全性
B²则与传统的单体式 Rollup 不同,B²采用「1.5 层架构」:即 Rollup 层负责交易执行和状态更新,而数据可用性(DA)层则独立运行并负责存储原始交易数据。这些数据在经过链下 Labeling 与整理后被定期提交至比特币主网,实现对最终性的确认。
B² Network 的 DA(Data Availability)层——B² Hub——属于 Layer1.5,把批次数据先做 Reed-Solomon + KZG 编码切片,再把 Layer2 提交的 zero-knowledge proof 聚合成 Taproot 承诺提交到比特币主网,从而继承了比特币网络的终结性与不可篡改性。
B² Network 采用去中心化的 blob 存储与轻节点取样 (sampling) 机制,任何验证者只需随机抽取极小比例的块片就能高概率检测数据是否完整,显著降低同步与验证成本。
在共识上,B² Hub 仅需提交简短的承诺与有效性证明,主网不再承担大体积数据负荷,Rollup 批次发布者则对可用性负责,形成「有效性外包 + 可用性保证」的模块化架构。通过把 DA 与执行层解耦,B² Rollup 可并行扩容、分片更新,而安全边界仍锚定比特币链,兼顾高吞吐、低成本与 L1 级安全。
这么做有 2 个好处,一个是模块化的设计,可以在不对 BTC 网络进行任何修改升级的情况下,进行无限的水平扩容;另外还可以通过 B² Network 的 DA 层——B² Hub,可以聚合存储证明和状态转化证明,提交到比特币网络,集成比特币网络的安全性;
但由于 L2 交易的最终确认需要先通过 B² Hub 的确认和聚合,再由 BTC 网络进行上链确认,并且在 BTC 网络上属于被动确认,属于乐观模式;此外,zero-knowledge proof 聚合成 Taproot 承诺,在 BTC 网络上进行乐观验证,还处于 POC 阶段,还没有最终落地;
项目进展:从技术实现到用户生态
截至目前,BSquare 总锁仓量(TVL)已突破 6 亿美元,链上日交易量峰值达 9 亿美元,拥有 50 万平台活跃用户。平台生态覆盖 100+ DApp,涵盖 DeFi、借贷、AI Agent 应用等场景。
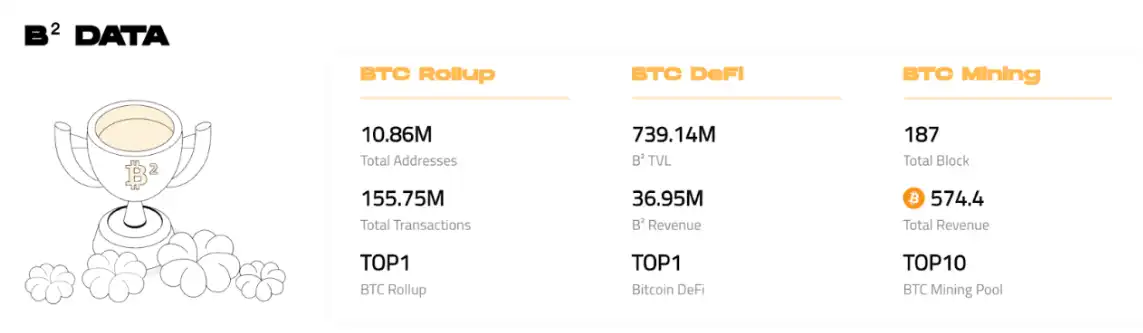
BSquare 链上数据一览,数据来源:https://www.bsquared.network/
与此同时,BSquare 还推出了首个 BTC 生息矿池「Mining Square」,这是一个给矿工准备的「余额宝」,为矿工提供了一个具备 BTC 原生收益的解决方案。目前该矿池并已经占据全网算力的 1%,且能够在矿池算力排名中排入前 10。
用 BTC Script 实现图灵机?解码 BitVM
BitVM 是一种构建在 BTC 主网上的扩展协议,其核心目标是实现无需更改共识机制、即可支持任意可验证计算的通用虚拟机环境。其原理借鉴了 optimistic rollup 的思想:大部分计算在链下完成,仅在发生争议时,将相关计算过程以「欺诈证明」的形式提交至链上验证。与以太坊的 Arbitrum 类似,BitVM 使用链下计算 + 链上验证的机制,但其独特之处在于利用比特币的脚本系统(Bitcoin Script)构建「逻辑门电路」,进而模拟出图灵完备的虚拟机。(类似于三体游戏中秦始皇的人列计算机)
BitVM 并不直接在链上运行 EVM 或 WASM,而是将这些高级虚拟机操作转译为比特币脚本中最基本的逻辑门(如 AND、OR、NOT 等)的组合,通过逻辑门构建一个庞大的「欺诈验证电路」。所有交易数据和计算在链下处理,只有在挑战发生时才将数据与计算步骤(以 Merkle Proof 等形式)提交链上。
BitVM2 是对原始 BitVM 的优化版本,引入了更模块化的计算结构和电路压缩机制,同时引入交互式欺诈证明、时间锁脚本、多签等机制增强协议的实用性和安全性。BitVM2 更加注重优化 on-chain 数据提交量,并试图引入如 OP_CAT 等可能在未来被激活的脚本操作码以提高电路构建效率。
发展现状
当前 BitVM 路线正逐渐从理论走向实践,其中代表性项目就是 Citrea,Citrea 将大量交易在链下执行,并通过 BitVM 将执行结果和证明提交到 BTC 网络进行验证。实现了 BTC L2 高效的扩容和安全性。Citrea 也是第一个能够在 BTC 上实现通用 L2 结算的解决方案,所有证明都原生地在 BTC 网络上的区块内验证。目前,Citrea 的主网尚未正式上线,仍处于测试网阶段。
而例如 Goat Network 则致力于探讨 BitVM2 的可能性。Goat 的白皮书展示了基于电路逻辑与 Merkle 树结构的欺诈证明机制。Goat 强调将 BTC 上的计算拓展为图灵完备的状态机,并尝试构建一种新的 BTC L2 框架,允许智能合约执行与资产交互在比特币主链之上原生完成。Goat 的实现中还包括数据可用性层(DA 层)的集成,以及电路压缩机制优化,推动了 BitVM 从实验性方案迈向可实际部署。
截止今年 6 月,Goat Network 的锁仓量已经突破 1 亿美元。
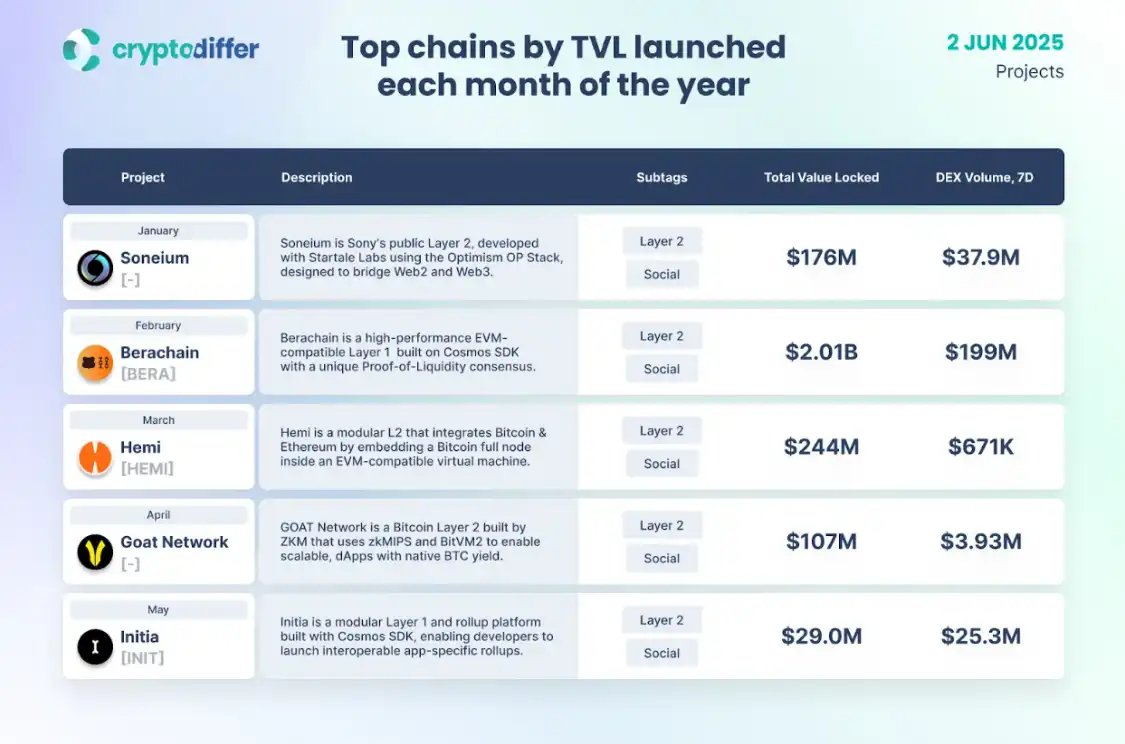
Top chains by TVL launched each month of the year, CryptoDiffier; 数据来源:https://x.com/GOATRollup/status/1929596963286114614
尽管 BitVM 系列的协议优势非常明显:极致原生,无需更改 BTC 共识就可以实现图灵完备的计算,具备极高的安全性与原生性;而且其结构天然支持欺诈证明、低数据上链率和极致的去中心化。
然而 BitVM 劣势也源于其技术:BTC Script 构成的逻辑门电路再模拟 EVM 或 WASM,这本身的结构将会史诗级的复杂和庞大,也因此 BitVM 的开发复杂度极高、电路构建的工作量非常巨大。并且现阶段还缺乏成熟的开发者生态与标准化工具。
多路径并进,价值承载之争仍未定局
BTC L2 各个解决方案在技术实现上各有侧重。例如闪电网络专注于支付效率,经过多年发展已形成成熟的节点网络,适合用于微支付和链下结算。RGB 和 RGB++更关注资产安全性,利用客户端验证机制保障资产状态。ZK-Rollup 路线由于大多采用成熟的 EVM 方案+模块的安全验证极致,目前拥有较强的可组合性与跨链拓展能力,对于 DeFi,AI Agent 等场景适应得更快。BitVM 则进一步追求极致的原生性,以不改动 BTC 共识的方式在链上实现智能合约能力,尽管仍处早期,但代表了 BTC 计算能力的一种极限尝试。
虽然目前尚未定数,但我们可以看到,真正具备长期生命力的方案,必须尽量满足三点:BTC 原生兼容性、安全性可验证、以及对上层应用的良好支持能力。并且目前技术栈的融合趋势愈发明显,比如闪电网络结合稳定币、ZK Rollup 与 RGB 的集成探索。
未来,BTC L2 一定是多极竞争格局,不同方案将服务于不同的核心场景:支付、合约、资产、存储、AI 等分工协作,共同支撑 BTC 生态的长期繁荣。这场竞赛还远未结束,真正的胜者将由资产沉淀能力与开发者生态共同决定。而 BTC 作为全球最强共识资产,其生态边界将因美元稳定币的涌入和 L2 模块化创新而不断外延,迎来一场「支付主权 + 合约扩展」的双向升级。
近些天,随着美国 GENIUS 稳定币法案的落地,标志着全球稳定币监管逐渐清晰,逐渐完善。「支付稳定币」被合法纳入美元体系,有望带动包括 USDT、USDC 在内和其它新兴稳定币加速进入链上支付场景。正如 Tether CEO 指出,新兴市场才是稳定币落地的主战场,USDT 的 60% 增长来自加密圈之外的实际支付需求。
而 GENIUS 法案为稳定币的链上使用提供了明确的法律路径,也为 BTC L2 承载美元资产打开了合规通道。USDT 作为最早诞生于 BTC 网络的稳定币,如今正率先重返 BTC 生态,这不仅是对技术路线的回归,更体现出 BTC 作为结算层的战略价值。可以预见,未来稳定币支付体系若构建于 BTC L2 之上,将是最原生、最安全、最符合比特币精神的路径。借助 BTC L2 的可组合性和资产协议能力,BTC 网络有望承接现实世界的支付结算需求,实现稳定币流通与价值沉淀于一体的共生格局。
参考资料:
· https://eprint.iacr.org/2025/709
· https://riema.notion.site/Bitcoin-Thunderbolt-1d7f5aa90cdd803b8a73d080c83af098
· https://x.com/kevinliub/status/1919499375035756580?s=46
· https://www.theblockbeats.info/flash/289746
· https://lbank-exchange.medium.com/rgb-protocol-a-promising-approach-for-asset-issuance-on-the-bitcoin-network-after-brc20-357bd74f0c4c
· https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/iMQPXFPWBpT9dQLyR8rzUg
· https://www.btcstudy.org/2023/09/12/the-potential-of-RGB-protocol/
· https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzk0OTYwMDM1Mg==&mid=2247487024&idx=1&sn=0241778d2e1fbed796a6beaeb3c07c4a&chksm=c21c27cca1e00c1d214dc01d1b6368b8e9198afa94d4bc16d5b5e1dadbd9402dd029a87747e9&scene=132&exptype=timeline_recommend_article_extendread_samebiz#wechat_redirect
· https://www.binance.com/zh-CN/square/post/23302994992353
本文来自投稿,不代表 BlockBeats 观点。
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



