以太坊或许并没有输掉这场收益之战,它只是以不同的方式赢得了胜利。
撰文:Marie Poteriaieva
编译:Shaw,金色财经
固定收益不再只是传统金融的专利。链上收益已成为加密货币的核心支柱。而以太坊作为最大的 PoS 区块链,处于核心地位,其经济依赖于用户锁定其 ETH 以帮助保护网络并赚取收益。
然而,以太坊并非唯一的选择。如今,加密货币用户可以接触到越来越多种类的收益型产品,其中一些产品与以太坊的质押收益直接竞争,这可能会削弱以太坊的区块链。收益型稳定币提供了更大的灵活性,并更容易接触传统金融,其收益与美国国债和合成策略挂钩。
与此同时,DeFi 借贷协议扩大了存款人可用的资产范围和风险状况。两者通常都能带来比以太坊质押更高的收益,这引出了一个关键问题:以太坊是否正在悄然输掉这场收益之战?
以太坊质押收益下降
以太坊质押收益是验证者因维护网络安全性而获得的收益。它来自两个来源:共识层奖励和执行层奖励。
共识奖励由协议发放,取决于质押的 ETH 总量。按照设计,网络中质押的以太币(ETH)越多,每个验证者的奖励就越低。该公式遵循反平方根曲线,确保随着更多资金进入系统,收益逐渐减少。执行层的奖励包括优先费用(用户为使其交易被纳入区块而支付的费用)和最大可提取价值(MEV),即通过优化交易顺序获得的额外利润。这些额外奖励会根据网络使用情况和验证者策略而波动。
自 2022 年 9 月合并以来,以太坊的质押收益率逐渐下降。总收益率(包括共识奖励和小费)从峰值的 5.3% 左右降至 3% 以下,这反映了 ETH 质押总量的增长以及网络的日趋成熟。事实上,目前质押的 ETH 超过 3500 万枚,占其总供应量的 28%。
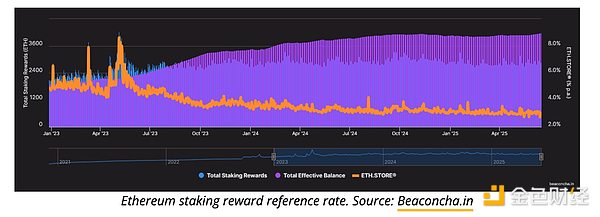
然而,只有独立验证者(即运行自己的节点并锁定 32 ETH 的人)才能获得全部质押收益。虽然他们可以获得 100% 的奖励,但他们也承担着保持在线、维护硬件和避免受到处罚的责任。大多数用户会选择更便捷的方案,例如 Lido 等流动性质押协议或交易所提供的托管服务。这些平台简化了访问流程,但会收取费用(通常在 10% 到 25% 之间),这进一步降低了用户的最终收益。
虽然以太坊低于 3% 的年质押收益率看似不高,但与其竞争对手 Solana 相比仍具有优势。Solana 目前的平均网络年利率约为 2.5%(最高年利率为 7%)。实际收益率方面,以太坊的收益率甚至更高:其净通胀率仅为 0.7%,而 Solana 的净通胀率为 4.5%,这意味着以太坊上的质押者随着时间的推移,权益稀释程度更低。但以太坊的主要挑战并非来自其他区块链,而是其他能够提供收益的替代协议的兴起。
收益型稳定币获得市场份额
收益型稳定币让用户持有与美元挂钩的资产,同时获得被动收入,这些收入通常来自美国国债或合成策略。与 USDC 或 USDT 等不向用户支付收益的传统稳定币不同,这些新稳定币协议会将部分基础收益分配给用户。
五大收益稳定币——sUSDe、sUSDS、SyrupUSDC、USDY 和 OUSG 占据了 114 亿美元市场的 70% 以上,并使用不同的方法来产生收益。
sUSDe 由贝莱德投资的 Ethena 公司发行,采用合成 delta 中性策略,涉及 ETH 衍生品和质押奖励。其收益率在加密货币领域名列前茅,历史年利率在 10% 至 25% 之间。尽管当前收益率已降至 6% 左右,但 sUSDe 仍然领先于大多数竞争对手,但由于其复杂的、依赖市场的策略,风险也较高。
sUSDS 由 Reflexer 和 Sky(前 MakerDAO)开发,由 sDAI 和 RWA 支撑。其收益率较为保守,目前为 4.5%,侧重于去中心化和风险规避。
SyrupUSDC 由 Maple Finance 发行,通过代币化国债和 MEV 策略实现收益。其发行时收益率达两位数,目前收益率为 6.5%,仍高于大多数中心化替代方案。
Ondo Finance 发行的 USDY 将短期国债代币化,收益率为 4.3%,目标客户是受监管且风险较低的机构。同样来自 Ondo 的 OUSG 由贝莱德的短期国债 ETF 支持,收益率约为 4%,且符合完整的 KYC 要求,并高度重视合规性。
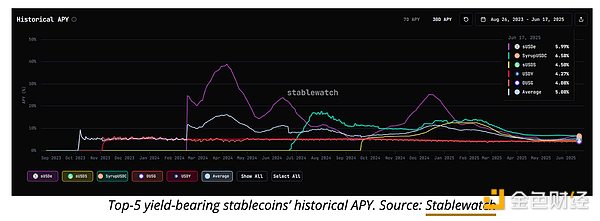
这些产品之间的主要区别在于它们的抵押品、风险状况和可访问性。sUSDe、SyrupUSDC 和 sUSDS 完全是 DeFi 原生且无需许可的,而 USDY 和 OUSG 则需要 KYC 并迎合机构用户。
收益型稳定币正迅速受到青睐,它们将美元的稳定性与曾经专属于机构投资者的收益机会完美结合。过去一年,该领域增长了 235%,而且随着对链上固定收益的需求不断增长,其发展势头丝毫没有放缓的迹象。
DeFi 借贷仍然以以太坊为中心
像 Aave、Compound 和 Morpho 这样的去中心化借贷平台,允许用户通过向借贷池提供加密资产来赚取收益。这些协议根据供需关系通过算法设定利率。当借贷需求上升时,利率也会上升,这使得 DeFi 借贷收益率更具动态性,而且通常与传统市场不相关。
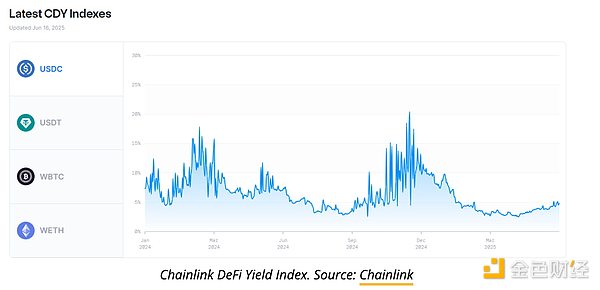
Chainlink DeFi 收益率指数显示稳定币的借贷利率通常在 USDC 5% 左右,USDT 3.8% 左右。在牛市或投机狂潮期间(例如 2024 年 2 月至 3 月和 11 月至 12 月),借贷需求激增,收益率往往会飙升。与根据央行政策和信用风险调整利率的银行相比,DeFi 借贷是由市场驱动的。这创造了更高回报的机会,但也使借贷者面临独特的风险,例如智能合约漏洞、预言机故障、价格操纵和流动性紧缩。
然而矛盾的是,许多此类产品本身却建立在以太坊之上。收益型稳定币、代币化国债以及 DeFi 借贷协议很大程度上依赖于以太坊的基础设施,在某些情况下,甚至将 ETH 直接纳入其收益策略。
以太坊仍然是传统金融和加密原生金融领域最值得信赖的区块链,并且在托管 DeFi 和风险资产(RWA)方面继续保持领先地位。随着这些领域的普及,它们推动了网络使用率的上升,交易费用的增加,并间接增强了 ETH 的长期价值。从这个意义上讲,以太坊或许并没有输掉这场收益之战——它只是以不同的方式赢得了胜利。
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



