
一、引言
回顾区块链十余年的技术演进史,以太坊始终扮演着引领者与开拓者的双重角色。从 2015 年的创世区块,到 2022 年完成能源消耗骤降 99.95% 的 The Merge,再到 2024 年使 Layer2 费用大幅降低的 EIP‑4844,每一次升级都深刻改变了去中心化应用的可能边界。如今,面对 Solana、Sui 等新兴高性能公链的猛烈冲击以及市场对低费用、高速度、易用性的需求,以太坊又站在了新的十字路口——Spectra升级。在 ETH 价格低迷、资本加速流向高速 Layer1 的背景下,Spectra 的成败不仅关乎以太坊自身的性能与体验,也将重塑加密市场资金、开发者与用户的流向逻辑。
本文将以通俗易懂的语言,系统梳理以太坊升级路线图,拆解 Spectra 升级的内容与意义,并深入分析其对加密市场的潜在影响。希望通过这篇文章,读者能够理解为什么 Spectra 可能是以太坊的下一把火、又为何仍面临严峻挑战。
二、Spectra 升级的背景和内容
以太坊的发展可分为多个阶段:早期为工作量证明(PoW)共识,而后在2022年完成了转向权益证明(PoS)的“合并”升级(The Merge),使网络能耗骤降约99.95%,为后续扩容奠定基础。合并之后,以太坊官方路线图提出了“以太坊的六大愿景”,依次为: Merge、Surge、Scourge、Verge、Purge和Splurge。每个阶段对应不同目标,其共同目标是提升扩展性、降低成本,同时维护网络安全与去中心化。
合并(The Merge):2022 年以太坊主网与信标链完成融合,完成从 PoW 到 PoS 的共识机制切换,将网络能耗减少近 99.95%,并为未来的扩容技术(如提案-区块分离等)创造可能。
激增(The Surge):通过 Rollup 和数据可用性分片等技术(如 EIP-4844 引入的 Blob 数据),显著提升网络吞吐量,目标令以太坊在 L1+L2 总计达到 10 万+ TPS。该阶段还会持续推进数据可用性抽样(DAS)方案,开启数据抽样验证能力。
清祓(The Scourge):为提升抗审查和去中心化而设计,重点降低大型验证者和单点控制风险,如通过强制提案-区块分离(ePBS)等机制中和 MEV(矿工/验证者可提取价值)问题。
边缘(The Verge):原本计划采用 Verkle 树替代状态根 Patricia 树,使验证者可以通过极小的“见证”验证区块而无需完整状态,实现无状态客户端。此外,Verge 阶段还展望用零知识证明(SNARK/STARK)来高效验证执行,有望让任何设备(甚至手机)都能全节点验证网络。
净化(The Purge):通过历史数据过期、简化协议(如执行数据仅保留有限时间)、剔除老旧功能等手段,大幅降低节点对历史数据的存储压力。例如,EIP-4444 提议将历史区块和交易数据的保存期统一在一年内,配合未来的分布式存储机制,节点不再需永久保存所有历史状态。
放浪(The Splurge):包含各种杂项与细节优化,包括将 EVM 带入更高效稳定状态(如采用新型 EVM 对象格式 EOF)、深化账户抽象原生化(允许所有账户具有更智能的功能)、优化费用模型、引入更先进的密码学(可验证延时函数、混淆签名等)等。
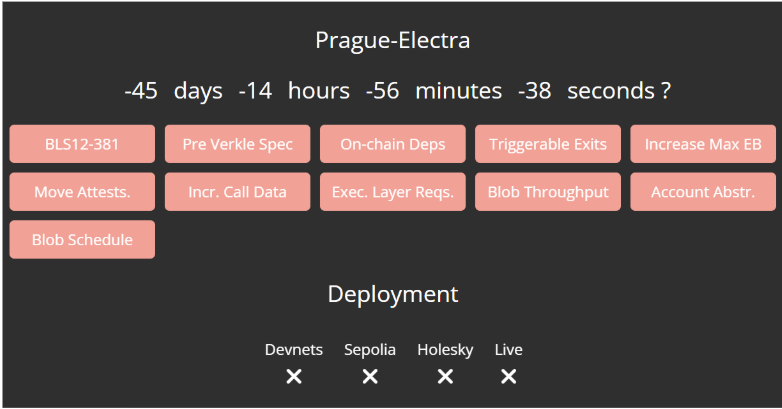
Spectra 升级(又称 Pectra,源自 Prague + Electra)计划于 2025 年 5 月7日正式上线,是自合并以来最重要的网络升级。此次升级聚焦提升可扩展性和用户体验,同时优化验证者运维。核心目标包括:智能账户支持、扩大数据吞吐、流畅的质押/退出流程等。Spectra 包含约 11 个核心 EIP,涵盖了执行层和共识层的多项改动。其中主要内容有:
账户抽象:EIP-7702允许普通外部账户(EOA)“临时”表现为智能合约,使钱包可以打包交易、设定操作条件、由第三方代付手续费等功能。这意味着用户以后无需持有 ETH 即可支付 Gas,可使用如 USDC、DAI 等稳定币来付费,大大简化了新手入门门槛。
验证者灵活性:引入 EIP-7251 将验证者的最大质押余额从 32 ETH 提升至 2048 ETH,使大型质押方可以将多个验证者整合为单个节点,从而减少运行多节点的开销。同时 EIP-7002 添加执行层触发退出机制,验证者可通过调用合约自行退出,而无需持有原始验证者私钥,这进一步简化了验证者的退出流程。这些改动将降低运营复杂度、提高网络可用性。
扩容与数据可用性:EIP-7691 将每区块可承载的 blob 数据量对半翻倍(平均值从 3 提升至 6,峰值从 6 至 9),有效提升 Layer2(Rollup)吞吐,缓解以往的拥堵问题。同时为了不使节点硬件需求过于苛刻,引入 PeerDAS(EIP-7594)——一种点对点数据可用性采样协议。PeerDAS 使得网络可通过随机抽样的方式确认 L2 数据是否可用,而无需每个节点都完整下载所有数据,在提高吞吐的同时保持节点的去中心化性。
状态优化:EIP-2935 在执行层引入新的系统合约,可供查询最近 8192 个区块哈希,为未来引入 Verkle 树等技术做好准备。具体来说,此合约让轻节点能够在不保存全部历史的情况下,获取相对较长历史的区块哈希,从而为去中心化的状态验证提供便捷支持。此外,EIP-7549 将 attestation 消息中的委员会索引移出签名范围,以简化共识节点的验证工作,并提升零知识证明电路的效率。
其他改进:Spectra 还包括将验证者存款纳入执行层(EIP-6110),使 ETH 存款在出块时直接并入信标链,简化了历史存款数据的验证;EIP-7840 将区块的 Blob 配置参数固定在客户端,统一了执行共识的参数;EIP-7623 调整了传统 calldata 的费用定价,引导开发者更多使用更高效的 Blob 存储。此外,还引入了 BLS12-381 曲线预编译(EIP-2537)等功能,以支持未来零知识协议和多签名应用。
通俗地说,Spectra 升级使以太坊网络能够在不牺牲去中心化的前提下跑得更快更稳。以太坊节点未来将能支持更大的数据量,同时所需的硬件门槛并不会成倍增长,因为新引入的 PeerDAS 机制减轻了每个节点的负担。更高的吞吐能力和更灵活的验证机制,将为用户带来更低的交易手续费和更快的确认时间,而开发者则能在此基础上设计更复杂、互动性更强的应用。
三、Spectra 升级对加密市场的影响分析
1.资金流出与 ETH持续低迷
今年以来,以太坊现货 ETF 累计净流出已超 1.1 亿美元,面临抛压 。机构减仓导致 ETH/BTC 比价跌至 0.019 的五年新低,然而SOLETH 比率则上涨 24 %。Q1 以来,ETH 网络平均 L1 Gas 费高出 Solana 20–30 倍,同期 ETH 处理量约 1.5 TPS,而 Solana 峰值突破 2,000 TPS。由于 32 ETH 质押门槛偏高,ETH 质押率仅 28 %,而 Solana 质押率达 65 % 。
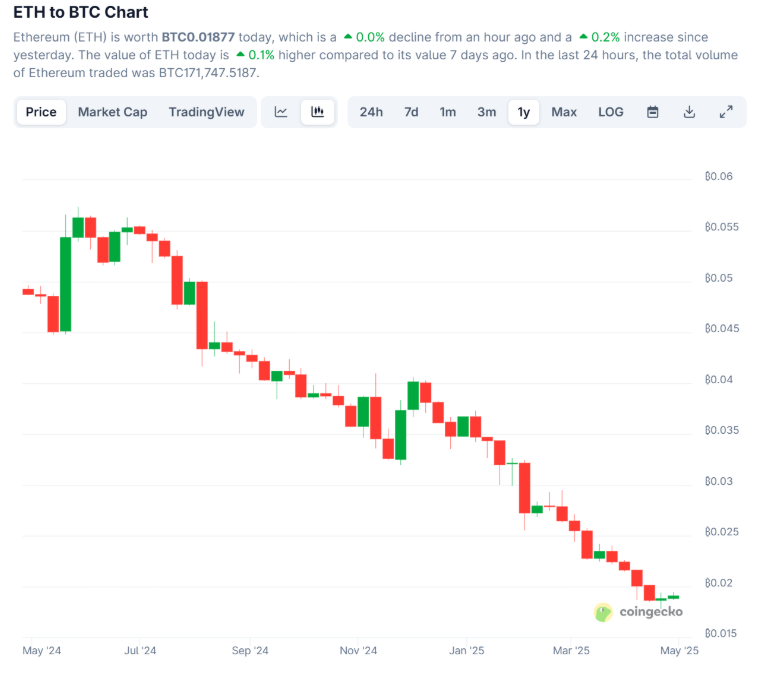
来源:https://www.coingecko.com/en/coins/ethereum/btc
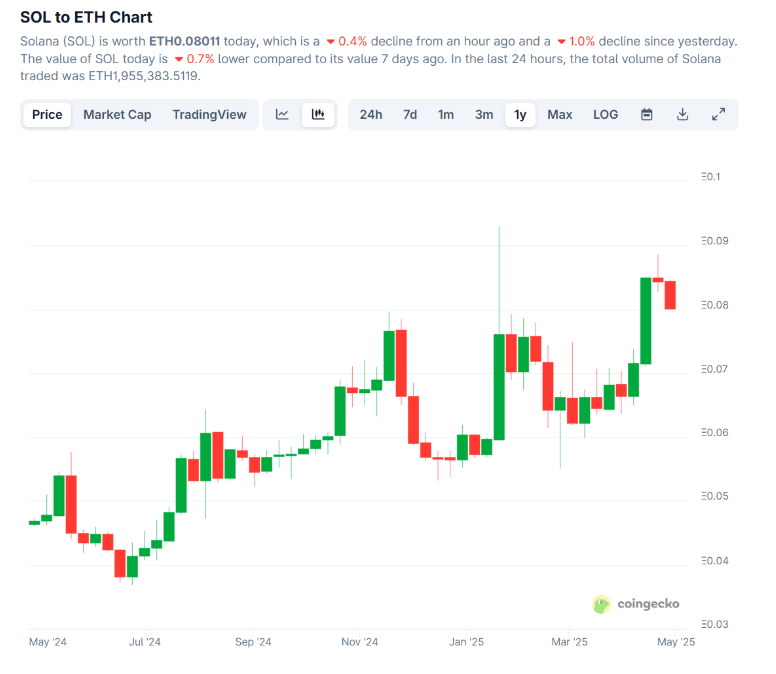
来源:https://www.coingecko.com/en/coins/solana/eth
2. Spectra 升级对 ETH 供需结构的重塑
智能账户(EIP‑7702) 允许用 USDC/DAI 直接支付 Gas,取消“先买 ETH”门槛,业内普遍预计能提升日活 15–25 % 。
Blob 容量翻倍 + PeerDAS 令 L2 平均手续费有望再降 40 %,Rollup 交易量预计 6 个月内提升 2–3 倍 。
EIP‑7251 把单验证者上限提高到 2,048 ETH,可将大型节点合并,减少“复投”质押奖励流失;若 20 % 的质押者合箱,年化新抛压理论上可下降 3–4 % 。
EIP‑7002 允许执行层发起主动退出,提升流动性;结合 ETF 规则禁止质押,Spectra 后或促使更多长线资金在链上直接质押以赚收益,减少二级市场流通筹码。
3. 对 L1和L2 的连锁影响
Solana 高负荷时仍偶现停机,且缺乏智能账户级别的原生抽象;Spectra 若显著改善 ETH 体验,可能分流部分高频交易与 DeFi 资金,抑制 SOL「翻盘」预期。
Sui 依赖游戏与社交场景差异化。Spectra 降费后,L2 游戏(如 Immutable、Xai)成本优势将凸显,或对 Sui 形成潜在竞争。
Layer2 项目将从升级中直接受益。更大的 Blob 容量和数据可用性改进,使 Arbitrum、Optimism 等项目的交易更加高效、费用更低,从而提高这些扩容方案的吸引力。随着升级落地,市场参与者预期整个加密生态(尤其是 Rollup 代币和 DeFi 平台)将迎来更多资金和用户涌入。
四、Spectra 升级带来的机遇与挑战
Spectra 升级为以太坊及整个行业带来诸多机遇:
1.有望巩固以太坊的竞争优势:通过显著提升扩展性和用户友好度,Spectra 使以太坊能够更好地应对 Solana、Avalanche、BNB Chain 等竞品的挑战。例如,随着以太坊提高了处理能力和降低了手续费,投资者和开发者将更倾向于在以太坊生态中持续投入,而非转向其他链。
2.提升以太坊对机构的吸引力:更高的可扩展性和稳定性,结合即将支持的企业级功能(如原生隐私和合约账户等),有望吸引金融科技和传统金融机构进一步参与 Web3 领域。这符合以太坊成为“真正全球化、安全基础设施”的长期愿景。
3.对普通用户更加友好:友好的支付方式和更低的入门门槛则可能推动大众用户的普及,有助于加密市场的整体成长。
然而,Spectra 同时也面临挑战:
1.技术复杂性和实施风险:此次升级集成了多项前沿技术(PeerDAS、Verkle 等),在测试阶段就曾出现意外情况:两次测试网激活时验证者出现失误,导致网络分叉,开发者不得不做第三次测试来修复问题。这凸显出大规模协议升级的复杂度,未来任何相似的改动都需极为谨慎。
2.Layer2 生态的碎片化:当前以太坊上有多种 L2 解决方案,如何实现更好的跨链互操作和流动性共享,依然需要更多标准和基础设施的支撑。
3.竞争对手的压力:其他公链不甘落后,也在加紧推进扩容和用户体验改进,Spectra 虽提升了以太坊的领先优势,但其他链的技术迭代将持续存在。从策略上看,以太坊需要在提升性能的同时,持续加强去中心化和安全属性以保持优势。
五、以太坊后续升级展望与总结
展望未来,以太坊路线图仍在不断演进。完成 Spectra 后,接下来的重点包括进一步完善协议和引入下一代技术。以太坊基金会已提出在 2025 年之后的路线中纳入 Fusaka和 Glamsterdam两大升级目标。其中 Fusaka 将引入 PeerDAS 等更完整的数据可用性采样方案,使以太坊在不“吞掉”全网数据量的前提下,进一步实现极高吞吐;Glamsterdam 则专注于 Gas 成本优化和协议效率改进,使网络在更复杂负载下保持高性能,特别对深入整合的 Layer2 Rollup 和 ZK 技术提供支持。这两个升级将把以太坊推向真正的全球化高吞吐结算层。
总之,Spectra 升级使以太坊在扩容和用户体验上迈出重要步伐,这为 DeFi/NFT、大型应用和机构级别用例提供了机遇。但与此同时,升级的技术难度高、外部竞争加剧、监管环境尚未明朗、以及多层级生态互操作的难题都对以太坊提出了更高要求。未来,以太坊生态能否充分利用这些机遇,并有效应对挑战,将决定其在全球加密市场中的地位。
关于我们
Hotcoin Research 作为 Hotcoin 生态的核心投研中枢,专注为全球加密资产投资者提供专业深度分析与前瞻洞察。我们构建"趋势研判+价值挖掘+实时追踪"三位一体的服务体系,通过加密货币行业趋势深度解析、潜力项目多维度评估、全天候市场波动监测,结合每周双更的《热币严选》策略直播与《区块链今日头条》每日要闻速递,为不同层级投资者提供精准市场解读与实战策略。依托前沿数据分析模型与行业资源网络,我们持续赋能新手投资者建立认知框架,助力专业机构捕捉阿尔法收益,共同把握Web3时代的价值增长机遇。
风险提示
加密货币市场的波动性较大,投资本身带有风险。我们强烈建议投资者在完全了解这些风险的基础上,并在严格的风险管理框架下进行投资,以确保资金安全。
Website:https://lite.hotcoingex.cc/r/Hotcoinresearch
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




